The nut welding equipment market has experienced steady growth, driven by increasing demand for efficient, high-strength fastening solutions in automotive, construction, and heavy manufacturing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global resistance welding equipment market was valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by automation trends and the need for precision in assembly processes, particularly in electric vehicle (EV) production where nut welding ensures reliable battery and chassis component attachment. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence projects rising adoption of inverter-based welding systems, which offer improved energy efficiency and control—features increasingly prioritized by modern manufacturers. As demand for durable, automated fastening solutions climbs, several key players have emerged as leaders in nut welder innovation and reliability. The following list highlights the top nine nut welder manufacturers shaping the industry through technological advancement, global reach, and performance-driven design.
Top 9 Nut Welder Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Global Leader in Fastening Technology
Domain Est. 2012
Website: stanleyengineeredfastening.com
Key Highlights: Stud Welding Systems. Trusted worldwide, Nelson® stud welding systems enable rapid, durable fastening in structural steel, automotive, and power applications….
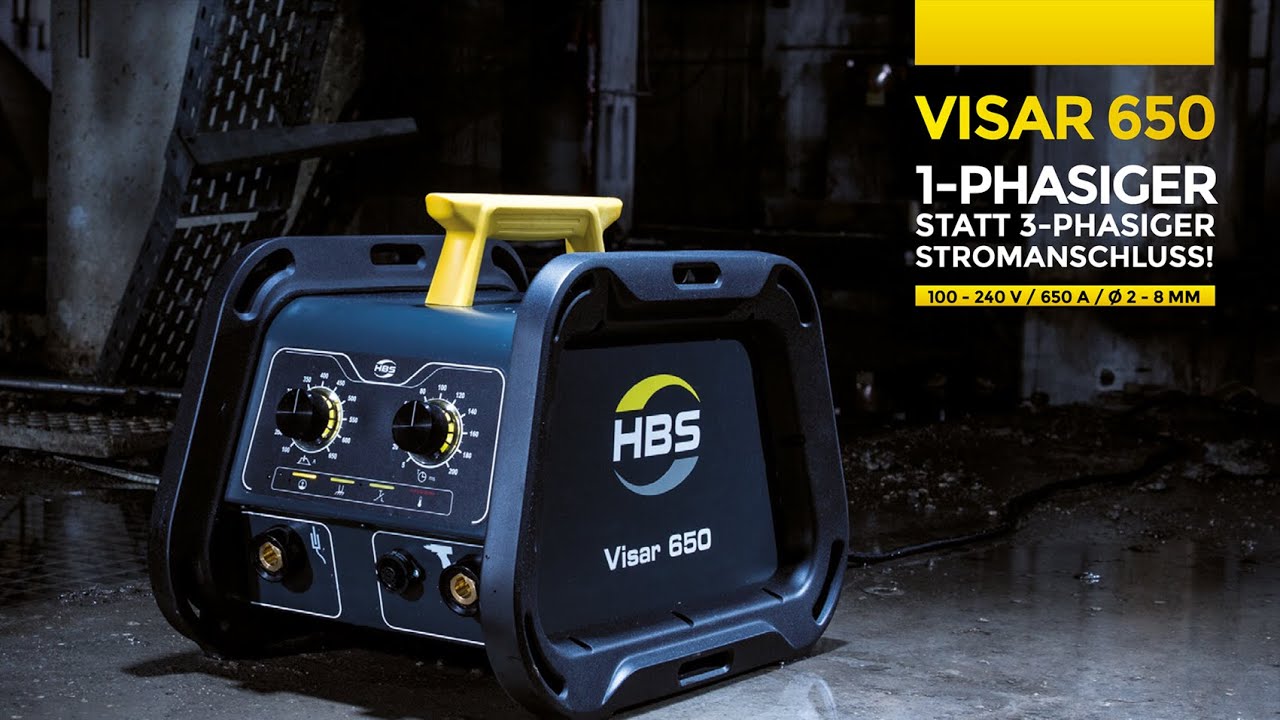
#2 HBS is technology leader in nut and stud welding technology
Website: hbswelding.systems
Key Highlights: We offer you the right solution from stud welding equipment to stud welding guns to welding elements, depending on the welding process….
#3 Global Leader in Plastic Welding Technologies
Domain Est. 1995
Website: dukane.com
Key Highlights: Dukane is a global leader in plastic welding technologies – ultrasonic, vibration, laser, infrared & hot plate. Enhance quality & efficiency now….
#4 PEM – PennEngineering
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pemnet.com
Key Highlights: PEM offers innovative fastening solutions for a variety of applications across industries like Automotive Electronics, Consumer Electronics, Datacom and more….
#5 Resistance Welders
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tjsnow.com
Key Highlights: T. J. Snow offers a complete line of standard and custom designed resistance spot welders and projection welders, including automated multi-gun and special ……
#6 Nut and Stud Welding Electrodes
Domain Est. 1997
Website: cntrline.com
Key Highlights: An extensive variety of nut and stud welding electrodes are supplied by CenterLine. Our high-quality designs and assembly styles provide numerous features ……
#7 Weld Nuts
Domain Est. 1999
Website: buckeyefasteners.com
Key Highlights: 5/16-18 SQUARE WELD NUT-LONG PILOT. Item No. 2006. Plain C1010 High-Welding Quality, Low Carbon Steel…
#8 Spot Welders, Custom Nut Welder, Robotic Cells, TRC Welding …
Domain Est. 2001
Website: trcwelding.com
Key Highlights: We offer a wide range of Resistance Spot Welders, Resistance Nut Welders, Standard and Custom Resistance and Arc Welding Machines, and Tooling….
#9 Projection Weld Nuts
Domain Est. 2001
Website: jhpfasteners.com
Key Highlights: Monroe-JHP Fasteners is a leading weld nut distributor. Contact us for more information regarding our premium wholesale weld nut options, or request a quote ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Nut Welder
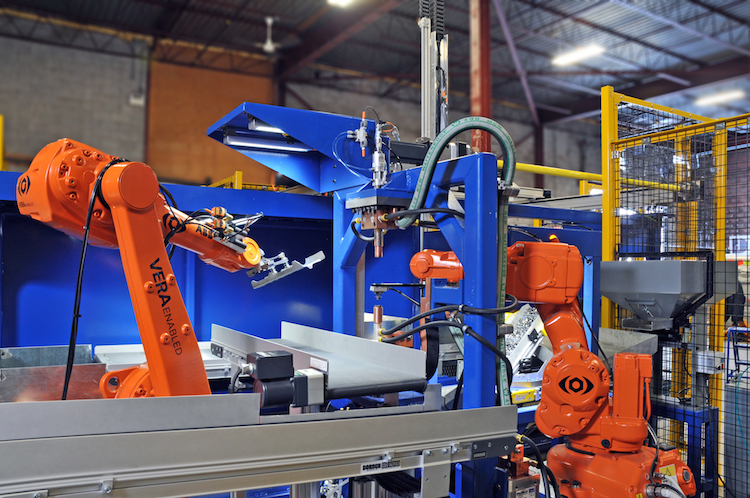

2026 Market Trends for Nut Welder
The nut welding equipment and services sector is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, sustainability mandates, and evolving manufacturing demands. For companies like Nut Welder, adapting to these trends will be critical for maintaining competitiveness and capturing growth opportunities across key industries.
Rising Demand from Electric Vehicles and Advanced Manufacturing
The proliferation of electric vehicles (EVs) is a primary catalyst reshaping the nut welding landscape. EV production requires high-precision, reliable fastening solutions for battery packs, powertrains, and lightweight chassis components. Nut Welder stands to benefit from increased demand for automated projection welding systems capable of handling aluminum and mixed-material assemblies. Additionally, advanced manufacturing practices such as modular construction and Industry 4.0 integration will drive adoption of smart welding cells equipped with IoT sensors and real-time monitoring, enabling predictive maintenance and enhanced traceability—areas where Nut Welder can differentiate its offerings.
Growth in Automation and Smart Welding Technologies
By 2026, automation will be a dominant trend across automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment sectors. Manufacturers will prioritize robotic integration and fully automated welding lines to improve throughput, consistency, and worker safety. Nut Welder is expected to expand its portfolio of robotic-compatible weld studs and process control systems. The integration of AI-driven quality assurance—such as vision systems and data analytics for weld integrity verification—will become standard, positioning companies that invest in digital welding solutions ahead of competitors still reliant on manual processes.
Sustainability and Lightweighting Imperatives
Environmental regulations and consumer demand for energy-efficient products are accelerating the use of lightweight materials like high-strength steel, aluminum, and composites. These materials present unique challenges for traditional welding methods, requiring specialized techniques such as capacitor discharge (CD) and short-cycle welding to prevent warping and ensure joint strength. Nut Welder is well-positioned to innovate in low-heat-input technologies and eco-friendly production processes. Furthermore, circular economy principles may drive demand for reusable or recyclable fastening systems, prompting R&D into sustainable materials and end-of-life disassembly solutions.
Expansion into Emerging Markets and Diversified Applications
Beyond traditional automotive and construction sectors, nut welding applications are expanding into renewable energy (e.g., solar mounting systems), rail infrastructure, and consumer electronics. Emerging markets in Southeast Asia, India, and Latin America are investing heavily in industrial modernization, creating new export and partnership opportunities for equipment providers. Nut Welder may pursue strategic alliances with local distributors or establish regional service centers to support global clients with faster deployment and technical support.
Supply Chain Resilience and Digitalization
Ongoing supply chain volatility will compel manufacturers to prioritize suppliers with proven reliability and transparent operations. By 2026, digital supply chain platforms that offer real-time inventory tracking, automated ordering, and logistics integration will be essential. Nut Welder can strengthen customer loyalty by adopting digital twin technology for equipment simulation, remote diagnostics, and customized training platforms—enhancing service delivery while reducing downtime.
In summary, the 2026 market for Nut Welder will be defined by innovation in automation, material science, and digital integration. Success will depend on the ability to deliver agile, sustainable, and intelligent fastening solutions tailored to the evolving needs of high-growth industries.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Nut Welder: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing a nut welder—especially from overseas suppliers or lesser-known manufacturers—can present significant challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to production delays, safety hazards, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key risks to consider.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Weld Performance
Low-cost or unverified suppliers may offer nut welders that do not consistently deliver the required weld strength or penetration. This can result in faulty welds, structural failures in end products, and costly rework. Inadequate quality control during manufacturing often leads to unit-to-unit variability.
Substandard Materials and Components
To reduce costs, some manufacturers use inferior materials in critical components such as electrodes, transformers, or control systems. This compromises durability, increases maintenance needs, and shortens the equipment’s operational lifespan.
Lack of Compliance with International Standards
Many budget nut welders fail to meet essential safety and performance standards (e.g., ISO, CE, UL). Sourcing non-compliant equipment can expose your company to regulatory penalties, workplace safety issues, and voided insurance coverage.
Insufficient Technical Documentation and Support
Poorly documented machines—missing manuals, unclear schematics, or lack of calibration data—hinder installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance. Limited after-sales support from the supplier can lead to extended downtime.
Inaccurate Specifications and Misrepresentation
Some suppliers exaggerate technical capabilities (e.g., weld speed, amperage range, duty cycle). Buyers may discover too late that the machine cannot handle their production requirements, leading to unexpected costs and operational bottlenecks.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Counterfeit or Cloned Equipment
A major concern when sourcing from certain regions is the risk of purchasing equipment that infringes on existing patents or trademarks. Some manufacturers replicate branded nut welders without authorization, potentially exposing the buyer to legal liability.
Lack of IP Ownership Clarity
When customizing or co-developing a nut welder, unclear agreements on IP ownership can result in disputes. Suppliers may claim rights over design improvements or software, limiting your ability to modify, service, or scale the technology.
Embedded Software and Firmware Issues
Modern nut welders often include proprietary control software. Unauthorized or pirated firmware may be installed to cut costs, creating cybersecurity vulnerabilities and potential breaches of software licensing agreements.
Difficulty Enforcing IP Rights Overseas
If IP infringement occurs, enforcing rights in foreign jurisdictions can be legally complex, time-consuming, and expensive. Legal remedies may be limited, especially in countries with weak IP protection frameworks.
Supply Chain Transparency Gaps
Without visibility into the supplier’s manufacturing chain, it’s difficult to verify whether components or designs are legitimately sourced. This opacity increases the risk of inadvertently using IP-infringing parts.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: audit suppliers, request third-party certifications, verify IP compliance, and include clear contractual terms on quality standards and IP ownership. Whenever possible, engage legal and technical experts during the sourcing process to safeguard your operations and intellectual assets.
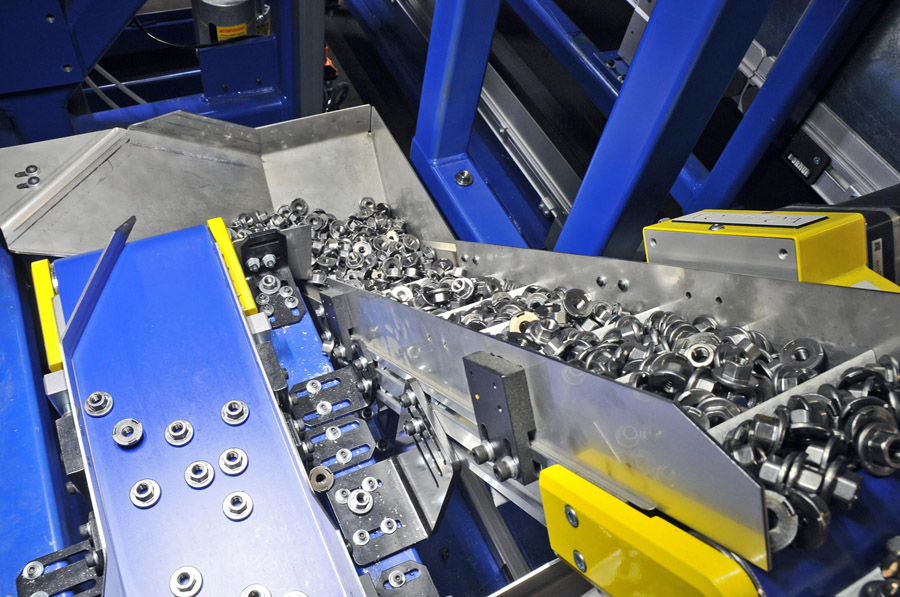

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Nut Welder
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and legally compliant handling, transportation, installation, and use of Nut Welders in industrial environments.
Equipment Specifications and Documentation
Ensure all Nut Welders meet relevant technical standards such as ISO, ANSI, or IEC, as applicable. Maintain complete documentation including user manuals, safety data sheets (SDS) for consumables, calibration records, and certification of electrical safety (e.g., CE, UL, or CSA marks). Keep equipment serial numbers and model specifications on file for traceability.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhere to all local, national, and international regulations governing industrial equipment. This includes compliance with OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) standards in the U.S., the EU Machinery Directive, or equivalent regulations in other regions. Verify that all operators are trained and certified according to recognized welding standards such as AWS D1.1 or ISO 9606.
Transportation and Handling
Secure Nut Welders during shipment using protective packaging and immobilization to prevent damage. Use appropriate lifting equipment when moving heavy units and follow manufacturer-specified weight limits and handling procedures. Label packages with handling instructions such as “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture.”
Storage Requirements
Store Nut Welders in a dry, temperature-controlled environment free from dust, moisture, and corrosive agents. Keep equipment off the floor on pallets or shelves to prevent water damage. Store welding studs, ferrules, and other consumables in sealed, labeled containers to maintain integrity.
Installation and Operational Safety
Install Nut Welders on stable, level surfaces with adequate ventilation. Ensure proper grounding and electrical connections meeting local codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S.). Implement lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance. Use personal protective equipment (PPE), including welding helmets, flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and safety footwear.
Emissions and Environmental Controls
Control fumes and sparks generated during welding processes using local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems. Regularly inspect and maintain fume extraction equipment. Dispose of used ferrules, slag, and damaged consumables in accordance with environmental regulations (e.g., EPA or equivalent).
Maintenance and Calibration
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for all components. Keep a log of inspections, repairs, and calibration activities. Recalibrate welding timers, amperage controls, and lift mechanisms periodically to ensure weld consistency and quality.
Training and Personnel Certification
Ensure all operators and maintenance personnel receive documented training specific to the Nut Welder model in use. Training should cover operational procedures, hazard recognition, emergency response, and compliance requirements. Retrain personnel when equipment or processes change.
Recordkeeping and Audits
Maintain comprehensive records of equipment usage, maintenance, operator certifications, safety incidents, and compliance inspections. Conduct regular internal audits to verify adherence to logistical and regulatory standards, and prepare for external audits by regulatory bodies.
Incident Reporting and Corrective Actions
Establish a clear procedure for reporting equipment malfunctions, safety near-misses, or compliance deviations. Investigate incidents promptly, implement corrective actions, and document outcomes to prevent recurrence and demonstrate due diligence.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Nut Welder:
After a thorough evaluation of technical requirements, supplier capabilities, cost considerations, and long-term operational needs, sourcing a nut welder should be approached strategically to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and cost-efficiency. The selected nut welding solution must align with production volume, material specifications, and automation compatibility while meeting industry quality and safety standards.
Partnering with reputable suppliers offering proven technology, responsive technical support, and comprehensive after-sales service is critical. Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—beyond initial purchase price—including maintenance, training, and integration costs will contribute to long-term success.
In conclusion, a well-informed sourcing decision, based on technical validation, supplier assessment, and lifecycle analysis, will ensure the integration of a robust and efficient nut welding system that enhances manufacturing productivity and product quality.