The global NEMA enclosures market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for protective electrical enclosures across industrial, commercial, and infrastructure sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the NEMA enclosures market was valued at approximately USD 2.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by increasing adoption in oil & gas, manufacturing, and energy industries, where equipment protection against harsh environments is critical. As compliance with NEMA standards becomes more stringent, particularly for types such as NEMA 3R, 4X, and 4, the need for reliable, high-performance enclosures has led to the prominence of key manufacturers specializing in durable, corrosion-resistant designs. Based on production capacity, global reach, and innovation in material engineering, the top three NEMA enclosures manufacturers—Rittal, Eaton, and Hammond Manufacturing—have emerged as market leaders, collectively holding a significant share of the North American and global markets. Their dominance is further supported by strategic investments in automation, expanded product portfolios, and increasing focus on sustainability in manufacturing processes.
Top 3 Nema Enclosures Types Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 NEMA Enclosures
Domain Est. 1999
Website: nemaenclosures.com
Key Highlights: Nema Enclosures manufactures industrial NEMA enclosures with powder-coated carbon steel, 304 stainless steel, 316 stainless steel, or 5052 aluminum….
#2 What are the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA …
Domain Est. 2019
Website: spire-is.com
Key Highlights: The following provides an overview of the NEMA Enclosure Types. Enclosure types 7, 8, 9, and 10 are for hazardous locations and are not included ……
#3 Enclosures
Domain Est. 1994
Website: nema.org
Key Highlights: Enclosures. An electrical enclosure is a cabinet or box that protects electrical or electronic equipment and prevents electrical shock….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Nema Enclosures Types
2026 Market Trends for NEMA Enclosures Types
The market for NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) enclosures is poised for notable evolution by 2026, driven by technological innovation, industrial digitization, and shifting regulatory and sustainability priorities. Below is an analysis of key trends expected to shape the demand and development of various NEMA enclosure types in the coming years.
Increased Demand for Higher Environmental Protection Ratings
NEMA enclosure types offering superior protection against environmental hazards—particularly NEMA 4, 4X, 6, 6P, and 12—are expected to experience accelerated demand. With industrial IoT (IIoT) and smart manufacturing expanding into harsher environments (e.g., outdoor installations, washdown areas in food & beverage, and offshore applications), the need for enclosures resistant to water ingress, corrosion, and submersion is growing. NEMA 4X stainless steel enclosures, in particular, will see robust growth in chemical processing, wastewater treatment, and marine sectors due to their corrosion resistance and durability.
Surge in Adoption of NEMA 12 and NEMA 13 in Industrial Automation
As factories implement more sophisticated control systems and robotics, enclosures that protect against dust, dirt, and non-corrosive coolants—such as NEMA 12 and NEMA 13—will become increasingly critical. These enclosures are essential for safeguarding programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), and drive systems in manufacturing plants. The trend toward closed-loop automation and predictive maintenance will further fuel demand, requiring reliable enclosures to house sensitive electronics in dusty or oily environments.
Growth in Customized and Modular NEMA Enclosures
Standard off-the-shelf NEMA enclosures will continue to dominate, but a growing trend toward modular, scalable, and customizable solutions will rise by 2026. End users in sectors like renewable energy, data centers, and electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure require enclosures tailored to specific spatial, thermal, and connectivity needs. Modular NEMA enclosures that allow for easy expansion, integration of cooling systems, and pre-wired configurations will gain market share, reducing installation time and lifecycle costs.
Integration of Smart Monitoring and IoT-Enabled Features
NEMA enclosures are evolving beyond passive protection to become intelligent components of connected systems. By 2026, expect to see more enclosures—especially in NEMA 4X and 12 types—equipped with embedded sensors for temperature, humidity, door status, and vibration. These IoT-enabled enclosures will feed data into facility management systems, enabling predictive maintenance and enhancing operational uptime. This trend is particularly relevant in critical infrastructure such as power substations and telecom facilities.
Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures will drive innovation in enclosure materials. Recycled stainless steel, aluminum, and advanced polymers will gain traction as manufacturers aim to reduce carbon footprints. Additionally, lightweight composite enclosures meeting NEMA 4 or 4X standards will emerge as alternatives in transportation and remote installations where weight and logistics matter. Energy-efficient designs, such as enclosures with passive thermal management or solar reflectivity, will also become more common.
Regional Market Diversification and Supply Chain Localization
Global supply chain disruptions have prompted a shift toward regional manufacturing and sourcing. By 2026, North American and European markets will favor locally produced NEMA enclosures to ensure compliance and reduce lead times. Meanwhile, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America will experience rising demand for NEMA-compliant enclosures due to infrastructure upgrades and foreign direct investment in manufacturing, though local standards may coexist with NEMA types.
Conclusion
By 2026, the NEMA enclosure market will be characterized by a shift toward higher protection ratings, intelligent features, and sustainability. Enclosure types such as 4X, 12, and 6P will lead growth, while customization, modularity, and IoT integration will redefine product expectations. Manufacturers who anticipate these trends and innovate accordingly will be well-positioned to capture value in an increasingly competitive and demanding industrial landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing NEMA Enclosures (Quality and IP Ratings)
Sourcing NEMA enclosures requires careful attention to detail, as overlooking key factors can lead to equipment failure, safety hazards, and costly replacements. Below are common pitfalls related to quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings.
Confusing NEMA Ratings with IP Ratings
A frequent mistake is assuming NEMA ratings directly correlate with IP (Ingress Protection) ratings. While both address environmental protection, they are tested and certified under different standards. For example, a NEMA 4X enclosure offers protection against corrosion, hose-directed water, and is watertight, but its closest IP equivalent—IP66—only partially aligns. Relying solely on IP ratings when NEMA compliance is required (common in North America) can result in non-compliant installations.
Overlooking Material Quality and Corrosion Resistance
Not all enclosures labeled as “stainless steel” or “fiberglass” are created equal. Substandard materials or thin gauge metals may meet basic NEMA specs temporarily but degrade quickly in harsh environments. For instance, a low-grade stainless steel enclosure may rust in coastal areas despite being labeled NEMA 4X. Always verify material composition, finish quality, and third-party certifications.
Assuming All Vendors Meet NEMA Standards
Many suppliers claim NEMA compliance without independent testing or certification. Unlike UL or CSA marks, NEMA does not perform certifications—manufacturers self-declare. This lack of oversight can lead to enclosures that fail under real-world conditions. Always request test reports or third-party verification (e.g., UL Type ratings) to confirm compliance.
Ignoring Gasket and Seal Integrity
The durability of gaskets and seals is critical to maintaining NEMA ratings. Poor-quality or improperly installed seals can degrade over time, allowing moisture, dust, or contaminants to enter. This is especially important for NEMA 4, 4X, and 6 enclosures used outdoors or in washdown environments. Check seal material (e.g., EPDM, silicone) and compression performance.
Mismatching Enclosure Type to Environment
Selecting the wrong NEMA type for the application is a common error. For example, using a NEMA 1 enclosure (indoor use only) in a wet or dusty outdoor setting compromises safety and equipment function. Similarly, assuming NEMA 12 (dust-tight) is sufficient for outdoor use ignores water ingress risks. Always match the NEMA type to environmental conditions—temperature, humidity, chemical exposure, and physical impact.
Neglecting Long-Term Maintenance and Accessibility
High-quality enclosures should allow for easy maintenance without compromising ratings. Poorly designed doors, corroded hinges, or degraded latches can break the environmental seal over time. Ensure that access points maintain IP/NEMA integrity even after repeated use, and consider serviceability during selection.
Focusing Only on Initial Cost
Opting for the cheapest option often leads to higher lifecycle costs due to premature failure, downtime, or safety incidents. A low-cost enclosure may appear compliant but fail under stress or exposure. Investing in reputable brands with proven performance reduces long-term risks and total cost of ownership.
By understanding these pitfalls and conducting due diligence in material quality, certification, and environmental matching, you can ensure reliable and safe enclosure performance in your application.
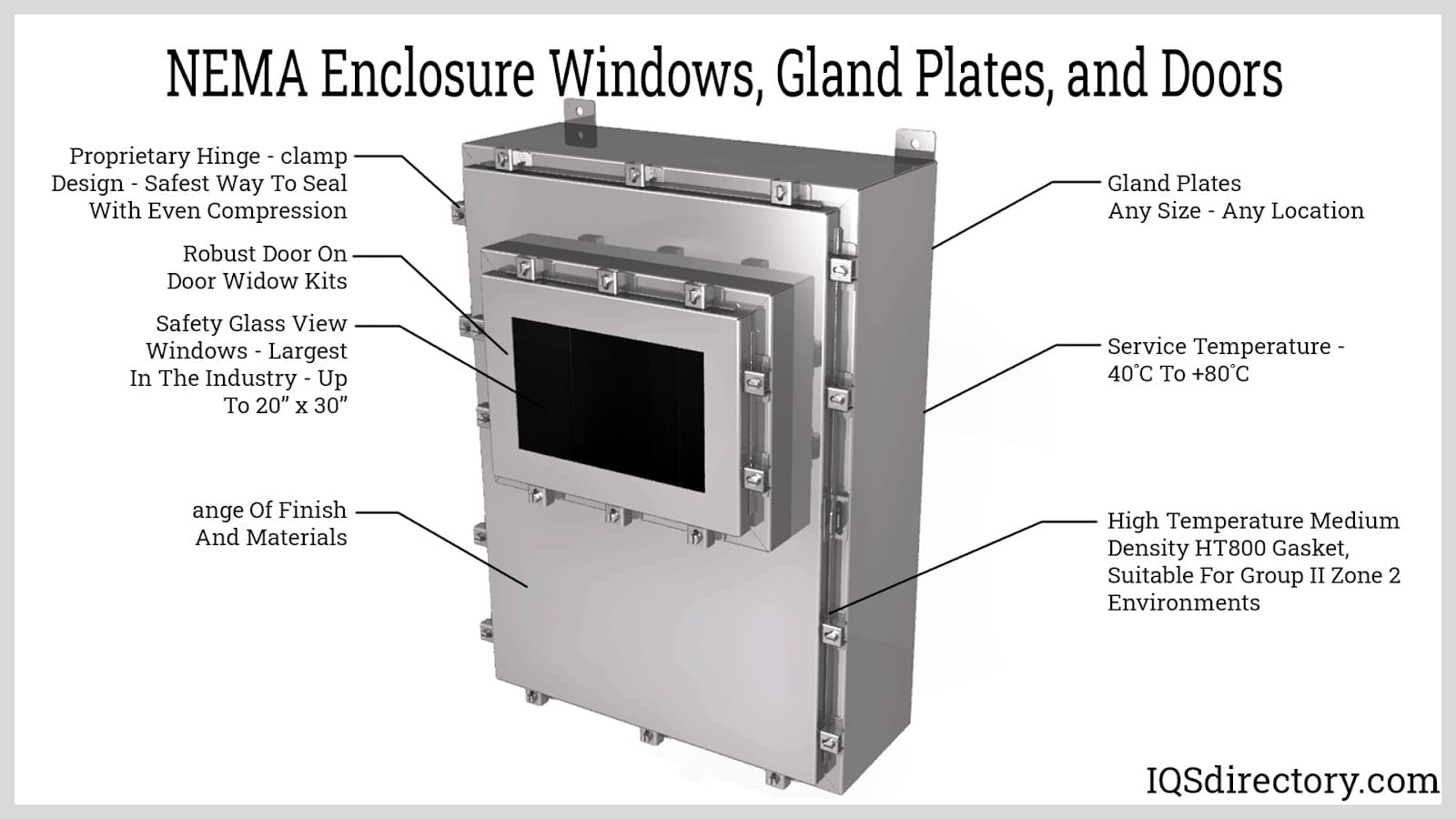
Logistics & Compliance Guide for NEMA Enclosure Types
Understanding NEMA Enclosure Standards
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) defines specific enclosure types to ensure electrical equipment is protected against environmental conditions such as dust, water, oil, and corrosive agents. These enclosures are commonly used in industrial, commercial, and outdoor applications. Compliance with NEMA standards is crucial for safety, performance, and regulatory approval. Each NEMA type corresponds to a defined level of protection, which directly impacts logistics, handling, storage, and installation practices.
Key NEMA Enclosure Types and Their Applications
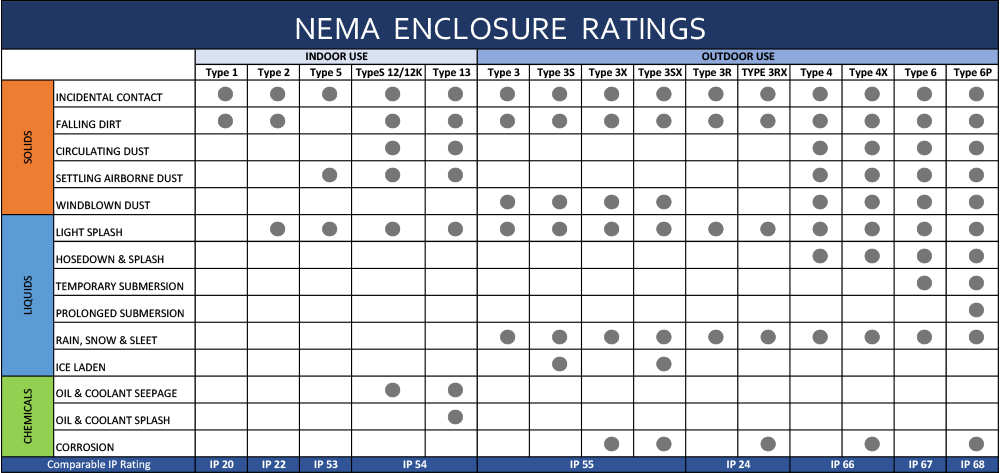
- NEMA 1: General indoor use; protects against light dust and accidental contact.
- NEMA 3R: Outdoor use; resists rain, sleet, and external ice formation.
- NEMA 4/4X: Watertight and dust-tight; suitable for washdown environments (4X adds corrosion resistance, often with stainless steel).
- NEMA 6/6P: Submersible; designed for temporary or prolonged water submersion.
- NEMA 7–9: Hazardous locations; for use in environments with explosive gases (Class I) or combustible dust (Class II).
- NEMA 12/13: Industrial indoor use; protects against dust, dripping liquids, and non-corrosive coolants.
Packaging and Shipping Considerations
Proper packaging is essential to maintain NEMA ratings during transit. Use robust, weather-resistant crates or pallets for outdoor-rated enclosures (e.g., NEMA 3R, 4X). Sealed plastic wrapping helps prevent moisture ingress and corrosion, especially for NEMA 4X and 6P enclosures. Clearly label packages with the NEMA type, orientation warnings, and handling instructions (e.g., “Do Not Invert,” “Protect from Moisture”). Avoid stacking incompatible types to prevent physical damage.
Storage and Environmental Precautions
Store enclosures in a dry, temperature-controlled environment whenever possible. NEMA 4X and stainless steel enclosures should be kept away from chloride-rich environments to prevent pitting corrosion. Prolonged outdoor storage should be avoided unless the enclosure is designed for such exposure (e.g., NEMA 3R or 4). Elevate pallets off the ground to prevent water absorption and pest infestation. Regularly inspect stored units for seal degradation, dents, or rust.
Compliance and Certification Requirements
Ensure all NEMA enclosures are certified and labeled with the correct NEMA type, manufacturer details, and relevant standards (e.g., UL 50, UL 508A). Documentation such as test reports, material certifications, and installation manuals must accompany shipments. For hazardous location enclosures (NEMA 7–9), certifications from recognized bodies like UL, CSA, or ATEX may be required depending on regional regulations. Always verify compliance with local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S.).
Handling and Installation Best Practices
Only trained personnel should handle and install NEMA enclosures. Maintain the integrity of gaskets, seals, and conduit entries during installation to preserve the rated protection level. Torque screws and fasteners to manufacturer specifications—over-tightening can damage seals. For NEMA 4X and 6P enclosures, confirm watertight integrity post-installation using recommended inspection procedures. Document installation and perform visual checks for compliance.
Maintenance and Inspection Regimes
Regular maintenance is vital to uphold NEMA ratings. Inspect seals, hinges, and fasteners for wear or corrosion, particularly in high-moisture or corrosive environments. Clean enclosures with non-abrasive agents to avoid surface damage. For NEMA 12 and 13 enclosures in dusty areas, schedule routine internal cleaning to prevent buildup that could impair function. Log all inspections and repairs for audit and compliance purposes.
Regional and International Compliance Considerations
While NEMA is primarily used in North America, projects with international components may require equivalency assessments (e.g., IEC 60529 IP ratings). For example, NEMA 4 is roughly equivalent to IP66, but differences in testing methods mean direct substitution isn’t always acceptable. Always consult local authorities and project specifications to ensure compliance across jurisdictions. Dual-certified enclosures (NEMA + IEC) can simplify logistics for global deployments.
Conclusion
Adhering to logistics and compliance guidelines for NEMA enclosures ensures safety, longevity, and regulatory acceptance. From proper shipping and storage to correct installation and maintenance, each step plays a role in preserving the integrity of the enclosure’s protection rating. Always source enclosures from reputable manufacturers with full certification documentation and train staff on handling procedures specific to each NEMA type.
Conclusion on Sourcing NEMA Enclosure Types
Selecting and sourcing the appropriate NEMA enclosure type is a critical decision that directly impacts the safety, reliability, and longevity of electrical and electronic equipment in various environments. NEMA ratings provide a standardized way to define the level of protection an enclosure offers against environmental factors such as dust, water, corrosion, and hazardous conditions.
When sourcing NEMA enclosures, it is essential to carefully evaluate the specific application requirements—including environmental exposure, location (indoor vs. outdoor), chemical or washdown conditions, and potential hazards (e.g., explosive atmospheres). Common types like NEMA 1, 4, 4X, and 12 serve distinct purposes, from basic indoor protection to full resistance against corrosive materials and high-pressure water jets.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include material selection (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum, or polycarbonate), compliance with relevant industry standards, availability, lead times, and total cost of ownership. Working with reputable suppliers who provide certified, tested enclosures ensures compliance and performance reliability.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of NEMA standards, combined with careful assessment of operational needs and sourcing from trusted manufacturers, enables organizations to select enclosures that provide optimal protection, reduce maintenance costs, and support long-term operational efficiency. Proper sourcing not only meets regulatory and safety requirements but also enhances the durability and performance of critical equipment in demanding environments.