The global electrical connectors market, which includes NEMA plug configurations, is experiencing steady growth driven by rising demand across industrial, commercial, and residential sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global electrical connectors market size was valued at USD 84.1 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing infrastructure development, advancements in building automation, and the proliferation of power-intensive electronic devices. With North America remaining a key regional market, adherence to standards set by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) is critical for safety, compatibility, and performance. As demand for reliable and standardized power connection solutions rises, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders in producing NEMA-compliant plug configurations. Below are the top 5 manufacturers recognized for their innovation, product breadth, and market presence in the NEMA electrical plug space.
Top 5 Nema Electrical Plug Configurations Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
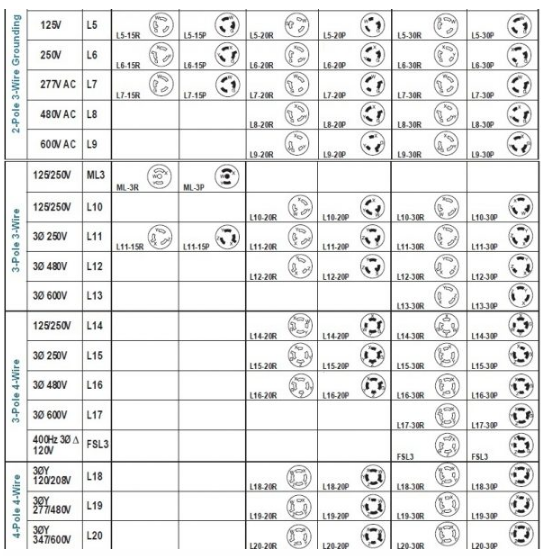
#1 Wiring Devices—Dimensional Specifications
Domain Est. 1994
Website: nema.org
Key Highlights: Covers the plugs, receptacles, and wall plates used in most electrical installations in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings….
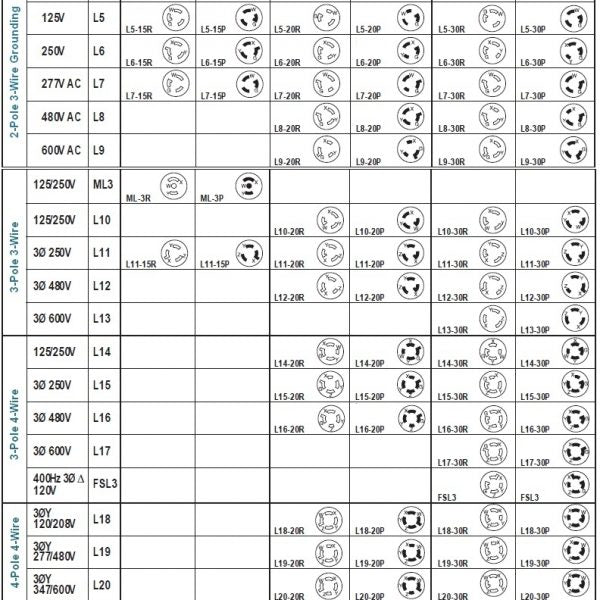
#2 NEMA Plug and Receptacle Configuration Chart
Domain Est. 1994
Website: grainger.com
Key Highlights: These charts show many of the possible NEMA straight-blade configurations, from the common wall socket to more rarely seen plugs and receptacles….
#3 NEMA Locking Reference Chart
Domain Est. 1996
Website: stayonline.com
Key Highlights: This NEMA receptacle chart provides technical drawings and specifications for NEMA locking plugs, receptacles, inlets, outlets, connectors and cords….
#4 NEMA Plug Charts
Domain Est. 1999
Website: americord.com
Key Highlights: These charts describe the layout of the connector plugs and sockets, voltage, and current limits, for their aim is to offer a uniform means of connecting ……
#5 North American heavy duty plugs and sockets
Domain Est. 2015
Website: plugsocketmuseum.nl
Key Highlights: North America is a mine of interesting plugs and sockets. Different devices for 125V, 208V, 250V, 277V and higher, rated at 15A, 20A, 30A, 50A or 60A; ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Nema Electrical Plug Configurations
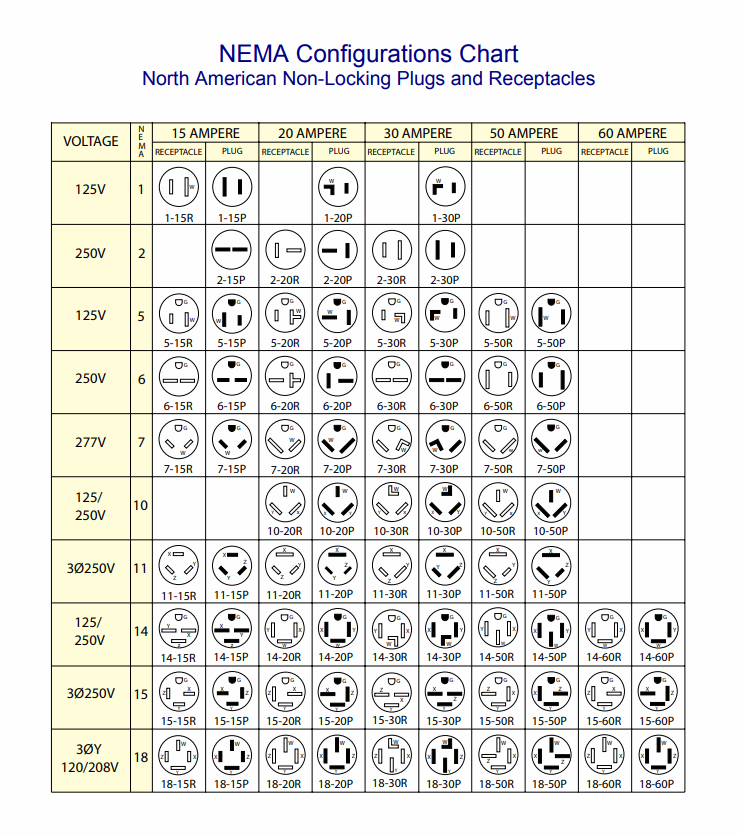
H2: 2026 Market Trends for NEMA Electrical Plug Configurations
As the global demand for standardized, safe, and efficient electrical connectivity continues to evolve, the market for NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) plug configurations is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by technological advancements, regulatory shifts, and increasing electrification across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, NEMA plug configurations are adapting to meet modern energy needs. Below is an analysis of key market trends shaping the NEMA plug landscape through 2026.
1. Rising Demand in Residential and Commercial EV Charging Infrastructure
With electric vehicle (EV) adoption accelerating worldwide—particularly in North America—the deployment of NEMA 5-15 and NEMA 14-50 outlets for Level 1 and Level 2 EV charging is expanding rapidly. By 2026, residential EV charging installations are expected to account for a major share of NEMA plug demand. The NEMA 14-50, traditionally used for recreational vehicles and large appliances, is increasingly being installed in homes to support faster EV charging. This trend is reinforced by government incentives and utility programs promoting home charging solutions.
2. Growth in Smart Building Integration
Smart homes and intelligent commercial buildings are incorporating NEMA outlets with integrated power monitoring, surge protection, and IoT connectivity. By 2026, smart NEMA receptacles—especially configurations like NEMA 5-15R and 5-20R—are expected to gain traction as part of energy management systems. These smart outlets enable real-time energy tracking, remote control, and load balancing, aligning with sustainability goals and grid modernization efforts.
3. Industrial and Data Center Expansion Driving Demand for Higher-Capacity Configurations
Industrial automation, data center growth, and renewable energy integration are increasing the need for higher-power NEMA configurations such as NEMA L14-30, L21-30, and L6-30. These locking plugs ensure secure connections for backup generators, server racks, and HVAC systems. The shift toward resilient and redundant power systems in critical facilities is expected to boost demand for weather-resistant and tamper-proof NEMA connectors in industrial settings.
4. Regulatory and Safety Standards Driving Standardization
Ongoing updates to the National Electrical Code (NEC), particularly the 2023 and anticipated 2026 editions, are emphasizing arc-fault and ground-fault protection for outlets in living areas and garages. These changes are increasing the adoption of NEMA configurations with built-in safety features, such as tamper-resistant (TR) and weather-resistant (WR) receptacles. Manufacturers are responding with compliant, future-ready products to meet code requirements.
5. Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt recyclable materials and energy-efficient designs in NEMA plug production. By 2026, expect increased use of bio-based plastics, reduced packaging waste, and longer product lifecycles. Additionally, modular and repairable designs may emerge to support circular economy principles.
6. Regional Market Disparities and Global Influence
While NEMA standards are predominantly used in North America, their influence extends to regions with U.S.-based infrastructure projects or export markets. However, competition from IEC standards (e.g., Type F, G) in international markets may limit global expansion. Nevertheless, U.S. military, telecom, and energy projects abroad continue to specify NEMA configurations, sustaining export demand.
7. Supply Chain Resilience and Domestic Manufacturing
Geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions have prompted a reevaluation of manufacturing strategies. By 2026, there is a growing trend toward reshoring NEMA plug production to North America, supported by policies like the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). This shift enhances supply chain reliability and reduces lead times for critical infrastructure projects.
Conclusion
By 2026, the NEMA electrical plug market will be shaped by electrification, digitalization, and regulatory evolution. While traditional configurations remain foundational, innovations in smart technology, safety compliance, and sustainability will define the next generation of NEMA products. Stakeholders—including manufacturers, installers, and policymakers—must align with these trends to ensure reliable, efficient, and future-ready electrical connectivity across sectors.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing NEMA Electrical Plug Configurations (Quality, IP)
When sourcing NEMA electrical plug configurations, overlooking certain critical factors can lead to safety hazards, equipment failure, or non-compliance. Below are common pitfalls related to quality and ingress protection (IP) ratings.
Poor Manufacturing Quality
One of the most prevalent issues is selecting plugs made from substandard materials or with inconsistent manufacturing practices. Low-quality NEMA plugs may use inferior thermoplastics that degrade quickly under heat or UV exposure, or feature poorly crimped contacts leading to arcing and overheating. These defects increase the risk of electrical fires and equipment damage, especially in industrial or outdoor environments.
Misunderstanding NEMA vs. IP Ratings
A frequent confusion arises between NEMA ratings and IP (Ingress Protection) codes. While both address environmental protection, they are not directly equivalent. NEMA ratings (e.g., NEMA 4, NEMA 6) are North American standards that include protection against water, dust, oil, and coolant, along with corrosion resistance and structural integrity. IP ratings (e.g., IP66, IP67) are international standards focusing strictly on solid and liquid ingress. Assuming IP67 equals NEMA 6P, for example, can lead to incorrect component selection if other NEMA-specific requirements (like rust resistance or external ice resistance) are needed.
Overlooking Environmental Compatibility
Sourcing a NEMA plug without verifying its suitability for the operating environment is a major pitfall. For instance, using a NEMA 5-15P (indoor-rated) plug in a wet or dusty outdoor setting can result in short circuits or corrosion. Always ensure the NEMA type (e.g., NEMA 3R for outdoor use, NEMA 4X for corrosive environments) matches the actual application conditions.
Falsified or Inaccurate Certification Claims
Some suppliers may claim their plugs meet specific NEMA ratings without independent certification. Without UL, CSA, or ETL listing, these claims are unreliable. Always verify certifications through official databases or request test reports to confirm compliance.
Inadequate Strain Relief and Cable Retention
Low-quality or poorly designed NEMA plugs often lack effective strain relief mechanisms. This can lead to internal wire disconnections due to cable movement or vibration, especially in mobile or industrial equipment. Ensure the plug design includes robust clamping features to maintain electrical integrity over time.
Incorrect Configuration or Pin Alignment
Using a plug with the wrong NEMA configuration (e.g., confusing NEMA 6-15P with NEMA 5-15P) can result in improper voltage delivery or unsafe connections. Always double-check voltage, amperage, and grounding requirements to avoid equipment damage or electrical hazards.
Neglecting Long-Term Durability and Maintenance
Even if a plug initially meets IP and NEMA standards, poor build quality can cause seals to degrade, threads to strip, or gaskets to fail prematurely. This reduces long-term protection and increases maintenance costs. Prioritize plugs from reputable manufacturers known for durability and consistent performance.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence in supplier selection, verification of certifications, and a clear understanding of both NEMA and IP standards in context.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for NEMA Electrical Plug Configurations
Understanding National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) plug configurations is essential for safe, compliant, and efficient logistics operations involving electrical equipment. This guide outlines key considerations for handling, transporting, and deploying devices with NEMA plugs in accordance with regulatory and operational standards.
Understanding NEMA Plug Types
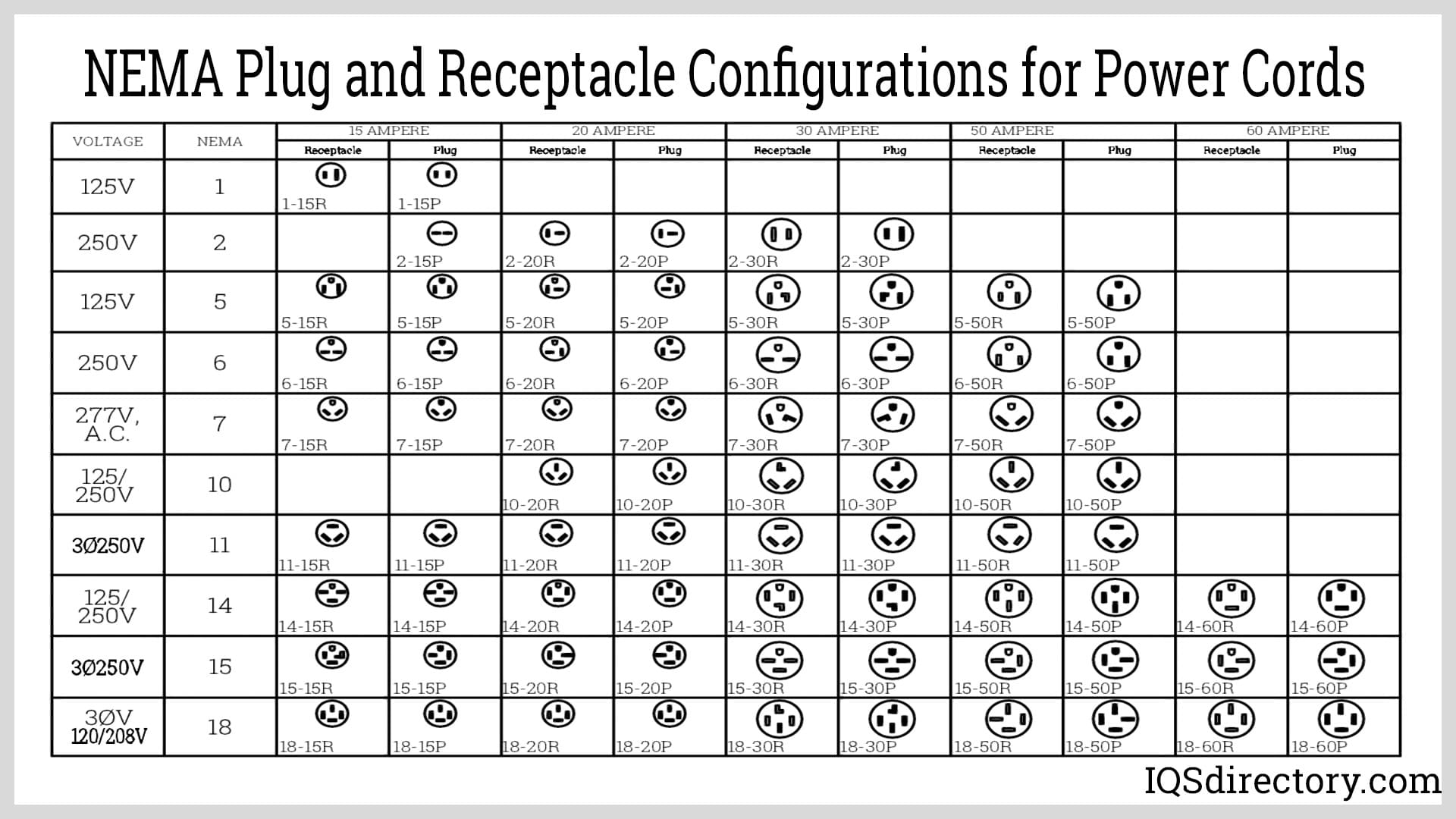
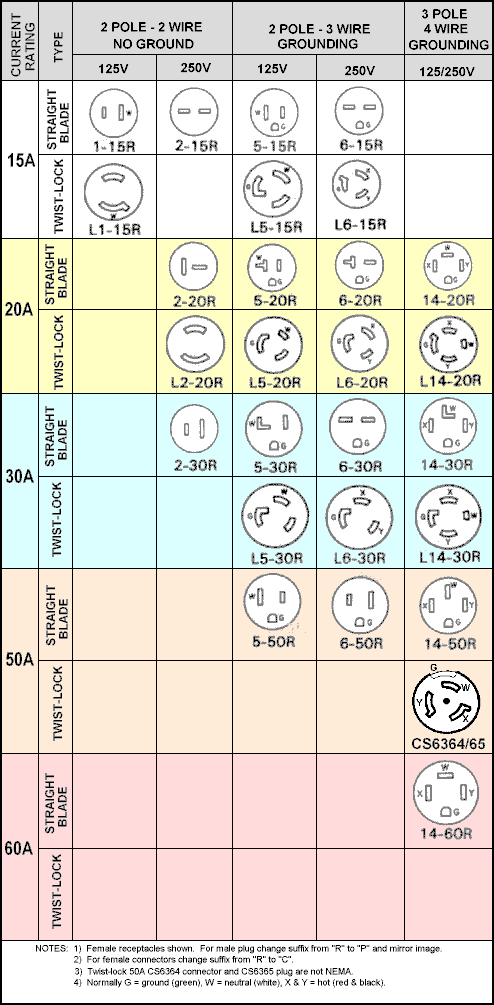
NEMA configurations are standardized by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association and are used primarily in North America. Each plug type is designated by a number-letter combination (e.g., NEMA 5-15P) that indicates voltage, current rating, grounding, and blade configuration. Key examples include:
- NEMA 5-15P: 125V, 15A, grounded plug (common household)
- NEMA 5-20P: 125V, 20A, grounded with one horizontal blade
- NEMA 6-15P/6-20P: 250V, 15A/20A, grounded (for higher power tools and HVAC)
- NEMA L5-30P: Twist-lock 125V, 30A (common in industrial and temporary power)
Ensure that equipment shipped or used in your operations matches the correct NEMA plug for voltage, amperage, and application requirements.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Adherence to NEMA plug standards supports compliance with major safety and electrical codes:
- National Electrical Code (NEC): Mandates proper wiring and plug configurations to prevent fire and shock hazards.
- OSHA Regulations: Requires safe electrical systems in workplaces; improper or modified plugs may violate safety standards.
- UL/ETL Certification: Equipment with NEMA plugs should be listed by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) to confirm compliance with safety standards.
Ensure all equipment with NEMA plugs is certified and used within its rated specifications. Never modify plugs to fit incompatible outlets—this violates safety codes and voids equipment certification.
Logistics Considerations for Equipment with NEMA Plugs
When transporting or deploying electrical equipment, pay attention to:
- Voltage and Frequency Compatibility: Confirm that equipment with NEMA plugs operates at 120V/240V, 60Hz (standard in North America). Equipment intended for international use may require transformers or adapters.
- Plug Interchangeability: Avoid using adapters that bypass grounding or alter amperage ratings. Use only UL-listed adapters when necessary.
- Storage and Handling: Protect plugs and cords from damage during transit. Inspect for fraying, bent blades, or cracked housing before use.
- Labeling and Documentation: Clearly label equipment with its NEMA plug type, voltage, and amperage. Include compliance documentation (e.g., UL listing) in shipment records.
Warehouse and Facility Deployment
In warehouse or industrial environments:
- Match NEMA plug types to appropriate receptacles (e.g., NEMA 5-20R for 20A circuits).
- Use twist-lock connectors (e.g., NEMA L-series) in high-vibration or outdoor settings to prevent accidental disconnection.
- Implement regular inspection programs to ensure plugs and outlets are in good condition.
- Train staff to recognize correct plug-receptacle pairings and report damaged equipment.
International Shipments and Export Compliance
Note that NEMA plugs are primarily used in the U.S., Canada, and Mexico. For international logistics:
- Verify that incoming equipment is compatible with local electrical systems.
- For exports, replace or supply appropriate power cords with region-specific plugs (e.g., IEC, Schuko).
- Maintain records of plug modifications or replacements to support compliance audits.
Conclusion
Proper handling of equipment with NEMA electrical plug configurations ensures operational safety, regulatory compliance, and logistical efficiency. Always verify plug ratings, maintain certification, and follow NEC and OSHA guidelines. By standardizing on correct NEMA configurations, logistics managers can reduce risk, prevent downtime, and ensure seamless integration of electrical equipment across facilities.
In conclusion, sourcing NEMA electrical plug configurations requires careful consideration of voltage, current rating, configuration type, and application environment to ensure compatibility, safety, and compliance with regional electrical standards. Understanding the specific NEMA designation—such as NEMA 5-15P, L5-30R, or 6-20P—is essential for selecting the right plug and receptacle for residential, commercial, or industrial use. Additionally, factors such as locking vs. non-locking designs, indoor vs. outdoor suitability, and adherence to codes like the NEC (National Electrical Code) play a crucial role in proper selection. When sourcing, it is important to procure from reputable suppliers who provide certified, UL-listed (or equivalent) products to guarantee performance and safety. Ultimately, accurate identification and proper sourcing of NEMA plugs help prevent equipment damage, reduce electrical hazards, and ensure seamless integration within electrical systems.