The global natural gas generator set market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for cleaner, reliable power generation and the rising adoption of distributed energy systems. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 24.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% through 2028. This expansion is fueled by stricter environmental regulations, advancements in natural gas infrastructure, and the push toward lower-emission alternatives to diesel generators. As industries, utilities, and commercial facilities seek resilient and sustainable backup power solutions, leading manufacturers are innovating to improve efficiency, emissions performance, and smart grid integration. In this dynamic landscape, a select group of companies stand out for their technological leadership, global reach, and comprehensive product portfolios—making them the top 10 natural gas generator set manufacturers shaping the future of energy resilience.
Top 10 Natural Gas Generator Set Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Natural Gas Generators
Domain Est. 1993
Website: cat.com
Key Highlights: 2-day deliveryCat industrial and commercial gas generator sets, at ratings from 100 to 4,500 ekW (100 to 4,500 kVA), operate on natural gas and a wide range of other ……
#2 Stationary Generators
Domain Est. 1995
Website: generac.com
Key Highlights: Generac Industrial Energy delivers powerful, reliable stationary generators built to meet the demands of today’s evolving energy landscape….
#3 Gillette Generators
Domain Est. 2000
Website: gillettegenerators.com
Key Highlights: Generators · Standby · Commercial Gas · Industrial Diesel · Portable · Prime · Prime Gas · T4F-Stage 5 Prime Diesel. Manuals. Standby Manuals….
#4 Worldwide Power Products
Domain Est. 2008
Website: wpowerproducts.com
Key Highlights: Largest Industrial-sized generator inventory in Texas. From diesel and natural gas generators to industrial engines; transfer switches to breakers and generator ……
#5 Taylor Power Systems
Domain Est. 2019
Website: taylorpowergenerators.com
Key Highlights: Taylor Power Systems provides dependable backup and prime power generators for residential, commercial, and industrial needs. Trusted for over 30 years, ……
#6 Cummins Generator Sets
Domain Est. 1990
Website: cummins.com
Key Highlights: We design, manufacture, and test all major components of our generator sets – the engine, alternator, and control systems – so they work in harmony from the ……
#7 Gas Engines
Domain Est. 1995
Website: jenbacher.com
Key Highlights: Jenbacher gas generator sets give you a power range of 200 kW to 10 MW with fuel flexibility to run either on natural gas or a number of other gases….
#8 Natural Gas Engines
Domain Est. 1996
Website: waukeshaengine.com
Key Highlights: From our newest generation of the 275GL+ gas engines to our mobileFLEX, VGF and legendary VHP Series, Waukesha provides the reliable power your operation needs….
#9 Gas Engines / Generator Sets
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mwm.net
Key Highlights: Gas engines, gensets, biogas and natural gas gensets, power generators for decentralised energy supply from MWM….
#10 Power Generation Products
Domain Est. 2018
Website: mtu-solutions.com
Key Highlights: Gas generator sets. mtu gas generator sets are fueled by natural gas, biogas or other gases and are perfect for a wide range of applications. Whether it’s ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Natural Gas Generator Set

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Natural Gas Generator Sets
The global market for natural gas generator sets is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving energy policies, technological advancements, and shifting demand dynamics across industrial, commercial, and residential sectors. Here is an analysis of key trends expected to shape the natural gas generator set market in 2026:
1. Increased Adoption Due to Energy Transition and Decarbonization Goals
Governments and corporations worldwide are intensifying efforts to reduce carbon emissions and transition toward cleaner energy sources. Natural gas, being one of the cleanest-burning fossil fuels, is increasingly favored as a transitional fuel in power generation. By 2026, stricter environmental regulations—especially in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific—are expected to accelerate the replacement of diesel and heavy fuel oil generator sets with natural gas alternatives. This trend is supported by initiatives such as the EU Green Deal and U.S. Inflation Reduction Act, which incentivize cleaner backup and distributed power solutions.
2. Growth in Distributed Energy Systems and Microgrids
The rise of decentralized energy systems is a major driver for natural gas generator sets. By 2026, microgrids and distributed generation (DG) systems integrating renewable sources like solar and wind will increasingly rely on natural gas generators for grid stability and backup power. Their ability to provide reliable, on-demand power makes them ideal for balancing the intermittency of renewables. Utilities and industrial parks are expected to adopt hybrid systems combining solar PV, battery storage, and natural gas gensets, enhancing energy resilience.
3. Technological Advancements and Efficiency Improvements
By 2026, manufacturers are expected to roll out next-generation natural gas generator sets featuring higher electrical efficiencies (exceeding 45% in combined heat and power applications), lower emissions (particularly NOx and methane slip), and improved digital integration. Innovations such as lean-burn combustion, advanced engine controls, and predictive maintenance using IoT sensors will enhance operational reliability and reduce lifecycle costs. Additionally, bi-fuel and dual-fuel capabilities (e.g., natural gas with hydrogen blending) are anticipated to gain traction as a pathway toward carbon neutrality.
4. Expansion in Emerging Markets
While North America and Europe remain key markets due to mature infrastructure and regulatory support, rapid industrialization in regions such as Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America will drive demand for reliable power solutions. Natural gas generator sets are expected to gain market share in countries expanding gas pipeline infrastructure and LNG import terminals. For instance, India and Nigeria are investing in gas-based power to reduce reliance on diesel and improve grid reliability, creating growth opportunities for generator OEMs.
5. Integration with Renewable Gases and Hydrogen Readiness
A pivotal trend by 2026 will be the growing compatibility of generator sets with renewable natural gas (RNG) and hydrogen blends. As RNG production from biogas and waste streams increases, generator sets capable of running on 100% RNG will appeal to sustainability-focused customers. Furthermore, manufacturers are developing hydrogen-ready engines that can operate on natural gas-hydrogen mixtures (up to 25–30% H2), positioning natural gas generators as a flexible bridge technology in the hydrogen economy.
6. Rising Demand for CHP and Energy Efficiency Incentives
Combined Heat and Power (CHP) systems, which utilize waste heat from generator sets for heating or cooling, will see increased deployment in sectors such as healthcare, data centers, and district energy. By 2026, government incentives and carbon pricing mechanisms are expected to make CHP systems more economically attractive, further boosting demand for high-efficiency natural gas generators.
7. Supply Chain and Infrastructure Challenges
Despite positive momentum, market growth may be constrained by uneven natural gas infrastructure, especially in remote and developing regions. Pipeline access, gas pricing volatility, and LNG logistics could impact adoption rates. However, modular and containerized generator solutions, along with small-scale LNG and compressed natural gas (CNG) technologies, are expected to mitigate some of these challenges.
Conclusion
By 2026, the natural gas generator set market will be shaped by a confluence of environmental regulations, energy security concerns, and technological innovation. While competition from battery storage and renewable energy grows, natural gas gensets will maintain a critical role as a reliable, flexible, and cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuel generators—especially in hybrid systems and regions with expanding gas infrastructure. OEMs that prioritize efficiency, emissions reduction, and fuel flexibility will be best positioned to capitalize on these emerging opportunities.
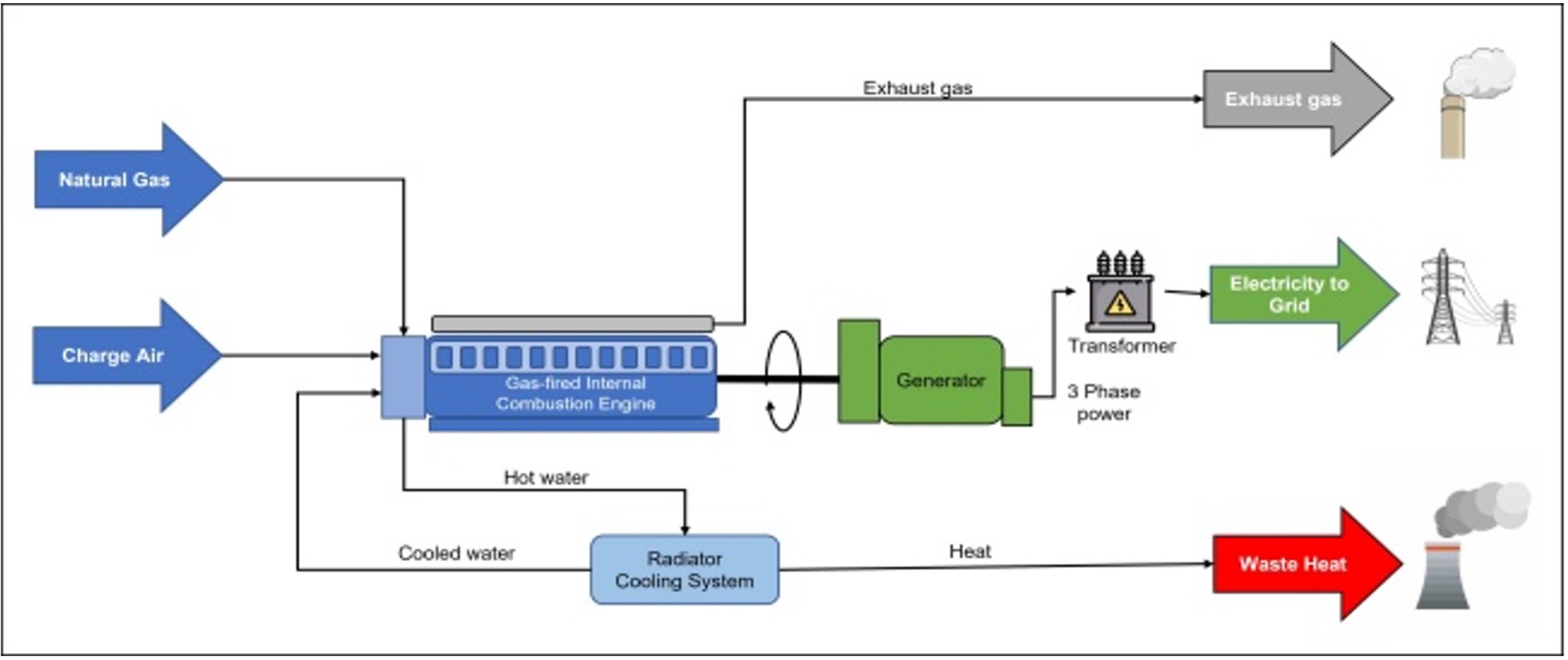
H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Natural Gas Generator Sets (Focus on Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing natural gas generator sets involves technical, commercial, and legal considerations. Two critical areas where buyers often encounter challenges are quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance issues, safety hazards, financial loss, and legal exposure. Below are the common pitfalls in each area:
1. Quality-Related Pitfalls
a. Substandard Components and Materials
– Pitfall: Suppliers may use low-grade materials or non-OEM parts (e.g., alternators, engines, control systems) to reduce costs, leading to premature failure, reduced efficiency, or safety risks.
– Impact: Higher maintenance costs, unplanned downtime, and shorter lifespan.
– Mitigation: Require detailed technical specifications, request material certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM), and conduct factory acceptance tests (FAT).
b. Inadequate Testing and Certification
– Pitfall: Generators may lack proper certification for emissions (e.g., EPA, Euro V), safety (e.g., UL, CE), or performance (e.g., ISO 8528).
– Impact: Non-compliance with local regulations, operational shutdowns, or environmental penalties.
– Mitigation: Verify third-party certifications and insist on performance testing under load conditions before delivery.
c. Poor Noise and Emissions Control
– Pitfall: Some suppliers underestimate noise attenuation or emissions compliance, especially in urban or sensitive environments.
– Impact: Violation of local ordinances, community complaints, or project delays.
– Mitigation: Specify noise levels (dBA at 1m/7m) and emissions requirements (NOx, CO, CH4) in the procurement contract.
d. Incomplete or Misleading Performance Data
– Pitfall: Suppliers may quote “ideal” performance figures (e.g., standby vs. prime power) without clarifying operating conditions (ambient temperature, altitude, fuel quality).
– Impact: Underperformance in real-world conditions.
– Mitigation: Define required power output under site-specific conditions and validate with site acceptance tests (SAT).
e. Lack of After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
– Pitfall: Choosing suppliers with weak local service networks leads to extended downtimes.
– Impact: Increased OPEX and operational risk.
– Mitigation: Evaluate the supplier’s service footprint, spare parts inventory, and response time guarantees.
2. Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
a. Use of Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components
– Pitfall: Some manufacturers replicate branded engines or control systems (e.g.,模仿 Caterpillar, Cummins, or MTU) without licensing.
– Impact: Voided warranties, poor reliability, and potential legal action against the end-user.
– Mitigation: Require proof of OEM partnerships or licensing agreements. Conduct IP due diligence on key components.
b. Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Control Software
– Pitfall: Control panels or monitoring systems may use pirated or unlicensed software, violating copyright laws.
– Impact: System instability, lack of updates, and liability for IP infringement.
– Mitigation: Request software licensing documentation and verify authenticity with original developers.
c. Ambiguous Ownership of Custom Designs
– Pitfall: If the generator set is customized (e.g., skid design, integration with existing systems), IP ownership may not be clearly assigned.
– Impact: Disputes over modifications, upgrades, or resale rights.
– Mitigation: Define IP ownership and usage rights in the contract (e.g., who owns drawings, firmware, integration logic).
d. Grey Market Imports and Brand Infringement
– Pitfall: Some suppliers source generator sets through unauthorized channels, selling branded products without warranty or support.
– Impact: No access to OEM technical support, voided warranties, and potential trademark liability.
– Mitigation: Purchase only through authorized distributors and verify serial numbers with OEMs.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
- Conduct Supplier Audits: Visit manufacturing facilities to assess quality control processes.
- Require Full Documentation: Technical specs, test reports, certifications, and IP licenses.
- Engage Independent Inspectors: Use third-party agencies for pre-shipment inspections.
- Include Penalties in Contracts: For non-compliance with quality or IP terms.
- Verify OEM Authenticity: Cross-check engine and alternator serial numbers with original manufacturers.
Conclusion
Sourcing natural gas generator sets requires due diligence beyond price and delivery terms. Prioritizing quality assurance and IP compliance mitigates operational, legal, and financial risks. A thorough procurement strategy — including technical validation, legal review, and supply chain transparency — ensures reliable, compliant, and sustainable power solutions.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Natural Gas Generator Set
-
Overview
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, installation, and operation of a natural gas generator set (genset). Adherence to regulatory standards, safety protocols, and logistical best practices ensures operational efficiency, legal compliance, and personnel safety. -
Regulatory Compliance
2.1 Environmental Regulations
– EPA Standards (U.S.): Ensure genset meets applicable emission standards under the Clean Air Act, including NSPS Subpart JJJJJJ for stationary CI internal combustion engines.
– Local Air Quality Permits: Verify requirements with regional or state environmental agencies (e.g., CARB in California).
– GHG Reporting: Facilities may need to report greenhouse gas emissions under EPA’s Mandatory Reporting Rule (40 CFR Part 98).
2.2 Safety and Operational Standards
– NFPA 54 (National Fuel Gas Code): Governs safe installation and use of natural gas equipment.
– NFPA 70 (NEC): Addresses electrical system installation per Article 700 (Emergency Power Systems) and Article 445 (Generators).
– NFPA 110: Standard for Emergency and Standby Power Systems—defines performance requirements.
– OSHA 29 CFR 1910: Covers workplace safety, including hazard communication and lockout/tagout procedures.
2.3 Building and Zoning Codes
– Local building departments require permits for structural modifications, fuel line connections, and ventilation.
– Setback requirements (e.g., distance from property lines, buildings, and air intakes) must be followed.
- Transportation & Handling
3.1 Pre-Shipment Preparation
– Secure all components: fasten moving parts, seal openings, and drain fluids if required.
– Use skid-mounted design with lifting points clearly marked; confirm weight and center of gravity.
3.2 Shipping Requirements
– Ground Transport: Comply with DOT regulations (49 CFR) for oversize/overweight loads if applicable.
– International Shipments: Adhere to IMDG Code (for sea) or IATA (air, if components are shipped separately). Natural gas gensets are generally non-hazardous when not fueled.
– Documentation: Include packing list, bill of lading, and certificate of conformity.
3.3 Receiving & Unloading
– Inspect for damage upon delivery.
– Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., forklift, crane) with adequate capacity.
– Ensure clear access path and level installation surface.
- Installation & Commissioning
4.1 Site Preparation
– Foundation: Construct a level, vibration-isolated concrete pad with proper drainage.
– Ventilation: Provide adequate airflow to prevent overheating and accumulation of exhaust gases.
– Fuel Supply: Connect to natural gas line per local utility specs; install shutoff valves, regulators, and flexible connectors. Use certified piping materials (e.g., black iron or CSST where permitted).
4.2 Electrical Integration
– Connect through a transfer switch compliant with NEC requirements.
– Bonding and grounding per NEC Article 250.
– Load testing to verify performance under full and partial load.
4.3 Emissions & Noise Controls
– Install mufflers and exhaust treatment systems if required.
– Perform sound attenuation measures to meet local noise ordinances (e.g., <70 dBA at 7 meters).
- Operational Compliance
5.1 Routine Maintenance
– Follow manufacturer’s maintenance schedule (e.g., oil changes, filter replacements, spark plug inspection).
– Keep logs of maintenance, runtime, and repairs for regulatory audits.
5.2 Emissions Monitoring
– Conduct periodic emissions testing (e.g., NOx, CO, VOCs) as required by permit.
– Maintain records for at least 5 years.
5.3 Emergency Preparedness
– Install gas leak detectors and automatic shutoff systems.
– Develop and train staff on emergency response plans (e.g., gas leaks, fire, power failure).
-
Documentation & Recordkeeping
-
Retain:
- Equipment manuals and warranties
- Installation permits and inspection reports
- Emissions test results
- Maintenance logs
-
Operator training records
-
Decommissioning & Disposal
-
Follow EPA and local regulations for decommissioning.
- Recycle or dispose of fluids (oil, coolant) and components (batteries, filters) per RCRA guidelines.
-
Purge and cap natural gas lines safely.
-
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and compliance with environmental, safety, and operational regulations are critical for the successful deployment of a natural gas generator set. Engage qualified engineers, contractors, and regulatory consultants to ensure full adherence throughout the equipment lifecycle.
Conclusion:
Sourcing a natural gas generator set presents a strategic and sustainable energy solution for businesses and facilities seeking reliable backup or primary power with reduced environmental impact. Natural gas generators offer numerous advantages, including lower emissions compared to diesel or gasoline alternatives, stable fuel supply through existing pipeline infrastructure, and reduced operating costs over time due to cleaner combustion and lower maintenance requirements. Additionally, these units support compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations and contribute to corporate sustainability goals.
When sourcing a natural gas generator set, it is essential to consider factors such as power output requirements, site conditions, fuel availability, regulatory compliance, and long-term operational costs. Partnering with reputable suppliers and conducting thorough due diligence ensures the selection of a reliable, efficient, and appropriately sized unit tailored to specific energy needs.
In conclusion, investing in a natural gas generator set is a forward-thinking decision that balances operational reliability, cost-efficiency, and environmental responsibility, making it a viable and advantageous option for modern power generation needs.