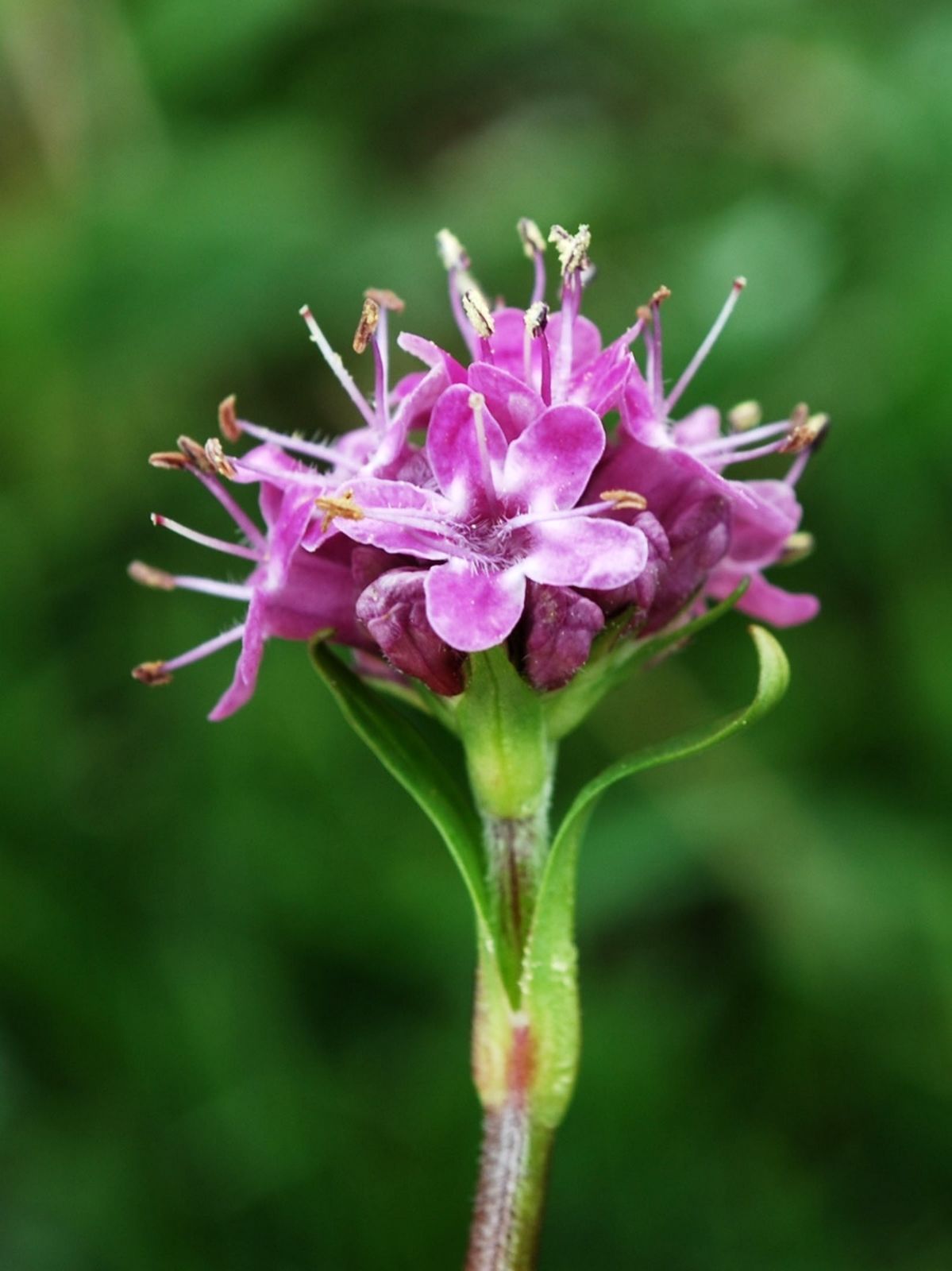
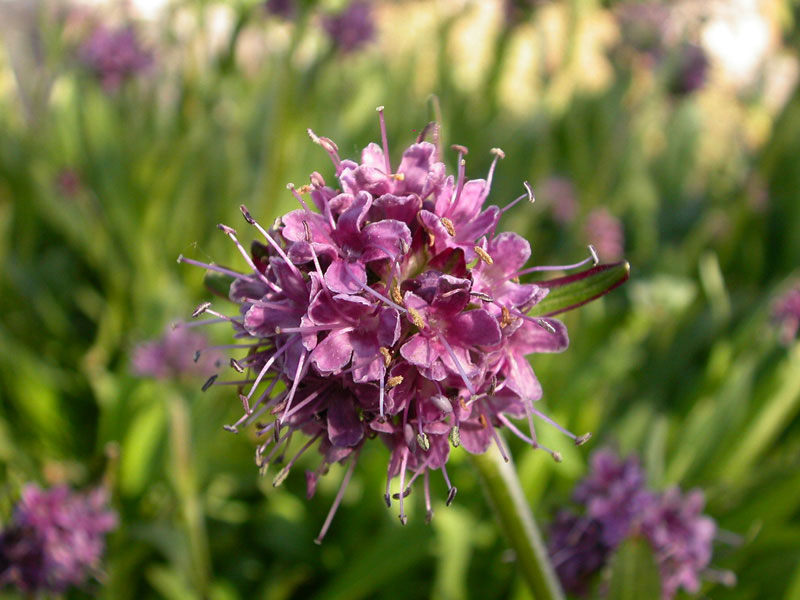
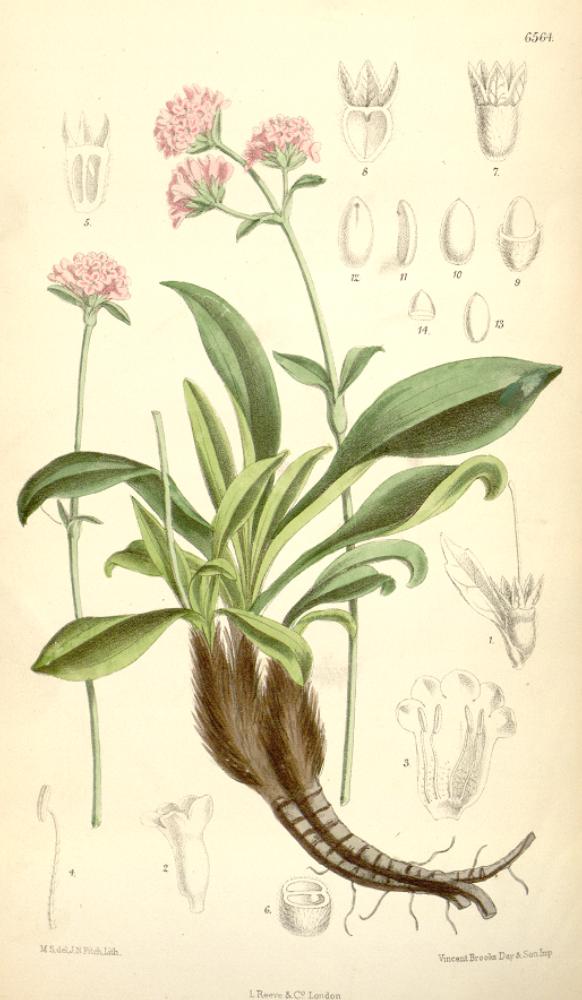
The global market for Nardostachys grandiflora, commonly known as spikenard, has seen steady growth due to rising demand in the natural fragrance, herbal medicine, and aromatherapy sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the essential oils market—which includes high-value botanicals like Nardostachys grandiflora—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% from 2023 to 2028. Spikenard essential oil, prized for its earthy aroma and anti-inflammatory properties, is gaining traction among premium skincare brands and holistic wellness companies. This surge in demand has intensified sourcing competition, leading to increased cultivation and processing activities, particularly in the Himalayan regions of India and Nepal. With Grand View Research noting a growing preference for plant-based therapeutics and sustainable raw materials, manufacturers of Nardostachys grandiflora are scaling production while ensuring ethical harvesting practices to meet both regulatory and consumer expectations. As supply chains adapt to these market dynamics, a select group of producers has emerged at the forefront of quality, traceability, and innovation.
Top 6 Nardostachys Grandiflora Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Nardostachys jatamansi (D.Don) DC.
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sciencedirect.com
Key Highlights: Indian spikenard is a critically endangered medicinal plant which grows at high altitudes in the alpine and sub-alpine regions of the Himalayas….
#2 Evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer activity of extract and …
Domain Est. 1997
Website: pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Key Highlights: Nardostachys jatamansi DC is a Himalayan medicinal herb that has been described in various traditional systems of medicine for its use in cancer….
#3 sustainability of trade in wild plants—A data
Domain Est. 1998
Website: academic.oup.com
Key Highlights: We integrate ecological and trade data to advance sustainability assessments, using the critically endangered Nardostachys jatamansi in Nepal to exemplify the ……
#4 (DOC) Nardostachys grandiflora
Domain Est. 1999
Website: academia.edu
Key Highlights: Nardostachys grandiflora, also known as Jatamansi or Spikenard, has been traditionally used in Ayurvedic medicine for various neurological disorders and ……
#5 Jatamansi
Domain Est. 2006
Website: fairwild.org
Key Highlights: Common name: Jatamansi / Spikenard / Nard. Plant parts used: Oil (from root) / Rhizome / Root. Scientific name: Nardostachys jatamansi (syn. N. grandiflora)….
#6 Jatamansi Oil – Nepal’s Herbal Product Pioneer
Website: hppcl.com.np
Key Highlights: Jatamansi oil is obtained by steam distillation of dried rhizomes of nardostachys Grandiflora D.C. It is commonly called Jatamansi In Nepali….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Nardostachys Grandiflora

H2: Market Trends for Nardostachys Grandiflora (Spikenard) in 2026
By 2026, the global market for Nardostachys grandiflora—commonly known as spikenard—is projected to experience steady growth, driven by rising demand across the fragrance, aromatherapy, and traditional medicine sectors. Key market trends shaping the trajectory of spikenard include sustainability challenges, increasing premiumization in natural products, and expanding interest in Ayurvedic and holistic wellness.
-
Growing Demand in Aromatherapy and Natural Fragrances
The essential oil derived from Nardostachys grandiflora roots remains a prized ingredient in high-end perfumery and aromatherapy due to its deep, earthy, and balsamic aroma. With consumers increasingly favoring natural and plant-based ingredients, luxury fragrance brands and wellness companies are incorporating spikenard oil into premium product lines. This trend is expected to intensify by 2026, particularly in North America and Europe. -
Expansion in Traditional Medicine and Ayurveda
Spikenard has long been used in Ayurvedic, Tibetan, and traditional Chinese medicine for its anti-inflammatory, sedative, and antimicrobial properties. As global interest in integrative and alternative medicine continues to rise, pharmaceutical and nutraceutical companies are investing in clinical research to validate traditional claims. This is likely to open new commercial avenues for standardized spikenard extracts by 2026. -
Sustainability and Supply Chain Pressures
Nardostachys grandiflora is a high-altitude Himalayan plant facing overharvesting and habitat degradation. Classified as an endangered species in parts of India and Nepal, wild harvesting is increasingly regulated. By 2026, market growth will depend heavily on sustainable cultivation initiatives. Agroforestry models and community-based farming in regions like Sikkim and Uttarakhand are gaining traction, supported by government and NGO partnerships. -
Price Volatility and Market Premium
Due to low yield (approximately 0.5–1.5% essential oil per root dry weight) and extended growth cycles (5–7 years), spikenard oil remains one of the most expensive essential oils globally. Prices are expected to remain high in 2026, with a premium placed on certified organic and ethically sourced products. Traceability and fair-trade certification will become key differentiators in the premium market. -
Geopolitical and Regulatory Influences
Export regulations in source countries (primarily India, Nepal, and Bhutan) are tightening to protect biodiversity. CITES monitoring and national conservation policies may limit raw material exports, encouraging local value addition such as on-site distillation and extract production. This could shift market dynamics toward regional processing hubs and increase import costs for international buyers. -
Innovation in Biotechnology and Cultivation
Research into tissue culture propagation and improved agronomic practices is underway to enhance yield and reduce cultivation time. By 2026, advances in biotech-assisted farming may begin to stabilize supply, though widespread commercial adoption will depend on funding and scalability.
Conclusion
The 2026 market for Nardostachys grandiflora will be defined by a tension between rising demand and ecological constraints. Success will favor stakeholders who invest in sustainable sourcing, transparent supply chains, and scientific validation of health benefits. As the global wellness economy expands, spikenard is poised to maintain its status as a niche yet high-value botanical, provided conservation and cultivation efforts keep pace with market needs.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Nardostachys grandiflora: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Adulteration and Substitution
Nardostachys grandiflora, commonly known as spikenard, is frequently adulterated due to its high market value and limited supply. Common adulterants include lower-cost essential oils such as vetiver, patchouli, or synthetic compounds designed to mimic its aroma. Additionally, less potent or unrelated plant materials may be mixed in, reducing therapeutic efficacy and misleading consumers.
2. Variability in Essential Oil Composition
The chemical profile of spikenard essential oil varies significantly based on geography, altitude, harvesting time, and distillation methods. Sourcing from inconsistent or undocumented origins can lead to batch-to-batch variability, impacting product performance and reliability, especially in aromatherapy or pharmaceutical applications.
3. Poor Harvesting and Processing Practices
Overharvesting of wild Nardostachys grandiflora roots—its primary source for essential oil—threatens sustainability. Improper drying, fermentation, or distillation techniques further degrade oil quality, leading to lower yields and diminished aromatic or medicinal properties.
4. Lack of Standardization and Certification
Many suppliers do not provide GC/MS (gas chromatography/mass spectrometry) reports or adhere to ISO or other quality standards. Without third-party verification, it is difficult to confirm authenticity, purity, or compliance with regulatory requirements, especially for export markets.
Intellectual Property and Ethical Sourcing Pitfalls
1. Biopiracy and Misappropriation of Traditional Knowledge
Nardostachys grandiflora has been used for centuries in traditional medicine systems such as Ayurveda and Tibetan medicine. Commercial entities may exploit this traditional knowledge without acknowledging or compensating source communities, raising concerns under the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit-Sharing (ABS).
2. Unlicensed Use of Geographical Indications (GIs) or Traditional Terms
Some suppliers may falsely label products as “Himalayan spikenard” or use culturally significant names to imply authenticity or superior quality without legal rights or adherence to GI protections. This misrepresentation can mislead consumers and undermine legitimate producers.
3. Patenting of Naturally Occurring Compounds
Attempts to patent extracts, formulations, or uses of Nardostachys grandiflora derived directly from traditional knowledge may constitute unethical bioprospecting. Such actions can restrict access for local communities and lead to legal disputes over ownership and innovation rights.
4. Inadequate Benefit-Sharing Agreements
Ethical sourcing requires fair compensation and collaboration with local harvesters and indigenous groups. Failure to establish transparent benefit-sharing mechanisms not only violates international guidelines but also risks reputational damage and supply chain instability.
Conclusion
Sourcing Nardostachys grandiflora responsibly demands rigorous quality control, transparent supply chains, and respect for intellectual property and traditional knowledge. Buyers should prioritize certified sustainable sources, demand verifiable analytical data, and ensure compliance with ABS frameworks to avoid legal, ethical, and commercial pitfalls.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Nardostachys grandiflora (Spikenard)
Overview of Nardostachys grandiflora
Nardostachys grandiflora, commonly known as Spikenard or Jatamansi, is a flowering plant in the Valerianaceae family native to the Himalayan regions of India, Nepal, Bhutan, and parts of China. Its rhizomes and roots are valued in traditional medicine (especially Ayurveda), aromatherapy, and high-end perfumery for their earthy, woody fragrance and therapeutic properties. Due to overharvesting and habitat loss, it is a regulated species with specific international and national compliance requirements.
CITES and International Trade Regulations
Nardostachys grandiflora is listed under Appendix II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES). This means:
– International trade is permitted only with appropriate CITES export permits or re-export certificates.
– Permits are issued only when the specimens were legally acquired and when export will not be detrimental to the survival of the species in the wild.
– Importing countries may also require CITES documentation upon entry.
– Commercial shipments must be accompanied by validated CITES permits issued by the Management Authority of the exporting country.
National Regulations and Harvesting Restrictions
- India: Spikenard is included in Schedule VI of the Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, which restricts its collection and trade. Harvesting is banned in many states without special permits from forest departments. Export requires both CITES permits and documentation under the Foreign Trade Policy (FTP).
- Nepal: Listed under the National Parks and Wildlife Conservation Act. Harvesting and export require government authorization and are often limited to cultivated sources.
- China and Bhutan: Similar restrictions apply; wild harvesting is tightly controlled, and export is generally limited to cultivated or sustainably sourced material.
Sustainable Sourcing and Cultivation
- Wild populations of Nardostachys grandiflora are declining due to overexploitation. Sustainable sourcing is critical.
- Encourage the use of cultivated or organically farmed sources where available.
- Suppliers should provide documentation proving sustainable harvest practices, including chain-of-custody certification.
- Consider third-party certifications such as FairWild or Organic (e.g., USDA, EU) to ensure ethical and ecological standards.
Documentation and Import/Export Requirements
For legal international shipment:
– CITES Export Permit or Re-export Certificate: Mandatory for cross-border movement.
– Phytosanitary Certificate: Required by many countries to confirm plant material is free from pests and diseases.
– Certificate of Origin: To verify where the material was harvested or processed.
– Commercial Invoice and Packing List: For customs clearance.
– Import Permit: Some countries require a prior import permit for CITES-listed species.
Transportation and Handling
- Dried rhizomes and roots should be packed in moisture-resistant, breathable containers to prevent mold.
- Label packages clearly with scientific name (Nardostachys grandiflora), CITES status, and permit numbers.
- Use reliable freight forwarders experienced in handling CITES-regulated botanicals.
- Monitor temperature and humidity during transit, especially for essential oil derivatives.
Compliance Best Practices
- Verify supplier compliance with national and CITES regulations before procurement.
- Maintain detailed records of all permits, invoices, and certifications for at least five years.
- Conduct regular audits of supply chains to ensure adherence to sustainability and legal standards.
- Stay updated on changes in CITES listings and national legislation affecting trade.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with CITES or national regulations can result in:
– Seizure of shipments by customs authorities.
– Fines and legal action against importers/exporters.
– Suspension or revocation of trading licenses.
– Reputational damage and loss of market access.
Conclusion
Trading in Nardostachys grandiflora requires strict adherence to international conservation regulations and national laws. Due diligence in sourcing, proper documentation, and commitment to sustainable practices are essential for legal and ethical commerce. Always consult with national CITES Management Authorities and customs experts before initiating shipments.
Conclusion on Sourcing Nardostachys jatamansi (formerly Nardostachys grandiflora):
Sourcing Nardostachys jatamansi—commonly known as spikenard—requires a balanced approach that respects ecological sustainability, socio-economic considerations, and regulatory frameworks. As a high-value medicinal and aromatic plant native to the Himalayan region, it faces significant threats from overharvesting, habitat degradation, and climate change, leading to its classification as an endangered species by various conservation bodies.
Sustainable sourcing must prioritize wild collection practices that adhere to fair trade and ethical harvesting standards, ensuring long-term conservation and equitable benefits for local communities. Cultivation initiatives show promise in reducing pressure on wild populations, though they require further research and investment to improve yield and quality consistency.
Certifications such as FairWild, organic, and CITES compliance play a crucial role in responsible procurement. Businesses and stakeholders must engage transparently with supply chains, support community-based conservation efforts, and invest in research to promote cultivation and sustainable wild management. Ultimately, the future of Nardostachys jatamansi sourcing depends on collaborative, science-based, and ethically grounded approaches that ensure both ecological integrity and cultural continuity.