The global motorcycle keyless ignition market is gaining significant momentum, driven by rising consumer demand for advanced security, convenience, and integration with smart technology. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global motorcycle accessories market—of which keyless ignition systems are a high-growth segment—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.2% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by the increasing adoption of electronic ignition systems in both premium and mid-range motorcycles, particularly in regions like Asia-Pacific and North America. As OEMs and aftermarket brands prioritize anti-theft features and seamless user experiences, keyless ignition systems have become a benchmark in modern motorcycle design. With innovations in RF transponder technology, Bluetooth connectivity, and immobilizer integration, several manufacturers are leading the charge in developing reliable, secure, and scalable solutions. Based on market presence, product innovation, and technological adoption, the following seven companies stand out as the top manufacturers in the motorcycle keyless ignition space.
Top 7 Motorcycle Keyless Ignition Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
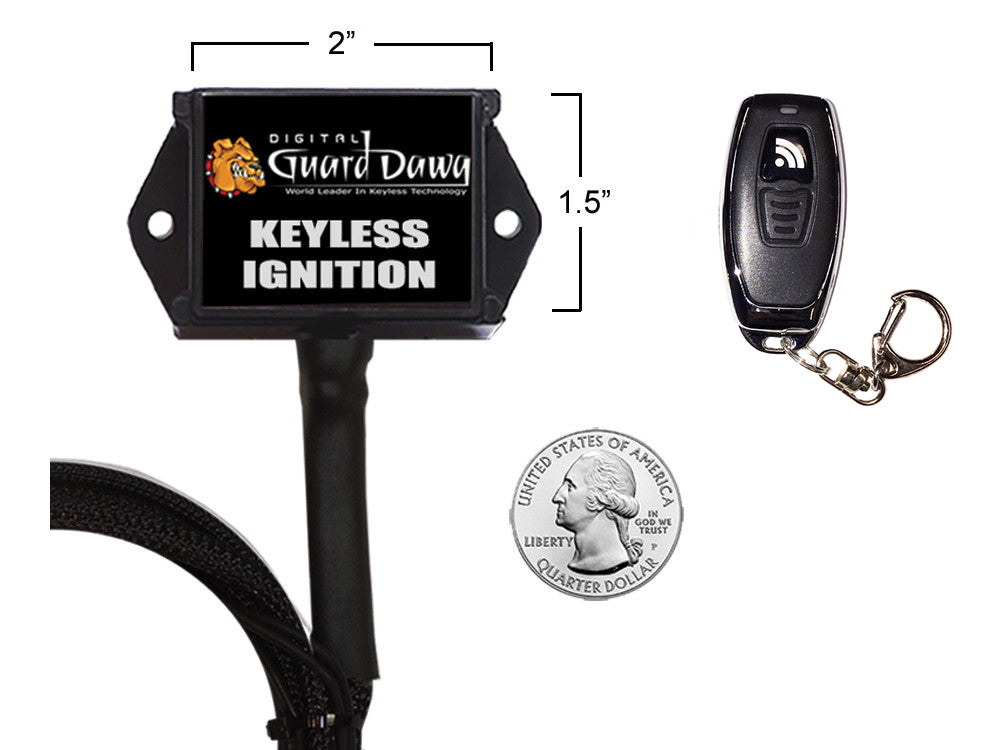
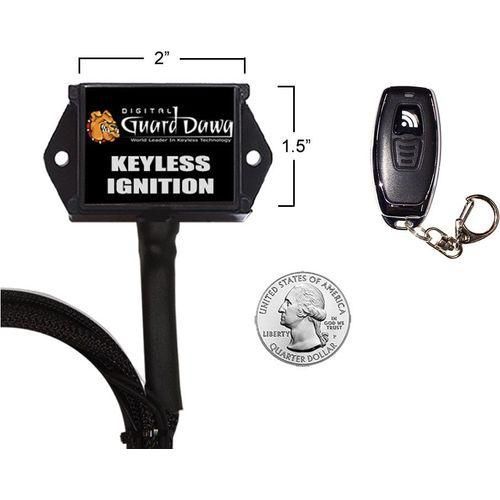
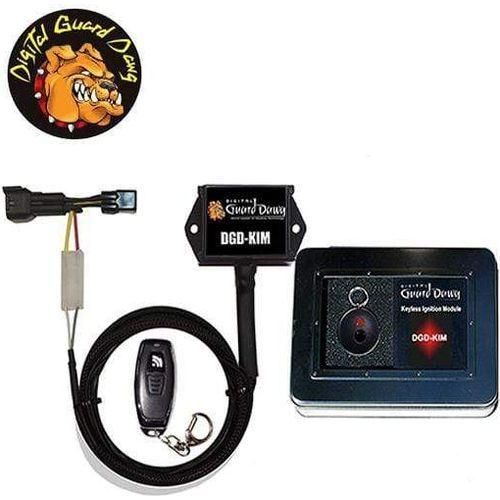
#1 Digital Guard Dawg Keyless Ignition And Security Module
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cyclegear.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 3.2 8 The Digital Guard Dawg Keyless Ignition Module completely eliminates the need for the factory key switch and all the hassles associated with using a key!…
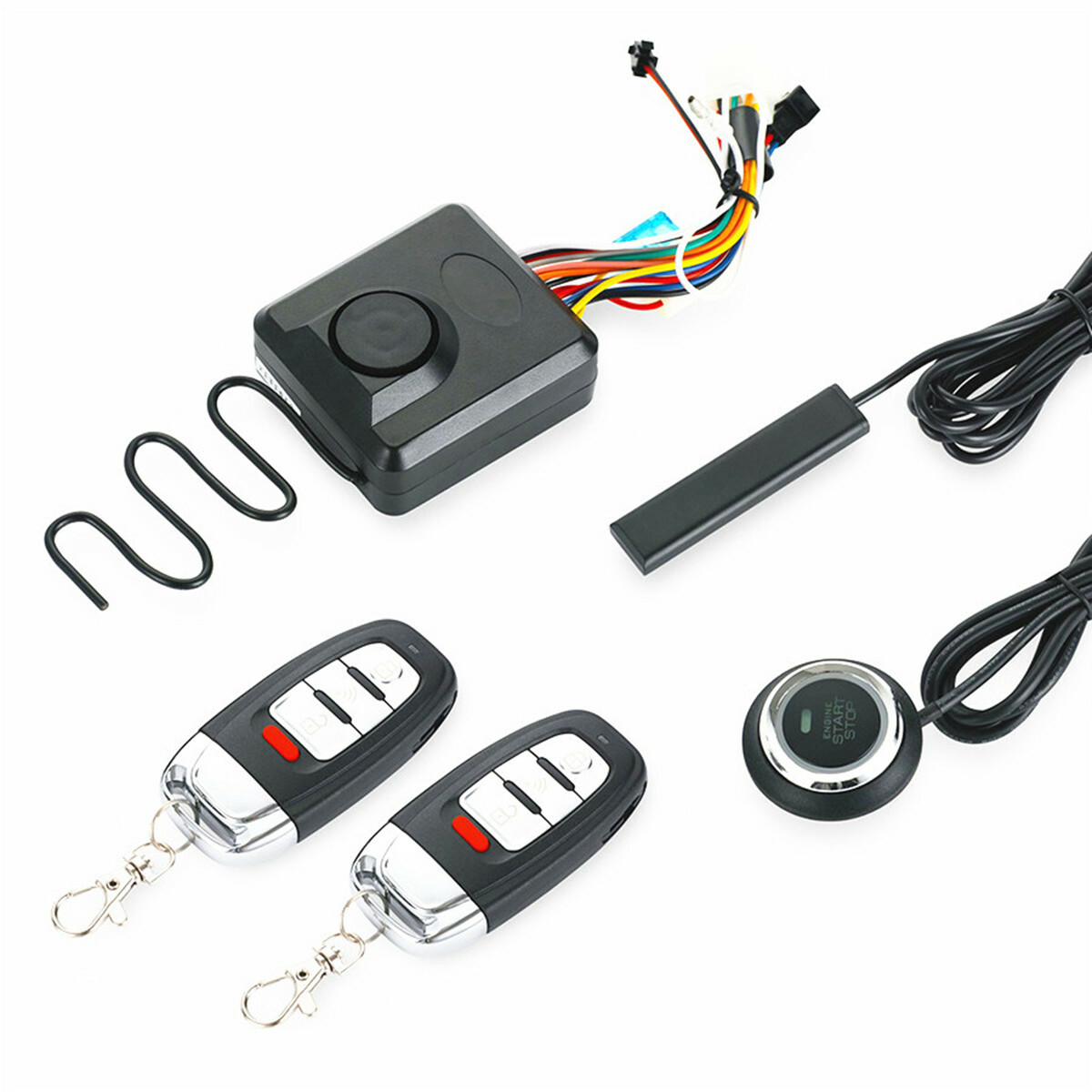
#2 Keyless Ignition Systems
Domain Est. 1998
Website: nhtsa.gov
Key Highlights: Keyless Ignition Systems, as they are commonly called, usually consist of a device (also known as a key fob or a FOB) carried by the driver….
#3 Keyless Motorcycle Ignition Systems
Domain Est. 2006
Website: digitalguarddawg.com
Key Highlights: Designed for a wide range of motorcycles, our modules eliminate the hassle of traditional keys, offering a seamless, secure, and convenient push-button start….
#4 Question about Digital Guard Dawg Keyless Ignition
Domain Est. 2008
Website: thevog.net
Key Highlights: It is plug and play. You can set it for automatic where proximity to the fob enables it or manual where you push a button on the fob….
#5 Digital Guard Dawg Keyless Ignition
Domain Est. 2008
Website: buywitchdoctors.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsDigital Guard Dawg Keyless motorcycle ignitions are an innovative security solution designed specifically for Victory & Indian motorcycles….
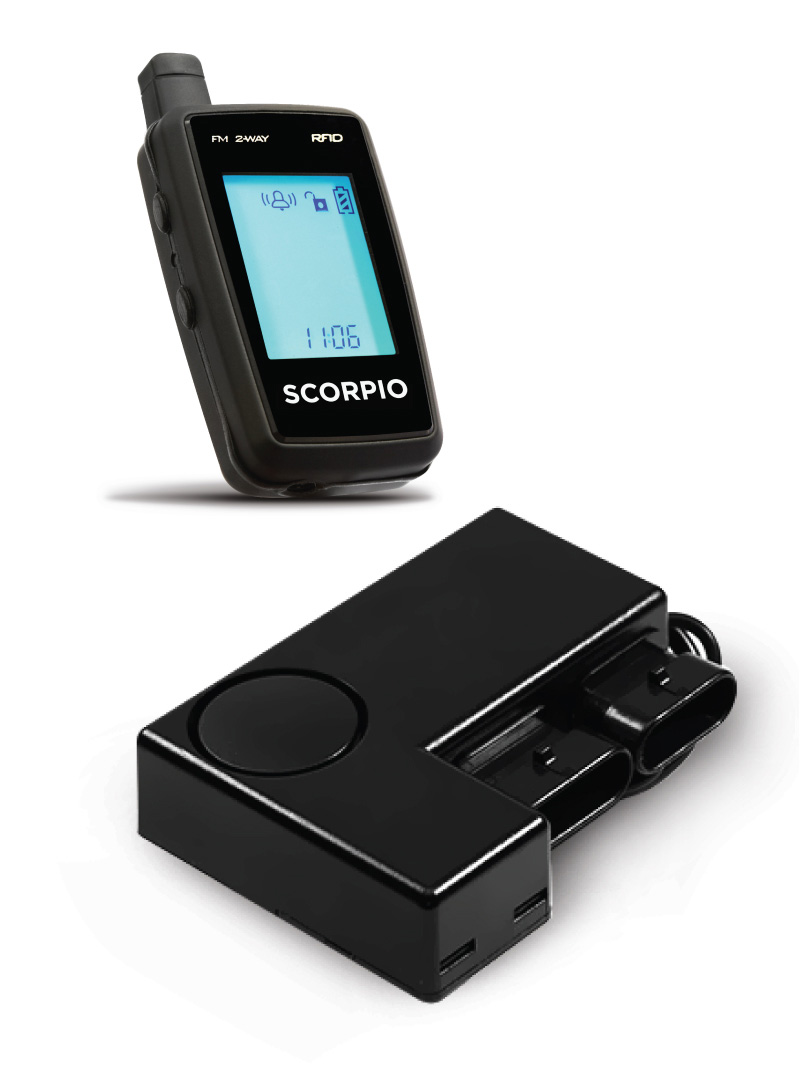
#6 Scorpio Alarms
Domain Est. 2012
Website: ridescorpio.com
Key Highlights: 14-day returnsScorpio is the best motorcycle alarm. The hands-free motorcycle security system detects movement in mass, alerting you to violations before they happen….
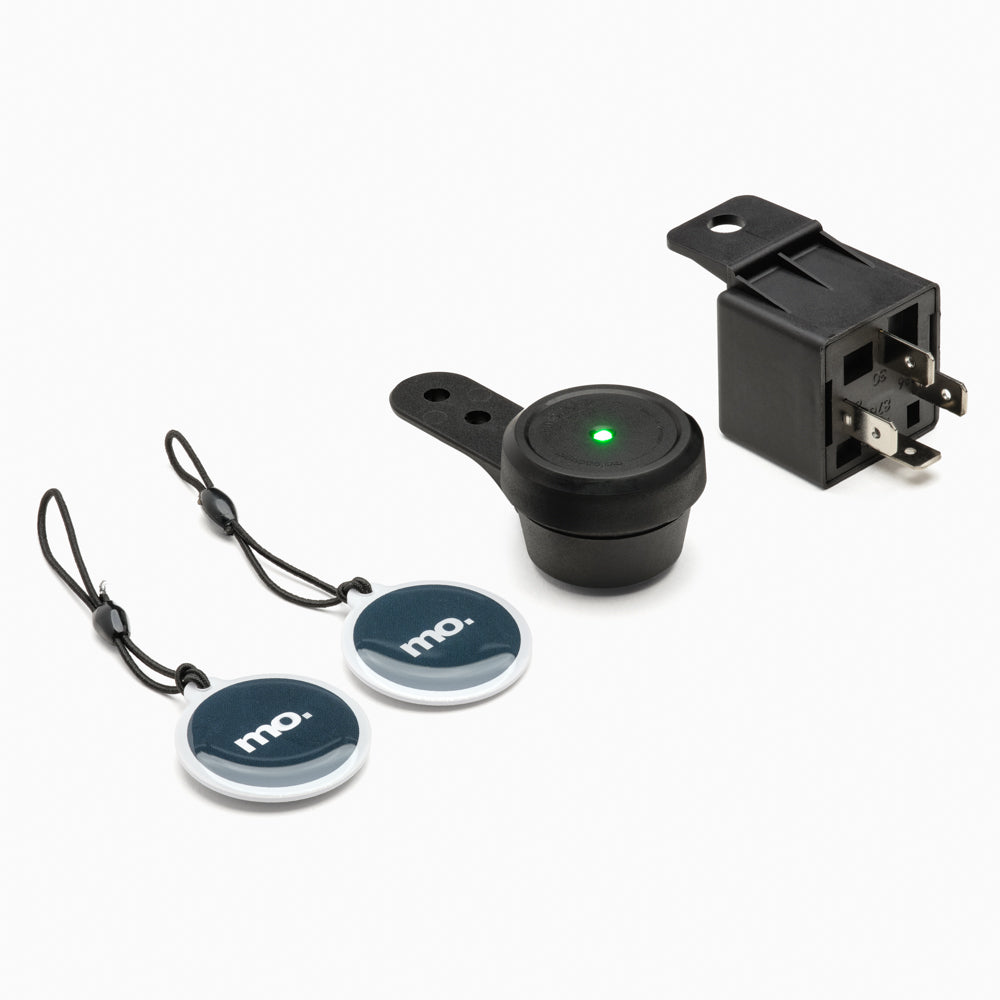
#7 mo.lock NFC
Domain Est. 2023
Expert Sourcing Insights for Motorcycle Keyless Ignition

2026 Market Trends for Motorcycle Keyless Ignition Systems
Rising Adoption Driven by Consumer Demand for Convenience and Security
By 2026, the motorcycle keyless ignition market is expected to experience substantial growth, primarily fueled by increasing consumer demand for advanced convenience and enhanced security features. Riders are increasingly prioritizing seamless, tech-integrated experiences similar to those found in modern automobiles. Keyless ignition systems—enabling engine start via proximity sensors, smartphone apps, or wearable devices—align with this shift toward smart mobility. The elimination of physical keys reduces the risk of theft and loss, while features like encrypted RF signals and biometric authentication are becoming standard expectations. OEMs are responding by integrating keyless systems into mid-tier and premium motorcycle models across Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe.
Expansion into Mid-Range and Entry-Level Segments
While keyless ignition was initially limited to high-end motorcycles, 2026 trends indicate a notable expansion into mid-range and even select entry-level models. Advancements in component miniaturization and cost-effective manufacturing have lowered production costs, enabling broader deployment. Brands such as Honda, Yamaha, and KTM are expected to offer keyless systems as standard or optional features on commuter and adventure bikes priced under $10,000. This democratization is particularly evident in emerging markets like India and Southeast Asia, where younger, tech-savvy riders are driving demand for modern features at competitive price points.
Integration with Smart Ecosystems and Mobile Connectivity
A defining trend in 2026 is the deeper integration of keyless ignition systems with broader smart motorcycle ecosystems. Keyless systems now frequently serve as gateways to smartphone-connected platforms, allowing riders to remotely start the engine, monitor vehicle status, receive maintenance alerts, and enable geofencing or anti-theft alerts via dedicated apps. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and NFC technologies are being leveraged for seamless pairing with smartphones and smartwatches. Some manufacturers are incorporating voice-assisted start capabilities and multi-user access profiles, enhancing personalization and usability.
Emphasis on Cybersecurity and Authentication Innovation
As reliance on digital access grows, cybersecurity has become a critical focus in the development of motorcycle keyless systems. By 2026, manufacturers are implementing dynamic encryption, rolling codes, and two-factor authentication to prevent relay attacks and unauthorized access. Innovations such as behavioral biometrics—using patterns in ride behavior or device interaction to verify identity—are being tested in premium models. Regulatory bodies in the EU and North America are also expected to introduce cybersecurity standards for connected motorcycle components, shaping industry-wide compliance practices.
Regional Market Dynamics and Competitive Landscape
Regionally, Asia-Pacific is projected to lead market growth in 2026, driven by rapid urbanization, rising disposable income, and government support for smart transportation in countries like China and India. Europe and North America will continue to lead in technological innovation, with established players like Bosch, Denso, and NXP Semiconductors partnering with OEMs to develop next-gen keyless platforms. The competitive landscape is also seeing increased involvement from tech startups offering modular, aftermarket keyless solutions, expanding options for retrofitting older models.
Sustainability and Power Efficiency Improvements
Sustainability concerns are influencing keyless system design, with manufacturers focusing on low-power consumption components to extend battery life and reduce environmental impact. Energy-efficient sensors and wake-up circuits ensure that systems remain responsive without draining the motorcycle’s battery during extended idle periods. In 2026, solar-assisted key fobs and rechargeable smart tags are gaining traction, reflecting a broader industry shift toward eco-conscious technology integration.
In summary, the 2026 motorcycle keyless ignition market reflects a convergence of convenience, security, and digital connectivity, with expanding accessibility, enhanced cybersecurity, and ecosystem integration setting the trajectory for future innovation.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Motorcycle Keyless Ignition Systems (Quality & IP)
Sourcing motorcycle keyless ignition systems offers efficiency and modern features, but it comes with significant risks if due diligence is not performed—especially regarding product quality and intellectual property (IP) rights. Overlooking these areas can lead to operational failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Component Standards
Many suppliers, particularly in competitive low-cost markets, use substandard electronic components (e.g., low-grade microcontrollers, unreliable sensors). These components may function initially but fail prematurely under vibration, heat, or moisture—common conditions for motorcycles.
2. Inadequate Environmental Protection
Motorcycles are exposed to extreme weather, dust, and road debris. Sourcing keyless systems without verified ingress protection (IP) ratings (e.g., IP65 or higher) risks water ingress, corrosion, and short circuits. Beware of suppliers that claim high IP ratings without third-party certification (e.g., IEC 60529 testing reports).
3. Poor Integration and Compatibility
Keyless systems must interface seamlessly with a motorcycle’s ECU, immobilizer, and wiring harness. Generic or poorly engineered systems often cause compatibility issues, leading to engine start failures, false alarms, or dashboard errors. Always verify compatibility with target motorcycle models.
4. Lack of Durability Testing
Reputable manufacturers conduct vibration, thermal cycling, and long-term endurance tests. Suppliers that cannot provide test data may be offering unproven designs prone to field failure, increasing warranty claims and customer dissatisfaction.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
1. Risk of Infringing Patented Technologies
Keyless ignition systems often incorporate patented technologies—such as rolling code encryption, proximity detection algorithms, or anti-theft protocols. Sourcing from suppliers who replicate branded OEM systems (e.g., Honda SMART Key, BMW Keyless Ride) may result in unintentional IP infringement and legal exposure.
2. Unverified Design Ownership
Some suppliers offer “white-label” systems designed by third parties. Without clear IP assignment or licensing agreements, buyers may unknowingly distribute products that violate design patents or utility models, risking cease-and-desist orders or customs seizures.
3. Use of Open-Source Code Without Compliance
Embedded firmware in keyless systems may use open-source software (e.g., under GPL licenses). If suppliers fail to comply with licensing terms (e.g., source code disclosure), downstream buyers can inherit legal liabilities even if unaware.
4. Counterfeit or Clone Products
Low-cost suppliers may offer systems that mimic well-known brands in appearance and function. These clones often infringe on trademarks and patents. Purchasing such products exposes the buyer to IP litigation and brand damage, especially in regulated markets like the EU or North America.
Mitigation Strategies
- Demand Certifications: Require test reports for environmental protection, EMC, and reliability.
- Conduct Factory Audits: Evaluate manufacturing processes and quality control firsthand.
- Verify IP Documentation: Ask for proof of design rights, patent licenses, or freedom-to-operate opinions.
- Use Legal Safeguards: Include IP indemnification clauses in supplier contracts.
- Prototype and Field Test: Validate performance under real-world riding conditions before mass procurement.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures a reliable, legally compliant keyless ignition solution that enhances rider experience without hidden risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Motorcycle Keyless Ignition Systems
This guide outlines the essential logistics considerations and regulatory compliance requirements for the distribution, import, and sale of motorcycle keyless ignition systems in global markets.
Product Classification and HS Codes
Accurate product classification is critical for customs clearance and duty assessment. Keyless ignition systems for motorcycles typically fall under the following Harmonized System (HS) codes:
- 8537.10: Boards, panels, consoles, desks, cabinets, etc., equipped with two or more apparatus of headings 8535 or 8536, for electrical control or distribution circuits. This may apply if the ignition system includes integrated control modules.
- 8512.20: Electrical lighting or signaling equipment (excluding lamps of heading 8539), windshield wipers, defrosters, and demisters, for cycles or motor vehicles. While primarily for lighting, some customs authorities may classify electronic control units under broader vehicle electronics.
- 8504.40: Battery chargers. Not applicable unless the system includes charging circuitry.
- 9026.20: Instruments and apparatus for measuring or checking the flow, level, pressure, or other variables of liquids or gases. Not applicable.
Recommendation: Verify classification with local customs authorities or a licensed customs broker, as interpretations may vary by country.
Import Regulations and Documentation
Importers must prepare the following documentation to ensure smooth customs clearance:
- Commercial Invoice: Must detail product description, quantity, unit price, total value, Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF), and Harmonized System code.
- Packing List: Itemizes contents of each shipping container, including weights and dimensions.
- Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB): Proof of shipment and contract of carriage.
- Certificate of Origin: Required by some countries to determine eligibility for preferential tariffs under trade agreements.
- Technical Datasheets and User Manuals: Provide details on system functionality, compatibility, and safety features.
- RoHS and REACH Compliance Declarations: Required for shipments to the European Union.
Failure to provide accurate documentation may result in delays, fines, or seizure of goods.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
European Union (EU)
- ECE Regulations: Keyless ignition systems must comply with UNECE Regulation No. 78 (security devices for power-driven vehicles) and Regulation No. 122 (approval of steering equipment). Additionally, EMC Directive 2014/30/EU ensures electromagnetic compatibility.
- Radio Equipment Directive (RED) 2014/53/EU: Applies if the system uses wireless communication (e.g., Bluetooth, RFID).
- RoHS Directive 2011/65/EU: Restricts hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium.
- REACH Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006: Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
- CE Marking: Mandatory; indicates conformity with EU safety, health, and environmental standards.
United States
- Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS): While FMVSS does not specifically regulate keyless ignitions, compliance with FMVSS No. 114 (Theft Protection and Rollaway Prevention) is required for any system affecting vehicle starting and immobilization.
- FCC Part 15: Governs electromagnetic interference for any device emitting radio frequencies (e.g., Bluetooth, RF transceivers).
- DOT Certification: Optional but recommended for aftermarket parts to demonstrate safety compliance.
Canada
- Motor Vehicle Safety Act (MVSA): Regulated by Transport Canada. Compliance with CMVSS 114 (similar to FMVSS 114) is mandatory.
- ISED Certification: Required for radio-frequency devices under RSS-210 or RSS-247 (Industry Canada standards).
Australia and New Zealand
- ADR (Australian Design Rules): Compliance with ADR 79/00 (Theft Protection) may be applicable.
- RCM Marking: Required for electrical and electronic products, indicating compliance with EMC and safety standards (AS/NZS CISPR 25, AS/NZS 60950.1).
China
- CCC Certification (China Compulsory Certification): Required for automotive electronic components. Keyless ignition systems may fall under category 8, “Automotive Electrical Products.”
- SRRC Certification: Mandatory for wireless modules (e.g., Bluetooth, RFID) operating in China.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
- Multilingual Labeling: In EU and Canada, labels and manuals must be in official languages (e.g., English, French, German, Spanish).
- CE/FCC/ISED Marks: Must be visibly displayed on product and packaging.
- Warning Labels: Include instructions for proper installation and warnings about electromagnetic interference or improper use.
- Barcode and Tracking: Include GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) for inventory and logistics tracking.
Shipping and Handling
- Temperature and Humidity: Store and ship in controlled environments. Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures (< -20°C or > 60°C) and high humidity (> 85% RH).
- ESD Protection: Use anti-static packaging for electronic control units to prevent electrostatic discharge damage.
- Secure Packaging: Use shock-absorbent materials and rigid containers to prevent damage during transit.
- Incoterms: Clarify responsibilities using standard Incoterms (e.g., FOB, DDP) to avoid disputes over shipping, insurance, and customs duties.
Aftermarket Installation and Warranty
- Certified Installers: Recommend installation by certified technicians to ensure compliance with vehicle manufacturer warranties and local regulations.
- Warranty Registration: Provide online registration for consumer warranty validation.
- Recall Preparedness: Establish a system to manage product recalls in compliance with national regulations (e.g., NHTSA in the U.S., RAPEX in the EU).
Environmental and End-of-Life Compliance
- WEEE Directive (EU): Producers must register and provide take-back options for waste electrical equipment.
- Battery Disposal: If the system includes a backup battery, provide disposal instructions per local regulations (e.g., EPA guidelines in the U.S.).
Conclusion
Successfully distributing motorcycle keyless ignition systems requires a thorough understanding of international logistics and regulatory landscapes. Proactive compliance with classification, import, safety, and environmental standards ensures market access, minimizes delays, and protects brand reputation. Engage certified consultants and testing laboratories to validate conformity before market entry.
In conclusion, sourcing a motorcycle keyless ignition system offers numerous advantages, including enhanced convenience, improved security, and a modern upgrade to older or standard ignition setups. By eliminating traditional keys, riders benefit from features such as push-button starts, proximity sensors, and integration with smartphone apps or transponder fobs. When sourcing such systems, it is essential to consider compatibility with your motorcycle model, reliability of the brand, ease of installation, and available customer support. Additionally, opting for reputable suppliers or OEM-recommended products ensures both performance and long-term durability. With careful research and proper installation, a keyless ignition system can significantly elevate the riding experience while adding a layer of sophistication and security to your motorcycle.