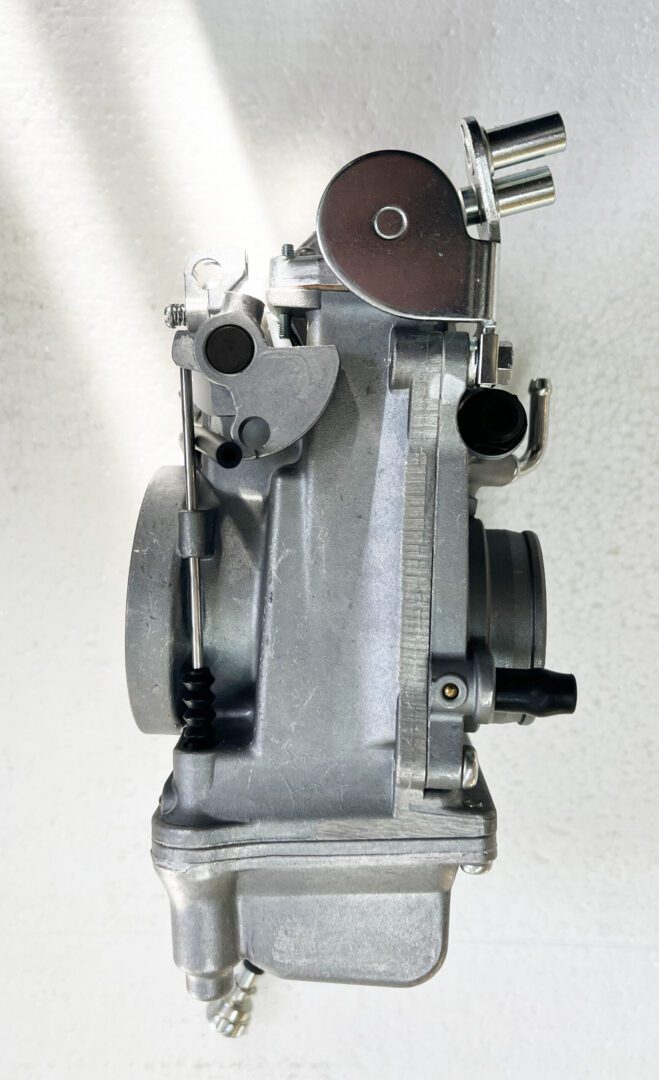
The global motorcycle carburetor market continues to hold steady relevance despite the rise of electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems, particularly in emerging economies where cost-effective two-wheelers dominate. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the motorcycle carburetor market was valued at approximately USD 1.8 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.2% during the forecast period (2023–2028). This growth is driven by sustained demand in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa, where manufacturers prioritize affordability and ease of maintenance in small-displacement motorcycles. Additionally, the aftermarket segment accounts for a significant share due to the widespread use of carbureted engines in older and entry-level models. With such persistent demand, a competitive landscape has emerged among specialized manufacturers who balance precision engineering with cost efficiency. Here, we spotlight the top 9 motorbike carburetor manufacturers shaping the industry through innovation, scalability, and global distribution networks.
Top 9 Motor Bike Carburetor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
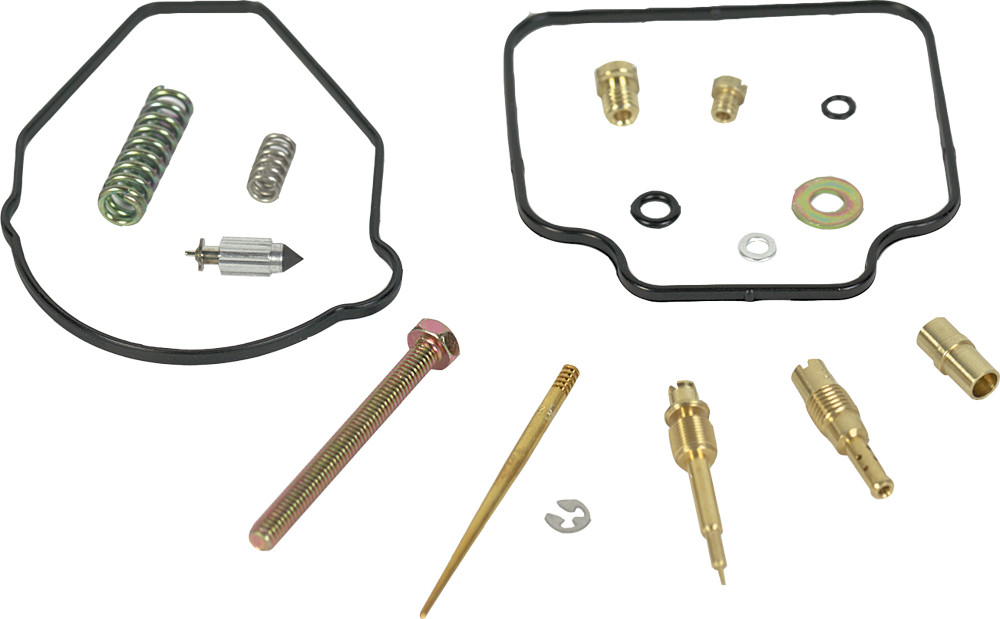
#1 Shindy Products
Domain Est. 2002 | Founded: 1986
Website: shindypro.com
Key Highlights: Shindy Products, Inc. was established in 1986. Specializing in importing only the top quality motorcycle and ATV parts from Japan….
#2 Amal Carb
Domain Est. 2007
Website: amalcarb.co.uk
Key Highlights: We are the worlds sole manufacturer of Amal Carburettors and spares. Amal carburetters were at the heart of the British motorcycle industry being fitted to ……
#3 CV Performance
Domain Est. 2007
Website: cv-performance.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer and distributor of quality performance parts for Harley Davidson v-twin motorcycles. CV carburetor jets, tuning parts, fuel injection, ……
#4 Mikuni American Corporation
Domain Est. 1994
Website: mikuni.com
Key Highlights: The Mikuni Group manufactures superior products for a wide range of industries, including automotive, commercial vehicles, powersports, general purpose, ……
#5 Sudco Intl. Corp.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: sudco.com
Key Highlights: These products include Carburetors and Carburetor Rebuild Kits, Replacement Carburetor Jetting, Fuel Injection modules and Ignition Tuning Modules, and ……
#6 Bing Carburetor
Domain Est. 1999
Website: bingcarburetor.com
Key Highlights: BING CARBURETORS FOR MOTORCYCLES, MOPEDS, BOATS, CHAINSAWS, JACKHAMMERS AND MORE THIS WEB SITE IS SPECIFIC FOR MOTORCYCLES AND GROUND EQUIPMENT ONLY IF ……
#7 carburetor
Domain Est. 2005
Website: yoshimura-jp.com
Key Highlights: FCR-MJN & CR carburetor · Add to Favorites. ENGINE Z1. YOSHIMURA KEIHIN FCR-MJN35 CARBURETOR (SILVER BODY) · Add to Favorites. ENGINE Z1 · Add to Favorites. ENGINE….
#8 Powersports products: KEIHIN Carburetors
Domain Est. 2014
Website: aftermarket.astemo.com
Key Highlights: Available in a wide range of throttle bore sizes, PE is a round slide, general purpose carburetor applicable to two-stroke and four-stroke engines….
#9 spare parts motorcycle carburetors
Website: athena.eu
Key Highlights: 3–5 day delivery 14-day returnsBuy Athena’s carburetors for motorcycles and scooters online: a wide selection of spare parts at affordable prices. Delivery throughout Italy in 48h….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Motor Bike Carburetor

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Motorbike Carburetors
The motorbike carburetor market is undergoing significant transformation as it approaches 2026, shaped by evolving regulatory standards, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. While the global trend is moving toward fuel injection systems, carburetors continue to maintain relevance in specific market segments. Below are key trends expected to define the motorbike carburetor landscape in 2026:
-
Decline in Developed Markets, Resilience in Emerging Economies
In North America, Western Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific, carburetor demand is steadily declining due to stringent emissions regulations and the widespread adoption of electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems. However, in developing regions such as Southeast Asia, Africa, and South Asia, carburetors remain popular due to lower manufacturing costs, easier maintenance, and compatibility with older or budget-friendly two-wheelers. Countries like India, Indonesia, and Nigeria will continue to drive demand for carbureted motorcycles, especially in rural and entry-level urban transportation segments. -
Cost-Effectiveness Driving Aftermarket Demand
Despite the OEM shift toward EFI, the aftermarket for carburetors is expected to remain robust through 2026. Many existing motorcycles, particularly in emerging markets, rely on carburetors, creating sustained demand for replacement parts, tuning kits, and repair services. The lower cost of carburetors compared to EFI systems makes them a preferred choice for repairs and custom bike builds, especially among hobbyists and small workshops. -
Technological Refinements and Hybrid Solutions
Innovations in carburetor design—such as adjustable air-fuel mixtures, improved choke mechanisms, and integration with basic electronic controls—are enhancing performance and efficiency. Some manufacturers are exploring hybrid systems that combine carburetion with electronic assist modules to meet tighter emission norms while retaining cost benefits. These transitional technologies may prolong the carburetor’s lifecycle in niche applications. -
Impact of Electric Mobility
The rise of electric motorcycles poses a long-term threat to all internal combustion engine (ICE) components, including carburetors. As governments incentivize EV adoption and phase out ICE vehicles, the overall market for carburetors will face pressure. However, the transition will be gradual, especially in regions with limited charging infrastructure, allowing carburetor demand to persist through 2026. -
Growth in Custom and Vintage Motorcycle Enthusiasm
A growing global interest in vintage and custom motorcycles supports carburetor demand. Enthusiasts often prefer carburetors for their mechanical simplicity, nostalgic appeal, and ease of tuning. This cultural trend, particularly strong in the U.S., Japan, and parts of Europe, ensures a steady niche market for high-quality carburetors and performance upgrades. -
Consolidation Among Manufacturers
As OEM demand decreases, smaller carburetor manufacturers may consolidate or pivot to specialized markets. Leading suppliers are expected to focus on export opportunities, aftermarket solutions, and partnerships with regional two-wheeler assemblers in developing economies to sustain revenue.
In conclusion, while the motorbike carburetor market faces structural decline due to technological and environmental shifts, it is expected to remain viable through 2026—particularly in cost-sensitive and legacy-dependent markets. Strategic adaptation by manufacturers and sustained aftermarket demand will be crucial for navigating this transitional phase.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Motorcycle Carburetors (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing motorcycle carburetors, especially from international suppliers or third-party manufacturers, involves several risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) rights. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for distributors, retailers, and OEMs to avoid legal issues, customer dissatisfaction, and brand damage.
Poor Manufacturing Quality and Inconsistent Performance
One of the most frequent issues is receiving carburetors made with substandard materials or imprecise tolerances. Low-cost suppliers may use inferior aluminum, rubber diaphragms, or brass components that degrade quickly under heat and vibration. This leads to fuel leaks, poor idle, inconsistent air-fuel ratios, and premature failure. Inconsistent calibration across units can also result in performance variability, making it difficult to ensure reliable engine operation across different bikes.
Lack of Proper Quality Control and Testing
Many generic or aftermarket suppliers skip rigorous testing procedures such as flow bench calibration, leak testing, or durability cycling. Without these checks, carburetors may appear functional on arrival but fail under real-world operating conditions. Absence of ISO or other quality certifications from the manufacturer increases the risk of receiving non-compliant or unreliable components.
Counterfeit or Replica Carburetors Infringing on IP
A significant IP risk involves sourcing carburetors that are unauthorized copies of well-known brands like Keihin, Mikuni, or Dell’Orto. These counterfeit products often replicate trademarks, logos, and design patents without licensing. Distributing or selling such replicas exposes buyers to legal action for trademark and patent infringement, including customs seizures, fines, and reputational harm.
Misrepresentation of Compatibility and Specifications
Suppliers may falsely advertise carburetors as direct replacements for specific motorcycle models or OEM equivalents. In reality, the porting, venturi size, or jetting may differ, leading to poor engine performance or emissions non-compliance. This misrepresentation can result in customer complaints, returns, and warranty claims, particularly when the product does not meet advertised performance claims.
Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Reputable carburetor manufacturers provide technical documentation, including part numbering systems, service manuals, and compliance certifications. Generic or illicit suppliers often lack such documentation, making it difficult to verify authenticity, support end-users, or comply with regulatory requirements in certain markets.
Supply Chain Transparency and Ethical Sourcing Risks
Sourcing from unknown manufacturers or intermediaries may involve indirect support of unethical labor practices or environmentally harmful production methods. Without supply chain visibility, businesses risk association with poor labor standards or non-compliance with import regulations such as REACH or RoHS.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence—verifying supplier credentials, requesting sample testing, ensuring IP compliance, and confirming adherence to quality standards. Partnering with authorized distributors or licensed manufacturers reduces both quality and legal risks, ensuring long-term reliability and brand integrity.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Motor Bike Carburetor
Product Classification & HS Code
Motor bike carburetors are typically classified under Harmonized System (HS) codes related to internal combustion engine parts. The most common HS code is 8409.91, which covers “Parts suitable for use solely or principally with the engines of heading 8407 (internal combustion piston engines).” However, national tariff schedules may vary, so confirm the exact code with your destination country’s customs authority. Proper classification ensures accurate duty calculation and compliance with import regulations.
Import/Export Regulations
Exporting or importing motor bike carburetors may be subject to export controls, especially if components are manufactured in regulated jurisdictions or contain controlled materials. Some countries restrict the import of carburetors due to emissions standards (e.g., favoring fuel-injected systems). Exporters must verify licensing requirements under regulations such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or EU Dual-Use Regulations. Always check destination-specific import restrictions and required documentation.
Emissions & Environmental Compliance
Carburetors must comply with emissions standards in the target market. Regions such as the European Union, United States, and Japan enforce strict emissions regulations (e.g., Euro 5, EPA standards). Carburetors intended for on-road motorcycles may need certification from bodies like the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) or European Commission. Non-compliant units may be denied entry or subject to fines. Aftermarket and off-road carburetors may have different compliance pathways—verify application context.
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
Carburetors must be securely packaged to prevent damage during transit, typically using anti-corrosion wrapping, foam inserts, and sturdy outer cartons. Labeling should include: product description, HS code, country of origin, manufacturer details, and any compliance marks (e.g., CE, EPA). Hazard labels are generally unnecessary unless flammable residues are present. Include multilingual instructions or labels if required by the destination country.
Shipping & Transportation
Carburetors are generally non-hazardous and can be shipped via air, sea, or ground freight without special handling. Ensure proper declaration on the air waybill or bill of lading with accurate weight, dimensions, and commodity description. For air freight, comply with IATA guidelines; for sea freight, adhere to IMDG Code requirements if applicable. Use logistics partners experienced in automotive parts shipping for optimized routing and customs clearance.
Customs Documentation
Essential documentation includes:
– Commercial Invoice (detailed description, value, terms of sale)
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (may be required for preferential tariffs)
– Product Compliance Certificates (e.g., EPA, ECE)
– Export Declaration (as required by exporting country)
Ensure all documents are consistent to avoid customs delays or penalties.
Duties, Taxes & Tariff Engineering
Import duties vary by country and depend on the HS code and trade agreements. For example, under USMCA or EU free trade agreements, duty rates may be reduced or eliminated with a valid Certificate of Origin. Conduct tariff engineering if possible—such as classifying carburetors as “engine parts” rather than complete assemblies—to optimize duty costs legally. Always consult a customs broker for accurate duty forecasting.
Aftermarket & Certification Considerations
Aftermarket carburetors may face stricter scrutiny. Some countries require type approval or homologation before sale. Ensure products meet local safety and performance standards. Retain technical documentation and test reports to demonstrate compliance during customs inspections or market surveillance audits.
Returns & Warranty Logistics
Establish a clear process for handling product returns, warranty claims, or recalls. Include return authorization (RMA) procedures and designate regional service centers if applicable. Comply with destination country rules on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) if the carburetor includes electronic components (e.g., solenoids).
Conclusion
Successfully managing the logistics and compliance of motor bike carburetors requires attention to classification, regulations, emissions standards, and documentation. Partner with experienced freight forwarders and customs brokers, and stay updated on regulatory changes in both origin and destination markets to ensure smooth international trade operations.
In conclusion, sourcing a motorcycle carburetor requires careful consideration of compatibility, quality, supplier reliability, and cost. It is essential to identify the correct make, model, and engine specifications to ensure proper fitment and optimal performance. Whether purchasing OEM parts for authenticity or aftermarket options for affordability and availability, evaluating the reputation of the supplier and the availability of warranties or return policies is crucial. Additionally, considering factors such as local availability, import regulations, and long-term maintenance needs can influence the decision-making process. Ultimately, a well-researched sourcing strategy ensures a reliable, efficient carburetor that enhances the motorcycle’s performance and rider satisfaction.