The global laser market is undergoing rapid expansion, driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, electronics, and aerospace. According to Grand View Research, the global fiber laser market size was valued at USD 2.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the rising adoption of fiber lasers in material processing applications due to their high efficiency, reliability, and lower maintenance requirements. Meanwhile, MOPA (Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) lasers—known for their exceptional pulse control and versatility in fine engraving and cleaning—are gaining market traction, particularly in high-precision microfabrication. As industries shift toward advanced laser technologies, leading manufacturers are innovating to meet evolving performance and cost demands. In this competitive landscape, understanding the strengths and specializations of the top MOPA and fiber laser manufacturers is critical for businesses aiming to optimize their production capabilities.
Top 9 Mopa Laser Vs Fiber Laser Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
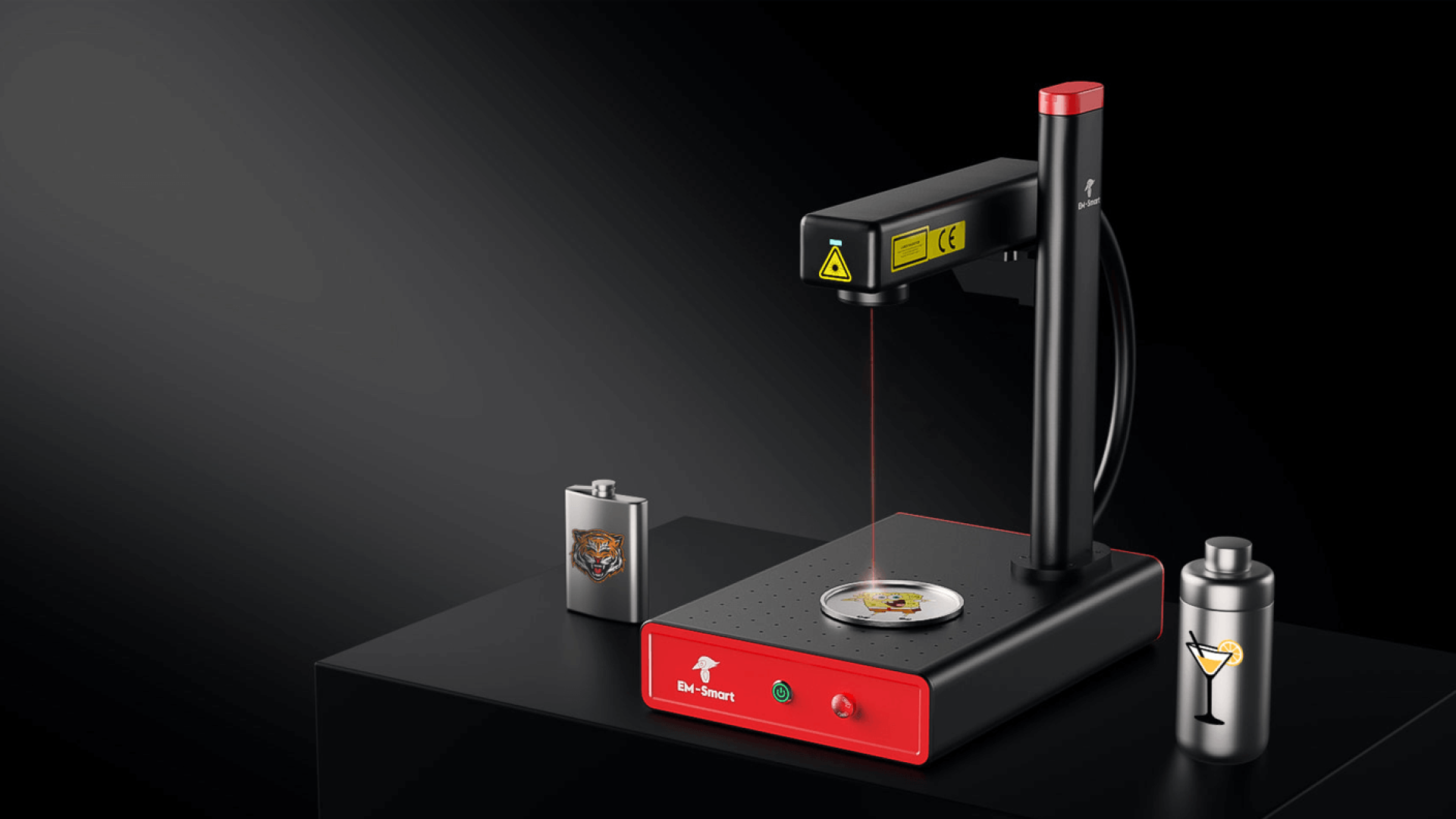
#1 How does MOPA fiber laser engraving technology work?
Website: gravotech.us
Key Highlights: Explore the MOPA fiber laser: how it works, its advantages and limits, and the best materials and applications for this laser engraving technology….
#2 MOPA Laser vs Fiber Laser
Website: igoldenlaser.com
Key Highlights: While both deliver high power laser light, they differ in their design, output characteristics and suitability for various manufacturing tasks….
#3 Fiber vs. MOPA
Website: thunderlaser.com
Key Highlights: Fiber and MOPA are two different types of lasers, with the MOPA having a larger amplitude capable of producing different colors and contrast….
#4 MOPA Fiber Lasers
Website: en.jptoe.com
Key Highlights: JPT develops advanced MOPA fiber lasers with high peak power, adjustable pulse width, and excellent beam quality. Widely used in precision marking, ……
#5 The Differences Between CO2, MOPA Fiber and UV Lasers
Website: permanentmarking.com
Key Highlights: In this post, we’ll take a look at MOPA fiber lasers vs. UV lasers vs. CO 2 lasers, examining the differences and similarities between the options….
#6 What’s the difference between fiber laser and MOPA laser engraving …
Website: barchlaser.com
Key Highlights: The fiber laser or Q switched machines have a better rate of engraving speed over some plastics and over some metal materials….
#7 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics manufactures high-performance fiber lasers, amplifiers, and laser systems for diverse applications and industries. Discover your solution….
#8 Fiber vs. MOPA Laser Cutting
Website: tri-star-technologies.com
Key Highlights: The major difference between fiber and MOPA laser cutting is the control and pulse duration. The pulses of standard fiber lasers are fixed, while the pulse ……
#9 Inside the Fiber Laser
Website: laserphotonics.com
Key Highlights: A MOPA laser is a fiber laser with variable pulse capabilities. MOPA stands for Master Oscillator Power Amplifier – this was a breakthrough that ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Mopa Laser Vs Fiber Laser
H2: Market Trends in 2026 – MOPA Laser vs Fiber Laser
As industrial laser technologies continue to evolve, the competition between MOPA (Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) lasers and standard fiber lasers is intensifying. By 2026, key market trends indicate a divergence in application focus, performance expectations, and regional adoption, shaping the future of laser-based manufacturing. Here’s a detailed analysis of how MOPA and fiber lasers are positioned to perform in the evolving market landscape.
1. Technological Differentiation and Application Expansion
MOPA lasers, a specialized variant of fiber lasers, offer superior pulse control, adjustable pulse width, and high peak power—making them ideal for precision applications like color marking on stainless steel, anodized aluminum, and selective ablation in electronics. By 2026, increasing demand for high-contrast, fine-feature marking in consumer electronics, medical devices, and automotive components is expected to drive MOPA laser adoption.
Standard fiber lasers, on the other hand, dominate in high-power continuous wave (CW) and quasi-CW operations. They remain the go-to solution for cutting, welding, and deep engraving in heavy industries such as automotive, aerospace, and shipbuilding. Advancements in power efficiency and beam quality have further solidified their position in large-scale metal processing.
2. Market Growth and Regional Dynamics
The global industrial laser market is projected to exceed $20 billion by 2026, with Asia-Pacific—particularly China, South Korea, and India—leading demand. In these regions, rising automation, electronics manufacturing, and government incentives for smart manufacturing are boosting both MOPA and fiber laser sales.
China, the largest consumer of industrial lasers, is witnessing a surge in MOPA laser use for smartphone and EV battery marking. Conversely, in North America and Europe, fiber lasers continue to dominate due to their integration into high-throughput manufacturing lines and robotic welding cells.
3. Cost and ROI Considerations
While MOPA lasers typically carry a 20–30% price premium over standard fiber lasers, their flexibility in pulse parameter tuning justifies the investment in niche precision tasks. By 2026, falling component costs and improved manufacturing scalability are expected to narrow this gap, making MOPA systems more accessible to mid-tier manufacturers.
Fiber lasers benefit from economies of scale, mature supply chains, and widespread service networks, resulting in lower total cost of ownership (TCO). Their robustness and minimal maintenance make them favorable for continuous operation environments.
4. Emerging Applications and Industry 4.0 Integration
The integration of lasers with Industry 4.0 technologies—such as IoT-enabled monitoring, AI-driven process optimization, and digital twins—is accelerating. MOPA lasers are particularly well-suited for smart factories due to their programmable pulse profiles, enabling real-time adaptation for variable marking or surface treatment tasks.
Fiber lasers are being enhanced with intelligent beam delivery and adaptive optics, supporting dynamic cutting and welding in flexible production systems. Hybrid systems combining MOPA and standard fiber sources are also emerging, offering multi-functionality within a single platform.
5. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Both laser types boast high wall-plug efficiency (up to 40%), but MOPA lasers offer finer energy control, reducing thermal damage and material waste. As sustainability becomes a key purchasing criterion, manufacturers are favoring MOPA for eco-friendly micro-processing applications.
Conclusion
By 2026, MOPA lasers will carve out a strong niche in high-precision, high-value industries, driven by demand for aesthetic and functional surface engineering. Fiber lasers will maintain dominance in high-power industrial applications due to reliability, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. The market is not a zero-sum competition—rather, it reflects a segmentation where each technology serves distinct but complementary roles in the advanced manufacturing ecosystem.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing MOPA Laser vs Fiber Laser (Quality and IP)
When selecting between MOPA (Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) and standard fiber lasers for industrial applications, buyers often encounter pitfalls related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Understanding these challenges is critical to making an informed procurement decision.
Overlooking Pulse Control and Material Compatibility
A common mistake is assuming all fiber lasers offer the same level of pulse flexibility. Standard fiber lasers typically use Q-switching, which limits control over pulse duration and frequency. In contrast, MOPA lasers provide independent control over pulse parameters, allowing fine-tuning for delicate applications like color marking on plastics or annealing stainless steel. Sourcing a standard fiber laser for such tasks can lead to poor mark quality, material damage, or inconsistent results—especially on heat-sensitive substrates.
Underestimating Build Quality and Component Sourcing
Buyers often focus on specifications without verifying the actual build quality. Low-cost suppliers may use inferior optical components, diodes, or cooling systems in both MOPA and fiber lasers, leading to premature failure, power instability, or beam quality degradation. It’s essential to audit the manufacturer’s component sourcing practices and demand test reports on beam profile (M²), long-term power stability, and thermal management.
Ignoring Software and Firmware Limitations
Many budget MOPA lasers come with proprietary software that lacks flexibility or regular updates. This can limit pulse parameter customization or integration with existing production systems. Additionally, locked firmware can prevent performance optimization or troubleshooting, reducing operational efficiency. Always verify software openness, update policies, and compatibility with common industrial controllers (e.g., PLCs, CNC systems).
Falling for Misleading Specifications
Suppliers may advertise peak power or pulse frequency without disclosing duty cycle limitations or actual average power under continuous operation. For example, a MOPA laser advertised with high peak power might overheat quickly if used beyond its duty cycle, resulting in inconsistent marking or engraving. Request real-world performance data under sustained workloads to validate claims.
Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing from low-cost manufacturers—especially in regions with weak IP enforcement—can expose buyers to legal and operational risks. Some suppliers may use copied or reverse-engineered MOPA technology, infringing on patents held by established laser innovators. If your company uses such equipment, you could face liability or supply chain disruption if the manufacturer is sued. Always vet the supplier’s IP compliance and request documentation on technology licensing or original design rights.
Neglecting Service, Support, and Spare Parts Availability
Long-term reliability depends on accessible technical support and spare parts. Some MOPA lasers use custom or proprietary components that are difficult to replace if the supplier vanishes or refuses support. Ensure the supplier offers a clear service agreement, local technical support, and availability of critical spares (e.g., pump diodes, fiber modules) for at least five years.
Assuming All Fiber Lasers Are Interchangeable
Not all “fiber lasers” are equal. Standard fiber lasers are cost-effective for basic metal marking, but they cannot replicate the versatility of true MOPA systems. Buyers who choose a cheaper fiber laser to save costs may later face expensive rework or need to invest in a second laser system, negating initial savings. Clearly define application requirements—especially regarding material variety and marking quality—before deciding on the laser type.
By avoiding these common sourcing pitfalls, businesses can ensure they select a reliable, high-quality laser system that meets both technical needs and IP integrity standards.
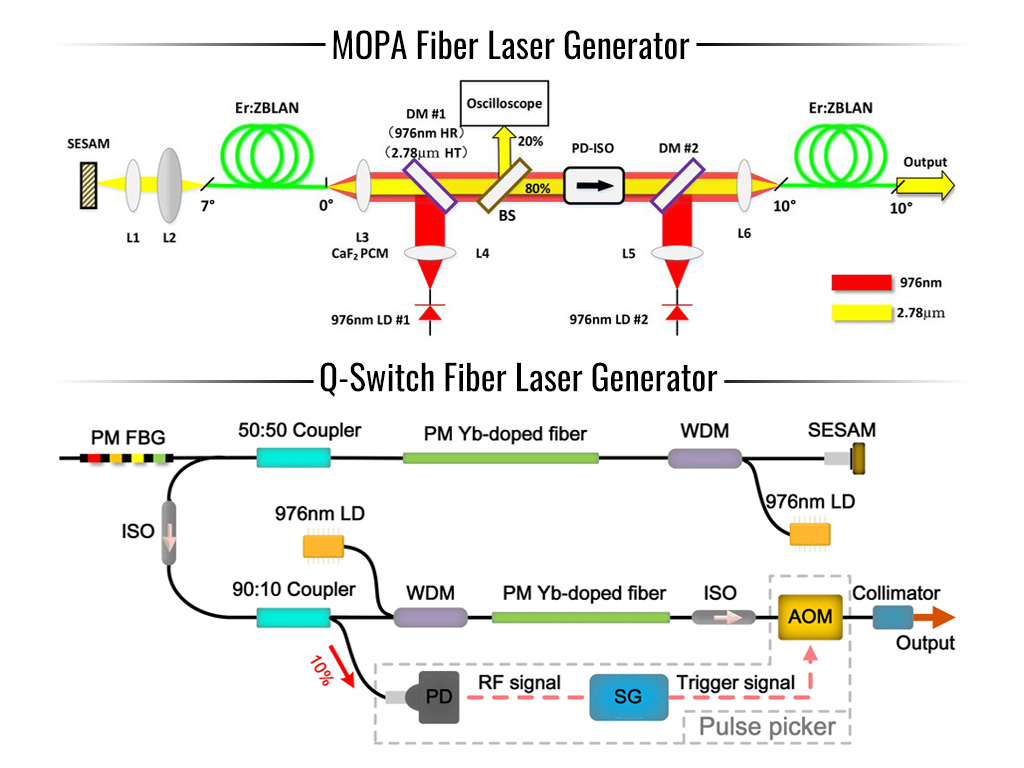
Logistics & Compliance Guide: MOPA Laser vs Fiber Laser
When selecting between MOPA (Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) lasers and standard fiber lasers for industrial applications, understanding the logistics and compliance implications is essential. Both technologies offer distinct advantages and challenges in terms of transportation, installation, regulatory standards, and operational safety. This guide outlines key considerations for businesses evaluating these laser systems.
Regulatory Standards and Safety Compliance
Both MOPA and fiber lasers must comply with international and regional safety regulations, including IEC 60825 (laser safety), FDA 21 CFR Part 1040.10 (U.S. laser product requirements), and CE marking directives (e.g., Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and EMC Directive 2014/30/EU). However, differences in pulse control and peak power can affect compliance:
-
MOPA Lasers: Due to their ability to produce shorter, high-peak-power pulses across a wide range of pulse durations, MOPA systems may generate higher peak irradiance. This often necessitates enhanced safety enclosures, interlock systems, and stricter access controls. Compliance documentation must reflect higher classification (e.g., Class 4 laser), requiring detailed risk assessments and safety protocols.
-
Standard Fiber Lasers: Typically operate with longer pulse widths and lower peak power (in non-MOPA configurations), making them slightly easier to integrate into existing safety frameworks. However, they still fall under Class 4 laser requirements and require proper labeling, interlocks, and operator training.
Transportation and Packaging Requirements
Lasers are sensitive optical and electronic systems requiring careful handling during shipping.
-
MOPA Lasers: Often include additional internal components (e.g., pulse-controlled seed lasers and amplifiers), which may increase sensitivity to shock and vibration. Manufacturers typically require specialized packaging with anti-static materials, shock-absorbing foam, and climate-controlled shipping for long distances. Import/export documentation must include detailed technical specifications, especially for systems exceeding certain power thresholds subject to ITAR or dual-use regulations (e.g., EU Dual-Use Regulation 2021/821).
-
Fiber Lasers: Generally more robust due to simpler internal architecture, but still require secure packaging to protect fiber connections and optical components. Standard industrial fiber lasers are widely shipped globally with standard export controls, though high-power units (>500W) may require additional licensing depending on destination country.
Installation and Facility Requirements
Installation logistics differ based on system complexity and operational needs.
-
MOPA Lasers: Require stable power supplies and often need dedicated cooling systems (e.g., chillers) due to higher thermal loads during pulsed operation. Facilities must ensure proper grounding, EMI shielding, and laser-safe zones. Integration with CNC or robotic systems may require additional software compatibility checks and safety interlocks.
-
Fiber Lasers: Generally easier to install with plug-and-play connectivity. Many models come with integrated air or water cooling. Power requirements are typically lower than MOPA equivalents for similar average power, simplifying facility integration. However, beam delivery via fiber optic cables still demands routing protection and bend-radius compliance.
Environmental and Operational Compliance
Both laser types must meet environmental regulations regarding energy efficiency, waste heat, and material processing byproducts.
-
MOPA Lasers: Higher peak powers can lead to increased particulate emissions during marking or cleaning applications, necessitating robust fume extraction systems compliant with OSHA or EU Directive 2004/37/EC (carcinogens and mutagens). Energy consumption may be higher during high-frequency pulsing, impacting sustainability reporting.
-
Fiber Lasers: More energy-efficient in continuous or long-pulse modes, contributing to lower carbon footprint. However, processing certain materials (e.g., plastics, coatings) still requires fume management and adherence to local air quality regulations (e.g., EPA NESHAP standards).
Maintenance and Service Logistics
Ongoing compliance includes maintenance records and service access.
-
MOPA Lasers: More complex internal components may require specialized technician training and OEM support. Spare parts logistics (e.g., seed diodes, isolators) should be planned for; downtime can be critical in production environments.
-
Fiber Lasers: Known for reliability and long service intervals. Many components are modular, simplifying field repairs. Remote diagnostics are commonly supported, aiding compliance with uptime and maintenance tracking requirements.
Conclusion
While both MOPA and fiber lasers meet core regulatory standards, MOPA systems demand more rigorous compliance measures due to their advanced pulse control and higher peak performance. Logistics planning should account for stricter safety protocols, specialized packaging, and service support. Fiber lasers offer simpler deployment and lower operational complexity, making them favorable for standard industrial applications. Evaluate your application needs, regulatory environment, and logistical capabilities when choosing between these technologies.
Conclusion: Sourcing MOBA Laser vs. Fiber Laser
When sourcing between MOBA lasers and fiber lasers, the decision ultimately depends on your specific application requirements, budget constraints, and long-term operational goals.
Fiber lasers are best suited for high-power industrial applications requiring deep penetration, high cutting or welding speeds, and long-term reliability—such as metal cutting, welding, and heavy manufacturing. They offer excellent beam quality, low maintenance, high efficiency, and longer lifespans, making them a cost-effective solution for high-volume production environments.
MOBA lasers, while less common and typically associated with specialized marking applications (particularly in the coding and serialization industry), offer distinct advantages in high-contrast, fine marking on sensitive materials like plastics and coated surfaces. Their unique pulse modulation capabilities allow for precise, non-damaging marks ideal for medical devices, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
In summary:
– Choose fiber lasers for robust, high-power industrial processing of metals with minimal maintenance.
– Opt for MOBA lasers when precision, high-contrast marking on sensitive or heat-conductive materials is critical.
When sourcing, consider total cost of ownership, service support, compatibility with existing systems, and supplier reputation. For most general industrial needs, fiber lasers provide broader versatility and scalability. However, in niche applications demanding ultra-fine, damage-free marking, a MOBA laser may be the superior investment. Always validate your choice with application-specific testing before final procurement.