The global monk fruit market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising consumer demand for natural, low-calorie sweeteners amid increasing health consciousness and the prevalence of lifestyle-related diseases such as diabetes and obesity. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global monk fruit market was valued at USD 68.9 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by growing adoption in food and beverage, dietary supplements, and pharmaceutical sectors, particularly as manufacturers seek clean-label alternatives to sugar and artificial sweeteners. As one of the purest forms of monk fruit extract, monk fruit juice concentrate has become a key ingredient in this shift—offering intense sweetness with zero glycemic impact. With supply chain dynamics evolving and demand rising across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, identifying the leading manufacturers capable of delivering high-quality, scalable, and certified products has become critical. Below are the top six monk fruit juice concentrate manufacturers shaping the industry through innovation, certifications, and reliable production capacity.
Top 6 Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
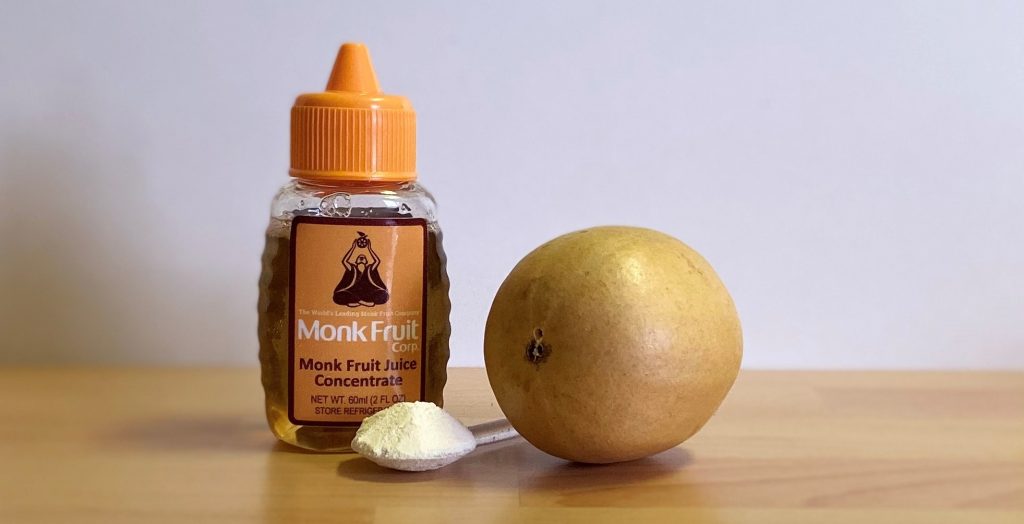
#1 Monk Fruit Corp
Domain Est. 2015
Website: monkfruitcorp.com
Key Highlights: Monk fruit juice is 20 times sweeter than apple juice. … Monk fruit is 100% natural and GMO-free. … Nothing artificial and no added sugar = zero worries….
#2 Everything You Need To Know About Monk Fruit Sweeteners
Domain Est. 2000
Website: ific.org
Key Highlights: Monk fruit sweeteners are produced by removing the seeds and skin of the fruit, crushing the fruit, and then filtering and extracting its sweet ……
#3 Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate
Domain Est. 2004
Website: bulknaturaloils.com
Key Highlights: In stock $40.57 deliveryJul 9, 2025 · Organic Monk fruit juice is a viscous liquid with a yellow to amber appearance and characteristic flavor profile, roughly 15-20 times sweeter …
#4 MONK FRUIT
Domain Est. 2007
Website: layncorp.com
Key Highlights: Layn offers the market’s largest Monk Fruit product portfolio in both extract and liquid form, from Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate and Monk Fruit Juice Powder to ……
#5 How is Monk Fruit Processed & Extracted?
Domain Est. 2009
Website: monkfruit.org
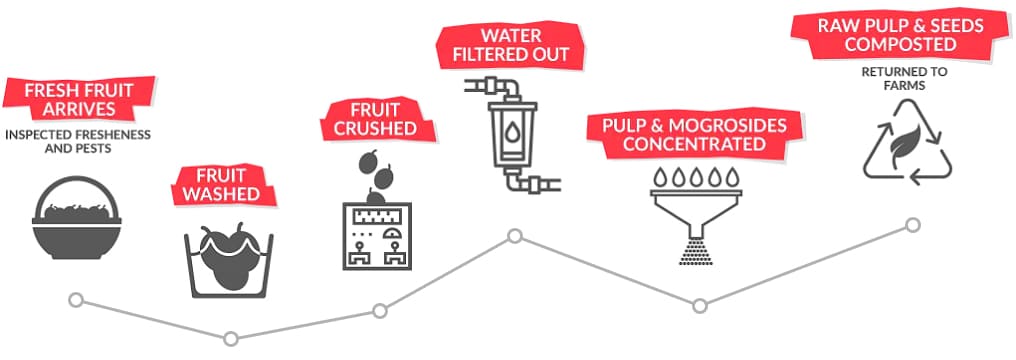
Key Highlights: The fruit is crushed to release its natural, sweet juice. The crushed fruit is mixed with hot water to make a sweet infusion. The infusion is filtered….
#6 Monk Fruit Extract
Domain Est. 2020
Website: heng-li-yuan.com
Key Highlights: Specifications: Mogrosides 7%~95%,Mogroside V 20%~95%,Monk fruit juice powder,Monk fruit concentrate juice … Official Website Of Guilin HengLiYuan Biotech Co….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate
The global market for monk fruit juice concentrate is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by shifting consumer preferences, technological advancements, and evolving regulatory landscapes. As a natural, zero-calorie sweetener, monk fruit (Luo Han Guo) has gained traction as a healthier alternative to sugar and artificial sweeteners, positioning its juice concentrate as a key ingredient across food and beverage sectors.
-
Rising Demand for Natural Sweeteners
By 2026, increasing health consciousness and the global push to reduce sugar consumption are expected to fuel demand for monk fruit juice concentrate. With obesity, diabetes, and metabolic disorders on the rise, consumers are actively seeking clean-label, plant-based sweeteners. Monk fruit aligns with this trend due to its zero glycemic index and absence of aftertaste—key advantages over stevia and artificial sweeteners. -
Expansion in Product Applications
Monk fruit juice concentrate is no longer limited to niche health products. By 2026, its use is anticipated to broaden across mainstream categories such as soft drinks, dairy alternatives, baked goods, dietary supplements, and even savory condiments. Major food and beverage companies are investing in reformulation strategies to include monk fruit, supported by improved extraction and stabilization technologies that enhance its solubility and shelf life. -
Innovation in Extraction and Blending Technologies
Advancements in biotechnology and fermentation processes are making monk fruit juice concentrate more cost-effective and scalable. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to increasingly adopt enzymatic conversion and fermentation-based production (e.g., bioconversion of mogrosides) to meet growing demand while reducing reliance on raw fruit supply, which is limited by seasonal and geographic constraints. -
Geographic Market Growth
While North America and Europe remain dominant markets due to strong regulatory approvals and consumer awareness, Asia-Pacific is projected to witness the fastest growth by 2026. China, the native region of monk fruit, is expanding commercial cultivation and export capacity. Meanwhile, Japan and South Korea are embracing monk fruit in functional foods and beverages, driven by traditional herbal medicine acceptance. -
Regulatory Support and Standardization
By 2026, clearer regulatory guidelines from bodies such as the FDA, EFSA, and China’s NHC are expected to standardize labeling and acceptable daily intake (ADI) levels, fostering market confidence. GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) affirmations and increased JECFA evaluations will further legitimize monk fruit concentrate as a mainstream ingredient. -
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Partnerships
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with key players like Tate & Lyle, PureCircle (Ingredion), and GLG Life Tech Corporation enhancing production capacity and forming strategic alliances with beverage giants like Coca-Cola and PepsiCo. Contract manufacturing and vertical integration are emerging trends to secure supply chains and reduce costs. -
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
By 2026, sustainability will play a critical role in market differentiation. Brands are expected to emphasize traceable sourcing, fair-trade practices, and eco-friendly processing methods. Consumer demand for transparency will push suppliers to adopt blockchain and digital tracking systems for monk fruit cultivation and processing.
In summary, the 2026 market for monk fruit juice concentrate is characterized by robust growth, innovation, and diversification. As a premium natural sweetener, it is well-positioned to capitalize on global wellness trends, technological advancements, and expanding food industry applications, making it a cornerstone of the future sweetener market.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate can be highly beneficial for creating natural, zero-calorie sweetened products. However, several critical pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can undermine your supply chain, product integrity, and market position. Awareness of these risks is essential for successful sourcing.
Inconsistent or Poor Quality Due to Variable Processing
One of the most frequent issues is receiving Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate with inconsistent potency, flavor profile, or purity. Quality can vary significantly based on:
- Growing Conditions: Monk fruit (Siraitia grosvenorii) is highly sensitive to climate, soil, and harvest timing. Fruits harvested too early or late yield lower levels of mogrosides—the sweet compounds responsible for sweetness—leading to weaker concentrates.
- Extraction Methods: Different manufacturers use varying extraction techniques (e.g., water extraction vs. ethanol). Poorly controlled processes can degrade mogrosides or leave behind undesirable bitter notes or off-flavors.
- Concentration Variability: Concentrates may be labeled with generic mogroside content (e.g., 50%), but the actual ratio of key mogrosides (like Mogroside V) can differ, affecting sweetness intensity and aftertaste. Without standardized testing, inconsistent batches can disrupt product formulation.
To mitigate this, insist on detailed Certificates of Analysis (CoA) specifying mogroside profile and require third-party lab verification.
Adulteration and Lack of Purity Verification
Monk fruit is expensive to produce, making adulteration a real risk. Common adulterants include:
- Dilution with fillers: Maltodextrin, inulin, or other sweeteners may be added to bulk up the concentrate, reducing cost but diluting potency.
- Blending with other sweeteners: Some suppliers blend monk fruit with stevia or erythritol without disclosure, misleading buyers about purity.
- Artificial additives: Unapproved preservatives or anti-caking agents may be present, especially in lower-tier suppliers.
Always conduct independent testing (e.g., HPLC for mogroside profiling) and require full ingredient transparency in supply agreements.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Monk fruit sweetener technology is heavily protected by patents, particularly in the U.S., EU, and China. Key IP pitfalls include:
- Patented Extraction Methods: Many advanced, taste-improved extraction processes are patented. Sourcing concentrate produced using a patented method without a license can expose your company to infringement claims—even if you didn’t manufacture it.
- Brand and Formulation IP: Some suppliers market proprietary branded monk fruit ingredients (e.g., “Nectresse,” “LycoRed’s MogroPure®”). Using these without proper authorization can lead to legal disputes.
- Geographic and Use Limitations: Patents may restrict the use of certain extracts in specific applications (e.g., beverages vs. baked goods) or regions. Ignoring these can result in cease-and-desist orders or litigation.
Conduct thorough IP due diligence: require suppliers to disclose any patent coverage and obtain legal clearance for your intended use and market.
Insufficient Traceability and Supply Chain Transparency
Many suppliers, especially those sourcing through intermediaries, lack full traceability from farm to concentrate. This poses risks such as:
- Unverified farming practices: Use of pesticides or non-GMO claims that cannot be substantiated.
- Chain of custody gaps: Difficulty proving the origin of the fruit, increasing vulnerability to fraud.
- Regulatory non-compliance: Inability to meet food safety standards (e.g., FDA, EFSA) due to undocumented processing steps.
Demand full supply chain mapping and audit rights as part of your sourcing agreement.
Overlooking Regulatory Compliance and GRAS Status
Not all monk fruit concentrates are equally accepted in global markets. Pitfalls include:
- Non-GRAS or Unnotified Ingredients: In the U.S., only certain monk fruit extracts have GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) status. Using a non-GRAS concentrate can delay product launches or lead to regulatory action.
- Regional Regulatory Differences: China, the U.S., EU, and Japan have varying requirements for acceptable forms and uses of monk fruit. A concentrate compliant in one market may not be in another.
Verify that your supplier’s product has the necessary regulatory approvals for your target markets.
Conclusion
Sourcing high-quality, legally compliant Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate requires diligence beyond price and availability. Prioritize suppliers with transparent processes, verifiable quality controls, and clear IP licensing. Conduct independent testing and legal review to avoid quality inconsistencies and intellectual property disputes that could jeopardize your product and brand.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate
Product Overview
Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate, derived from the Siraitia grosvenorii fruit, is a natural, zero-calorie sweetener increasingly used in food and beverage applications. Due to its high purity and sensitivity to environmental conditions, proper logistics and compliance measures are essential throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory Classification
Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate is classified as a Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) substance by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) when used as a sweetener. It is also approved for use in the European Union, Canada, China, and other major markets. Importers and distributors must ensure compliance with local food additive regulations, including maximum usage levels and labeling requirements.
International Trade Compliance
Import/Export Documentation
Accurate documentation is critical for cross-border shipments. Required documents typically include:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
– Certificate of Free Sale (if required by the importing country)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Phytosanitary Certificate (if applicable)
Ensure Harmonized System (HS) code 1212.99 is correctly applied, though local variations may exist. Confirm the specific code with customs authorities in the destination country.
Labeling Requirements
Labels must comply with the regulations of the destination market. Key requirements include:
– Product name (e.g., “Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate”)
– List of ingredients
– Net weight
– Name and address of manufacturer or distributor
– Lot number and batch traceability
– Storage conditions
– Shelf life or expiration date
In the U.S., use of the term “natural” must adhere to FDA guidelines. In the EU, compliance with Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 on food additives is mandatory.
Packaging and Handling
Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate is typically shipped in food-grade drums (e.g., 200L HDPE) or intermediate bulk containers (IBCs) lined with polyethylene. Packaging must:
– Be hermetically sealed to prevent contamination and moisture ingress
– Use UV-protected materials if exposed to light
– Be labeled with proper handling instructions (e.g., “Keep Refrigerated,” “Do Not Freeze”)
Handle with care to avoid punctures or leaks. Use clean, sanitized equipment during loading and unloading.
Storage Conditions
Store in a cool, dry, and dark environment. Recommended conditions:
– Temperature: 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F)
– Relative Humidity: Below 65%
– Avoid direct sunlight and strong odors
Do not store near volatile chemicals or non-food substances. Rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out) to ensure product freshness.
Transportation Requirements
Temperature Control
Maintain cold chain integrity during transit. Use refrigerated (reefer) containers or trucks set between 2°C and 8°C (36°F–46°F). Monitor temperature continuously with data loggers and provide records upon delivery.
Transit Time
Limit transit duration to minimize degradation. For international shipments, aim for delivery within 30 days, depending on origin and destination.
Carrier Qualifications
Use carriers with experience in food-grade, temperature-sensitive freight. Verify compliance with:
– FDA Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) Sanitary Transportation Rule (U.S.)
– EU Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 on food hygiene
– GDP (Good Distribution Practice) for medicinal products if applicable
Quality Control and Testing
Each batch must undergo quality testing prior to shipment. The Certificate of Analysis should include:
– Brix level
– pH
– Microbial limits (total plate count, yeast/mold, E. coli, Salmonella)
– Purity and mogroside content (typically ≥ 40–50%)
– Heavy metals (lead, arsenic, cadmium, mercury)
– Residual solvents (if applicable)
Retain samples for at least one year beyond the shelf life for traceability.
Shelf Life and Expiry
Typical shelf life is 18–24 months when stored properly. Clearly mark expiration date on packaging. Do not distribute or use expired product. Monitor for signs of spoilage (e.g., off-odors, discoloration, microbial growth).
Recall and Traceability Procedures
Implement a robust traceability system that allows full lot tracking from raw material to final shipment. In the event of a recall:
– Notify regulatory authorities immediately
– Isolate affected batches
– Communicate with customers and distributors
– Conduct root cause analysis and corrective actions
Maintain records for a minimum of three years.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
Ensure raw materials are sourced from farms practicing sustainable agriculture. Monitor compliance with:
– Fair labor practices
– Environmental protection standards
– Biodiversity conservation
Prefer suppliers with third-party certifications such as Organic, Fair Trade, or Rainforest Alliance where applicable.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance are critical to ensuring the safety, quality, and marketability of Monk Fruit Juice Concentrate. Adherence to international regulations, temperature control, accurate documentation, and rigorous quality assurance will mitigate risks and support long-term success in global markets.
In conclusion, sourcing monk fruit juice concentrate requires a strategic approach that balances quality, sustainability, regulatory compliance, and cost-effectiveness. As a natural, zero-calorie sweetener with growing demand in the health-conscious and functional food markets, monk fruit concentrate offers significant potential for product differentiation. However, due to its limited global production—primarily centered in Southern China—procurement involves careful supplier vetting to ensure authenticity, consistent quality, and adherence to food safety standards such as FDA GRAS, EU Novel Food regulations, or other regional requirements.
Establishing long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers, ideally those committed to sustainable farming and transparent supply chains, can help mitigate risks related to supply volatility and price fluctuations. Additionally, conducting thorough due diligence, including third-party lab testing and on-site audits, ensures purity and absence of unwanted fillers like maltodextrin or artificial additives.
Ultimately, sourcing monk fruit juice concentrate successfully hinges on a proactive, informed strategy that aligns with both business objectives and consumer expectations for clean-label, natural sweetening solutions. As market demand continues to rise, early investment in strong supply chain relationships will position companies favorably in the competitive landscape of natural sweeteners.