The global secure and currency paper market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for anti-counterfeiting solutions and the continued reliance on physical currency despite digital payment trends. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global banknote and security paper market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.2% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research reported in 2022 that the global security paper market was valued at USD 2.9 billion and is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period of 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by stringent regulatory requirements, increased government spending on currency production, and advancements in paper-based security features such as watermarks, security threads, and embedded microprinting. As central banks upgrade existing currency series and introduce new denominations, the role of specialized money printing paper manufacturers becomes increasingly critical. Below are the top six manufacturers leading innovation and supply in this niche but vital segment of the global financial infrastructure.
Top 6 Money Printing Paper Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Currency Print Orders
Domain Est. 1998
Website: federalreserve.gov
Key Highlights: Currency Print Orders. 2026 Federal Reserve Note Print Order. The Board of Governors, as the issuing authority for Federal Reserve notes, ……
#2 Currency and Coins
Domain Est. 1998
Website: home.treasury.gov
Key Highlights: US currency is produced by the Bureau of Engraving and Printing and US coins are produced by the US Mint. Both organizations are bureaus of the US Department ……
#3 Bureau of Engraving and Printing (BEP)
Domain Est. 1999
Website: usa.gov
Key Highlights: The Bureau of Engraving and Printing (BEP) produces United States currency notes and serves to ensure that adequate amounts of currency and coin are in ……
#4
Domain Est. 2009
Website: bep.gov
Key Highlights: Home. Engraving & Printing. Your guide to United States currency production. Explore the currency production process from design to delivery….
#5 $1 Note
Domain Est. 2015
Website: uscurrency.gov
Key Highlights: These printable coloring sheets of denominations $1, $2, $5, $10, $20, and $100 are intended for children, parents, and teachers….
#6 FNMT
Website: fnmt.es
Key Highlights: Production of security paper for passports, banknotes and more… Security Paper · Responsive Image. Circulating Currency….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Money Printing Paper

2026 Market Trends for Money Printing Paper
As global economies evolve and digital transactions gain momentum, the market for money printing paper—specialized substrate used in the production of banknotes—faces transformative shifts. By 2026, several key trends are expected to shape the demand, supply, and technological landscape of this niche but critical industry.
Rising Demand for Secure and Durable Substrates
Central banks and monetary authorities continue to prioritize security and longevity in banknote production. In 2026, the demand for high-security money printing paper embedded with advanced anti-counterfeiting features—such as watermarks, security threads, and fluorescent fibers—is expected to grow. Governments are investing in next-generation substrates to combat increasingly sophisticated counterfeiting operations, driving innovation in paper composition and manufacturing processes.
Shift Toward Hybrid and Polymer Substrates
While traditional cotton-based paper remains dominant in many regions, there is a growing shift toward hybrid (cotton-polymer blend) and full polymer banknotes. Countries like Canada, the UK, and Australia have already transitioned to polymer, citing benefits such as enhanced durability, resistance to moisture, and longer circulation life. By 2026, emerging economies are expected to follow suit, potentially reducing the market share of conventional paper. However, cotton-based money printing paper will retain relevance in countries with established paper-based banknote systems and cultural preferences.
Regional Variations in Market Growth
Asia-Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing market for money printing paper by 2026, driven by rising populations, urbanization, and increased cash usage in countries like India, Indonesia, and the Philippines. In contrast, Europe and North America may see stagnant or declining demand due to the rapid adoption of digital payments. Nevertheless, periodic banknote redesigns and currency renewals in these regions will sustain a baseline need for high-quality printing paper.
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
Environmental regulations are influencing the production of money printing paper. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to adopt more sustainable practices, including sourcing cotton from certified farms, reducing water and energy consumption, and minimizing chemical use. Recyclable and biodegradable components are being explored, although challenges remain due to the need for extreme durability and security.
Geopolitical and Supply Chain Dynamics
The supply chain for money printing paper is highly concentrated, with a limited number of global suppliers such as Crane & Co. (USA), ArjoWiggins (UK/France), and Louisenthal (Germany). Geopolitical tensions and trade restrictions could impact the availability and pricing of specialty paper. As a result, some nations are investing in domestic production capabilities to ensure monetary sovereignty and supply resilience by 2026.
Impact of Digital Currencies
The rise of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) poses a long-term challenge to physical currency demand. While cash is not expected to disappear by 2026, its role may diminish in technologically advanced economies. This could lead to reduced order volumes for money printing paper, especially for smaller denominations. However, in regions with low digital infrastructure or high cash reliance, physical banknotes—and thus money printing paper—will remain essential.
Conclusion
The money printing paper market in 2026 will be shaped by a complex interplay of security needs, technological innovation, regional economic conditions, and the digital transformation of finance. While demand may plateau or decline in some parts of the world, ongoing requirements for secure, durable, and trusted physical currency will ensure the industry remains relevant—albeit transformed—by the middle of the decade.
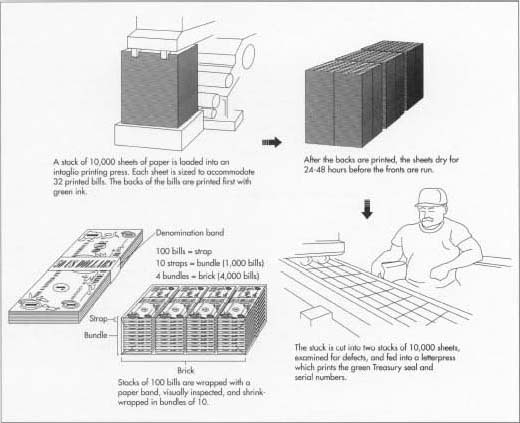
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Money Printing Paper (Quality, IP)
Sourcing money printing paper is a highly specialized and sensitive process, typically reserved for national governments and authorized central banks. Attempting to source such materials without proper authority involves significant legal, technical, and ethical risks. Below are key pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) that organizations—especially unauthorized ones—should be aware of.
Poor Quality Control and Inadequate Security Features
Money printing paper is not standard paper—it is a high-security substrate embedded with advanced features to prevent counterfeiting. Sourcing from unverified suppliers often results in substandard materials lacking essential characteristics:
- Missing Security Elements: Genuine currency paper includes watermarks, security threads, color-shifting inks, microprinting, and UV-reactive fibers. Low-quality substitutes often omit or poorly replicate these, making them easily detectable and useless for legitimate purposes.
- Inconsistent Fiber Composition: Authentic banknote paper is typically made from cotton or polymer blends engineered for durability and specific tactile properties. Inferior paper may degrade quickly, tear easily, or feel noticeably different, compromising authenticity.
- Batch Inconsistencies: Unauthorized suppliers often lack the precision manufacturing controls needed for uniform color, thickness, and texture across batches, leading to detectable variations.
Intellectual Property and Legal Violations
Currency design and production are protected by stringent intellectual property laws and international agreements:
- Copyright and Trademark Infringement: National currencies are protected works. Reproducing or imitating their design elements—even unintentionally—violates copyright and trademark laws in most jurisdictions.
- Breach of Anti-Counterfeiting Regulations: Sourcing materials intended for currency production without authorization may violate laws such as the U.S. Counterfeit Access Device and Computer Fraud and Abuse Act or similar statutes worldwide.
- Patented Technologies: Many security features (e.g., holographic strips, specialized inks, and substrate treatments) are patented. Using paper incorporating these without licensing constitutes IP infringement.
Supply Chain Risks and Counterfeit Materials
The supply chain for security paper is tightly controlled. Unauthorized sourcing channels are prone to:
- Black Market Sources: Suppliers offering “money-grade” paper are often operating illegally, increasing the risk of receiving counterfeit or diverted materials, which can lead to criminal liability.
- Lack of Traceability: Legitimate security paper is tracked and audited. Illicit paper lacks provenance, making it unsuitable for any official or compliant use.
Reputational and Operational Consequences
Even exploratory inquiries into sourcing such materials can raise red flags:
- Scrutiny from Authorities: Financial and law enforcement agencies monitor attempts to acquire high-security materials. Unauthorized sourcing may trigger investigations.
- Damage to Institutional Credibility: Legitimate organizations risk severe reputational harm if linked to currency-related procurement, regardless of intent.
Conclusion
Sourcing money printing paper outside authorized government channels is fraught with legal, technical, and ethical pitfalls. The combination of stringent quality requirements and robust IP protections makes unauthorized access both impractical and illegal. Any organization requiring secure documentation should pursue certified security printing solutions through legitimate, regulated vendors.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Money Printing Paper
Money printing paper is a highly sensitive and regulated material used exclusively in the production of banknotes. Due to its critical role in maintaining currency integrity, its handling, transportation, and storage are subject to stringent logistical and compliance requirements. This guide outlines the essential protocols to ensure security, regulatory adherence, and operational integrity throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory Oversight and Legal Framework
Money printing paper is classified as a controlled material under national and international laws. Key regulatory bodies include central banks, finance ministries, and law enforcement agencies. Compliance with legislation such as anti-counterfeiting laws, export controls, and national security regulations is mandatory. Unauthorized possession, transfer, or disposal of this paper constitutes a criminal offense in most jurisdictions. All parties involved must operate under government-issued licenses and adhere to strict reporting requirements.
Security Protocols for Handling and Storage
Handling money printing paper requires the highest level of physical and procedural security. Storage facilities must be secured with surveillance systems, access controls (e.g., biometric authentication), intrusion detection, and 24/7 monitoring. Only authorized personnel with security clearances may access the material. Inventory must be tracked in real time using tamper-proof logging systems, with regular audits conducted to verify accountability. Any loss or discrepancy must be reported immediately to the relevant authorities.
Transportation and Chain of Custody
Transportation of money printing paper must be conducted under armed escort or equivalent security measures, depending on national protocols. Vehicles used must be armored, GPS-tracked, and sealed to prevent tampering. A documented chain of custody is required at all stages, with handover procedures involving dual authorization and digital logging. Routing should be confidential and subject to change to mitigate risk. Air, land, and sea transport must comply with national security directives and international hazardous or sensitive cargo regulations where applicable.
Supplier and Partner Vetting
All suppliers, logistics providers, and subcontractors must undergo rigorous background checks and be pre-approved by the issuing central bank or monetary authority. Contracts must include clauses enforcing compliance with security standards, non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), and liability for breaches. Third parties must demonstrate proven experience in handling high-value, sensitive materials and maintain equivalent security certifications.
Export and Import Controls
International movement of money printing paper is highly restricted and typically requires special permits from both the exporting and importing countries. Compliance with the Wassenaar Arrangement (for dual-use goods) and national export control lists is essential. Documentation must include end-use certifications, government authorizations, and detailed descriptions of the material. Customs declarations must be accurate and submitted in advance to avoid delays or seizures.
Environmental and Disposal Procedures
Defective or surplus money printing paper must never enter the commercial waste stream. Secure destruction procedures—such as shredding combined with chemical treatment or incineration under supervision—are required. Disposal must be documented with certificates of destruction and reported to regulatory authorities. Environmental regulations must be followed to prevent contamination from inks or security additives.
Training and Personnel Compliance
All personnel involved in the logistics chain must undergo regular training on security protocols, legal responsibilities, and emergency procedures. Training records must be maintained, and refresher courses conducted annually. Employees must sign confidentiality and compliance agreements, and any suspicious activity must be reported through established whistleblower or security channels.
Incident Reporting and Response
A formal incident response plan must be in place for breaches, thefts, or losses. This includes immediate notification protocols to law enforcement and the issuing monetary authority, containment procedures, forensic investigation, and corrective actions. Drills and simulations should be conducted regularly to ensure preparedness.
Auditing and Continuous Compliance
Regular internal and external audits are mandatory to verify adherence to security and compliance standards. Audit findings must be addressed promptly, and corrective action plans implemented. Compliance records, including transport logs, access reports, and inventory audits, must be retained for a minimum period as defined by national regulations—typically seven years or longer.
Adherence to this guide ensures the integrity of currency production and protects national financial systems from counterfeiting and security breaches. Any deviation from these protocols may result in severe legal penalties and reputational damage.
In conclusion, sourcing money printing paper is a highly specialized and tightly regulated process, restricted exclusively to authorized government institutions and central banks. The paper used for printing currency is not commercially available and is manufactured under strict security protocols by select, government-approved suppliers. It incorporates advanced security features such as watermarks, security threads, color-shifting inks, and specialized fibers to prevent counterfeiting. Due to the sensitive nature of this material, private entities cannot legally acquire or produce it. Any effort to source such paper must adhere to national and international regulations, emphasizing the importance of legality, security, and collaboration with official monetary authorities. Ultimately, the integrity of a nation’s currency depends on the controlled and secure sourcing of its substrate, ensuring trust and stability in the financial system.