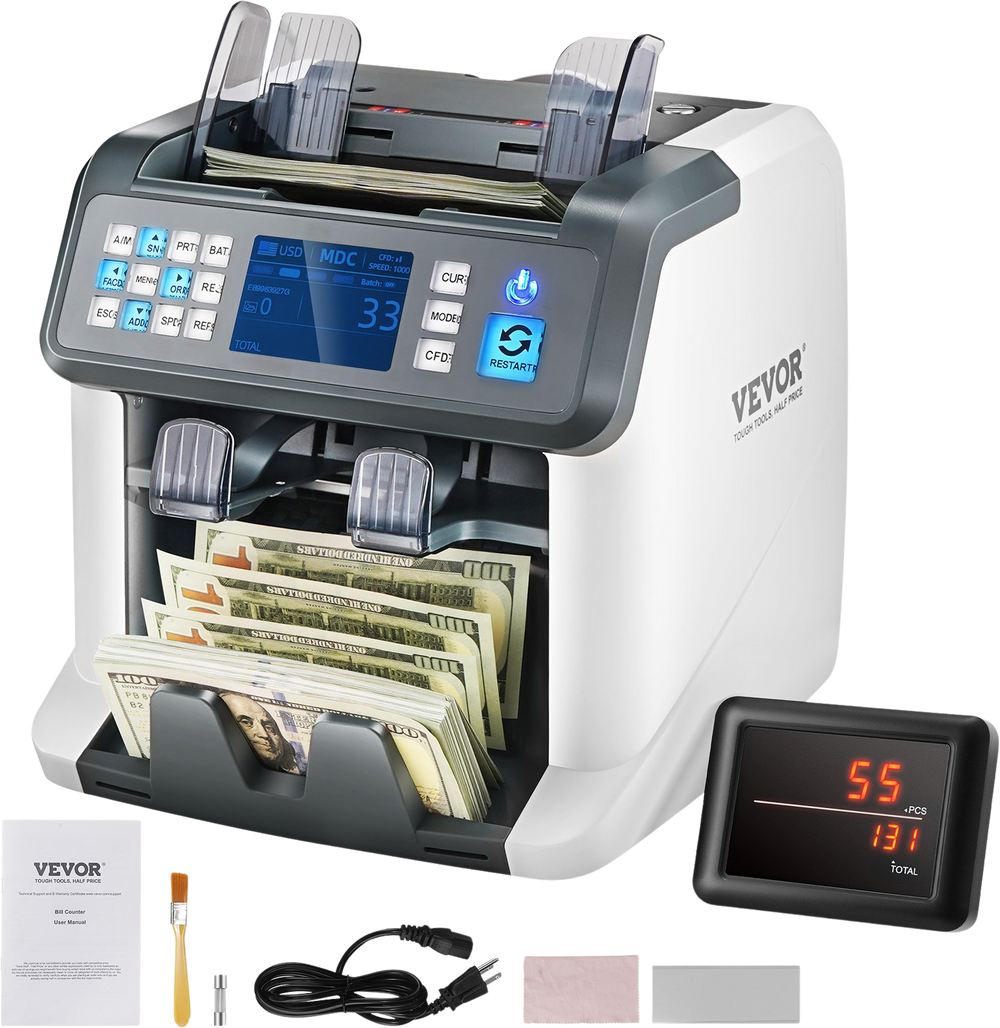
The global currency and money counting machine market has experienced steady growth, driven by increasing demand for automated cash handling solutions across banking, retail, and financial institutions. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the Automatic Currency Counting Machine Market was valued at USD 1.25 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights the broader cash handling equipment market’s expansion, citing rising cash transaction volumes in emerging economies and the need for accuracy and fraud detection as key growth catalysts. With advancements in counterfeit detection, data integration, and high-speed processing, manufacturers are innovating rapidly to meet evolving industry needs. As competition intensifies, nine key players have emerged as leaders, combining technological precision, global reach, and robust R&D to dominate the market landscape.
Top 9 Money Checking Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Banknote Equipment Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2009
Website: bep.gov
Key Highlights: Banknote Equipment Manufacturers (BEM) – companies that produce any type of equipment that handles banknotes (cash handling equipment) for commercial purposes, ……
#2 Integrated and automated payment technology
Domain Est. 2013
Website: cranepi.com
Key Highlights: Crane Payment Innovations enables integrated and automated payment technology across the globe. Reliable, flexible, and secure cash and cashless solutions….
#3 Tellermate
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tellermate.com
Key Highlights: Tellermate are known worldwide for our Money Counting Machines and intelligent cash drawers. We’re people you can count on….
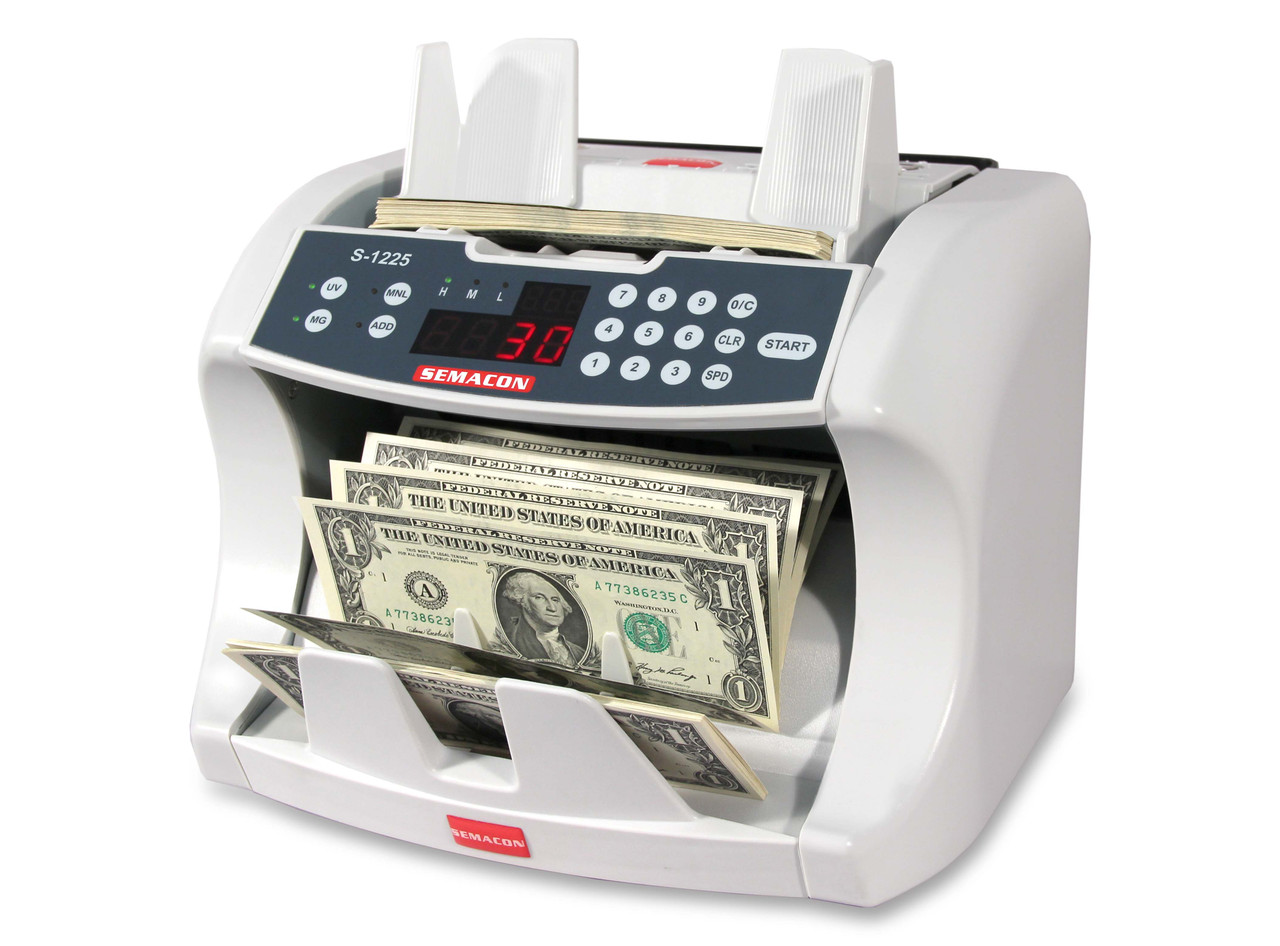
#4 Semacon Currency Counter and Coin Counter Money Handling …
Domain Est. 2000
Website: semacon.com
Key Highlights: Every Semacon machine undergoes extensive burn-in, rigorous quality assurance testing and precision calibration at our US manufacturing facility….
#5 AccuBANKER
Domain Est. 2001
Website: accubanker.com
Key Highlights: Money counters, coin and bill counters, and counterfeit bill detectors from one of the industry’s most trusted cash handling solution provider, AccuBANKER….
#6 MHM Inc
Domain Est. 2001
Website: moneyhandlingmachines.com
Key Highlights: These brands include Glory, Talaris, DeLaRue, Brandt, Nautilus Hyosung, NCR and more. We specialize in new and reconditioned coin sorters, coin counters, ……
#7 Bill Counters
Domain Est. 2001
Website: safescan.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsSafescan offers a large selection of bill counters for counting & sorting bills including counterfeit detection. Safescan money counting machines are ac…
#8 Money Counters
Domain Est. 2003
Website: zzap.com
Key Highlights: Streamline your cash handling operation with ZZap money counters, scales, counterfeit detectors and pos safes. Buy with a 3 year warranty….
#9 Carnation Enterprises
Website: carnation-inc.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $50 30-day returnsCash counters, bill counters, and mixed denomination money counters with counterfeit detection – businesses love us. Count on us to count your …
Expert Sourcing Insights for Money Checking Machine

2026 Market Trends for Money Checking Machines
Rising Demand Driven by Automation and Security Needs
By 2026, the global market for money checking machines is expected to experience steady growth, primarily fueled by increasing demand for automation in financial and retail environments. Businesses across banking, retail, gaming, and transportation sectors are prioritizing efficiency and fraud prevention, leading to higher adoption of advanced currency validation technologies. The need to reduce human error, minimize counterfeit risks, and streamline cash handling processes is accelerating investment in intelligent money checking systems equipped with AI and machine learning capabilities.
Integration of AI and Smart Authentication Technologies
A key technological trend shaping the 2026 landscape is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning algorithms into money checking machines. These enhancements enable real-time analysis of banknotes using multi-spectral imaging, magnetic ink detection, and micro-pattern recognition, significantly improving counterfeit detection accuracy. Vendors are focusing on developing smarter machines that adapt to evolving counterfeit techniques, offering over-the-air (OTA) updates and cloud-based monitoring for continuous performance optimization.
Growth in Cash Handling Automation Across Emerging Markets
Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are projected to contribute significantly to market expansion by 2026. As these regions experience urbanization and formalization of retail and financial services, the demand for reliable cash processing infrastructure rises. Government initiatives to modernize banking systems and combat counterfeit currency are further driving procurement of money checking machines in both commercial and public sectors.
Emphasis on Compact, Multi-Functional Devices
Market competition is pushing manufacturers toward compact, versatile designs that combine counting, counterfeit detection, fitness sorting, and data reporting in a single unit. These all-in-one machines are especially popular among small and medium enterprises (SMEs), convenience stores, and postal services. By 2026, user-friendly interfaces, touchscreen controls, and integration with point-of-sale (POS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems will be standard features, enhancing operational efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance and Standardization
Increasing regulatory scrutiny around anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) protocols is influencing machine capabilities. Money checking machines are expected to support digital logging of transaction data and generate audit trails to meet compliance requirements. International standards such as ISO 18011 for currency handling equipment will play a crucial role in product development and certification, especially in European and North American markets.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Considerations
Environmental concerns are beginning to impact product design. By 2026, energy-efficient models with low power consumption and recyclable components will gain preference, particularly among corporates with strong ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) commitments. Some manufacturers are exploring modular designs to extend product lifecycles and reduce electronic waste.
In summary, the 2026 money checking machine market will be defined by intelligent automation, enhanced security, regulatory alignment, and broader accessibility—positioning these devices as essential tools in the global cash ecosystem despite the rise of digital payments.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Money Checking Machines (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing money checking machines—devices used to authenticate and count currency—can be complex, especially when balancing cost, performance, and legal compliance. Two critical areas where businesses often encounter challenges are product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational inefficiencies, financial losses, and legal liabilities.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Authentication Technology
Many low-cost machines lack advanced counterfeit detection features such as UV, IR, magnetic (MG), and watermark scanning. Sourcing machines without comprehensive sensor arrays increases the risk of accepting counterfeit notes, directly impacting business revenue and reputation.
2. Poor Build Quality and Durability
Cheaper models may use substandard materials and components, leading to frequent breakdowns, jamming, or miscounts. This results in higher maintenance costs, downtime, and reduced operational efficiency—especially in high-volume environments like banks or retail chains.
3. Inconsistent Performance Across Currency Types
Some machines are optimized for specific currencies (e.g., USD or EUR) but perform poorly with others. Buyers may face issues when processing mixed or foreign currencies if the machine isn’t properly calibrated or lacks multi-currency support.
4. Lack of Calibration and Quality Control
Manufacturers with weak quality assurance processes may deliver units with inconsistent accuracy. Without proper factory testing and certification (e.g., ISO standards), machines may not meet declared performance specifications.
5. Insufficient After-Sales Support and Calibration Services
Even high-quality machines require periodic calibration and maintenance. Sourcing from suppliers without reliable technical support, spare parts availability, or service networks can lead to prolonged outages and increased total cost of ownership.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
1. Use of Counterfeit or Cloned Firmware
Some suppliers use reverse-engineered or pirated software to power their machines. This not only undermines performance and security but exposes buyers to legal liability for using non-licensed technology, especially in regulated industries.
2. Infringement of Patented Detection Technologies
Leading money checking machine manufacturers often hold patents on specific sensor configurations, algorithms, or mechanical designs. Sourcing machines from vendors that infringe these patents can result in legal action, shipment seizures, or forced product removals in certain markets.
3. Lack of Transparency in Supply Chain
OEMs or third-party suppliers may obscure the origin of core components or software. Without due diligence, businesses risk purchasing machines that incorporate stolen IP or are assembled in violation of international trade laws.
4. No Licensing or Certification Documentation
Reputable machines typically come with documentation proving compliance with IP rights and industry standards (e.g., CE, FCC, or central bank approvals). Absence of such documentation is a red flag indicating potential IP violations or substandard quality.
5. Exposure to Legal and Reputational Damage
Using machines with infringing technology can lead to lawsuits, fines, or reputational harm—especially for financial institutions or large retailers committed to ethical sourcing and compliance.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including site visits and reference checks.
– Request technical specifications, certifications, and proof of IP ownership or licensing.
– Test machines rigorously with real-world currency samples before bulk procurement.
– Prioritize suppliers with transparent supply chains and strong after-sales support.
– Consult legal experts when sourcing high-volume or mission-critical equipment.
By focusing on both quality assurance and IP compliance, organizations can ensure reliable, secure, and legally sound operations when deploying money checking machines.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Money Checking Machine
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the import, distribution, and operation of Money Checking Machines (also known as currency validators, counterfeit detectors, or banknote verification devices).
Regulatory Compliance
Money Checking Machines are subject to various national and international regulations due to their role in financial security and anti-counterfeiting. Key compliance areas include:
- Anti-Counterfeiting Standards: Devices must comply with central bank guidelines (e.g., ECB, Federal Reserve, Bank of England) regarding detection capabilities for security features such as UV, IR, magnetic ink, watermarks, and holograms.
- Data Privacy Laws: If the machine stores or transmits data (e.g., serial numbers, timestamps), compliance with GDPR (EU), CCPA (California), or other data protection regulations is required.
- EMC and Electrical Safety: Adherence to standards such as IEC 60950 (safety) and IEC 61326 (EMC) is mandatory for electronic equipment. CE marking (Europe), FCC (USA), or other regional certifications may be required.
- Export Controls: Some advanced verification technologies may be subject to export regulations (e.g., EAR in the U.S.) if they include encryption or dual-use components.
Import and Customs Requirements
Ensure smooth cross-border movement by addressing:
- HS Code Classification: Use the correct Harmonized System (HS) code (e.g., 9031.49 for measuring or checking instruments) to determine tariffs and regulations.
- Duties and Taxes: Calculate import duties, VAT, or GST based on destination country regulations.
- Documentation: Prepare commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/airway bill, certificate of origin, and any required technical specifications or test reports.
- Product Certification: Verify that the machine has necessary certifications for the target market (e.g., CE, UKCA, FCC, CCC for China).
Transportation and Handling
Proper logistics execution ensures devices arrive undamaged and on time:
- Packaging: Use anti-static, shock-resistant packaging to protect sensitive electronic components.
- Shipping Mode: Choose air freight for speed or sea freight for bulk shipments, considering cost and lead time.
- Temperature and Humidity: Avoid exposure to extreme conditions during transit; store and ship within manufacturer-specified environmental ranges.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”) and compliance marks.
Installation and Operational Compliance
Post-delivery steps to ensure legal and safe use:
- User Training: Train operators on correct usage, maintenance, and reporting of suspected counterfeit notes.
- Audit Trail: Maintain logs of machine usage and detection events if required by local financial regulations.
- Regular Maintenance: Follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning and calibration to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Software Updates: Apply security and detection algorithm updates to keep pace with evolving counterfeit threats.
Disposal and End-of-Life
Dispose of machines responsibly:
- E-Waste Regulations: Follow WEEE (EU), EPA (USA), or local e-waste laws for proper recycling.
- Data Sanitization: If the device stores any data, ensure secure erasure before disposal or recycling.
Adhering to this guide ensures legal operation, minimizes supply chain disruptions, and supports the integrity of financial transactions. Always consult local authorities and legal counsel for jurisdiction-specific requirements.
Conclusion:
Sourcing a money checking machine is a strategic investment that enhances financial security, improves operational efficiency, and ensures compliance with anti-counterfeiting regulations. By carefully evaluating machine features—such as counterfeit detection capabilities, currency compatibility, processing speed, durability, and ease of use—organizations can select a solution that best fits their specific needs. Additionally, considering factors like supplier reliability, after-sales service, warranty, and total cost of ownership ensures long-term value and performance. In an environment where financial integrity is paramount, a high-quality money checking machine not only protects against losses from counterfeit currency but also streamlines cash handling processes, ultimately contributing to greater accuracy, trust, and customer satisfaction. Therefore, thorough research and informed decision-making are essential in sourcing the right machine to safeguard financial operations.