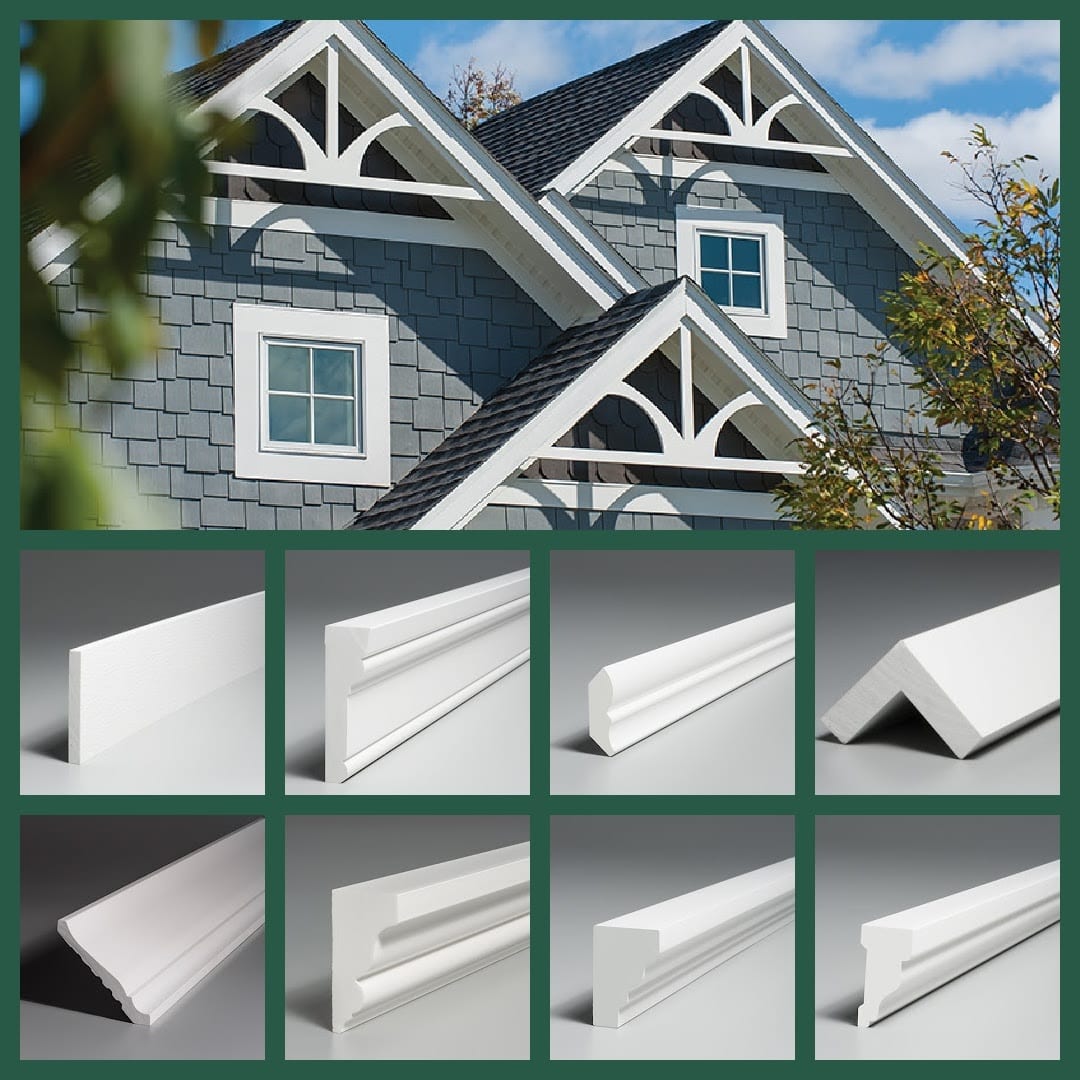
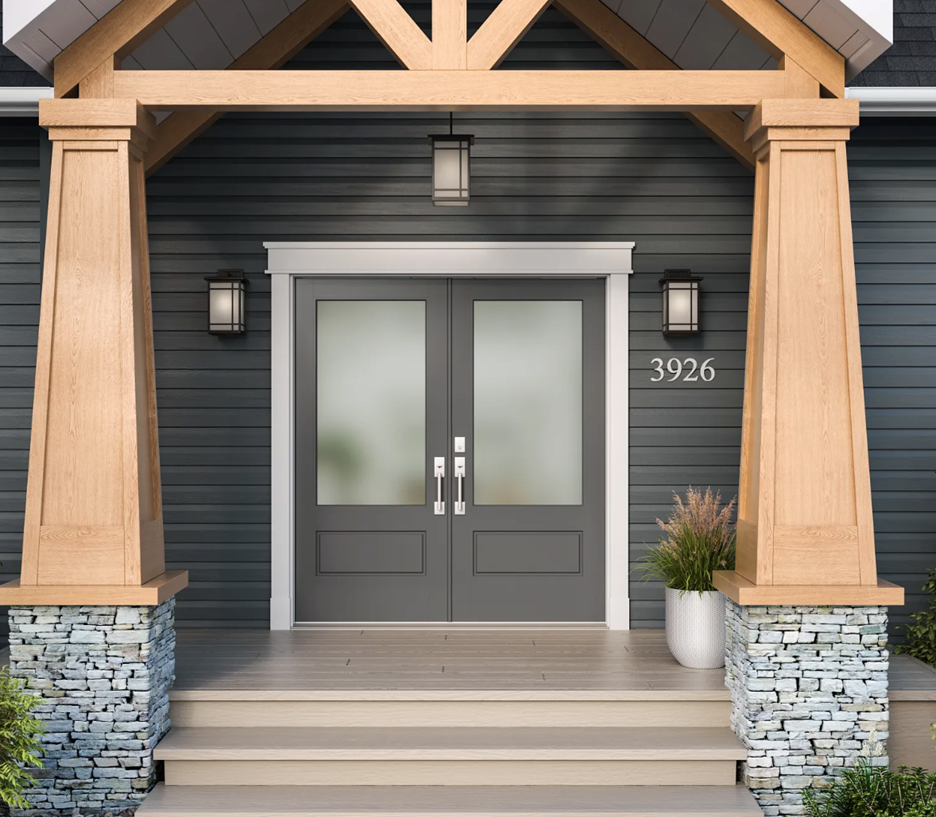
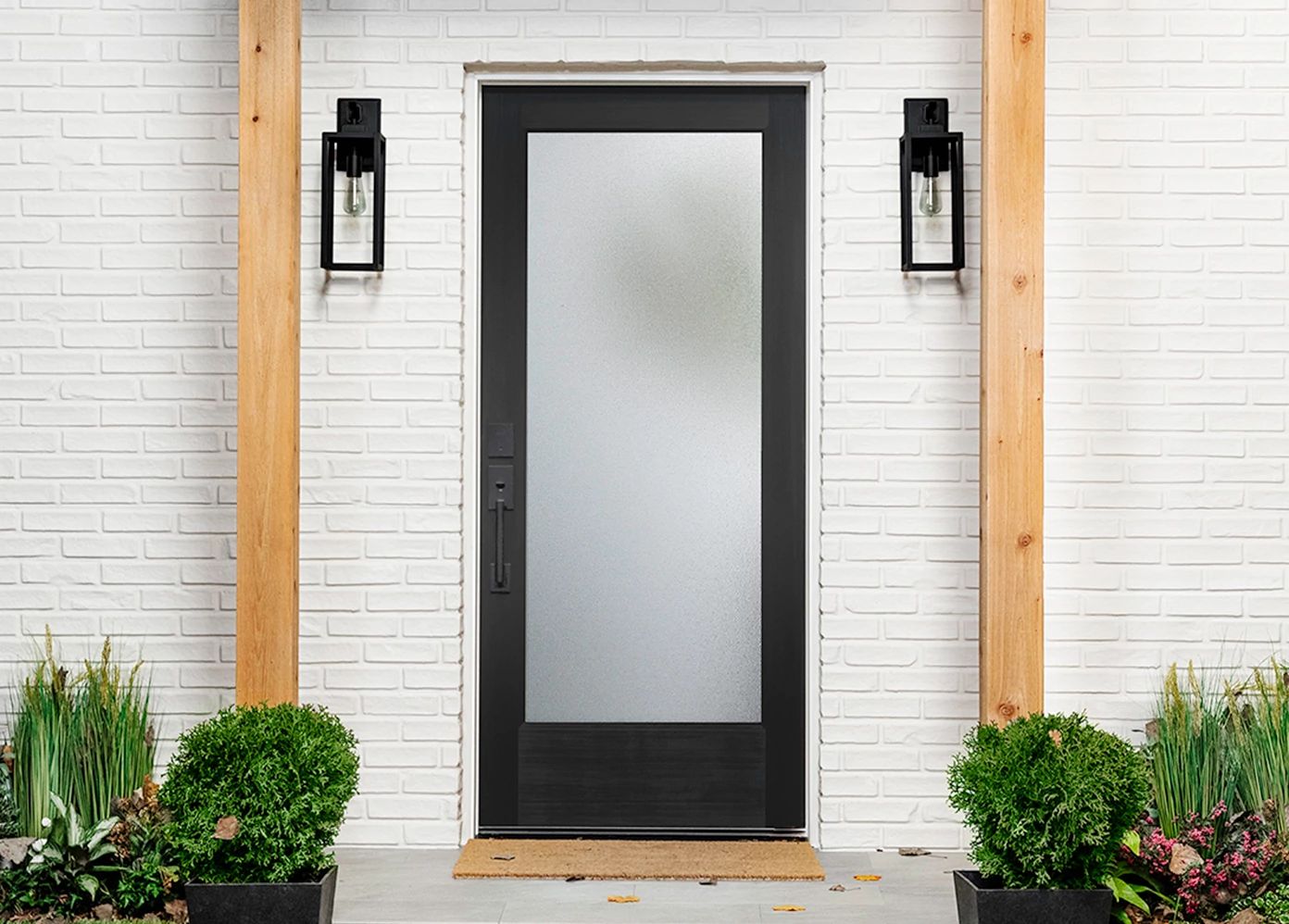
The global molding and doors manufacturing industry is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising residential and commercial construction activities, increasing demand for energy-efficient and aesthetically appealing building products, and advancements in manufacturing technologies. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global doors and windows market was valued at USD 203.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion reflects heightened consumer focus on home improvement, smart building integration, and sustainable materials, all of which influence product innovation across the molding and doors sector. With North America and Europe leading in demand due to stringent energy regulations and renovation trends, and the Asia-Pacific region emerging as a fast-growing market due to urbanization and infrastructure development, the competitive landscape is evolving rapidly. In this data-backed report, we profile the top 10 molding and doors manufacturers that are shaping the industry through scale, innovation, and strategic market presence.
Top 10 Molding And Doors Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Ply Gem
Domain Est. 2000
Website: plygem.com
Key Highlights: Ply Gem is the #1 exterior home building products manufacturer in North America. Browse our vast selection of residential building products….
#2 Metrie Moulding, Trim & Doors
Domain Est. 2003
Website: metrie.com
Key Highlights: For over 100 years, Metrie has been North America’s trusted millwork partner—largest manufacturer of solid wood and composite moulding, trim, and doors….
#3 Masonite Residential
Domain Est. 1995
Website: masonite.com
Key Highlights: Explore the best selection of interior and exterior doors for your home. Masonite doors are crafted from the highest quality materials for every home style….
#4 Ferche Millwork
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ferche.com
Key Highlights: We not only offer high quality standard mouldings & veneered millwork, but we can produce custom products to your specifications….
#5
Domain Est. 1996
Website: jeld-wen.com
Key Highlights: Shop JELD-WEN windows and doors built for quality, energy effi ciency, and timeless design that enhance comfort, style, and performance in every home….
#6 Moulding, Millwork, Millwork Supplies & Trim
Domain Est. 1998
Website: bldr.com
Key Highlights: Builders FirstSource carries door and window mouldings in a wide variety of styles, ranging from classic to modern. Get a Quote. MOULDING FINISHING APPLIQUES….
#7 Mr. Moulding LLC – Crown Moulding
Domain Est. 1999
Website: mrmoulding.com
Key Highlights: At Mr. Moulding, Mouldings & Doors in Sacramento, CA, we’re committed to providing you with the knowledge and solutions for all your moulding & door needs….
#8 Tucker Door & Trim
Domain Est. 2000
Website: tuckerdoor.com
Key Highlights: Henrico, VA 23231. 1-800-899-1739. Albany Location. 1020 Pecan Grove Drive. Albany, GA 31701. 1-866-432-2822. 229-432-2322. Page load link. Go ……
#9 Van Millwork
Domain Est. 2001
Website: vanmillwork.com
Key Highlights: Home · Products · Doors · Interior Doors · Exterior Doors · Mouldings · Baseboards · Casings · Crowns + Coves · Panels & Bands · Miscellaneous….
#10 D&D Mouldings & Millwork
Domain Est. 2007
Website: ddmouldings.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to D&D Mouldings & Millwork, your trusted source for top-quality interior doors, trim, stair parts, and hardware in Noblesville, Indiana….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Molding And Doors

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Molding and Doors
The molding and doors market is poised for notable transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in materials, sustainability demands, smart home integration, and shifting consumer preferences. As the construction and renovation sectors rebound globally, several key trends are expected to shape the industry landscape.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Materials
Environmental concerns are increasingly influencing consumer and builder choices. By 2026, demand for sustainable molding and door products made from recycled wood, FSC-certified lumber, and low-VOC finishes is expected to rise significantly. Manufacturers are investing in bio-based composites and non-toxic adhesives to meet green building standards such as LEED and BREEAM. This shift is particularly strong in North America and Europe, where regulatory pressures and consumer awareness are highest.
Smart Door Technology Integration
Smart home ecosystems are expanding rapidly, and doors are becoming key access points for home automation. By 2026, smart doors with integrated biometric locks, remote access control, and real-time security monitoring are expected to gain mainstream adoption. These features will be complemented by aesthetic molding designs that conceal wiring and sensors, maintaining visual appeal while enhancing functionality.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Consumers are increasingly seeking personalized home solutions. The demand for customizable molding profiles and door styles—ranging from classic traditional to minimalist modern designs—is set to grow. Digital design tools and 3D modeling will allow homeowners and architects to visualize and order bespoke products with greater ease. Mass customization, enabled by advanced CNC machining and modular manufacturing, will support this trend without sacrificing cost-efficiency.
Growth in Prefabricated and Modular Construction
The rise of off-site construction methods is influencing demand for standardized yet adaptable door and molding systems. In 2026, the market will see increased adoption of pre-finished, pre-hung doors and coordinated trim packages designed for quick installation in modular homes and multifamily developments. This trend supports faster build times and reduced labor costs, appealing to developers and contractors alike.
Material Innovation and Durability
Engineered wood, composite materials, and uPVC are gaining ground over traditional solid wood due to their resistance to warping, moisture, and pests. By 2026, high-performance composites that mimic the look of natural wood while offering superior durability will dominate both residential and commercial segments. These materials are especially popular in humid or high-traffic environments such as bathrooms, kitchens, and entryways.
Regional Market Dynamics
North America and Europe will remain the largest markets, driven by home renovation cycles and strict energy efficiency regulations. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region—particularly China and India—will see rapid growth due to urbanization and rising disposable incomes. Local manufacturers are expected to expand production of affordable, stylish molding and door solutions tailored to regional tastes.
Conclusion
The molding and doors market in 2026 will be defined by innovation, sustainability, and technology integration. Companies that embrace eco-conscious practices, invest in smart features, and offer customizable, high-quality products will be best positioned to capture growing market opportunities. As consumer expectations evolve, the industry must balance aesthetics, functionality, and environmental responsibility to remain competitive.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Molding and Doors (Quality, IP)
Poor Material Quality and Inconsistent Finishes
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing molding and doors—especially from overseas manufacturers—is inconsistent material quality. Suppliers may use lower-grade wood, composite materials, or subpar MDF that are prone to warping, cracking, or delamination. Additionally, finishes such as paint, stain, or veneer may lack uniformity across batches, leading to visible mismatches in color, texture, or sheen. This inconsistency can compromise the aesthetic integrity of a project and result in costly rework or customer dissatisfaction.
Inadequate Quality Control Processes
Many suppliers, particularly those in low-cost manufacturing regions, lack rigorous in-house quality control systems. Without standardized inspection protocols, defects such as misaligned joints, improper milling, or dimensional inaccuracies often go undetected until after delivery. Relying solely on final random inspections increases the risk of receiving large volumes of non-conforming products. Implementing third-party inspections at key production stages can mitigate this, but it adds cost and complexity.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks and Design Infringement
Sourcing custom-designed molding profiles or door styles poses significant IP risks. Suppliers may inadvertently—or intentionally—replicate patented or trademarked designs. Worse, once you share detailed technical drawings or physical samples, there’s a risk the supplier could produce and sell identical products to your competitors. This not only undermines your market differentiation but may lead to legal disputes. Always use strong non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and clearly define IP ownership in contracts.
Lack of Design Protection and Reverse Engineering
Even with an NDA, enforcing IP rights across international borders is challenging. Some manufacturers may reverse engineer your provided samples or drawings and sell the designs independently. This is especially common in regions with weaker IP enforcement. To minimize exposure, limit the amount of sensitive design information shared, consider filing design patents in key markets, and work with trusted, vetted suppliers with a track record of respecting IP.
Hidden Costs from Revisions and Rework
Initial quotes may appear competitive, but poor quality often leads to hidden costs. Defective or out-of-spec parts may require rework, replacement shipping, or expedited freight to meet project deadlines. Furthermore, repeated quality issues can delay entire construction or renovation timelines, resulting in contractual penalties or reputational damage.
Misaligned Tolerances and Dimensional Inaccuracy
Molding and doors require precise dimensional tolerances to ensure proper fit and finish during installation. Sourced products often deviate from specified measurements due to poor tooling, inconsistent machining, or inadequate calibration. Even minor discrepancies can lead to gaps, misalignment, or difficulty in assembly—especially in large-scale or modular construction projects.
Limited Traceability and Supplier Transparency
Many suppliers outsource components or raw materials without full transparency. This lack of traceability makes it difficult to verify claims about sustainable sourcing, material origin, or compliance with environmental regulations (e.g., formaldehyde emissions in MDF). Without clear supply chain visibility, brands risk reputational damage or non-compliance with industry standards.
Failure to Verify Certifications and Compliance
Sourced molding and doors may not meet regional building codes or environmental standards such as CARB, FSC, or EPA TSCA Title VI. Assuming compliance without proper documentation or third-party testing can lead to rejected shipments, fines, or project delays. Always request up-to-date certification documents and consider independent lab testing for critical batches.
Overlooking Long-Term Supplier Reliability
Chasing the lowest price often leads to partnerships with unstable suppliers who may lack the capacity or financial health to support long-term projects. Sudden production halts, communication breakdowns, or changes in ownership can disrupt supply chains. Conduct due diligence on supplier stability, production capacity, and past client references before committing to long-term contracts.
Ineffective Communication and Language Barriers
Misunderstandings due to language differences or unclear technical specifications can result in incorrect product interpretations. Terms like “semi-gloss,” “hardwood,” or “custom profile” may be subject to interpretation. Providing detailed CAD drawings, physical samples, and bilingual documentation helps reduce ambiguity and ensures alignment on quality expectations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Molding and Doors
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations specific to the manufacturing, transportation, and distribution of molding and door products. Adhering to these standards ensures product integrity, regulatory compliance, and efficient supply chain operations.
Product Handling and Packaging Standards
Molding and doors are susceptible to damage from impact, moisture, and improper handling. Proper packaging and handling protocols are essential:
- Protective Packaging: Use edge protectors, corner guards, and shrink wrap to prevent chipping, scratching, and warping during transit.
- Palletization: Securely stack products on durable, standardized pallets. Use banding or stretch wrap to prevent shifting.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with product type, dimensions, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”), and barcodes for inventory tracking.
- Moisture Protection: Include desiccants and moisture barriers, especially for wood-based products shipped internationally or stored in humid environments.
Transportation and Freight Management
Due to the size, weight, and fragility of molding and doors, transportation planning is critical:
- Freight Mode Selection: Choose between LTL (Less-Than-Truckload), FTL (Full Truckload), or flatbed carriers based on volume and delivery urgency. Flatbeds are often required for oversized door units.
- Load Securing: Ensure cargo is properly blocked, braced, and tied down to prevent movement during transit.
- Carrier Qualifications: Partner with carriers experienced in handling building materials and equipped with appropriate trailers and lifting equipment.
- Delivery Scheduling: Coordinate with customers or job sites to minimize wait times and ensure prompt offloading.
Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
Compliance with regional and international regulations is mandatory for market access and legal operation:
- Material Sourcing Regulations: Comply with laws such as the U.S. Lacey Act, which prohibits trade in illegally sourced wood. Maintain chain-of-custody documentation.
- Emissions Standards: Adhere to formaldehyde emission regulations (e.g., CARB Phase 2 in California, EPA TSCA Title VI) for composite wood products like MDF and particleboard used in doors and moldings.
- Labeling Requirements: Include required labels indicating compliance with safety and environmental standards (e.g., EPA, CARB, FSC, or PEFC certification).
- Import/Export Documentation: Prepare accurate customs declarations, certificates of origin, and phytosanitary certificates when shipping internationally.
Storage and Inventory Control
Proper warehousing practices maintain product quality and streamline fulfillment:
- Climate-Controlled Storage: Store wood and composite products in dry, temperature-stable environments to prevent warping, swelling, or cracking.
- Racking Systems: Use vertical racks for doors and horizontal racks for molding to prevent bending and damage.
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO): Rotate stock to minimize aging and reduce the risk of obsolescence or moisture damage.
- Inventory Tracking: Utilize warehouse management systems (WMS) with barcode or RFID scanning for real-time visibility and accuracy.
Sustainability and Environmental Compliance
Growing emphasis on green building practices requires proactive sustainability measures:
- Sustainable Sourcing: Use materials certified by FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) or SFI (Sustainable Forestry Initiative).
- Waste Reduction: Implement recycling programs for wood scraps, packaging materials, and offcuts.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimize manufacturing and warehousing operations to reduce carbon footprint.
- Product End-of-Life: Provide guidance on recyclability or proper disposal of composite and engineered products.
Safety and Worker Compliance
Ensure all logistics operations follow occupational health and safety standards:
- OSHA Compliance: Train staff in safe material handling, forklift operation, and use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Hazard Communication: Label and store adhesives, finishes, and treated wood products according to OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard (HazCom).
- Ergonomic Practices: Use mechanical aids (e.g., lift tables, door handlers) to reduce strain during loading and unloading.
By following this logistics and compliance framework, manufacturers and distributors of molding and doors can ensure product quality, meet regulatory obligations, and maintain efficient, responsible supply chain operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Molding and Doors:
Sourcing molding and doors requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, availability, and long-term durability. After evaluating various suppliers, materials, and manufacturing methods, it is clear that selecting the right partners and products is critical to ensuring architectural consistency, functional performance, and customer satisfaction. Key considerations such as material composition (e.g., solid wood, engineered wood, PVC, or composites), finish options, lead times, and compliance with sustainability standards play a significant role in the decision-making process.
Partnering with reliable suppliers who offer consistent quality, customization capabilities, and strong logistical support helps mitigate risks related to delays or defects. Additionally, incorporating energy-efficient and low-maintenance materials can provide long-term value for both residential and commercial projects. By establishing clear specifications, conducting thorough due diligence, and fostering strong supplier relationships, organizations can streamline procurement, reduce total cost of ownership, and achieve superior design outcomes.
In conclusion, a well-structured sourcing strategy for molding and doors not only supports project timelines and budgets but also enhances the overall aesthetic and functional quality of the built environment. Continuous evaluation and adaptation to market trends and material innovations will further ensure competitiveness and customer satisfaction in the long run.