The global molded fiberglass market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and renewable energy. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the fiberglass market was valued at USD 34.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by the material’s high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and versatility in complex mold applications. Additionally, rising environmental regulations favoring lightweight materials for fuel efficiency—particularly in electric vehicles and wind turbine blades—have further accelerated adoption. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in innovation, production capacity, and global reach. Below, we highlight the top 10 molded fiberglass manufacturers shaping this dynamic landscape.
Top 10 Molded Fiberglass Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LF Manufacturing – Manufacturer of fiberglass
Domain Est. 1997
Website: lfm-frp.com
Key Highlights: LFM provides the finest fiberglass tanks and vessels to service the Oilfield, Industrial, Water / Wastewater, Agricultural, and OEM markets….
#2 FGCI
Domain Est. 1997
Website: fgci.com
Key Highlights: Fiberglass Coatings is an industry leader in resin and coatings manufacturing and composite distribution. We have been serving the marine, industrial, scenic ……
#3 MFG Tray
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mfgtray.com
Key Highlights: Leading manufacturer of high-strength, glass-reinforced composite containers, trays, boxes, flats and totes for material handling….
#4 National Manufacturing Group: Fiberglass Molding
Website: nationalmanufacturing.group
Key Highlights: National Manufacturing Group is a leading source for composite & fiberglass moldings. Our multi-plant OEM suppliers provide custom FRP and thermoformed ……
#5 Fibre Glast Developments Corp LLC
Domain Est. 1995
Website: fibreglast.com
Key Highlights: Fibre Glast is a leading supplier of fiberglass & composite materials. A source for Carbon Fiber, Kevlar, Fiberglass, Resin, Gel Coat & much more….
#6
Domain Est. 1996
Website: edon.com
Key Highlights: COLUMN COVERS: Our fiberglass columns are molded in 1/2 sections with either lap joints, butt joints or reveal joints for ease of assembly and installation….
#7 Molded Fiber Glass Companies
Domain Est. 2000
Website: fiberglassfabricators.com
Key Highlights: At Molded Fiber Glass Companies, we have fiberglass products to suit your needs. Our core fiber molding technologies include directed fiber performing, ……
#8 Bedford Reinforced Plastics
Domain Est. 2010
Website: bedfordreinforced.com
Key Highlights: Bedford offers an extensive line of FRP products and services. We use a pultrusion process to form fiberglass-reinforced polymer, or FRP, into a strong but ……
#9 Fiberglass Custom Mold Making Services
Domain Est. 2011
Website: cmdtmfg.com
Key Highlights: CMDT specializes in expert fiberglass mold making with custom designs, reverse engineering, and rapid production. Request a quote for quality molds today!…
#10 MFG Construction and Water Products
Domain Est. 2017
Website: mfgcwp.com
Key Highlights: MFG CWP offers an extensive range of fiberglass concrete forms that consistently outperform comparative steel, wood, cardboard, Styrofoam or plastic ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Molded Fiberglass
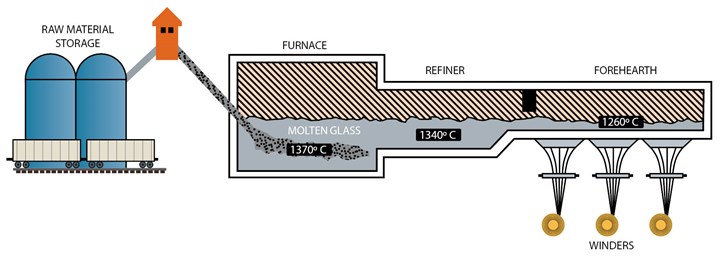
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Molded Fiberglass
The global molded fiberglass market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in materials science, increasing demand from key end-use industries, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. H2—focusing on the second half of the decade—reveals emerging trends that are shaping the trajectory of this composite material sector.
-
Growth in Renewable Energy Applications
One of the most influential drivers of the molded fiberglass market in 2026 is its expanding role in renewable energy, particularly in wind turbine blades. As nations accelerate their transition to clean energy, demand for durable, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant materials like molded fiberglass continues to rise. The push for longer and more efficient turbine blades—especially offshore—has increased reliance on fiberglass composites, with innovations in resin systems enhancing performance and fatigue resistance. -
Automotive Lightweighting and Electric Vehicle (EV) Expansion
The automotive industry remains a major consumer of molded fiberglass, with automakers prioritizing weight reduction to improve fuel efficiency and meet emissions regulations. In 2026, the shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) is further amplifying demand, as manufacturers use molded fiberglass in under-the-hood components, battery enclosures, and structural parts. While carbon fiber competes in high-end applications, fiberglass offers a cost-effective alternative for mass-market EVs, supporting scalability and affordability. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Initiatives
Environmental concerns are reshaping the molded fiberglass landscape. By 2026, regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability goals are pushing for recyclable and bio-based composite solutions. Although traditional fiberglass is difficult to recycle, advancements in thermoplastic resins and chemical recycling are gaining traction. Companies are investing in closed-loop manufacturing processes and exploring fiber recovery technologies to align with circular economy principles. -
Technological Advancements in Manufacturing
Automation and digitalization are transforming production methods. In 2026, automated molding processes such as high-pressure resin transfer molding (HP-RTM) and compression molding are becoming more prevalent, improving precision, reducing cycle times, and lowering labor costs. Integration with Industry 4.0 technologies—like IoT-enabled monitoring and AI-driven quality control—enables real-time optimization and predictive maintenance, enhancing overall efficiency. -
Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience
Asia-Pacific continues to dominate production and consumption, led by China, India, and Southeast Asian nations, where infrastructure and transportation sectors are expanding. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are focusing on reshoring and supply chain localization to mitigate geopolitical risks and ensure raw material availability. This regional rebalancing is prompting investment in domestic manufacturing capabilities and strategic partnerships. -
Rising Demand in Construction and Infrastructure
Molded fiberglass is increasingly used in construction for applications such as utility enclosures, bridge components, and architectural panels due to its durability, low maintenance, and resistance to harsh environments. By 2026, urbanization and infrastructure modernization projects—especially in developing economies—are expected to drive steady growth in this segment.
In conclusion, the 2026 molded fiberglass market reflects a dynamic interplay of innovation, sustainability, and industrial transformation. As industries seek high-performance, cost-effective materials, molded fiberglass remains a critical enabler—especially when enhanced through new technologies and eco-conscious practices. Companies that adapt to these H2 trends will be well-positioned to capture emerging opportunities in a competitive global landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Molded Fiberglass (Quality, IP)
Sourcing molded fiberglass components can be complex, with significant risks related to both quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these areas can lead to production delays, increased costs, and legal disputes. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality Inconsistencies and Process Deficiencies
Molded fiberglass products are highly sensitive to manufacturing processes, and minor deviations can drastically impact performance and appearance. Common quality pitfalls include:
– Inadequate Process Control: Suppliers may lack standardized procedures for resin mixing, layup, curing time, or temperature control, resulting in weak spots, delamination, or inconsistent wall thickness.
– Poor Surface Finish: Issues like pitting, air bubbles, or gel coat defects often stem from improper mold preparation or curing techniques, affecting both aesthetics and durability.
– Dimensional Inaccuracy: Without rigorous tooling and inspection protocols, parts may not meet design specifications, causing fitment problems in assembly.
– Lack of Testing and Certification: Suppliers may fail to perform or document critical tests (e.g., flexural strength, impact resistance, UV stability), leaving buyers without assurance of material performance.
To mitigate these risks, conduct on-site audits, require process documentation, and establish clear quality benchmarks with third-party inspection protocols.
Intellectual Property Exposure and Misappropriation
Molded fiberglass tooling and designs often represent significant R&D investment, making IP protection essential. Key IP-related pitfalls include:
– Unclear IP Ownership: Contracts may fail to specify who owns the molds, design files, and process know-how, potentially allowing suppliers to replicate or sell designs to competitors.
– Weak Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs): Inadequate legal safeguards can leave design data exposed during quoting and prototyping phases.
– Tooling Retention and Replication Risks: Suppliers may retain mold ownership or produce unauthorized parts after the contract ends, especially in jurisdictions with lax IP enforcement.
– Reverse Engineering Vulnerability: Physical parts shipped for approval can be scanned and duplicated if not protected by patents or design rights.
Protect IP by securing comprehensive agreements that assign ownership to the buyer, enforce strict confidentiality, and include audit rights. File appropriate patents or design protections early, and consider sourcing from regions with strong IP legal frameworks.
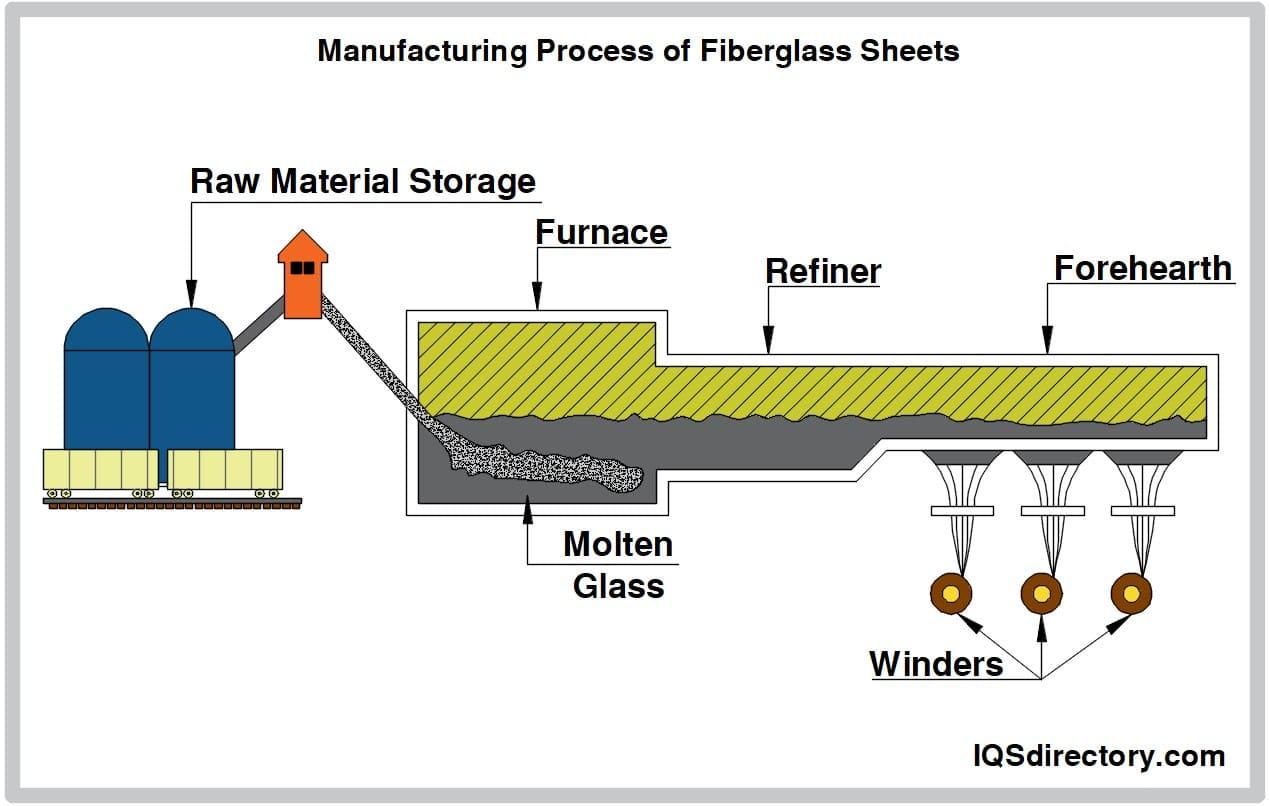
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Molded Fiberglass
Overview of Molded Fiberglass
Molded fiberglass is a composite material made from reinforced plastic using glass fibers embedded in a thermosetting resin matrix. It is widely used in automotive, marine, construction, and industrial applications due to its strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties. Proper logistics and compliance protocols are essential throughout the supply chain to ensure safety, regulatory adherence, and product integrity.
Regulatory Classification & Documentation
Molded fiberglass products are generally not classified as hazardous materials when fully cured, but uncured resins or raw materials used in production may be subject to chemical regulations. Ensure accurate classification under relevant systems:
- UN Number & Hazard Class: Cured molded fiberglass parts are typically non-hazardous (UN3082, Class 9 may apply only if contaminated with hazardous substances).
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Maintain up-to-date SDS for any resins, catalysts, or additives used in manufacturing—even if final products are non-hazardous.
- Customs Documentation: For international shipments, provide commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Harmonized System (HS) codes such as 3926.30 (other articles of plastics) or 7019.90 (glass wool and articles thereof) may apply depending on composition.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Proper packaging prevents damage during transit and ensures worker safety:
- Protective Packaging: Use edge protectors, corner boards, and moisture-resistant wrapping. Secure parts in crates or on pallets with stretch wrap or strapping.
- Stacking & Weight Distribution: Avoid stacking without adequate support; use dunnage to prevent deformation. Distribute weight evenly to prevent crushing during transport.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”), part numbers, and weight. Include any relevant compliance marks (e.g., CE, UL) when applicable.
Transportation Considerations
Molded fiberglass components vary in size and fragility, requiring tailored transport strategies:
- Mode Selection: Choose between road, rail, air, or sea based on size, urgency, and destination. Oversized parts may require specialized flatbed trucks or roll-on/roll-off (RoRo) shipping.
- Environmental Protection: Shield from moisture, UV exposure, and extreme temperatures—prolonged UV exposure can degrade surface resins over time.
- Hazardous Materials in Transit: If shipping uncured components or raw materials (e.g., styrene-based resins), classify and package according to IATA (air), IMDG (sea), or ADR (road) regulations.
Import/Export Compliance
International trade of molded fiberglass products must comply with destination country regulations:
- Tariff Classifications: Confirm correct HS codes with local customs authorities to avoid delays or penalties.
- Trade Agreements: Leverage free trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU agreements) where applicable to reduce tariffs.
- Product Standards: Comply with regional standards such as:
- USA: OSHA, EPA, and state-level environmental regulations
- EU: REACH, RoHS (if electronic components are embedded), and CE marking directives
- Other Regions: Check local industrial and environmental standards (e.g., CCC in China, INMETRO in Brazil)
Environmental & Safety Compliance
Manufacturers and logistics providers must adhere to environmental and workplace safety standards:
- Waste Management: Comply with disposal regulations for off-cuts, molds, and resin waste. Many resin components are classified as hazardous waste.
- Emissions Control: Monitor and control VOC emissions during manufacturing in accordance with EPA or EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) rules.
- Worker Safety: Provide PPE (gloves, respirators, eye protection) when handling uncured materials. Follow OSHA or equivalent guidelines for safe handling and ventilation.
Quality Assurance & Traceability
Maintain product integrity and regulatory compliance through robust QA practices:
- Batch Tracking: Implement traceability systems to track raw materials and finished goods by batch or lot number.
- Inspection & Certification: Conduct pre-shipment inspections. Provide material certification or test reports (e.g., tensile strength, flammability) when required by customers or regulators.
- Storage Conditions: Store finished goods in dry, covered areas away from direct sunlight and chemical exposure.
Emergency Response & Incident Management
Prepare for potential incidents during handling or transport:
- Spill Response: Have spill kits available if transporting uncured resins. Follow SDS guidelines for containment and cleanup.
- Fire Safety: Cured fiberglass is combustible; store away from ignition sources. Use appropriate fire suppression systems (e.g., dry chemical extinguishers for resin fires).
- Incident Reporting: Establish procedures for reporting accidents, damages, or non-compliance events to relevant authorities and stakeholders.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for molded fiberglass require attention to material classification, proper packaging, regulatory requirements, and safety protocols. By adhering to international standards and maintaining thorough documentation, companies can ensure smooth transportation, avoid penalties, and uphold product quality and environmental responsibility across the supply chain.
Conclusion on Sourcing Molded Fiberglass:
Sourcing molded fiberglass requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, lead times, and supplier reliability. Given its widespread use in industries such as automotive, marine, aerospace, and construction, molded fiberglass offers an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility. However, successful sourcing depends on clearly defining technical specifications, understanding manufacturing processes (such as compression molding, injection molding, or hand lay-up), and selecting suppliers with proven expertise and quality control systems.
Key considerations include evaluating supplier capabilities, ensuring compliance with industry standards, managing logistics for fragile or large components, and maintaining open communication throughout the supply chain. Additionally, sustainability concerns and advancements in composite recycling are becoming increasingly influential in material and supplier selection.
In conclusion, effective sourcing of molded fiberglass involves a comprehensive assessment of technical, operational, and strategic factors. By partnering with reliable manufacturers and staying informed about material innovations and market trends, organizations can secure high-performing, cost-efficient solutions that support long-term project and business goals.