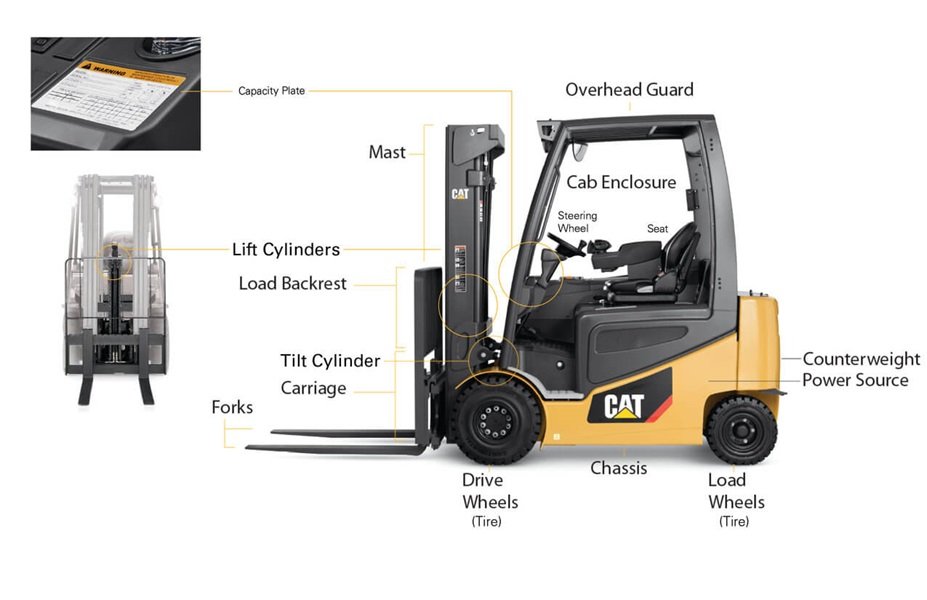
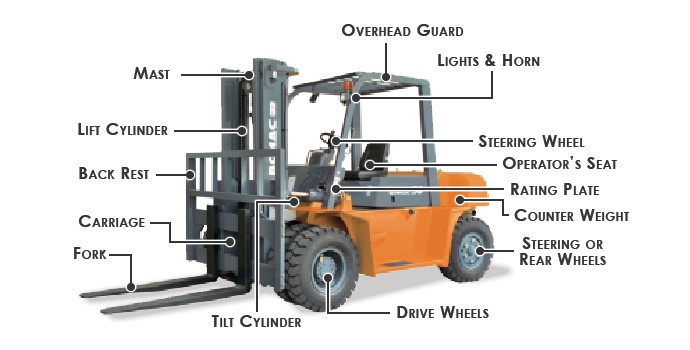
The global forklift truck market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for material handling solutions across logistics, manufacturing, and construction sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global forklift truck market was valued at USD 67.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2024 to 2029. With Mitsubishi Logisnext maintaining a strong position in the industry—ranked among the top forklift manufacturers worldwide—the demand for reliable, high-performance replacement parts has intensified. As fleets expand and service life cycles extend, the aftermarket for Mitsubishi forklift parts is becoming increasingly vital. This has led to the emergence of specialized manufacturers producing durable, OEM-compliant components such as pumps, engines, hydraulic systems, and electronic controls. Based on market trends and supply chain analysis, here are the top 6 manufacturers leading innovation and quality in Mitsubishi forklift parts production.
Top 6 Mitsubishi Fork Truck Parts Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Mitsubishi Logisnext Co., Ltd.
Domain Est. 2017
Website: logisnext.com
Key Highlights: This is the corporate website of Mitsubishi LogisNext, a comprehensive logistics equipment manufacturer that is making history in the fields of automated ……
#2 OEM Mitsubishi Parts Online
Domain Est. 1996
Website: parts.mitsubishicars.com
Key Highlights: The Official Parts Store Of Mitsubishi Motors. OEM Parts and Accessories Available For All Mitsubishi Models. We Ship Nationwide!…
#3 Mitsubishi Forklift Trucks
Domain Est. 1999
Website: mitforklift.com
Key Highlights: Mitsubishi forklift trucks and warehouse equipment, available to buy or hire with excellent service plans, unbeatable value and legendary reliability….
#4 Mitsubishi Forklift Parts
Domain Est. 2014
Website: liftpartswarehouse.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $649.99 · 30-day returns…
#5 Forklifts & Lift Trucks
Domain Est. 2020
Website: logisnextamericas.com
Key Highlights: The official Mitsubishi Forklift Trucks website for North America. We have the forklift solution for any industry and application backed by dealers across ……
#6 Mitsubishi Forklift Parts – Genuine Replacement Parts
Domain Est. 2021
Expert Sourcing Insights for Mitsubishi Fork Truck Parts

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Mitsubishi Forklift Truck Parts
As the global industrial and logistics sectors continue to evolve, the market for Mitsubishi forklift truck parts is expected to experience significant shifts by 2026. Driven by technological advancements, sustainability initiatives, and changing supply chain dynamics, several key trends are shaping the demand, availability, and innovation within this niche aftermarket sector.
Growing Demand for Genuine and Aftermarket Parts
By 2026, the demand for both genuine Mitsubishi forklift parts and high-quality aftermarket alternatives is projected to rise. This growth is fueled by an expanding global fleet of material handling equipment, particularly in emerging markets across Asia, Latin America, and Africa. As Mitsubishi forklifts remain a preferred choice for reliability and durability, operators seek cost-effective maintenance solutions—boosting the aftermarket segment. However, OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts will continue to dominate safety-critical applications due to performance assurance and warranty compliance.
Electrification and Hybrid Technology Integration
A major trend influencing parts demand is the industry-wide shift toward electric and hybrid forklifts. Mitsubishi Logisnext has already expanded its electric vehicle lineup (e.g., the BT Levio and EFX series), and this transition will accelerate by 2026. Consequently, demand for traditional internal combustion (IC) engine components—such as carburetors, fuel pumps, and exhaust systems—is expected to decline gradually. In contrast, components like lithium-ion batteries, battery management systems (BMS), electric motors, and regenerative braking systems will see rising demand. This shift will require parts suppliers to adapt their inventories and technical support capabilities.
Digitalization and Predictive Maintenance
The integration of telematics and IoT (Internet of Things) in forklift fleets is transforming maintenance strategies. By 2026, an increasing number of Mitsubishi forklifts will be equipped with sensors and connectivity features that enable real-time monitoring of component health. This trend will drive demand for smart parts and digital diagnostic tools. Predictive maintenance algorithms will alert operators to replace parts such as hydraulic pumps, steering systems, or mast chains before failure, reducing downtime. As a result, parts distributors will need to offer value-added services, including data analytics and remote diagnostics, to remain competitive.
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Global supply chain disruptions observed in recent years have prompted companies to reevaluate sourcing strategies. By 2026, Mitsubishi parts suppliers are expected to emphasize regional warehousing and localized production to mitigate risks. This localization trend will improve lead times and reduce costs for end-users, especially in key markets like North America, Europe, and Southeast Asia. Additionally, increased inventory of critical spare parts will become standard practice among authorized dealers and service centers.
Sustainability and Circular Economy Practices
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals are pushing the forklift industry toward greener practices. By 2026, remanufactured and recycled Mitsubishi forklift parts are expected to gain market share. Components such as transmissions, axles, and hydraulic cylinders can be refurbished to OEM standards, offering a sustainable and economical alternative. Mitsubishi and its partners may expand remanufacturing programs, contributing to a circular economy and reducing waste.
Skilled Technician Shortage and Training Needs
As forklift technology becomes more complex, there is a growing gap in skilled technicians capable of servicing modern Mitsubishi models. By 2026, parts suppliers and dealers may invest more in training programs and digital support tools (e.g., AR-assisted repair guides) to empower technicians. This trend will indirectly influence parts sales, as better-trained personnel can accurately diagnose issues and recommend the correct components, reducing returns and improving customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
The 2026 market for Mitsubishi forklift truck parts will be shaped by electrification, digitalization, sustainability, and supply chain innovation. Companies that adapt to these H2-level trends—by embracing new technologies, expanding service offerings, and supporting circular economy models—will be well-positioned to capture growth in this evolving aftermarket landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Mitsubishi Forklift Parts: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing parts for Mitsubishi forklifts can be challenging, especially when trying to balance cost, availability, and reliability. Two major areas where buyers often encounter problems are part quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial to maintaining equipment performance and avoiding legal and operational issues.
Poor Quality and Counterfeit Parts
One of the most significant risks when sourcing Mitsubishi forklift parts is receiving substandard or counterfeit components. These parts may appear identical to genuine Mitsubishi parts but are manufactured using inferior materials and processes. Common indicators of poor quality include inconsistent fitment, premature wear, and failure under normal operating conditions. Using such parts can lead to increased downtime, higher repair costs, and safety hazards for operators. Third-party suppliers, particularly those offering heavily discounted prices, are more likely to distribute counterfeit or low-quality replicas, especially for high-demand components like hydraulic pumps, control valves, and electronic control units.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Another critical concern is the potential violation of Mitsubishi’s intellectual property rights. Genuine Mitsubishi forklift parts are protected by trademarks, copyrights, and design patents. When non-OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts are produced using Mitsubishi’s branding, logos, or exact specifications without authorization, they may infringe on these IP rights. Purchasing or installing such parts—knowingly or unknowingly—can expose businesses to legal liability, especially in regions with strict IP enforcement. Additionally, using non-genuine parts may void warranties on newer forklifts or associated service agreements, further increasing long-term ownership costs.
To mitigate these risks, it is advisable to source parts through authorized Mitsubishi dealers or reputable suppliers with verifiable certifications. Always request documentation, such as part authenticity certificates or compliance statements, and avoid deals that seem too good to be true. Conducting due diligence helps ensure operational reliability and legal compliance while protecting your investment in material handling equipment.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Mitsubishi Fork Truck Parts
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the shipment, handling, and regulatory adherence related to Mitsubishi Fork Truck parts. Adherence to these guidelines ensures efficient operations, regulatory compliance, and product integrity.
Supply Chain Coordination
Ensure seamless coordination between suppliers, distribution centers, and end customers. Utilize integrated inventory management systems to monitor part availability, forecast demand, and prevent stockouts. Establish clear communication protocols with Mitsubishi-certified distributors and authorized service partners to align logistics schedules.
Packaging and Labeling Standards
All Mitsubishi Fork Truck parts must be packaged according to OEM specifications to prevent damage during transit. Use protective materials such as foam inserts, sealed plastic wrapping, and reinforced cartons. Each package must include a legible label with:
– Part number and description
– Quantity
– Serial number (if applicable)
– Country of origin
– Handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”)
– Compliance markings (e.g., CE, RoHS)
Import and Export Compliance
Adhere strictly to international trade regulations when shipping parts across borders:
– Obtain and maintain valid export licenses where required.
– Ensure accurate classification of parts under the Harmonized System (HS) codes.
– Prepare compliant commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
– Comply with import regulations of the destination country, including customs duties, tariffs, and product conformity requirements (e.g., EPA, DOT, or local safety standards).
Transportation and Handling
Use certified freight carriers experienced in handling industrial automotive components. Secure loads appropriately during transit to prevent shifting or impact. For heavy or oversized parts (e.g., engines, masts), employ specialized handling equipment and follow Mitsubishi’s handling guidelines. Maintain a chain of custody documentation for high-value components.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Ensure all parts meet relevant environmental and safety regulations:
– Confirm compliance with Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) and Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) directives for shipments to the EU.
– Follow proper disposal protocols for packaging materials in accordance with local environmental laws.
– Maintain documentation for conflict minerals reporting if applicable.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Retain all logistics and compliance records for a minimum of five years, including:
– Bill of lading
– Customs clearance documents
– Certificates of conformity
– Inspection reports
– Proof of delivery
Digital archiving is recommended for audit readiness and traceability.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Implement a traceability system to track parts from origin to final destination. Use barcode or RFID technology where possible. Conduct periodic audits to verify compliance with Mitsubishi’s quality standards and to ensure parts are genuine and not counterfeit.
Incident Management and Recalls
Establish a protocol for handling logistics-related incidents, including damaged shipments or compliance violations. In the event of a product recall, activate a rapid response plan to retrieve affected parts, notify regulatory bodies, and communicate with customers per Mitsubishi’s recall procedures.
By following this guide, stakeholders ensure the reliable, compliant, and efficient distribution of Mitsubishi Fork Truck parts while upholding brand integrity and customer safety.
In conclusion, sourcing Mitsubishi forklift parts requires careful consideration of quality, compatibility, availability, and cost. Opting for genuine OEM parts ensures reliability, optimal performance, and longevity of the equipment, which ultimately reduces downtime and maintenance costs. When OEM parts are not feasible, reputable aftermarket alternatives from certified suppliers can offer a cost-effective solution without significantly compromising quality. Establishing relationships with trusted suppliers, leveraging online marketplaces, and utilizing technical support from dealers or distributors further streamline the sourcing process. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn components using properly sourced parts contribute to enhanced operational efficiency and workplace safety. Therefore, a strategic and informed approach to sourcing Mitsubishi forklift parts is essential for maximizing equipment uptime and protecting your long-term investment.