Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Milk Storage Tanks
For dairy processors and food manufacturers, milk storage tanks represent a critical infrastructure investment that directly impacts product quality, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Whether you’re expanding capacity, replacing aging equipment, or entering new markets, selecting the right bulk milk tank requires navigating a complex landscape of specifications, suppliers, and standards.
The Challenge
Procurement teams face several key obstacles:
- Varying international standards between USA (3-A Sanitary Standards) and European (EHEDG) markets
- Balancing cost against quality when evaluating new versus reconditioned equipment
- Sizing decisions that affect both current operations and future scalability
- Material and construction specifications that determine longevity and sanitary compliance
The stakes are significant. An undersized or poorly specified tank creates bottlenecks, compromises milk quality, and risks regulatory violations. Overspending on unnecessary features strains capital budgets.
What This Guide Covers
| Section | Focus |
|———|——-|
| Types & Configurations | Vertical silos, horizontal tanks, multi-compartment options |
| Capacity Planning | Sizing methodologies for your production volume |
| Technical Specifications | Cooling systems, agitation, CIP compatibility |
| New vs. Used Equipment | Cost-benefit analysis and reconditioning considerations |
| Supplier Evaluation | Qualification criteria for global vendors |
| Compliance Requirements | USA and European regulatory frameworks |
This guide provides procurement professionals and operations managers with the technical knowledge and market intelligence needed to make informed purchasing decisions—whether sourcing 200-gallon bulk farm tanks or 4,000-gallon industrial storage systems.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Milk Storage Tanks Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for milk storage tanks
- Understanding milk storage tanks Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of milk storage tanks
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘milk storage tanks’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for milk storage tanks
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for milk storage tanks
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘milk storage tanks’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for milk storage tanks Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing milk storage tanks With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for milk storage tanks
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the milk storage tanks Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of milk storage tanks
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for milk storage tanks
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Milk Storage Tanks Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Milk Cooling Tanks – Dairy Farm – Paul Mueller Company
Domain: en.paulmueller.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: For more than 70 years, Mueller has been building milk cooling systems. And our hard work paid off: we have become one of the world’s largest suppliers. Our ……
2. Food and Dairy Tanks | Products and Service – DCI, Inc.
Domain: dciinc.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: We offer everything from silo-type storage tanks to fully customized processing vessels. As a 3-A certified manufacturer in both Minnesota and California, we’re ……
3. Milk and Dairy Mixing and Storage Tanks
Domain: mixingtanksusa.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Mixing Tanks USA manufactures stainless steel milk and dairy storage and mixing tanks and when it comes to tanks, Mixing Tanks USA leads the herd….
4. Raw Milk storage tanks and cream tanks, dairy and milk silos
Domain: gpi-tanks.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Gpi Tanks offers high-quality raw milk storage tanks and cream tanks, designed to maintain freshness and hygiene, ensuring safe and efficient dairy storage ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. New York Dairy Tank Manufacturers Suppliers – IQS Directory
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Dairy Tanks in New York ; Feldmeier Equipment, Inc. Syracuse, NY · 315-454-8608 ; Stainless Metals Inc. Woodside, NY · 718-784-1454 ; Miller Mechanical Services Inc….
6. Bulk Milk Tanks | Milkplan Bulk Tanks – Parts Dept
Domain: partsdepartmentonline.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: 30-day returnsFind bulk milk tanks and explore high-quality solutions to enhance dairy production. Shop now for superior equipment and unmatched ……
7. New MilkPlan small scale Cooling Tanks – Hamby Dairy Supply
Domain: hambydairysupply.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Free delivery over $250Please call 816-449-1314 to check stock and get a shipping quote on a new Milk cooling Tank. Milk Plan Verti tank series are available in capacities ranging ……
8. New & Used Dairy Bulk Tanks – Milk Cooling Tanks
Domain: heritage-equipment.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: BCast Stainless offers new stainless steel refrigerated bulk tanks, also known as farm tanks or milk coolers, in a range of sizes….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Understanding milk storage tanks Types and Variations
Understanding Milk Storage Tanks: Types and Variations
Selecting the appropriate milk storage tank directly impacts operational efficiency, product quality, and regulatory compliance. This section examines the primary tank types available to dairy processors, their distinguishing features, and optimal applications.
Milk Storage Tank Types: Comparison Overview
| Type | Key Features | Primary Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk Milk Cooling Tanks | Integrated refrigeration, paddle agitators, 200-4,000 gallon capacity | Farm-level collection, small-scale processing | Rapid cooling, compact footprint, versatile use | Limited capacity for large operations |
| Vertical Silo Tanks | Large capacity (5,000-50,000+ gallons), vertical orientation, automated CIP | Large-scale dairy processing facilities | Maximum storage capacity, space-efficient floor footprint | Higher installation costs, requires structural support |
| Horizontal Storage Tanks | Low-profile design, easy access, ground-level installation | Facilities with height restrictions, transport applications | Simplified maintenance access, lower center of gravity | Larger floor space requirement |
| Multi-Compartment Tanks | Separate storage sections within single unit, independent temperature control | Facilities handling multiple milk grades or products | Product segregation, operational flexibility | More complex cleaning protocols |
| Insulated Storage Tanks | Double-wall construction, thermal retention without active refrigeration | Short-term holding, pre-processing staging | Lower energy costs, simpler maintenance | No active temperature control |
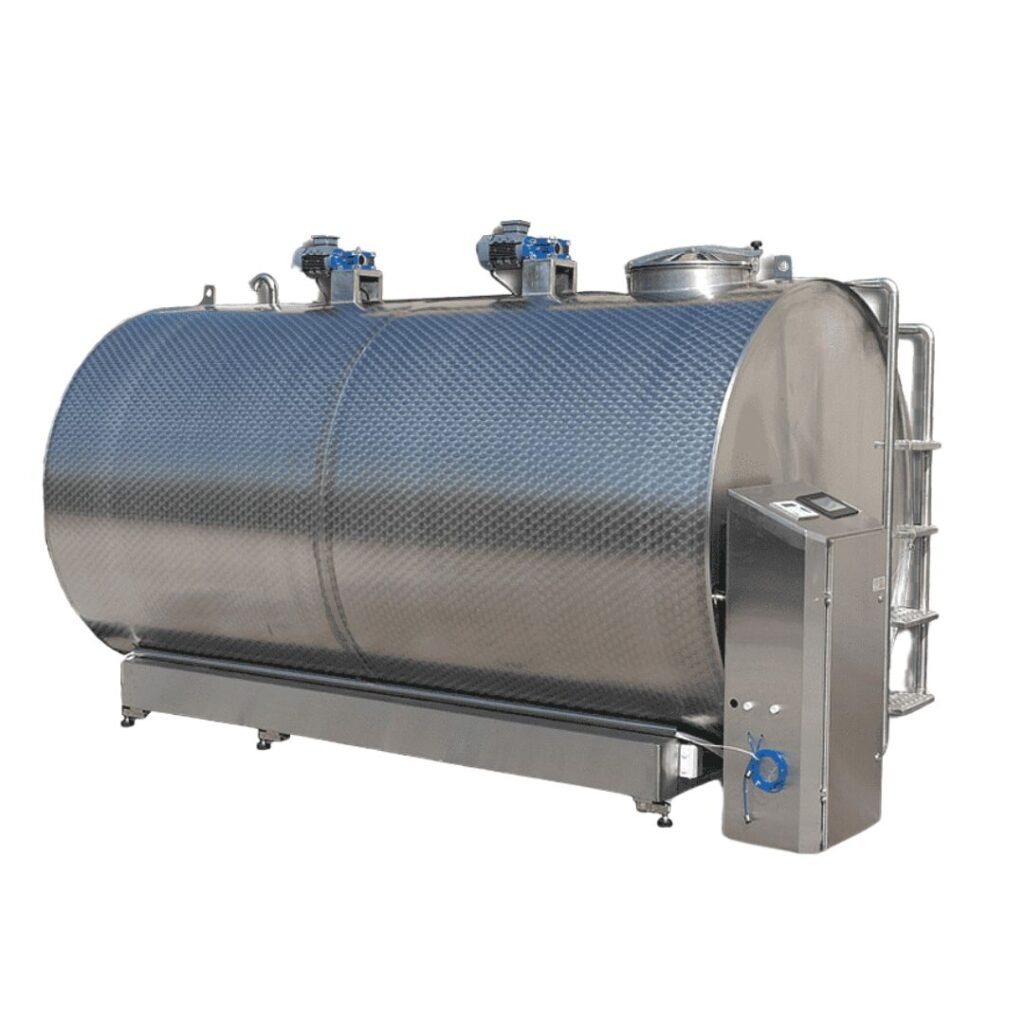
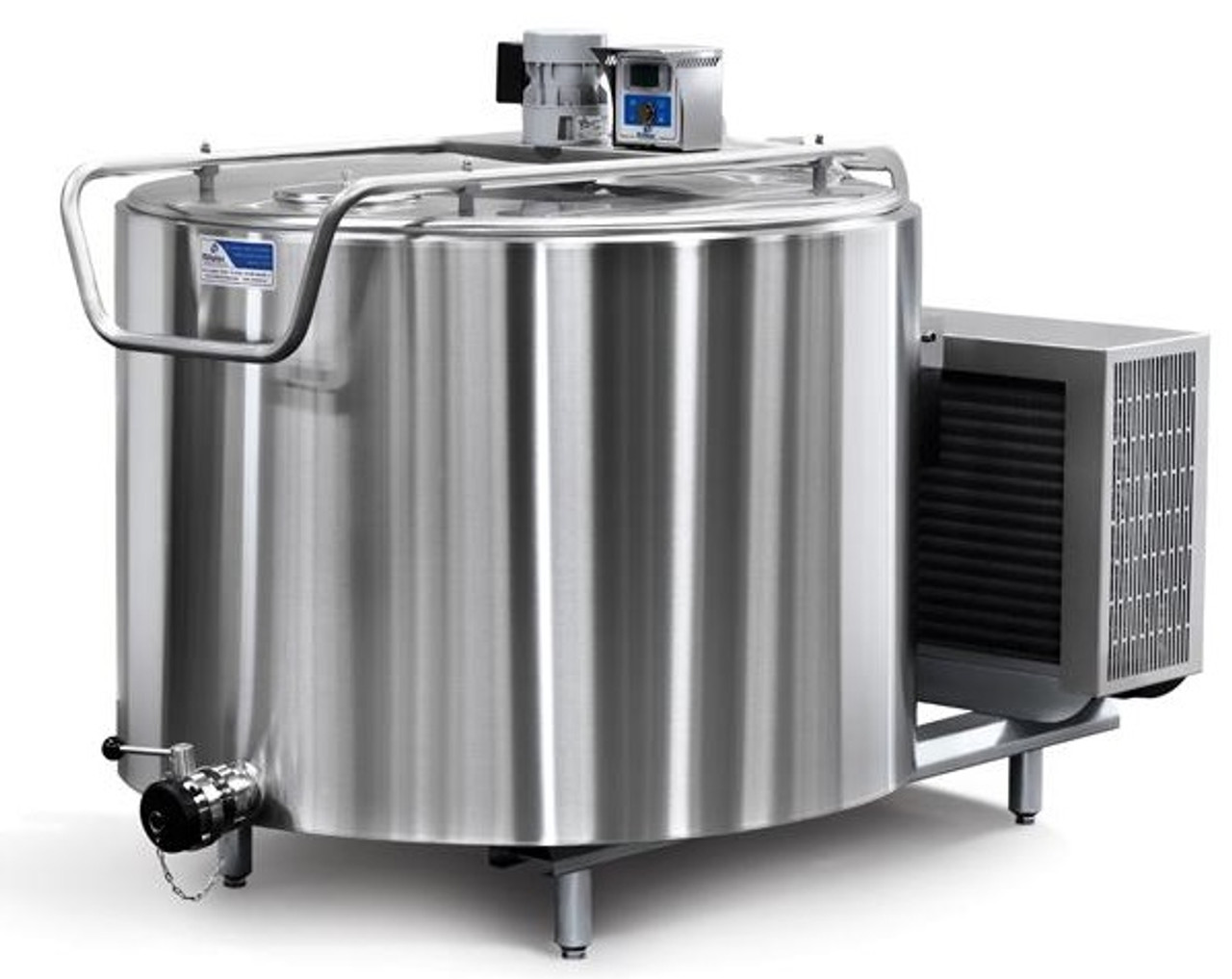
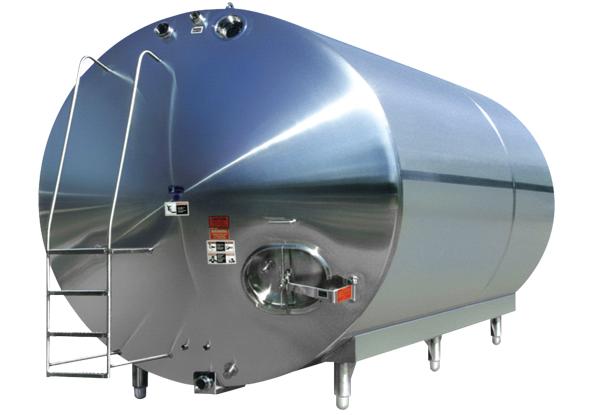
Bulk Milk Cooling Tanks
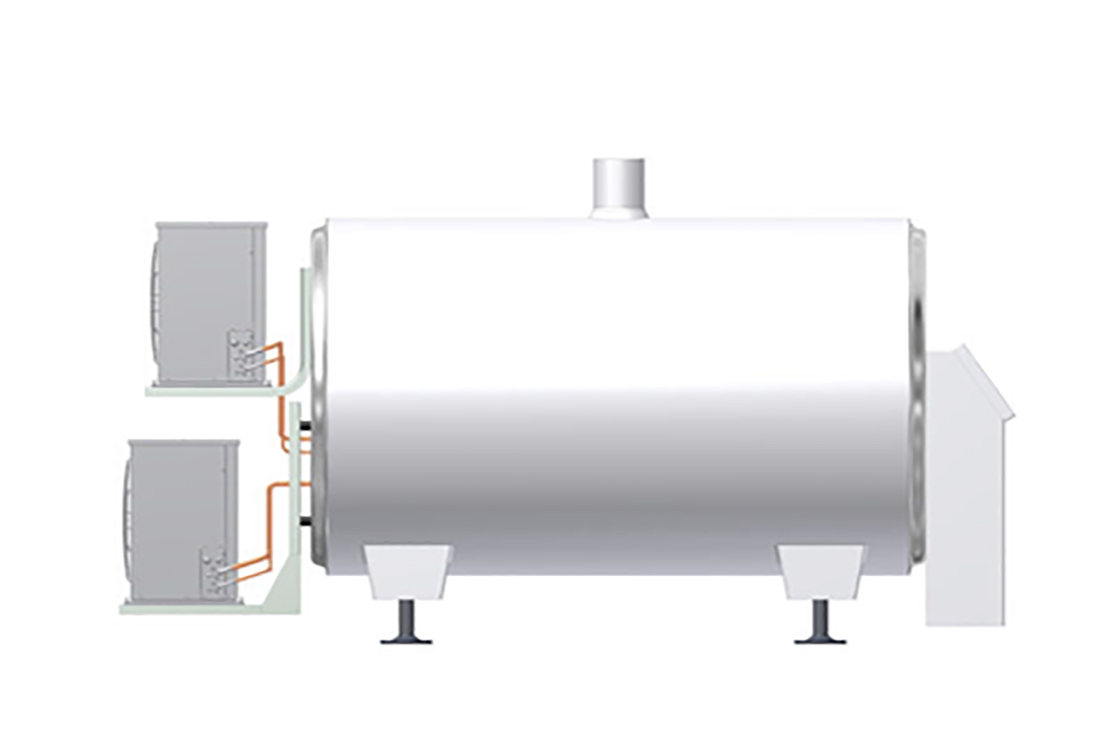
Bulk milk cooling tanks—also called bulk farm tanks or milk coolers—serve as the primary collection and cooling point in dairy operations. These units rapidly reduce milk temperature to safe storage levels (typically 4°C/39°F) immediately after collection.
Standard Features:
– 304 stainless steel construction for durability and sanitary compliance
– Top-entering manways with hinged, gasketed covers
– CIP (Clean-in-Place) spray balls for automated sanitation
– Paddle-type vertical agitators for uniform temperature distribution
– Sanitary clamp connections for hygienic product transfer
Capacity Range: 200 to 4,000 gallons (typical), with custom configurations available.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Best For: Dairy farms, small-to-medium processors, and facilities requiring versatile storage for milk, juices, honey, or other food-grade liquids.
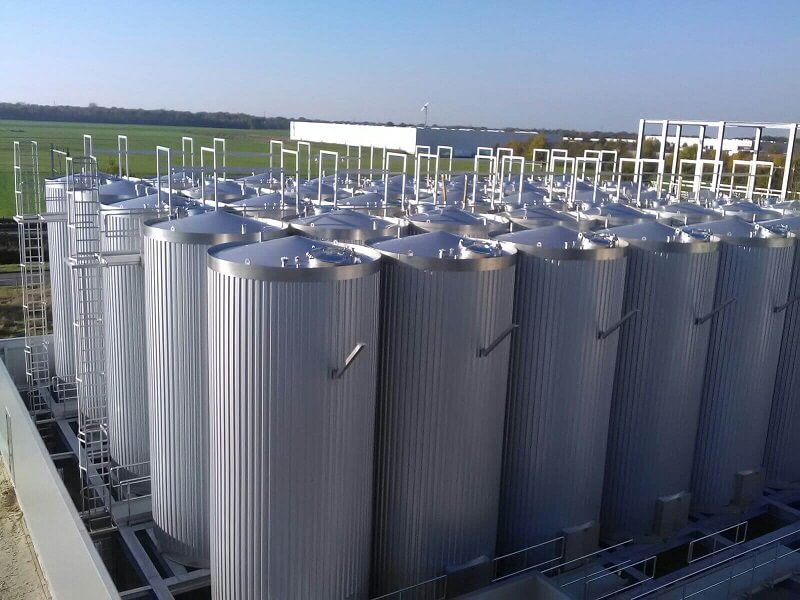
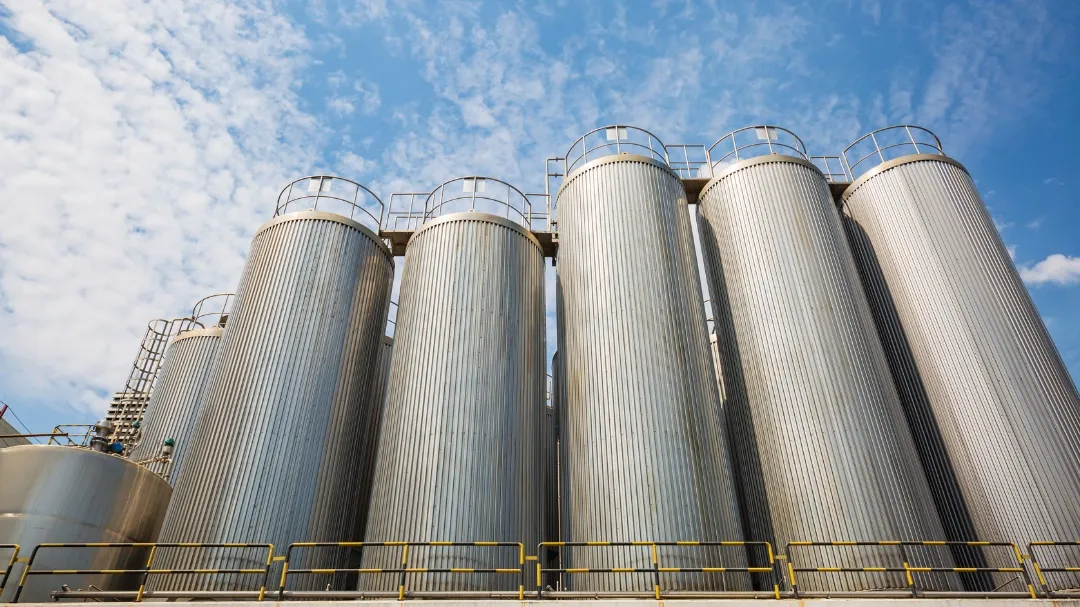
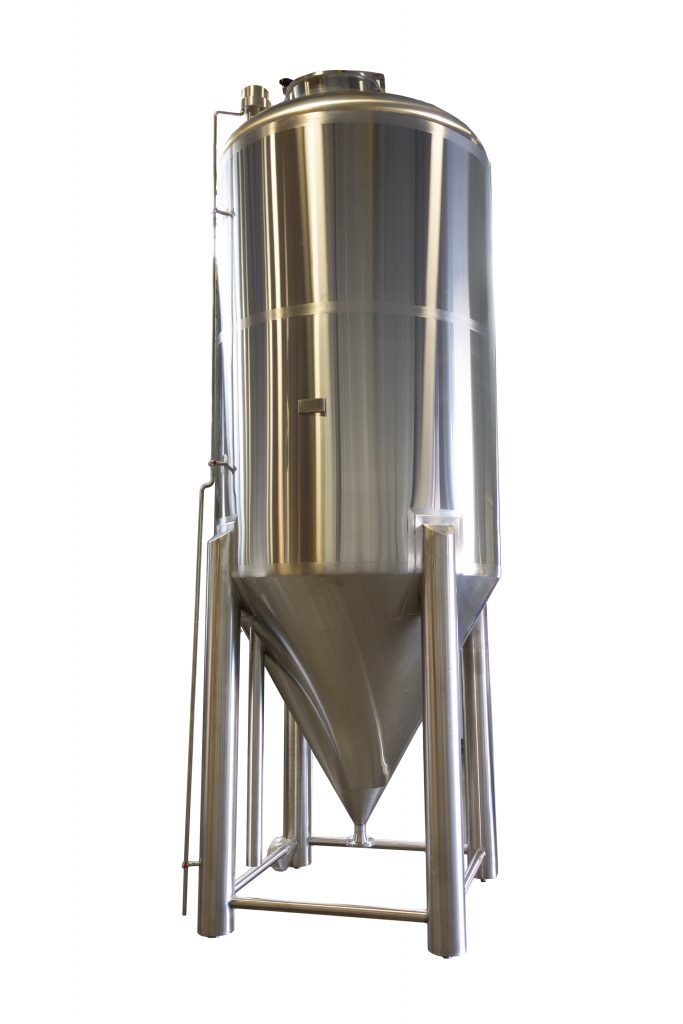
Vertical Silo Tanks
Vertical silo tanks maximize storage capacity while minimizing floor space requirements. These tall, cylindrical units are standard equipment in large-scale dairy processing plants handling high daily volumes.
Key Characteristics:
– Capacities exceeding 50,000 gallons
– Integrated agitation and temperature monitoring systems
– Automated CIP compatibility
– External insulation with protective cladding
Best For: Industrial dairy processors, co-ops consolidating supply from multiple farms, and facilities with premium floor space.
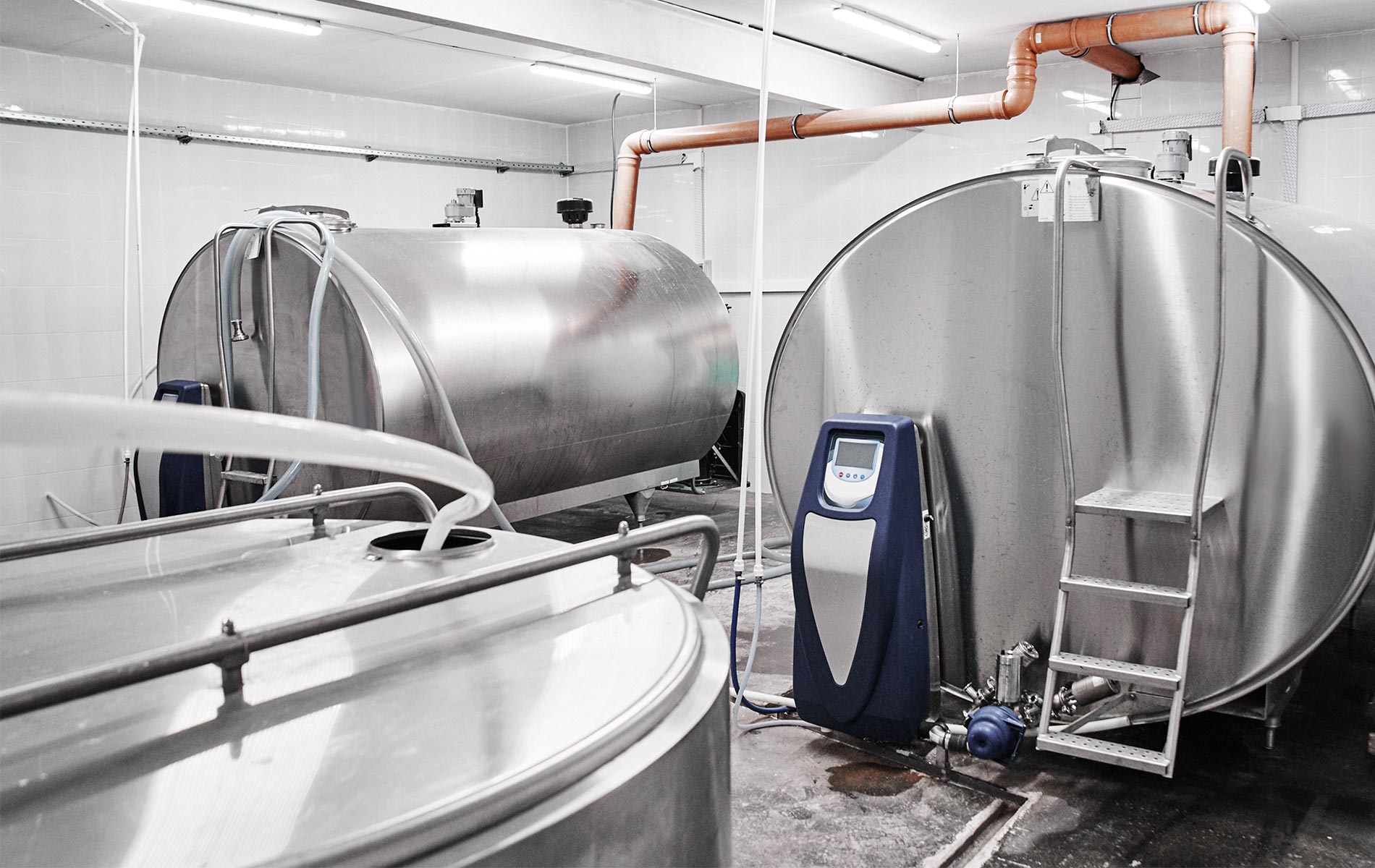

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
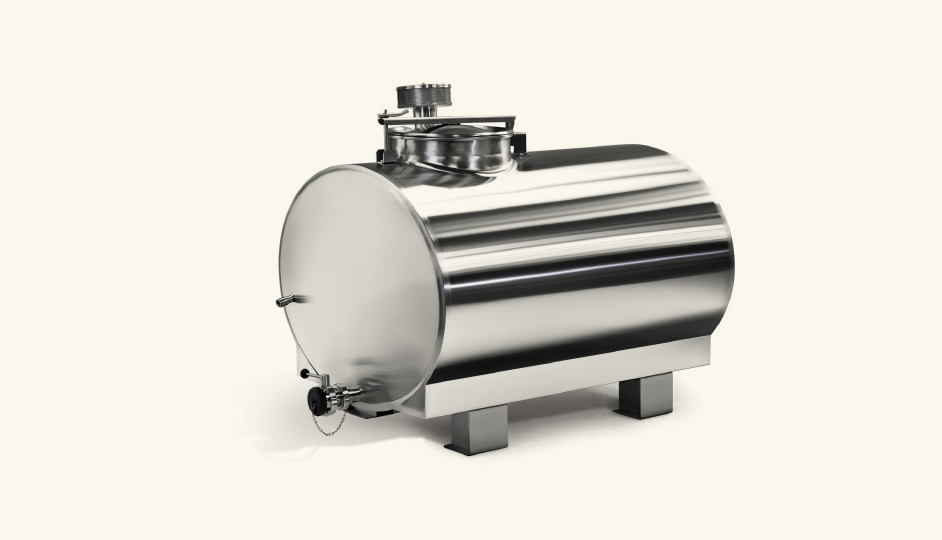
Horizontal Storage Tanks
Horizontal tanks offer practical advantages where vertical height is constrained or where ground-level access simplifies operations. Their lower profile makes them suitable for retrofit installations and mobile applications.
Key Characteristics:
– Ground-level access points for inspection and maintenance
– Stable, low center of gravity
– Available in single or multi-compartment configurations
Best For: Facilities with ceiling height limitations, mobile processing units, and operations prioritizing maintenance accessibility.
Multi-Compartment Tanks
Multi-compartment tanks enable simultaneous storage of different milk grades, products, or batches within a single unit. Each compartment operates independently with dedicated temperature controls and outlet connections.
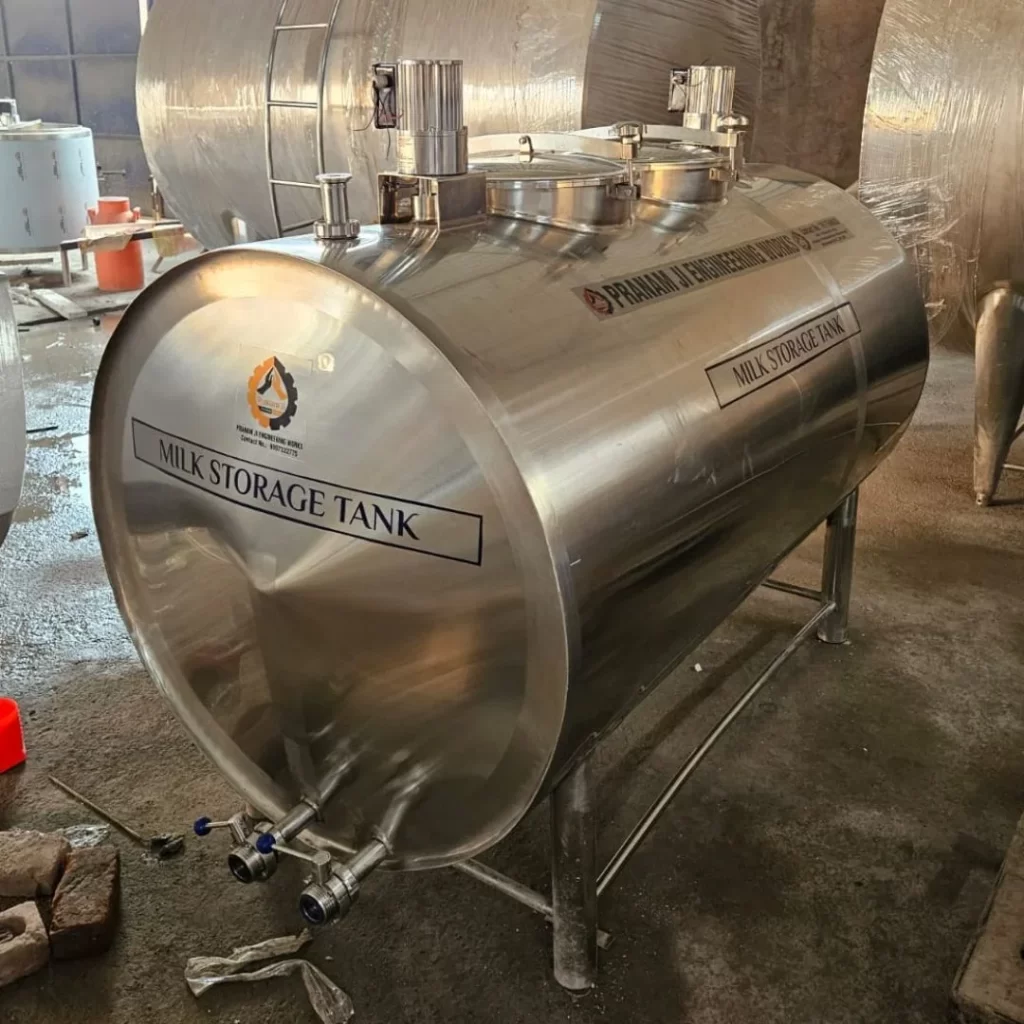

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Characteristics:
– Segregated storage zones
– Independent agitation and monitoring per compartment
– Reduced equipment footprint versus multiple single tanks
Best For: Processors handling organic and conventional milk, multiple fat content grades, or facilities requiring batch segregation for traceability.
Insulated Storage Tanks
Insulated tanks provide thermal retention through double-wall construction without active refrigeration. These units maintain temperature stability for short-term holding periods, typically as intermediate staging between processing steps.
Key Characteristics:
– Passive thermal management
– Lower capital and operating costs than refrigerated units
– Single or double-wall stainless steel construction
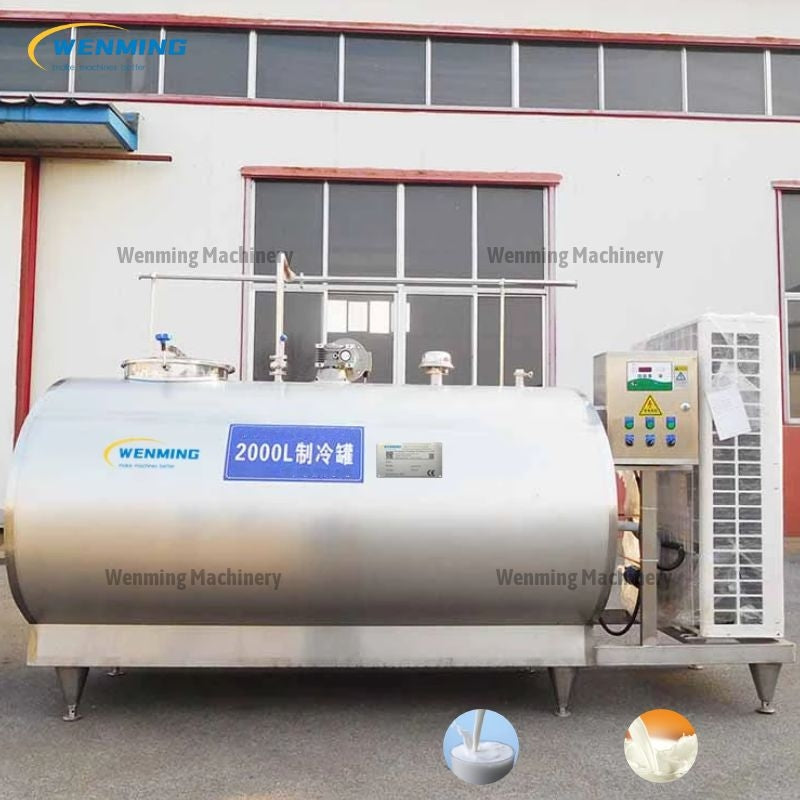

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Best For: Pre-processing staging, short-term holding, and facilities where milk arrives pre-chilled from farm bulk tanks.
Selection Considerations
When evaluating milk storage tank options, prioritize:
- Capacity requirements based on daily throughput and peak volume periods
- Space constraints including ceiling height and floor area
- Product handling needs such as multiple grades or organic certification
- Regulatory compliance for your operating region (FDA, EU standards)
- Total cost of ownership including energy consumption and maintenance
New, used, and custom-fabricated options exist across all tank types, allowing facilities to balance budget constraints with operational requirements.
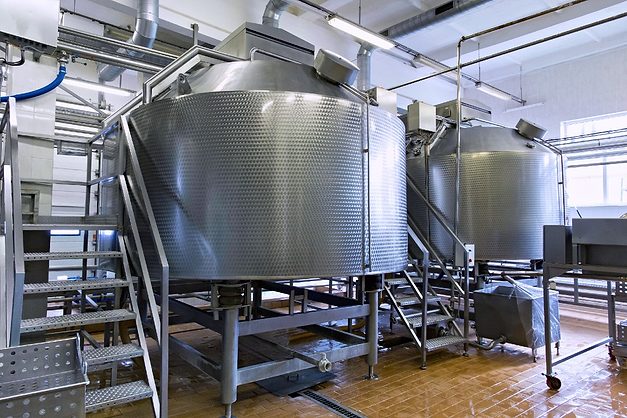
Key Industrial Applications of milk storage tanks
Key Industrial Applications of Milk Storage Tanks
Milk storage tanks, while designed primarily for dairy operations, serve critical roles across multiple industries due to their sanitary construction, precise temperature control, and durable 304 stainless steel design. Below is a comprehensive breakdown of industrial applications and their specific operational benefits.
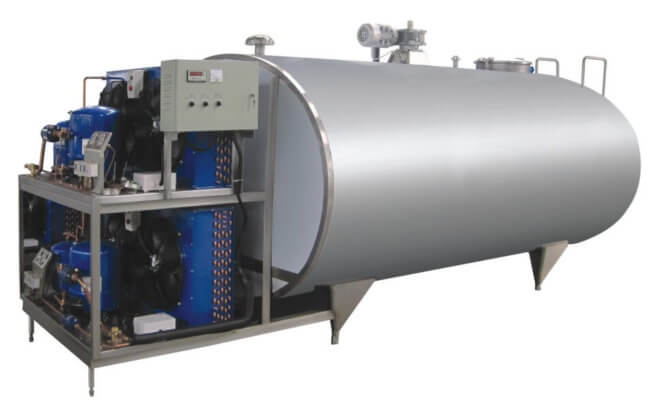

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Industry Application Matrix
| Industry | Primary Applications | Tank Specifications Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Dairy Processing | Raw milk cooling, bulk storage, pasteurization staging | Refrigerated cooling, vertical agitators, CIP spray balls |
| Beverage Manufacturing | Beer, wine, juice storage and fermentation | Sanitary clamp connections, temperature control, sealed manways |
| Food Processing | Liquid ingredient storage, sauce/syrup holding | Hinged gasketed covers, paddle agitators, sanitary design |
| Honey Processing | Bulk honey storage, liquefaction, blending | Temperature regulation, gentle agitation, food-grade surfaces |
| Cosmetics & Personal Care | Lotion, cream, and liquid product storage | Sanitary construction, mixing capabilities, contamination prevention |
| Chemical Processing | Ink, paint, oil, and specialty chemical holding | Corrosion-resistant stainless steel, sealed systems |
Detailed Benefits by Application
Dairy Operations
– Rapid cooling preserves milk quality and extends shelf life
– Agitation systems prevent cream separation during storage
– CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems reduce downtime between batches
– Capacity options from 200 to 4,000+ gallons accommodate operations of all scales
Beverage Production
– Maintains consistent fermentation temperatures for beer and wine
– Sanitary design meets FDA and USDA compliance requirements
– Sealed manways prevent contamination and oxidation
Multi-Industry Advantages
– 304 stainless steel construction ensures longevity and chemical resistance
– Modular sizing supports scalable production growth
– Reconditioning availability reduces capital expenditure for budget-conscious operations
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘milk storage tanks’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Milk Storage Tanks & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1: Temperature Fluctuations Compromising Milk Quality
Scenario: A mid-sized dairy processor notices inconsistent cooling performance in their aging bulk tanks, leading to temperature variations that threaten milk quality and regulatory compliance.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Problem: Inadequate refrigeration systems or worn components cause uneven cooling, risking bacterial growth and potential batch rejection. This results in product loss, failed quality audits, and damaged customer relationships.
Solution:
– Invest in modern bulk milk tanks with integrated refrigeration systems and reliable paddle-type vertical agitators for uniform temperature distribution
– Implement continuous temperature monitoring with automated alerts
– Schedule regular maintenance checks on compressors and cooling coils
– Consider upgrading to tanks with enhanced insulation properties
Pain Point 2: Sanitation and CIP System Inefficiencies
Scenario: A food processing facility repurposing dairy equipment struggles with inadequate cleaning cycles, leading to contamination risks and extended downtime between batches.
Problem: Older tanks lacking proper CIP (Clean-in-Place) infrastructure require manual cleaning, increasing labor costs, water usage, and contamination risk while reducing operational throughput.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Solution:
| Action | Benefit |
|——–|———|
| Select tanks with integrated CIP spray balls | Ensures complete interior coverage |
| Specify sanitary clamp connections | Enables faster disassembly for inspection |
| Choose hinged gasketed manway covers | Improves access for verification cleaning |
| Establish documented CIP protocols | Maintains compliance and consistency |
Pain Point 3: Capacity Limitations and Scalability Constraints
Scenario: A growing dairy operation faces seasonal production peaks that exceed their current storage capacity, forcing them to refuse orders or compromise storage protocols.
Problem: Fixed tank sizes create bottlenecks during high-demand periods, while oversized tanks during low periods waste energy and increase operational costs.
Solution:
– Assess production forecasts and select modular tank configurations (200–4,000 gallon options available)
– Consider a mix of new and reconditioned tanks to balance budget with capacity needs
– Evaluate multi-compartment tank options for product segregation flexibility
– Partner with suppliers offering custom fabrication for facility-specific requirements

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic Material Selection Guide for milk storage tanks
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Milk Storage Tanks
Selecting the appropriate material for milk storage tanks directly impacts operational longevity, regulatory compliance, product safety, and total cost of ownership. This guide examines the primary materials used in milk storage tank construction, their performance characteristics, and strategic considerations for procurement decisions.
Primary Material: 304 Stainless Steel
304 stainless steel dominates the milk storage tank market for compelling reasons. This austenitic chromium-nickel alloy contains approximately 18% chromium and 8% nickel, creating a passive oxide layer that resists corrosion from milk’s lactic acid content.
Key Performance Characteristics:
– Excellent resistance to organic acids produced during milk storage
– Non-reactive surface prevents flavor contamination
– Withstands repeated CIP (Clean-in-Place) cycles with alkaline and acidic detergents
– Maintains structural integrity across temperature fluctuations from refrigeration to sanitization
– FDA and USDA compliant for food contact applications
Operational Advantages:
– Service life exceeding 20-30 years with proper maintenance
– Smooth surface finish (typically 180 grit or better) minimizes bacterial adhesion
– Weldable construction allows for custom fabrication and field repairs
– Recyclable at end of life, supporting sustainability initiatives

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Alternative Material: 316 Stainless Steel
For operations requiring enhanced corrosion resistance, 316 stainless steel offers superior performance. The addition of 2-3% molybdenum provides increased resistance to chloride-induced pitting and crevice corrosion.
When to Specify 316 Grade:
– Facilities using chlorinated sanitizers at elevated concentrations
– Coastal installations with salt air exposure
– Operations processing milk with higher acidity levels
– Extended storage applications where corrosion risk compounds over time
The premium for 316 stainless typically ranges 15-25% above 304 grade pricing, requiring cost-benefit analysis based on specific operational conditions.
Secondary Material Considerations
Insulation Materials:
Modern bulk milk tanks incorporate polyurethane foam insulation between inner and outer shells. This closed-cell material delivers thermal efficiency ratings of R-6 to R-8 per inch, critical for maintaining the 35-38°F (2-3°C) temperature range required by dairy regulations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Gasket and Seal Materials:
– EPDM rubber: Standard choice for manway covers and sanitary connections
– Silicone: Preferred for high-temperature applications and extended chemical resistance
– PTFE: Specified for aggressive CIP chemical exposure
Agitator Components:
Paddle-type vertical agitators typically utilize the same stainless grade as the tank body, ensuring consistent corrosion resistance throughout the system.
Surface Finish Specifications
Surface finish directly affects cleanability and bacterial control:
| Finish Type | Ra Value (µin) | Application |
|---|---|---|
| #4 Sanitary | 25-35 | Standard dairy applications |
| #7 Polished | 10-20 | Enhanced cleanability requirements |
| Electropolished | 8-15 | Pharmaceutical-grade applications |
Most bulk milk tanks ship with #4 sanitary finish, meeting 3-A Sanitary Standards requirements while balancing cost and performance.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Regulatory Compliance Factors
Material selection must satisfy multiple regulatory frameworks:
United States:
– FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 (rubber articles)
– 3-A Sanitary Standards 01-07 (farm milk cooling and holding tanks)
– PMO (Pasteurized Milk Ordinance) requirements
European Union:
– EC Regulation 1935/2004 (materials in contact with food)
– EC Regulation 10/2011 (plastic materials)
– EN 1672-2 (hygiene requirements for food machinery)
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
Material selection influences costs beyond initial purchase price:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
304 Stainless Steel Tanks:
– Lower acquisition cost
– Adequate performance for standard dairy operations
– Reduced replacement part costs
316 Stainless Steel Tanks:
– Higher initial investment
– Extended service life in corrosive environments
– Lower long-term maintenance costs in challenging conditions
Material Selection Comparison Table
| Criteria | 304 Stainless Steel | 316 Stainless Steel | Carbon Steel (Not Recommended) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Baseline | +15-25% | -30-40% |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent | Poor |
| Chloride Resistance | Moderate | High | None |
| FDA/USDA Compliance | Yes | Yes | No |
| 3-A Standards Compliance | Yes | Yes | No |
| Expected Service Life | 20-30 years | 25-35 years | 5-10 years |
| CIP Chemical Compatibility | Good | Excellent | Poor |
| Weldability | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
| Thermal Conductivity | 16.2 W/m·K | 16.3 W/m·K | 50 W/m·K |
| Recyclability | High | High | Moderate |
| Maintenance Requirements | Low | Low | High |
| Recommended Application | Standard dairy operations | Coastal/high-chloride environments | Industrial non-food use only |
Strategic Procurement Recommendations
- Default to 304 stainless steel for standard dairy operations with conventional CIP protocols
- Specify 316 stainless steel when environmental factors or chemical exposure justify the premium
- Verify 3-A authorization on all tanks to ensure regulatory compliance
- Request mill certifications confirming material composition for quality assurance documentation
- Consider reconditioned equipment from reputable suppliers—used tanks in 304 stainless steel often deliver equivalent performance at reduced capital expenditure
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for milk storage tanks
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Milk Storage Tanks
The manufacturing of milk storage tanks demands precision engineering and rigorous quality protocols to meet the stringent hygiene requirements of the dairy industry. Understanding these processes helps procurement teams evaluate suppliers and make informed purchasing decisions.
Manufacturing Process Overview
1. Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with sourcing and preparing raw materials:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Stage | Process | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Procurement of 304 or 316L stainless steel sheets | Mill certificates verify composition and traceability |
| Incoming Inspection | Dimensional checks, surface quality assessment | Rejection of materials with pitting, inclusions, or contamination |
| Surface Preparation | Cleaning, degreasing, and protective film application | Prevents oxidation and contamination during fabrication |
Grade 304 stainless steel serves as the industry standard for bulk milk tanks, offering excellent corrosion resistance and durability for dairy applications. For environments with higher chloride exposure or more aggressive cleaning chemicals, manufacturers may specify 316L stainless steel.
2. Forming Operations
Forming transforms flat stainless steel sheets into tank components:
-
Shell Rolling: Flat sheets pass through plate rolling machines to create cylindrical sections. Multiple passes ensure uniform curvature without stress concentrations.
-
Head Forming: Tank ends (heads) are formed using hydraulic presses or spinning operations. Common configurations include:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Dished heads (most common for horizontal tanks)
- Flat heads with reinforcing rings
-
Conical bottoms for complete drainage
-
Component Fabrication: Nozzles, manways, and mounting brackets are cut and formed from appropriate gauge materials using laser cutting, plasma cutting, or waterjet methods.
3. Welding and Assembly
Assembly integrates all components into a functional vessel:
Welding Protocols
– Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding predominates for sanitary applications
– Automated orbital welding ensures consistent, repeatable weld quality on piping connections
– All welds on product-contact surfaces require full penetration with smooth, crevice-free profiles
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Assembly Sequence
1. Shell section longitudinal seam welding
2. Circumferential seam welding to join shell sections
3. Head-to-shell attachment
4. Nozzle and fitting installation
5. Jacket assembly (for refrigerated tanks)
6. Agitator mounting and alignment
7. Leg or skirt attachment
Refrigeration System Integration
Bulk milk cooling tanks incorporate direct expansion refrigeration systems. The evaporator coils are welded to the outer tank shell, then enclosed within an insulated jacket. This configuration enables rapid cooling to maintain milk quality.
4. Surface Finishing
Interior surface finish directly impacts cleanability and bacterial resistance:
| Finish Type | Ra Value (μin) | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Mill Finish | 125-250 | Non-product contact surfaces |
| #4 Dairy Finish | 25-35 | Standard product contact surfaces |
| Electropolished | 15-25 | High-purity applications |
Mechanical polishing progresses through increasingly fine abrasive grits. Electropolishing may follow to remove embedded particles and create a passive chromium oxide layer.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. Quality Control and Testing
Comprehensive quality assurance spans the entire manufacturing process:
In-Process Inspections
– Dimensional verification at each fabrication stage
– Weld visual inspection per AWS D18.1/D18.2 (Specification for Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel Tube and Pipe Systems in Sanitary Applications)
– Dye penetrant testing on all product-contact welds
– Surface roughness measurement using profilometers
Final Testing Protocols
| Test | Method | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrostatic Pressure | Fill with water, pressurize to 1.5x design pressure | No leaks, permanent deformation, or visible distress |
| Helium Leak Detection | Pressurize jacket with helium, scan with detector | No detectable leakage at refrigerant circuit |
| Surface Finish Verification | Profilometer readings at multiple locations | Meets specified Ra values |
| Dimensional Inspection | CMM or manual measurement | Within drawing tolerances |
| Agitator Function | Run at operating speed | Smooth operation, no vibration |
Quality Standards and Certifications
Reputable manufacturers maintain certifications demonstrating commitment to quality:
ISO 9001:2015
This quality management system standard ensures documented procedures, traceability, and continuous improvement processes govern all manufacturing operations.
3-A Sanitary Standards
The 3-A Sanitary Standards, Inc. establishes design and fabrication criteria specifically for dairy and food processing equipment. Key standards include:
– 3-A 01-10: Stainless Steel
– 3-A 02-11: Farm Milk Cooling and Holding Tanks
ASME Certification
For pressure-rated components, ASME U-stamp certification confirms compliance with Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code requirements.
European Standards
Equipment destined for European markets must comply with:
– EN 1672-2: Food processing machinery – Safety and hygiene requirements
– EC 1935/2004: Materials in contact with food
– EHEDG Guidelines: Hygienic design principles
Documentation Package
Complete documentation accompanies quality-manufactured tanks:
- Material certificates (mill test reports) for all stainless steel
- Weld procedure specifications (WPS) and welder qualifications
- Non-destructive examination reports
- Hydrostatic test certificates
- Surface finish reports
- Dimensional inspection records
- Operating and maintenance manuals
- Spare parts lists
Evaluating Manufacturer Quality
When assessing potential suppliers, consider these indicators:
- Facility Certifications: ISO 9001 registration, 3-A authorization
- Welding Credentials: AWS-certified welders, documented procedures
- Testing Capabilities: In-house NDT, calibrated measurement equipment
- Traceability Systems: Material lot tracking, serialized documentation
- Reference Installations: Verifiable customer installations in similar applications
- Warranty Terms: Coverage period, exclusions, response commitments
Manufacturers offering both new and reconditioned equipment should demonstrate equivalent quality protocols for each category, with reconditioning processes that restore tanks to meet original specifications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘milk storage tanks’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Milk Storage Tanks
Use this comprehensive checklist to systematically evaluate and procure milk storage tanks for your facility. Each phase builds on the previous to ensure you select equipment that meets operational, regulatory, and budgetary requirements.
Phase 1: Define Requirements
- [ ] Determine capacity needs
- Calculate daily milk volume (current and projected growth)
- Standard sizes range from 200 to 4,000+ gallons
-
Consider vertical silos for larger operations (10,000+ gallons)
-
[ ] Specify tank type
| Tank Type | Best For |
|———–|———-|
| Bulk milk cooling tanks | Farm-level collection and cooling |
| Horizontal tanks | Space-constrained facilities |
| Vertical silo tanks | High-volume processing plants |
| Multi-compartment tanks | Multiple product segregation | - [ ] Identify material requirements
- 304 stainless steel (standard dairy applications)
-
316 stainless steel (corrosive environments or enhanced durability)
- [ ] List essential features
- Refrigeration system specifications
- Agitator type (paddle-type vertical agitators are standard)
- CIP spray balls for cleaning
- Top-entering manways with hinged gasketed covers
- Sanitary clamp connections
Phase 2: Establish Budget Parameters
-
[ ] Evaluate new vs. used equipment
| Option | Advantages | Considerations |
|——–|————|—————-|
| New | Full warranty, latest features, customization | Higher upfront cost |
| Used/Reconditioned | Lower cost, faster ROI | Verify reconditioning quality |
| Custom fabrication | Exact specifications | Longer lead times | - [ ] Factor in total cost of ownership
- Purchase price
- Shipping and installation
- Electrical and refrigeration hookups
- Ongoing maintenance and parts
Phase 3: Identify and Vet Suppliers
- [ ] Research supplier categories
- OEM manufacturers
- Authorized distributors
- Used/reconditioned equipment dealers
-
Custom fabrication specialists
- [ ] Evaluate supplier credentials
- Years in dairy equipment industry
- Reconditioning and repair service capabilities
- Inventory availability (new and used)
-
Geographic coverage (USA, Europe)
- [ ] Request documentation
- Equipment certifications
- Material test reports (MTRs)
- Compliance with 3-A Sanitary Standards
- FDA/USDA and EU food contact material compliance
Phase 4: Request and Compare Quotes
- [ ] Prepare RFQ specifications
- Exact capacity requirements
- Material grade
- Required features and accessories
- Delivery timeline
-
Installation support needs
- [ ] Obtain minimum 3 quotes
-
[ ] Compare quotes using standardized criteria
| Criteria | Supplier A | Supplier B | Supplier C |
|———-|————|————|————|
| Unit price | | | |
| Delivery lead time | | | |
| Warranty terms | | | |
| Included accessories | | | |
| Installation support | | | |
| After-sales service | | | |
Phase 5: Conduct Due Diligence
- [ ] For new equipment
- Confirm manufacturing standards
- Review warranty coverage (parts and labor)
-
Verify spare parts availability
- [ ] For used/reconditioned equipment
- Request reconditioning report
- Inspect welds, seals, and surface finish
- Verify refrigeration system functionality
- Confirm agitator and motor condition
-
Request operational history if available
- [ ] Arrange site visit or video inspection (for high-value purchases)
Phase 6: Finalize Purchase Terms
- [ ] Negotiate contract terms
- Payment schedule (deposit, milestone, final)
- Delivery and freight responsibilities (FOB terms)
- Installation and commissioning scope
-
Training provisions
- [ ] Confirm compliance documentation
- Certificate of conformity
- Pressure vessel certifications (if applicable)
-
Electrical certifications (UL, CE marking)
- [ ] Establish warranty and service agreement
- Warranty duration and coverage
- Response time for service calls
- Access to replacement parts
Phase 7: Plan Installation and Commissioning
- [ ] Prepare facility infrastructure
- Concrete pad or floor reinforcement
- Electrical supply (voltage, phase, amperage)
- Refrigeration connections
- CIP system integration
-
Drainage provisions
- [ ] Schedule delivery and rigging
- Confirm equipment dimensions and weight
- Arrange crane or forklift access
-
Coordinate with installation team
- [ ] Conduct commissioning tests
- Refrigeration performance verification
- Agitator operation check
- Leak testing
- CIP cycle validation
Quick Reference: Key Questions for Suppliers
- What stainless steel grade is used, and can you provide MTRs?
- Does the tank meet 3-A Sanitary Standards and FDA/EU regulations?
- What is included in the standard package vs. optional accessories?
- What reconditioning work was performed (for used equipment)?
- What warranty and after-sales support do you offer?
- Can you provide references from similar dairy operations?
Red Flags to Avoid
- Suppliers unwilling to provide material certifications
- No clear reconditioning documentation for used equipment
- Unusually low pricing without explanation
- No warranty or service support options
- Inability to meet regulatory compliance requirements
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for milk storage tanks Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Milk Storage Tanks Sourcing
Understanding the full cost structure of milk storage tanks is essential for making informed procurement decisions. This analysis breaks down the key cost components and provides actionable strategies to optimize your investment.
Cost Breakdown by Component
Materials (40-55% of Total Cost)
| Material Component | Cost Impact | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 304 Stainless Steel | High | Industry standard; durable, corrosion-resistant |
| 316 Stainless Steel | 20-30% premium | Required for aggressive cleaning chemicals |
| Insulation | Moderate | Polyurethane foam standard; affects energy efficiency |
| Refrigeration Components | High | Compressors, condensers, evaporators |
| Agitator Systems | Moderate | Paddle-type vertical agitators standard |
| Fittings & Connections | Low-Moderate | Sanitary clamp connections, CIP spray balls |
Typical Price Ranges by Capacity
| Tank Capacity | New Equipment | Used/Reconditioned |
|---|---|---|
| 200-500 Gallons | $8,000-$18,000 | $3,500-$9,000 |
| 500-1,000 Gallons | $15,000-$30,000 | $7,000-$15,000 |
| 1,000-2,600 Gallons | $25,000-$55,000 | $12,000-$28,000 |
| 2,600-4,000 Gallons | $45,000-$80,000 | $20,000-$40,000 |
Labor Costs (15-25% of Total Cost)
- Manufacturing labor: Welding, assembly, quality testing
- Installation: Site preparation, electrical connections, plumbing integration
- Commissioning: System testing, calibration, staff training
- Customization: Additional fabrication for non-standard specifications
Logistics (10-20% of Total Cost)
| Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Freight | Oversized loads require specialized transport; distance significantly impacts cost |
| Rigging & Placement | Crane services, facility access requirements |
| Import Duties | Applicable for international sourcing (varies by country of origin) |
| Insurance | Transit coverage for high-value equipment |
Hidden Costs to Account For
- Electrical infrastructure upgrades for refrigeration systems
- Concrete pad installation for proper tank support
- CIP system integration if not included
- Regulatory compliance inspections and certifications
- Extended warranty programs
- Spare parts inventory for critical components
Cost-Saving Strategies
1. Consider Reconditioned Equipment
Fully reconditioned bulk milk tanks from reputable suppliers offer 40-60% savings versus new equipment while maintaining quality standards. Tanks undergo thorough inspection, repair, and testing before resale.
2. Right-Size Your Investment
- Calculate actual storage requirements based on peak production plus 15-20% buffer
- Avoid over-specifying capacity—larger tanks increase capital and operating costs
- Consider phased expansion with multiple smaller units
3. Standardize Specifications
- Stick to standard sizes (200-2,600 gallons) to avoid custom fabrication premiums
- Use industry-standard fittings and connections for easier maintenance and parts availability
- Select 304 stainless steel unless application specifically requires 316 grade
4. Optimize Logistics
- Consolidate shipments when purchasing multiple units
- Source from regional suppliers to reduce freight costs
- Schedule delivery during off-peak seasons for better rates
5. Negotiate Total Cost of Ownership
- Request bundled pricing for installation, commissioning, and training
- Negotiate extended warranty terms
- Secure service agreements with fixed labor rates
- Ask about trade-in value for existing equipment
6. Evaluate Multi-Use Potential
Bulk milk tanks’ sanitary design allows use across applications (dairy, beverage, cosmetics, chemicals). Consider equipment that can be repurposed if production needs change.
Procurement Checklist
- [ ] Define precise capacity and feature requirements
- [ ] Obtain quotes from minimum 3 suppliers (new and used)
- [ ] Request total installed cost, not just equipment price
- [ ] Verify warranty terms and service availability
- [ ] Confirm lead times and delivery schedules
- [ ] Review supplier reconditioning standards for used equipment
- [ ] Calculate 5-year total cost of ownership including energy and maintenance
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing milk storage tanks With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Milk Storage Tanks With Other Solutions
When evaluating milk storage solutions for dairy operations, processors must weigh multiple factors including capacity requirements, temperature control capabilities, regulatory compliance, and total cost of ownership. This analysis compares bulk milk storage tanks against two primary alternatives: traditional milk can systems and direct-to-tanker collection methods.
Comparison Overview
| Factor | Bulk Milk Storage Tanks | Milk Can Systems | Direct-to-Tanker Collection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity Range | 200–4,000+ gallons | 5–10 gallons per can | Variable (tanker-dependent) |
| Temperature Control | Integrated refrigeration; precise holding temps | Requires separate cooling; limited control | Minimal on-site storage; relies on rapid pickup |
| Initial Investment | $15,000–$80,000+ | $500–$2,000 total | Minimal equipment cost |
| Labor Requirements | Low (automated agitation, CIP-ready) | High (manual handling, cleaning) | Moderate (scheduling coordination) |
| Scalability | High (modular expansion possible) | Limited | Dependent on collection schedules |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets FDA/EU standards; sanitary design | Increasingly non-compliant for commercial use | Requires precise timing to meet cooling mandates |
| Material Construction | 304 stainless steel standard | Stainless steel or aluminum | N/A |
Detailed Analysis
Bulk Milk Storage Tanks
Bulk milk tanks represent the industry standard for commercial dairy operations. Key advantages include:
- Integrated cooling systems that rapidly reduce milk temperature to required holding levels (typically 4°C/39°F within regulatory timeframes)
- Sanitary design features including CIP spray balls, paddle-type vertical agitators, and sanitary clamp connections
- Versatility for multi-product facilities—the same tanks can store water, fruit juices, or other fluids
- Reduced contamination risk through enclosed systems with hinged gasketed covers and top-entering manways
The primary consideration is upfront capital expenditure, though this is offset by operational efficiency and extended equipment lifespan when using quality 304 stainless steel construction.
Milk Can Systems
Traditional can-based collection remains viable only for:
- Small-scale artisan operations
- Remote locations without infrastructure for bulk cooling
- Specialty products requiring segregated small batches
Limitations include labor intensity, inconsistent temperature maintenance, and increasing regulatory pressure in both US and EU markets pushing operations toward bulk systems.
Direct-to-Tanker Collection
This approach eliminates on-site storage but introduces significant operational constraints:
- Requires precise milking-to-collection scheduling
- Offers no buffer for collection delays or equipment failures
- Limits operational flexibility and expansion capability
- May not meet cooling time requirements during peak production
Recommendation Framework
| Operation Type | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|
| Commercial dairy (50+ cows) | Bulk milk storage tanks |
| Small artisan/specialty | Milk can systems or small-capacity bulk tanks |
| High-volume processors | Multi-tank bulk systems with vertical silo expansion |
| Operations with unreliable collection | Bulk tanks with extended capacity buffer |
For most commercial dairy operations in the US and Europe, bulk milk storage tanks deliver the optimal balance of regulatory compliance, operational efficiency, and long-term value. The availability of both new and reconditioned units provides entry points across budget ranges while maintaining quality standards.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for milk storage tanks
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Milk Storage Tanks
Understanding the technical specifications and industry terminology is critical when sourcing milk storage tanks for commercial dairy operations. This section covers the key properties and trade terms that inform procurement decisions.
Critical Technical Properties
| Property | Description | Typical Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | Stainless steel classification determining corrosion resistance and durability | 304 SS (standard), 316 SS (high-corrosion environments) |
| Capacity Range | Volumetric storage capability | 200–4,000+ gallons (farm tanks); larger for industrial silos |
| Surface Finish | Interior smoothness affecting cleanability and bacterial resistance | 2B, #4, or sanitary polish (Ra ≤ 0.8 µm) |
| Insulation Type | Thermal barrier maintaining milk temperature | Polyurethane foam, typically 2–3 inches |
| Cooling System | Refrigeration method for rapid temperature reduction | Direct expansion, ice bank, or glycol-cooled |
| Agitation | Mixing mechanism preventing cream separation | Paddle-type vertical agitators |
Tank Configuration Terminology
- Single Shell: Non-insulated tanks for ambient storage or secondary containment
- Double Shell (Jacketed): Insulated construction with cooling/heating capability
- Horizontal Tanks: Floor-mounted, lower profile installations
- Vertical Silo Tanks: Space-efficient upright configurations for high-volume operations
- Multi-Compartment Tanks: Segregated storage for different milk grades or products
Sanitary Design Features
- CIP (Clean-in-Place): Integrated spray ball systems enabling automated internal cleaning without disassembly
- Manway: Top-entering access port with hinged, gasketed covers for inspection and maintenance
- Sanitary Clamp Connections: Tri-clamp fittings meeting 3-A Sanitary Standards for hygienic product transfer
B2B Trade Terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | Lowest unit count a supplier will sell per transaction; typically 1 unit for tanks, higher for components |
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Supplier producing tanks under buyer’s brand specifications |
| Custom Fabrication | Tanks built to buyer-specified dimensions, features, or configurations |
| Reconditioned/Refurbished | Used equipment restored to operational standards with warranty |
| Lead Time | Production and delivery timeframe from order confirmation |
| FOB (Free on Board) | Shipping terms defining when ownership/risk transfers to buyer |
Compliance and Certification Terms
- 3-A Sanitary Standards: U.S. industry standards for dairy equipment design and fabrication
- FDA/USDA Compliant: Meets federal food safety requirements for dairy processing
- CE Marking: European conformity certification required for EU market entry
- PMO (Pasteurized Milk Ordinance): U.S. regulatory framework governing Grade A milk handling equipment
Procurement Considerations
When requesting quotes, specify:
- Required capacity and footprint constraints
- Cooling performance requirements (target temperature, cooldown time)
- Agitation specifications
- Connection sizes and types
- Voltage/phase requirements for electrical components
- Applicable certifications for your market
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the milk storage tanks Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Milk Storage Tanks Sector
Market Overview and Evolution
The milk storage tank sector has undergone significant transformation from basic farm-level cooling vessels to sophisticated, multi-purpose stainless steel systems. Modern bulk milk tanks—also referred to as bulk farm tanks or milk coolers—serve dual functions: rapid cooling and temperature-controlled storage. Their sanitary 304 stainless steel construction has expanded applications beyond dairy into beverages, cosmetics, chemicals, and food processing industries.
Current Sourcing Landscape
B2B buyers now navigate a market offering three distinct procurement pathways:
| Sourcing Option | Capacity Range | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| New Equipment | 200–2,600 gallons | Full warranty, latest efficiency standards, customization available |
| Used/Reconditioned | 200–4,000 gallons | Lower capital outlay, verified reconditioning, immediate availability |
| Custom Fabrication | Variable | Tailored specifications, longer lead times, integration flexibility |
Standard Specifications Driving Procurement Decisions
Current market-standard features include:
- 304 stainless steel construction for durability and corrosion resistance
- Top-entering manways with hinged gasketed covers
- CIP (Clean-in-Place) spray balls for sanitary compliance
- Paddle-type vertical agitators for consistent temperature distribution
- Sanitary clamp connections meeting food-grade regulations
Sustainability and Operational Efficiency Trends
Procurement decisions increasingly prioritize:
- Energy-efficient refrigeration systems reducing operational costs
- Extended equipment lifecycles through reconditioning programs
- Multi-industry versatility maximizing asset utilization
- Compliance with FDA and EU food safety standards
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
Evaluate suppliers offering reconditioning services and repair capabilities alongside new equipment sales. This dual-service model provides long-term value through maintenance partnerships and reduces total cost of ownership across your equipment lifecycle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of milk storage tanks
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Milk Storage Tanks
1. What capacity range is available for bulk milk storage tanks?
Bulk milk storage tanks are available in capacities ranging from 200 gallons to 4,000+ gallons for standard models. New refrigerated bulk tanks typically range from 200 to 2,600 gallons, while used and reconditioned units may extend to 4,000 gallons or more. For larger operations, vertical silo tanks offer significantly higher capacities.
2. What material specifications should we require for food-grade milk storage?
Standard specifications include:
| Component | Specification |
|---|---|
| Construction Material | 304 stainless steel (minimum) |
| Surface Finish | Sanitary polished interior |
| Connections | Sanitary clamp fittings |
| Gaskets | Food-grade, FDA-compliant |
304 stainless steel is the industry standard, offering durability, corrosion resistance, and compliance with dairy processing regulations.
3. What standard features are included with refrigerated bulk milk tanks?
Most commercial bulk milk tanks include:
- Top-entering manways with hinged, gasketed covers
- CIP (Clean-in-Place) spray balls
- Paddle-type vertical agitators
- Sanitary clamp connections
- Integrated refrigeration systems
- Temperature monitoring capabilities
4. Can milk storage tanks be repurposed for other applications?
Yes. Due to their sanitary design, bulk milk tanks are suitable for storing:
- Water and fruit juices
- Honey
- Wine and beer
- Cosmetics and personal care products
- Chemicals and oils
- Inks and paints
5. Should we consider new or used/reconditioned equipment?
| Factor | New Equipment | Used/Reconditioned |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Higher | 30-60% lower |
| Warranty | Full manufacturer warranty | Limited or as-is |
| Lead Time | May require production time | Often immediate availability |
| Customization | Fully customizable | Limited to existing specifications |
Reputable suppliers offer fully reconditioned used tanks that are ready for immediate connection and operation.
6. What cleaning and sanitation systems are compatible with these tanks?
Bulk milk tanks are designed for CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems, featuring integrated spray balls for automated cleaning cycles. This eliminates manual tank entry, reduces labor costs, and ensures consistent sanitation compliance with dairy processing standards.
7. Are custom fabrication options available?
Yes. Manufacturers offer custom fabrication services including:
- Non-standard capacities
- Modified inlet/outlet configurations
- Specialized agitation systems
- Custom mounting and footprint requirements
- Integration with existing processing lines
8. What support services should we expect from suppliers?
Comprehensive B2B suppliers typically provide:
- Reconditioning services for used equipment
- Repair services for existing installations
- Replacement parts (seals, gaskets, valves, fittings)
- Technical consultation for system integration
- Quote and specification assistance
Request documentation of reconditioning processes and warranty terms before purchasing used equipment.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for milk storage tanks
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion: Milk Storage Tanks
Successful milk storage tank procurement requires balancing immediate operational needs against long-term ROI. Key sourcing considerations include:
Priority Decision Factors
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Material Quality | 304 stainless steel ensures durability and regulatory compliance |
| Capacity Range | 200–4,000 gallons covers most dairy and alternative applications |
| Sanitary Design | Enables multi-purpose use across food, beverage, and chemical sectors |
| Reconditioning Options | Used tanks offer cost savings without compromising functionality |
Market Outlook
The milk storage tank market continues expanding beyond traditional dairy applications. Sanitary bulk tanks now serve:
- Craft beverage production (beer, wine)
- Honey and juice processing
- Cosmetics and chemical manufacturing
Procurement Recommendations:
- Evaluate new vs. reconditioned — Used tanks with full reconditioning deliver comparable performance at reduced capital expenditure
- Prioritize standard features — CIP spray balls, paddle agitators, and sanitary clamp connections reduce integration costs
- Consider scalability — Select suppliers offering custom fabrication for future capacity expansion
Strategic buyers should leverage suppliers providing comprehensive services—from equipment sourcing through reconditioning and repair—to minimize vendor complexity and ensure consistent quality standards across their processing infrastructure.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.