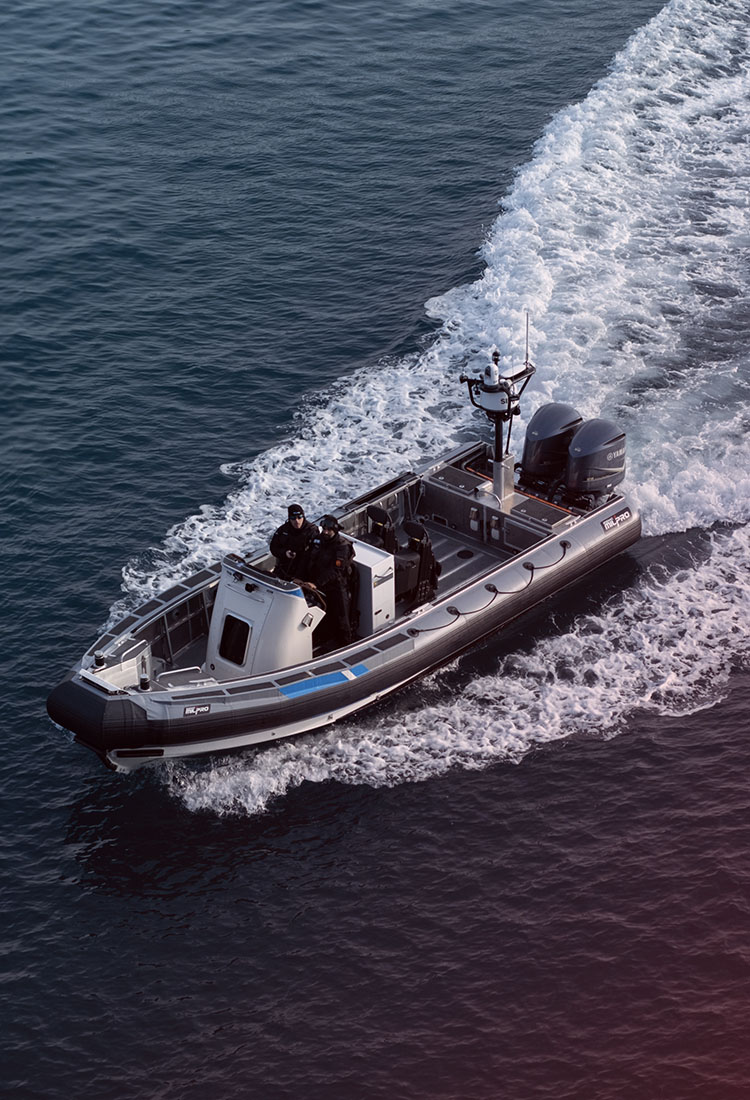
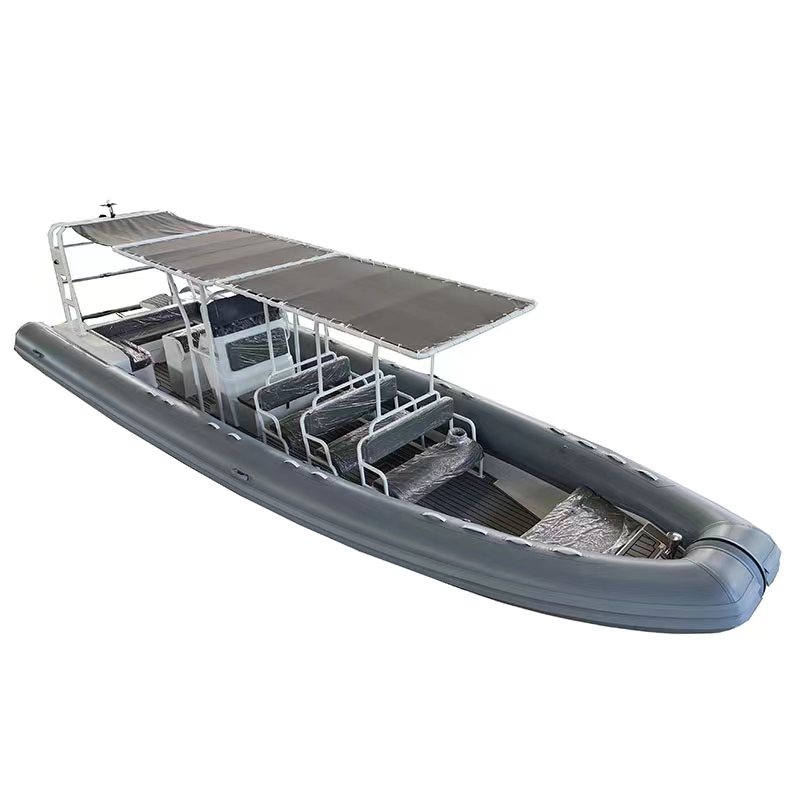
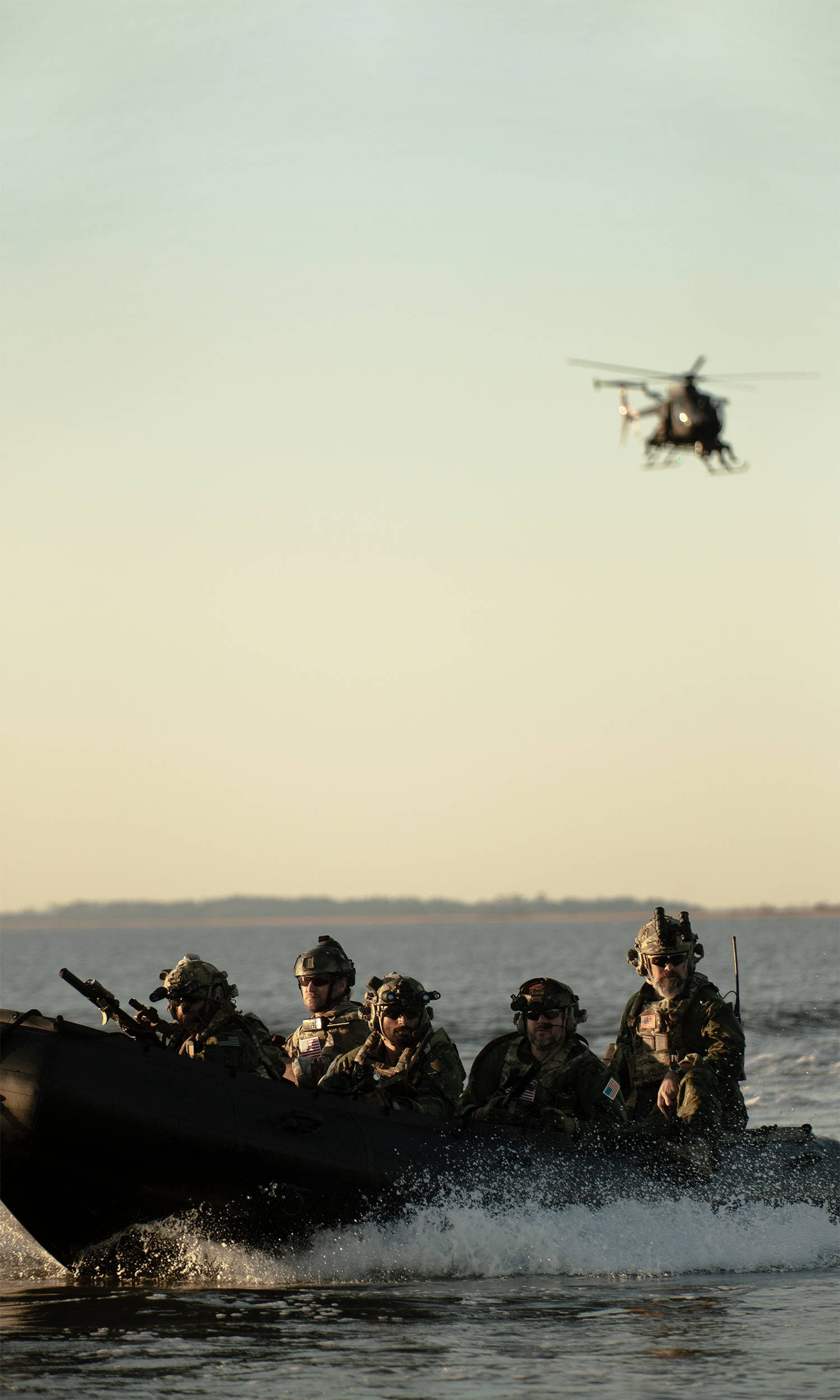
The global military rubber boat market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing maritime security concerns, rising defense expenditures, and the need for rapid deployment and coastal surveillance capabilities. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global rigid-hull inflatable boats (RIBs) market — a category that includes military-grade rubber boats — was valued at USD 1.85 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2024 to 2029, with defense and naval applications representing a significant portion of demand. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights expanding offshore patrol operations and modernization of naval fleets as key growth drivers, noting that the global RIB market size could exceed USD 2.7 billion by 2030. As governments invest in agile, durable, and high-performance maritime platforms, the demand for advanced military rubber boats has surged, positioning leading manufacturers at the forefront of defense and security innovation. The following list highlights the top 10 manufacturers shaping this critical sector with proven track records in performance, durability, and technological integration.
Top 10 Military Rubber Boat Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 USMI Boats
Domain Est. 1998
Website: usmi.com
Key Highlights: United States Marine, Inc. Boats & Vessels, About / Mission / Facilities, Quality & Craftsmanship, Service and Logistics Support, Careers, Contact Us…
#2 MST Group
Domain Est. 2002
Website: mstltd.com
Key Highlights: Marine Specialised Technology Group is one of the world’s leading companies that specialises in the new build, refit, and repair of boats up to 24m in length….
#3 BRIG USA
Domain Est. 2013
Website: brigusa.com
Key Highlights: Discover the world’s most advanced rigid inflatable boats for sale today. At BRIG, we fuse the cutting-edge design, technology and precision engineering….
#4 INMAR inflatable boat
Domain Est. 2014
Website: inmarboats.com
Key Highlights: Inmar Marine Group is your source for inflatable boats and Suzuki Marine outboard boat motors. Manufacturer of the finest military, rescue, and recreation ……
#5 Ribcraft
Domain Est. 2000
Website: ribcraft.com
Key Highlights: Ribcraft® designs and manufactures fully customisable Rigid Hull and Soft Inflatable Boats (RHIBs / RIBs & SIBs). Trusted worldwide for over 30 years….
#6 Zodiac Milpro™, the global leader in RIBs & inflatable boats
Domain Est. 2002
Website: zodiacmilpro.com
Key Highlights: Durable and adaptable aluminum RIBs for the most demanding missions. SRR. Built for professional and military units for day to day missions….
#7 Professional Grade RIBs
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ribcraftusa.com
Key Highlights: RIBCRAFT specializes in building professional grade rigid inflatable boats (RIBs) starting at 15′, that fulfill a variety of missions….
#8 RIB Boats
Domain Est. 2005
Website: asisboats.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to ASIS Boats. We specialize in making Rigid Inflatable Boats (RIB Boats) purpose-built for military, government, and professional clients worldwide……
#9 Wing Group
Domain Est. 2006
Website: winggroup.com
Key Highlights: The WING Group is the world leader in inflatable boats, life rafts, flotation, dry suits, technical apparel, and other tactical and survival solutions….
#10 Ocean Craft Marine: RHIB Boat
Domain Est. 2011 | Founded: 2011
Website: oceancraftmarine.com
Key Highlights: Since 2011, our team of experts has been delivering custom-built RHIB boats to the military and the professionals….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Military Rubber Boat

H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for Military Rubber Boats
The global military rubber boat market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving defense strategies, technological advancements, and increasing maritime security concerns. As nations modernize their naval capabilities and respond to asymmetric threats, military-grade inflatable and rigid-hull inflatable boats (RHIBs) are becoming critical assets for coastal defense, special operations, and rapid deployment missions. The following trends are expected to shape the 2026 landscape:
1. Rising Demand for Special Operations and Coastal Security
With the growing prevalence of piracy, smuggling, and hybrid warfare in littoral zones, military rubber boats are increasingly deployed by special forces and coast guards. Their high mobility, low radar signature, and ease of transport make them ideal for stealth insertion, surveillance, and rapid response. Countries in Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and West Africa are investing heavily in RHIB fleets, contributing to market growth.
2. Technological Integration and Enhanced Performance
By 2026, military rubber boats are expected to incorporate advanced materials such as hypalon-coated fabrics and reinforced composites, improving durability and resistance to extreme conditions. Integration of digital navigation systems, satellite communication, and modular weapon mounts will enhance operational effectiveness. Some platforms may also feature hybrid or electric propulsion to reduce acoustic signatures and support covert missions.
3. Emphasis on Lightweight and Transportable Designs
Military forces are prioritizing deployability and versatility. Lightweight rubber boats that can be air-dropped, carried by helicopters, or launched from larger vessels are in higher demand. This trend is particularly evident among NATO and allied forces seeking rapid response capabilities in contested maritime regions.
4. Geopolitical Tensions and Defense Budget Increases
Ongoing geopolitical instability in regions such as the South China Sea, the Baltic, and the Eastern Mediterranean is driving defense modernization. Many nations are allocating increased budgets to maritime security, directly boosting procurement of military rubber boats. The U.S., UK, France, India, and South Korea are expected to be key markets.
5. Growth in Commercial-to-Military Conversions
Some manufacturers are adapting commercial inflatable boat designs for military use with minimal modifications, reducing costs and development time. This trend is enabling smaller defense forces and non-traditional users (e.g., paramilitary or border agencies) to access capable platforms.
6. Sustainability and Lifecycle Management
Environmental concerns and lifecycle costs are influencing procurement decisions. By 2026, there will be greater emphasis on recyclable materials, energy-efficient manufacturing, and maintenance-friendly designs to extend service life and reduce total ownership costs.
Conclusion
The military rubber boat market in 2026 will be characterized by innovation, strategic necessity, and global expansion. As naval warfare evolves toward agile, distributed operations, these versatile vessels will play a pivotal role in modern defense arsenals. Market growth is projected at a CAGR of 5–7% through 2026, with key opportunities in emerging defense markets and next-generation technology adoption.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Military Rubber Boats (Quality, IP)
Sourcing military-grade rubber boats involves critical considerations beyond standard procurement. Overlooking key pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to compromised performance, safety risks, legal liabilities, and supply chain vulnerabilities.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Using Non-Military-Grade Materials
A major risk is sourcing boats made with commercial-grade rubber or fabrics that do not meet military specifications (e.g., NATO STANAGs, MIL-STD). Inferior materials degrade faster under UV exposure, extreme temperatures, and chemical contact, reducing operational lifespan and increasing maintenance costs.
Inadequate Construction and Seam Integrity
Military operations demand high durability. Poor welding or adhesive bonding of seams can lead to air leaks or catastrophic failure during deployment. Boats not built with double or triple-layer seams, or lacking reinforced stress points, may fail under heavy load or rough conditions.
Lack of Compliance with Military Standards
Procuring boats without proper certification to relevant military standards (e.g., for buoyancy, ballistic resistance, or inflation systems) undermines mission readiness. Vendors may claim compliance without third-party testing or documentation, leading to acceptance of substandard equipment.
Insufficient Testing and Quality Control
Reliable suppliers conduct rigorous in-house and independent testing (e.g., pressure tests, puncture resistance, endurance trials). Sourcing from manufacturers with weak QC processes increases the risk of receiving units with undetected defects that only emerge in the field.
Inconsistent Manufacturing and Batch Variability
Low-tier suppliers may lack process control, resulting in inconsistencies between production batches. This can affect fit, performance, and interoperability with military gear like motors, weapons mounts, or communication systems.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Procuring Counterfeit or Knock-Off Designs
Unauthorized replication of patented military boat designs (e.g., Zodiac-type hulls or specific valve systems) is common in unregulated markets. These copies often lack engineering integrity and may expose the buyer to legal action, especially if exported or used by allied forces.
Unlicensed Production and Technology Transfer
Some suppliers may offer “equivalent” boats that infringe on proprietary designs or manufacturing techniques. Engaging with such vendors risks violating IP rights held by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), potentially leading to customs seizures, legal disputes, or reputational damage.
Lack of IP Clarity in Contracts
Failing to address IP ownership in procurement contracts can result in ambiguity over modifications, spare parts, or future production rights. Military organizations may lose control over technical data packages (TDPs) or be restricted from local maintenance and repair.
Dependency on Proprietary Components Without License
Some boats incorporate patented subsystems (e.g., quick-deploy flooring, integrated radar reflectors). Sourcing boats with such components without usage rights can hinder in-house repairs and create long-term supply dependencies.
Exposure to IP Litigation and Export Restrictions
Using boats that infringe on IP can trigger lawsuits or trade barriers, particularly under ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) or similar frameworks. This can delay delivery, block deployment, or prohibit resale to partner nations.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: verifying material certifications, auditing manufacturing processes, ensuring standards compliance, and conducting IP risk assessments before contract award.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Military Rubber Boats
Overview and Purpose
This guide outlines the logistics and compliance requirements for the procurement, transport, storage, maintenance, and disposal of Military Rubber Boats (MRBs). These inflatable or rigid-hull inflatable boats (RHIBs) are critical assets for defense, border security, and special operations forces. Adherence to regulatory, safety, and operational standards is essential to ensure mission readiness and legal compliance.
Classification and Regulatory Framework
Military Rubber Boats are subject to national and international regulations based on their use, technology, and armament. Key regulatory frameworks include:
– ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) – Applies to U.S.-origin defense articles, including most MRBs listed on the U.S. Munitions List (USML Category VI). Export, transfer, or technical data sharing requires U.S. Department of State approval.
– EAR (Export Administration Regulations) – May apply if the boat incorporates dual-use components (e.g., navigation systems, engines). Administered by the U.S. Department of Commerce.
– Wassenaar Arrangement – Influences export controls for sensitive dual-use and conventional weapons in participating countries.
– National Defense Regulations – Host nation laws may impose additional controls on import, registration, and operational use.
Procurement and Acquisition Compliance
Ensure all procurement activities follow:
– Valid End-Use Certification: Required for export-controlled MRBs to confirm intended military application and non-diversion.
– Vendor Qualification: Suppliers must be registered with relevant authorities (e.g., DDTC for ITAR).
– Technical Data Controls: Blueprints, manuals, and software must be protected under ITAR or EAR restrictions.
– Contractual Obligations: Include compliance clauses, audit rights, and liability for unauthorized transfers.
Transportation and Shipping Logistics
Transport of MRBs involves multimodal logistics with strict handling requirements:
– Packaging: Deflated boats must be stored in moisture-resistant containers; rigid components require shock-absorbent crating.
– Marking and Labeling: Use IATA/DOT-compliant labels for hazardous materials (e.g., CO₂ cartridges, fuel). Include ITAR-controlled markings if applicable.
– Air, Sea, and Land Transport:
– Air: Comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (e.g., compressed gas cylinders).
– Sea: Follow IMDG Code for containerized shipments; secure vessels against saltwater corrosion.
– Land: Use secure, GPS-tracked vehicles with access logs for high-value or controlled shipments.
– Customs Documentation: Provide export licenses, commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
Storage and Inventory Management
Proper storage ensures longevity and operational readiness:
– Environmental Controls: Store in dry, temperature-controlled facilities away from UV exposure, ozone sources, and sharp objects. Ideal range: 10–25°C (50–77°F).
– Security Measures: Implement access controls, surveillance, and inventory tracking (e.g., RFID tags) for ITAR-controlled items.
– Rotation and Inspection: Conduct quarterly inspections for material degradation, valve integrity, and corrosion. Rotate stock to prevent aging.
Maintenance and Operational Compliance
Maintenance must follow OEM specifications and regulatory standards:
– Scheduled Servicing: Adhere to maintenance logs for engines, inflation systems, and hull integrity.
– Trained Personnel: Only authorized, cleared personnel should perform repairs involving controlled technology.
– Recordkeeping: Maintain service records for audit trails, including parts replaced and compliance certifications.
End-of-Life Management and Disposal
Disposal must prevent unauthorized reuse and environmental harm:
– Demilitarization: Render boats inoperable per military standards (e.g., shredding hulls, destroying control systems).
– Documentation: File disposal certificates with relevant authorities for ITAR-controlled items.
– Environmental Compliance: Recycle materials according to local waste regulations; dispose of hazardous components (e.g., batteries, fuel systems) via certified handlers.
Training and Personnel Clearance
All personnel involved in MRB logistics must:
– Hold appropriate security clearances (e.g., Secret or higher for ITAR data).
– Complete annual training in export controls, hazardous materials handling, and safety protocols.
– Sign non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) covering technical specifications and operational use.
Audit and Compliance Monitoring
Regular audits ensure adherence to legal and operational standards:
– Conduct internal reviews of shipping records, inventory logs, and maintenance reports.
– Prepare for external audits by defense departments or regulatory bodies (e.g., DDTC, BIS).
– Implement corrective actions for non-compliance incidents within 30 days.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management of Military Rubber Boats safeguards national security, prevents proliferation, and ensures operational effectiveness. Strict adherence to ITAR, EAR, and national protocols across the lifecycle—from procurement to disposal—is mandatory. Continuous training, documentation, and audit readiness are fundamental to sustained compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Military Rubber Boats
Sourcing military rubber boats requires a strategic approach that balances operational requirements, quality standards, cost-efficiency, and compliance with defense regulations. These specialized vessels are critical for a range of military operations, including reconnaissance, insertion/extraction of special forces, search and rescue, and amphibious missions, making reliability and performance non-negotiable.
After evaluating suppliers, materials, design specifications, and logistics, it is essential to partner with manufacturers that demonstrate proven experience in defense-grade inflatable boat production, adherence to military standards (such as NATO or MIL-SPEC certifications), and a track record of durability under extreme conditions. Key considerations include the boat’s material resilience (e.g., hypalon or PVC), engine compatibility, payload capacity, stealth features, and ease of deployment and maintenance.
Furthermore, long-term support, training, spare parts availability, and warranty provisions should be integral to the procurement decision. Engaging in thorough due diligence, conducting live demonstrations, and potentially initiating phased procurement or pilot programs can mitigate risks and ensure mission readiness.
In conclusion, a successful sourcing strategy for military rubber boats must prioritize performance, reliability, and vendor credibility, ensuring the acquisition of assets that enhance operational effectiveness and support the safety and success of military personnel in demanding environments.