The global microwave oven market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising consumer demand for convenience appliances and technological advancements in kitchen electronics. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global microwave oven market was valued at USD 11.87 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 16.34 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 5.47% during the forecast period. This expansion is mirrored in the increasing demand for reliable and high-performance components such as microwave diodes—critical for converting electrical energy into microwave radiation in magnetron systems. As microwave oven production scales across Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe, manufacturers of key internal components, including high-voltage diodes, are seeing intensified competition and innovation. The following list highlights the top 10 microwave oven diode manufacturers shaping this growing ecosystem, selected based on production volume, technical capabilities, global reach, and industry reputation.
Top 10 Microwave Oven Diode Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Macom
Domain Est. 1991
Website: macom.com
Key Highlights: MACOM designs and manufactures high-performance semiconductor products for the Telecommunications, Industrial and Defense, and Data Center industries….
#2 Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: This is Murata Manufacturing’s products-related website. You can view electronic component information, product and event news, exhibition, campaign and ……
#3 Vishay Intertechnology
Domain Est. 1995
Website: vishay.com
Key Highlights: Vishay electronic component solutions – MOSFETs, ICs, Diodes & Rectifiers, Optoelectronics, Resistors, Sensors, Inductors, Custom Magnetics, and Capacitors….
#4 Electronic Devices Inc.
Domain Est. 1999
Website: e-edi.com
Key Highlights: EDI designs & manufactures specialty rectifiers including high voltage fast recovery diodes, bridges, assemblies, and night vision components….
#5 SemiGen: RF/Microwave Assembly, Hi
Domain Est. 2009
Website: semigen.net
Key Highlights: SemiGen is a full service RF and Microwave manufacturer providing design, engineering, contract assembly, high frequency testing, and hi-rel screening/…
#6 Mini
Domain Est. 1995
Website: minicircuits.com
Key Highlights: Mini-Circuits is a global leader in the design and manufacturing of RF, IF, and microwave components from DC to 86GHz….
#7 Maury Microwave
Domain Est. 1996
Website: maurymw.com
Key Highlights: We design and manufacture the most advanced RF, microwave, and millimeter-wave products for precision calibration, device characterization, and measurement ……
#8 Global Communication Semiconductors, LLC
Domain Est. 1998
Website: gcsincorp.com
Key Highlights: New foundry process announcement includes mmW HBT, wide tuning range varactor, BAW filter and low voltage GaN/Si foundry processes. Please contact the foundry ……
#9 Diodes
Domain Est. 2000
Website: martinmicrowave.com
Key Highlights: 4-day delivery 30-day returns12KV Microwave Oven High Voltage Diode # CL04-12A 500ma. MSRP: Now: $14.99 Was: Add to Cart. 12KV Microwave Oven High Voltage Diode w/ Lead Wire HVR1X …
#10 Diodes
Domain Est. 2000
Website: microwaves101.com
Key Highlights: Diodes are two-terminal, nonlinear semiconductors used for generating, mixing, detection, and switching of microwave signals….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Microwave Oven Diode
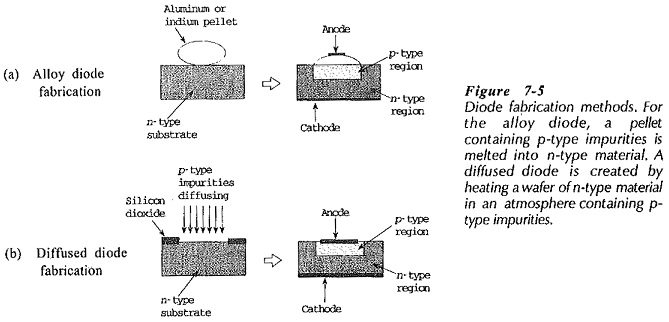
Microwave Oven Diode Market Trends in 2026
The global microwave oven diode market is expected to undergo significant transformation by 2026, shaped by evolving consumer demands, technological innovations, and shifts in manufacturing ecosystems. As a critical component in microwave ovens—responsible for converting AC voltage into DC to power the magnetron—the diode remains essential despite incremental advances in appliance design. This analysis examines key trends influencing the microwave oven diode market in 2026 under the broader context of home appliance electronics and energy efficiency standards.
Rising Demand for Energy-Efficient and Smart Appliances
By 2026, consumer preference for energy-efficient and smart kitchen appliances is driving innovation across the microwave oven supply chain. Microwave oven diodes are being optimized to support low-power operation and enhanced durability to align with energy-saving designs. Manufacturers are increasingly integrating diodes with higher surge current tolerance and lower forward voltage drops to reduce energy loss. Furthermore, in smart ovens with variable power settings and sensor-based cooking, diodes must perform reliably under fluctuating loads, prompting demand for more robust and thermally stable semiconductor materials.
Consolidation in Appliance Manufacturing and Supply Chain Dynamics
The microwave oven industry has seen consolidation among major OEMs, with companies like Whirlpool, Panasonic, Samsung, and LG dominating global production. This concentration is streamlining component procurement, including microwave oven diodes, leading to long-term supply agreements and tighter quality specifications. As a result, diode suppliers are investing in automated production lines and ISO-certified facilities to meet stringent OEM requirements, particularly in regions such as Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe where assembly hubs are expanding.
Shift Toward High-Voltage and Miniaturized Diode Designs
In response to space constraints in compact and over-the-range microwave ovens, diode manufacturers are focusing on miniaturization without compromising performance. By 2026, high-voltage silicon diodes with ratings above 12 kV and compact form factors are becoming standard. Additionally, advancements in encapsulation materials—such as enhanced epoxy resins—are improving thermal dissipation and resistance to moisture, extending diode lifespan in high-humidity environments.
Regional Market Growth and Emerging Economies
Asia-Pacific remains the largest market for microwave ovens—and by extension, microwave oven diodes—due to rising urbanization and disposable incomes in countries like India, Indonesia, and Vietnam. Local production incentives and government support for domestic electronics manufacturing are encouraging regional diode fabrication, reducing reliance on imports. In contrast, mature markets in North America and Western Europe are seeing slower growth but higher demand for premium, durable components as consumers upgrade to longer-lasting appliances.
Sustainability and Regulatory Influences
Environmental regulations such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH are shaping material choices in diode production. By 2026, lead-free soldering and halogen-free encapsulation are becoming industry norms. Moreover, extended producer responsibility (EPR) policies are pushing manufacturers to design for recyclability, influencing diode packaging and integration methods. Some companies are exploring recyclable metal-ceramic packaging as a sustainable alternative to traditional plastic housings.
Technological Substitution and Future Outlook
Although solid-state microwave technologies using RF amplifiers may eventually reduce reliance on magnetron-based systems—and thus on high-voltage diodes—such shifts remain limited to niche premium products as of 2026. The widespread adoption of vacuum tube magnetrons ensures continued demand for microwave oven diodes. However, diode manufacturers are diversifying into adjacent markets such as induction heating and industrial microwave systems to hedge against future technological disruption.
In conclusion, the microwave oven diode market in 2026 is characterized by steady demand, driven by global appliance production and incremental technological refinements. While not a high-growth semiconductor segment, it remains a stable market underpinned by reliability requirements, regulatory compliance, and regional manufacturing trends. Suppliers who invest in quality, sustainability, and customization will be best positioned to capture value in this mature yet essential component space.
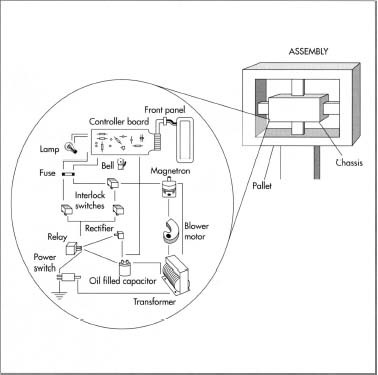
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Microwave Oven Diode (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing microwave oven diodes—critical components in high-voltage power circuits—requires careful attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance failures, safety hazards, or legal complications. Below are some common pitfalls encountered during the procurement process.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Substandard Material and Construction
One of the most frequent issues is receiving diodes made from inferior materials or with poor manufacturing practices. Low-quality diodes may use subpar silicon wafers, inadequate encapsulation, or inconsistent doping, leading to early failure under high-voltage stress. This can result in arcing, overheating, or complete breakdown in the microwave’s high-voltage circuit.
2. Inaccurate Electrical Specifications
Some suppliers, especially non-reputable ones, may provide diodes with misleading voltage and current ratings. For example, a diode advertised as 12kV may fail at much lower voltages due to inadequate reverse breakdown characteristics. This misrepresentation can compromise the safety and reliability of the entire microwave oven.
3. Lack of Certifications and Testing
Genuine microwave diodes should comply with safety standards such as UL, CE, or RoHS. Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide certification documentation increases the risk of using non-compliant parts. Additionally, absence of batch testing reports or traceability makes it difficult to ensure consistent quality.
4. Counterfeit or Recycled Components
In gray markets, counterfeit diodes—often harvested from discarded appliances and remarked—are common. These parts may appear new but have degraded performance due to prior use. Their inclusion can lead to unexpected failures and shorten appliance lifespan.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
1. Unauthorized Cloning or Reverse Engineering
Some manufacturers produce diodes that closely mimic the design and packaging of branded components (e.g., Panasonic, Toshiba) without proper licensing. While functionally similar, these clones may infringe on patented semiconductor designs or trademarked product forms, exposing buyers to potential IP litigation.
2. Misuse of Brand Logos and Part Numbers
Suppliers may falsely label generic diodes with well-known brand names or part numbers to imply authenticity. This not only violates trademark laws but also misleads purchasers about performance and origin, increasing liability risk.
3. Lack of IP Due Diligence in Sourcing Regions
Procuring from regions with weak IP enforcement may result in unintentional involvement with products that infringe on existing patents. Buyers assuming “functional equivalence” may still face legal exposure if the component design violates protected technology.
4. No Licensing Agreements or IP Warranties
Reputable suppliers often provide IP indemnification clauses in contracts. When sourcing cheaper alternatives, such legal protections are typically absent, leaving the buyer fully exposed if infringement claims arise post-purchase.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, buyers should source microwave oven diodes only from authorized distributors or OEM-approved manufacturers. Conducting supplier audits, verifying certifications, and ensuring clear IP terms in procurement agreements are essential steps to ensure both quality and legal compliance.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Microwave Oven Diode
Product Overview
A microwave oven diode is a high-voltage component used in the power supply circuit of microwave ovens to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) for the magnetron. It operates under high voltage and temperature conditions and must meet strict safety and performance standards.
Classification & HS Code
- HS Code: 8548.90.00 (Other electrical machine parts, not elsewhere specified)
Note: Confirm with local customs; some jurisdictions may classify under 8504.40 (diodes) or 8536.50 (electrical apparatus for circuits).
Packaging Requirements
- Primary Packaging: Anti-static bags or blister packs to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD).
- Secondary Packaging: Rigid inner boxes with cushioning (e.g., foam inserts) to prevent physical damage.
- Outer Packaging: Corrugated cardboard boxes marked with fragile and ESD-sensitive labels.
- Quantity per Carton: Clearly labeled; typically 100–500 units depending on size and weight.
Shipping & Transportation
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for air, sea, or land freight.
- Labeling:
- Proper shipping name: “Electronic Components – Not Restricted”
- UN number not typically required (non-hazardous)
- Include handling labels: “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Protect from Moisture”
- Temperature & Humidity: Store and transport in dry environments; avoid condensation. Ideal range: 10°C–30°C, <70% relative humidity.
- Stacking: Max 5–6 layers; avoid excessive pressure on lower cartons.
Regulatory Compliance
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Must comply with EU Directive 2011/65/EU (lead, cadmium, mercury, etc., within limits).
- REACH (SVHC): Confirm no substances of very high concern are present.
- WEEE (Waste Electrical Equipment): Marking not required on components, but manufacturer must comply with take-back obligations.
- Proposition 65 (California): Diodes may contain lead; ensure proper warnings if applicable.
Safety Standards & Certifications
- IEC/EN 60664-1: Insulation coordination for equipment within low-voltage systems.
- UL Recognized Component (File No. E####): Required for sale in North America.
- CB Scheme Certification: Facilitates global market access (IEC 60065 or IEC 60335-2-25).
- CE Marking: Mandatory for EU; indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental standards.
Import/Export Documentation
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Certificate of Origin
- RoHS/REACH Compliance Declaration
- Manufacturer’s Test/Compliance Report (e.g., UL File)
- Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
Storage Guidelines
- Environment: Dry, clean, temperature-controlled warehouse.
- Shelf Life: Indefinite if stored properly; inspect for corrosion or packaging damage after long storage.
- Handling: Personnel should use ESD-safe practices (wrist straps, grounded workstations).
End-of-Life & Disposal
- Recycling: Diodes contain recoverable metals (e.g., copper, silicon); recycle via certified e-waste handlers.
- Disposal: Not classified as hazardous waste if RoHS compliant; follow local electronic waste regulations.
Notes for Distributors & Resellers
- Verify compliance documentation before import.
- Retain technical files and certificates for audits.
- Label end products with appropriate safety certifications.
Always consult local regulations and update compliance status regularly due to evolving standards.
In conclusion, sourcing a microwave oven diode requires careful consideration of several key factors including voltage and current ratings, physical dimensions, compatibility with the specific microwave model, and adherence to safety standards. It is essential to obtain replacement diodes from reputable suppliers or manufacturers to ensure reliability and performance. Due to the high-voltage environment in which these components operate, using a diode that meets or exceeds the original specifications is critical to avoid premature failure or safety hazards. Additionally, proper handling and installation precautions should be observed to protect both the component and the technician. Ultimately, a well-sourced microwave oven diode contributes to the safe and efficient operation of the appliance, extending its service life and ensuring optimal performance.