The global microdrip irrigation market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for water-efficient agricultural practices and increasing adoption of precision farming technologies. According to Grand View Research, the global drip irrigation market size was valued at USD 5.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.3% from 2023 to 2030. A key contributor to this growth is the increasing deployment of microdrip systems, which offer superior water application efficiency, particularly in arid regions and high-value crop cultivation. Mordor Intelligence further projects that the drip irrigation market will expand at a CAGR of over 11% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, citing advancements in emitter technology and government initiatives promoting water conservation as critical drivers. As demand surges, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation, scalability, and global distribution in the microdrip segment—setting the benchmark for performance, durability, and smart integration. Below are the top seven microdrip manufacturers shaping the future of sustainable irrigation.
Top 7 Microdrip Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
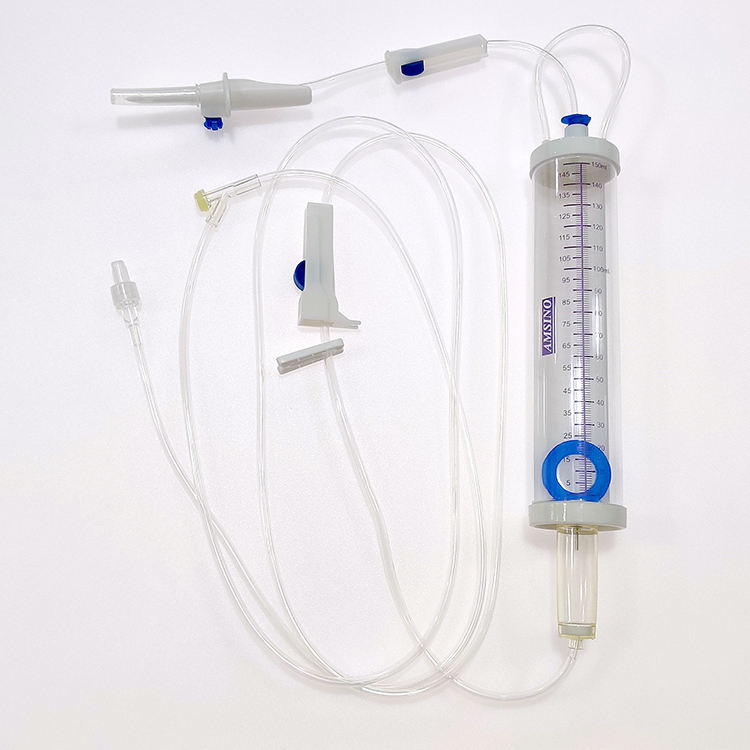
#1 Assembled Burette W/ Drip Chamber
Domain Est. 2006
Website: lily-medical.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.8 The Assembled Burette with Drip Chamber is a precision medical device designed for accurate fluid measurement and controlled infusion in clinical settings….
#2 N
Domain Est. 2018
Website: ndrip.com
Key Highlights: N-Drip transforms agriculture with disruptive, precise irrigation technology that conserves water, reduces energy and fertilizer use, and enhances yield ……
#3 I.V. Infusion Sets
Domain Est. 1998
Website: polymedicure.com
Key Highlights: I.V. Infusion Set with Micro Drip & Flow Regulator · Flow regulator integrated into I.V. infusion set for precise flow control · Flow rate 5ml/hr to 250ml/hr ……
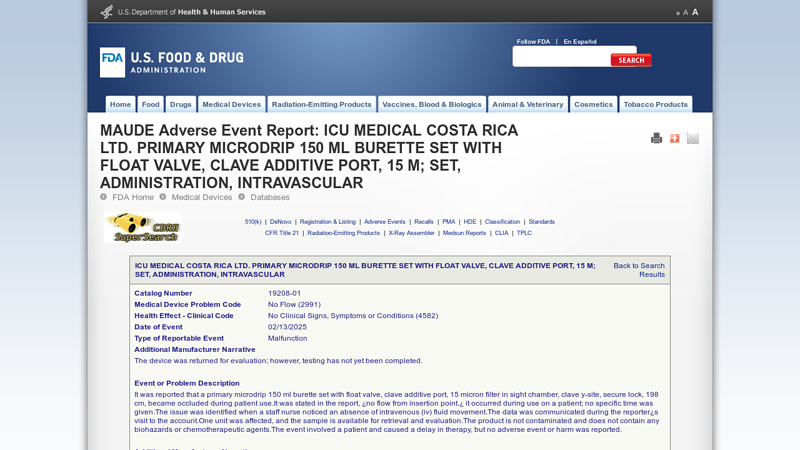
#4 MAUDE Adverse Event Report
Domain Est. 2000
Website: accessdata.fda.gov
Key Highlights: It was reported that a primary microdrip 150 ml burette set with float valve, clave additive port, 15 micron filter in sight chamber, clave y-site, ……
#5 Gardena micro drip irrigation Canada
Domain Est. 2016
#6 Microdrip Infusion Set
Domain Est. 2017
Website: yashcarelifescience.com
Key Highlights: Our Microdrip Infusion Set provides accurate control over fluid delivery, thanks to its carefully calibrated drip mechanism. Suitable for a wide range of ……
#7 Micro Drip Set, Polymed
Domain Est. 2021
Website: biomedsuppliers.com
Key Highlights: This Micro Drip Set is a premium quality micro drip iv set. This micro drip infusion set is manufactured by using quality assured material and advanced ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Microdrip

H2 2026 Market Trends Analysis for Microdrip Irrigation Systems
The microdrip irrigation sector is poised for significant evolution in the second half of 2026 (H2 2026), driven by escalating water scarcity, advancements in smart agriculture technologies, and supportive government policies promoting sustainable farming. This analysis explores key market trends shaping the microdrip industry during this period.
1. Accelerated Adoption in Emerging Economies
H2 2026 will see a surge in microdrip adoption across developing regions—particularly in South Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, and Latin America. Governments in countries like India, Kenya, and Brazil are expected to expand subsidies and launch large-scale irrigation modernization programs. These initiatives are designed to improve agricultural productivity amid climate volatility, directly boosting demand for affordable and efficient microdrip systems.
2. Integration with Smart Farming Technologies
The convergence of microdrip systems with IoT, AI, and sensor-based monitoring is becoming mainstream. By H2 2026, leading manufacturers are offering “smart microdrip” solutions featuring real-time soil moisture sensors, automated flow control, and cloud-based farm management platforms. These integrations enable precision irrigation, reducing water usage by up to 40% compared to traditional methods, and are increasingly adopted by commercial and high-value crop farmers.
3. Sustainability and ESG-Driven Investment
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria are influencing investment flows into agricultural technology. Financial institutions and agribusinesses are prioritizing water-efficient irrigation systems as part of climate resilience strategies. Microdrip solutions are increasingly viewed as key tools in reducing agriculture’s carbon and water footprint, attracting venture capital and green financing, particularly in Europe and North America.
4. Product Innovation and Durability Focus
In response to clogging and maintenance challenges, manufacturers are launching next-generation emitters with anti-clogging designs and self-flushing mechanisms. Additionally, there is a growing shift toward UV-resistant and recyclable materials to extend product lifespan and align with circular economy principles. These innovations are expected to reduce operational costs and improve system reliability, supporting wider adoption.
5. Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The microdrip market is experiencing consolidation, with major players like Netafim, Jain Irrigation, and Rain Bird acquiring niche tech startups or forming joint ventures. In H2 2026, partnerships between irrigation companies and agritech platforms are becoming common, enabling bundled offerings that combine hardware, software, and data analytics—a trend enhancing customer value and market competitiveness.
6. Regulatory Support and Water Pricing Policies
Increasingly stringent water regulations in drought-prone regions (e.g., California, Southern Europe, and Australia) are compelling farmers to transition to microdrip systems. Additionally, tiered water pricing models penalizing excessive usage are making microdrip irrigation economically advantageous. Policymakers are also integrating microdrip into national adaptation plans under climate agreements, further accelerating market growth.
Conclusion
By H2 2026, the microdrip irrigation market is transitioning from a niche efficiency tool to a core component of global sustainable agriculture infrastructure. Driven by technological innovation, environmental imperatives, and policy support, the sector is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9–11% through 2026. Companies that invest in smart integration, affordability, and scalability will be best positioned to capture emerging opportunities across diverse geographies and crop types.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Microdrip (Quality, IP)
Sourcing microdrip irrigation components—especially from overseas suppliers—can expose buyers to significant risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Being aware of these pitfalls is critical to ensuring system performance, longevity, and legal compliance.
Poor Manufacturing Quality and Inconsistent Performance
Microdrip emitters and tubing must deliver precise, uniform water flow over extended periods. Low-cost suppliers may use substandard materials or inconsistent manufacturing processes, leading to: clogged emitters, uneven water distribution, premature failure, and reduced crop yields. Variability in wall thickness, emitter spacing, or drip rate undermines irrigation efficiency and increases maintenance costs.
Counterfeit or IP-Infringing Products
Many reputable microdrip technologies are protected by patents and trademarks (e.g., Netafim, Rain Bird, Jain Irrigation). Unscrupulous suppliers may offer counterfeit or knockoff products that copy protected designs or branding. Purchasing such items exposes the buyer to legal liability, supply chain disruptions, and reputational damage—especially if used in commercial or government-funded agricultural projects.
Lack of Certification and Compliance
Genuine microdrip systems often carry certifications for agricultural use, durability, and chemical resistance (e.g., ISO standards, NSF, or country-specific marks). Imitation products frequently lack these certifications, making them unsuitable for long-term use and potentially non-compliant with local regulations or subsidy programs.
Inadequate Technical Support and Warranty
Reputable manufacturers provide agronomic support, installation guidance, and warranty coverage. Suppliers of low-quality or infringing microdrip products typically offer little to no technical assistance or recourse when failures occur—leaving buyers without support during critical growing seasons.
Supply Chain and Traceability Risks
When sourcing from unknown or unverified suppliers, traceability of components is often poor. This complicates quality control, makes recalls impossible, and increases the risk of inadvertently supporting unethical labor practices or environmental violations.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should verify supplier credentials, request product certifications, conduct third-party quality inspections, and consult legal experts to ensure IP compliance before placing large orders.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Microdrip
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the handling, transportation, storage, and regulatory adherence related to Microdrip IV administration sets. Adherence to these guidelines ensures patient safety, product efficacy, and regulatory compliance.
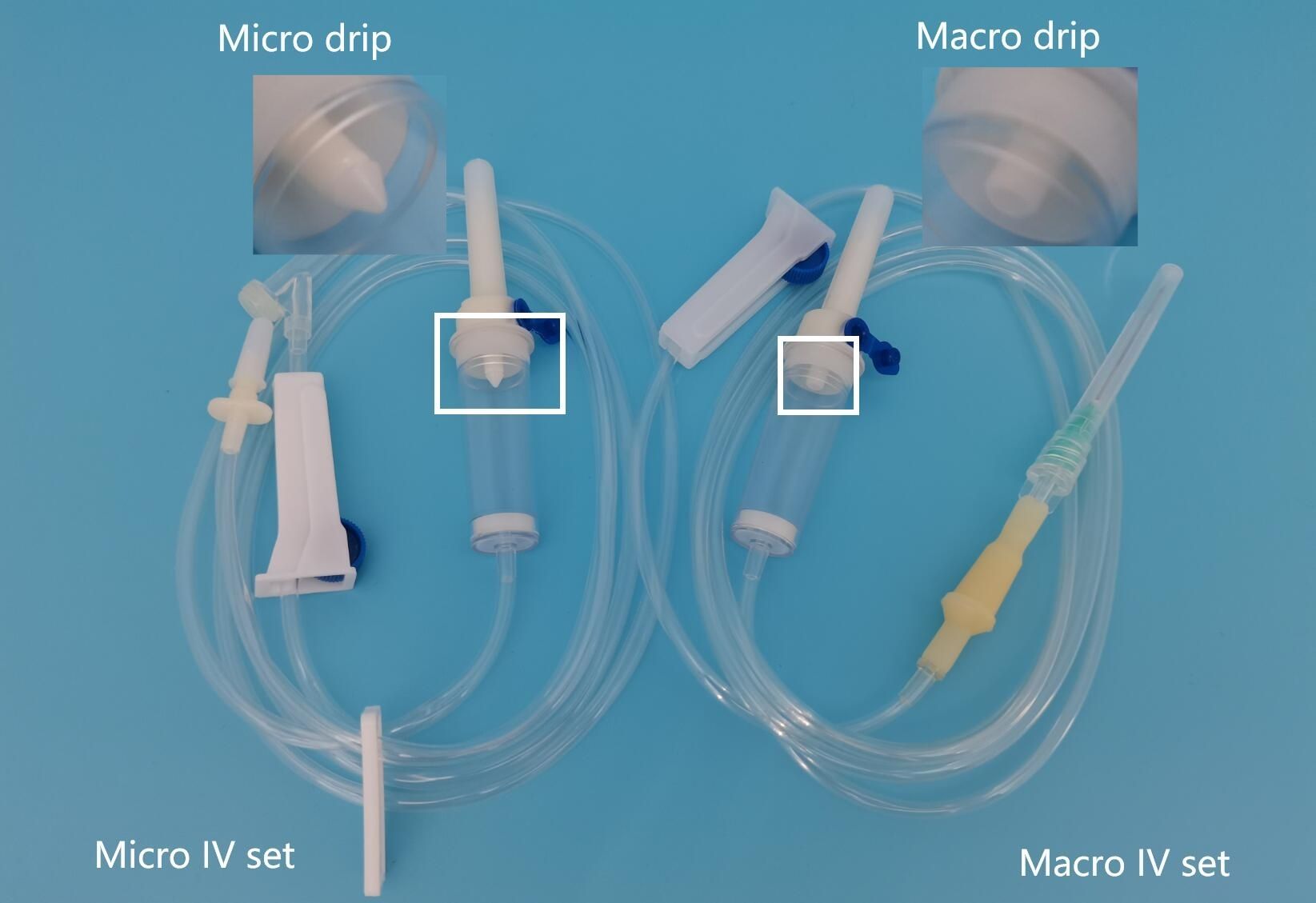
Product Overview
Microdrip IV sets are medical devices used to deliver intravenous fluids at precise, controlled rates. They are typically calibrated at 60 drops per milliliter (gtt/mL), allowing for accurate administration of small fluid volumes, particularly in pediatric, neonatal, or critical care settings.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
FDA Regulations (U.S.)
Microdrip sets are regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as Class II medical devices under 21 CFR Part 880. Compliance includes adherence to:
– Quality System Regulation (QSR) – 21 CFR Part 820
– Premarket Notification (510(k)) clearance
– Medical Device Reporting (MDR) for adverse events
– Unique Device Identification (UDI) requirements
– Labeling compliance per 21 CFR Part 801
International Standards
Compliance with international standards is required for global distribution:
– ISO 13485:2016 – Quality management systems for medical devices
– ISO 8536-4:2019 – Requirements for infusion sets
– CE Marking (EU MDR 2017/745) for European markets
– Health Canada Medical Devices Regulations (SOR/98-282)
– TGA (Australia) and other local regulatory body requirements
Labeling and Packaging
- All packaging must include UDI codes, lot numbers, expiration dates, and sterile barrier integrity indicators.
- Labeling must be accurate, legible, and include:
- Intended use
- Sterility statement
- Single-use only designation
- Latex-free and phthalate-free declarations (if applicable)
- Storage conditions
Storage and Handling
Environmental Conditions
- Store in a dry, cool environment with temperatures between 15°C and 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
- Protect from direct sunlight, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
- Maintain humidity levels below 60% to prevent packaging degradation.
Shelf Life Management
- Monitor expiration dates closely; do not distribute or use expired products.
- Implement a first-expiry, first-out (FEFO) inventory system.
- Regularly audit stock for expired or damaged units.
Handling Procedures
- Handle with clean, dry hands or gloves to maintain sterility.
- Avoid crushing, puncturing, or compressing packaged units.
- Do not open sterile packaging until point of use.
Transportation and Distribution
Shipping Requirements
- Use validated packaging to protect against physical damage, moisture, and temperature excursions.
- For temperature-sensitive shipments, use validated cold chain packaging if required.
- Ensure compliance with carrier-specific medical device shipping regulations (e.g., FedEx, UPS Healthcare).
Cold Chain (if applicable)
- While most Microdrip sets do not require refrigeration, transport conditions must remain within labeled storage limits.
- Use temperature monitoring devices for long-distance or international shipments.
- Document temperature data throughout transit.
Documentation
- Maintain shipping logs, certificates of conformance, and distribution records.
- Provide distributors and end-users with product inserts, IFUs (Instructions for Use), and safety data.
Inventory Management
Tracking and Traceability
- Utilize barcode or RFID systems to support UDI compliance and traceability.
- Maintain electronic records of lot numbers, quantities, and distribution points.
- Enable rapid recall response if necessary.
Stock Rotation
- Implement FEFO and FIFO (first-in, first-out) practices.
- Conduct regular cycle counts to ensure inventory accuracy.
Risk Management and Recalls
Risk Assessment
- Conduct risk analysis per ISO 14971 for all potential failure modes (e.g., packaging breach, contamination).
- Document risk controls for logistics processes.
Recall Procedures
- Establish a formal recall plan aligned with FDA and international requirements.
- Ensure the ability to quickly identify and retrieve affected lots.
- Notify regulatory bodies and customers within required timeframes.
Training and Personnel
Staff Training
- Train logistics, warehouse, and distribution staff on:
- Medical device handling protocols
- Regulatory compliance
- UDI and labeling requirements
- Recall procedures
- Maintain training records and conduct annual refreshers.
Audits and Quality Assurance
Internal Audits
- Conduct regular audits of storage, handling, and distribution processes.
- Verify compliance with ISO 13485 and FDA QSR.
Supplier and Distributor Oversight
- Qualify and monitor third-party logistics (3PL) providers.
- Ensure distributors comply with local regulations and storage requirements.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for Microdrip IV sets is critical to ensuring patient safety and regulatory adherence. By following this guide, organizations can maintain product integrity, meet global regulatory standards, and support reliable healthcare delivery. Regular review and updates to procedures are recommended to reflect evolving regulations and best practices.
Conclusion on Sourcing Microdrip Irrigation Systems
In conclusion, sourcing microdrip irrigation systems requires a strategic approach that balances cost, quality, reliability, and suitability for specific agricultural or landscaping needs. Microdrip systems offer significant benefits, including water efficiency, reduced runoff, precise delivery to plant roots, and lower energy requirements, making them a valuable investment for sustainable water management.
When sourcing microdrip components, it is essential to evaluate suppliers based on product durability, technical support, availability of parts, and compliance with industry standards. Local suppliers may offer quicker delivery and better after-sales service, while international suppliers might provide cost advantages or access to innovative technologies. Additionally, considering factors such as climate conditions, crop type, and system scalability ensures that the selected equipment will perform effectively over time.
Ultimately, selecting the right microdrip system from a reliable source contributes to long-term water conservation, improved crop yields, and operational efficiency. A well-informed sourcing decision supports both environmental sustainability and economic viability in irrigation management.