The global demand for precision electronics repair and miniaturized circuitry has driven rapid growth in the micro soldering equipment market, with increasing adoption in sectors such as telecommunications, medical devices, aerospace, and consumer electronics. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global soldering equipment market was valued at USD 4.27 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2024 to 2029, fueled by advancements in surface-mount technology (SMT) and the rising need for high-accuracy soldering tools. A key segment within this expansion is micro soldering irons—specialized tools designed for fine-pitch components and intricate PCB work—which are seeing heightened demand from electronics manufacturers and repair professionals alike. As the industry evolves, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, precision, and reliability. Below is a curated list of the top 9 micro soldering iron manufacturers shaping the future of electronic assembly and repair.
Top 9 Micro Soldering Iron Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
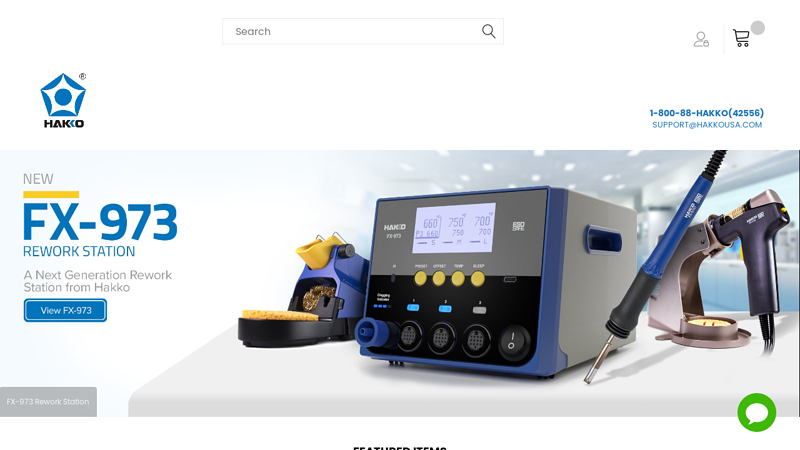
#1 American Hakko Products, Inc. of superior quality soldering …
Domain Est. 1997
Website: hakkousa.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $25We have been a leading producer and distributor of superior quality tools for soldering, desoldering, hot air, rework, and fume extraction systems….
#2 TAIYO ELECTRIC IND.CO.,LTD.|A comprehensive manufacturer of …
Domain Est. 2001
Website: en.goot.jp
Key Highlights: We are a one-stop soldering iron manufacturer that conducts research, development, design, manufacturing, and sales in a wide range of fields from household ……
#3 X-Tronic USA
Domain Est. 2011
Website: xtronicusa.com
Key Highlights: X-Tronic SX-90 • Platinum Series • 85W Precision Micro Soldering Iron Station • Lead Free • 3 Temp Presets • Temp in 4 Seconds • Calibration, Hibernation, & C°/ ……
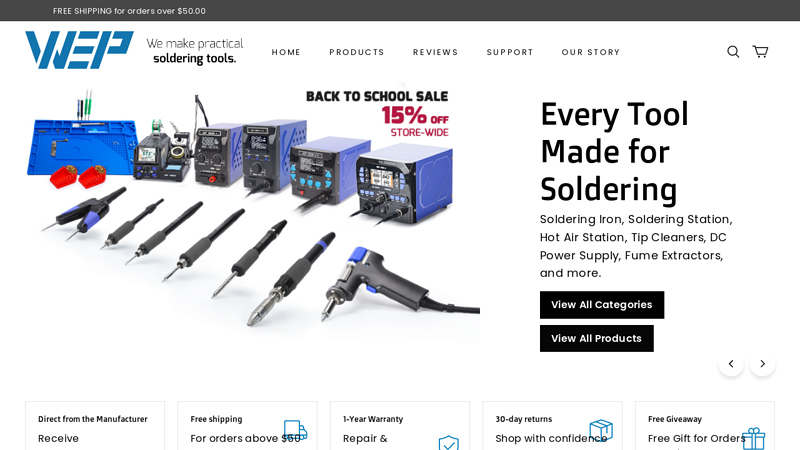
#4 WEP Tools
Domain Est. 2022 | Founded: 2000
Website: weptools.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $50 Free 30-day returnsWe are a soldering tool manufacturer since 2000, we’ve evolved from producing soldering irons for radios to crafting precision tools for t…
#5 Soldering Irons
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hisco.com
Key Highlights: $12.95 delivery 30-day returnsMicro Soldering Iron Handpiece Only redirect to product page. Compare. Hakko · Micro Soldering Iron Handpiece Only. Part #FM2032-51-3021. MFG #FM2032-…
#6 Soldering Tools & Supplies
Domain Est. 1997
#7 Soldering and Rework equipment for electronics
Domain Est. 2002
Website: jbctools.com
Key Highlights: JBC Tools is a leading global company specializing in advanced soldering and rework solutions. Offering high-performance soldering stations, irons, ……
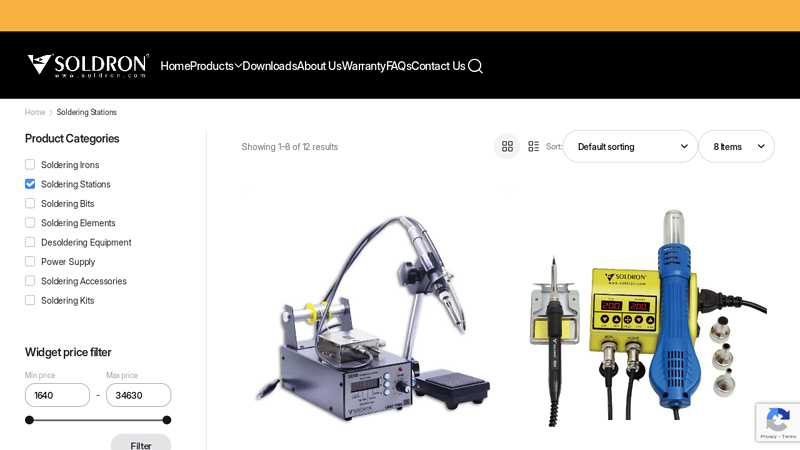
#8 Soldering Stations
Domain Est. 2006
Website: soldron.com
Key Highlights: 35+ Years of Indian Expertise. Proudly designed and manufactured in India for over three decades, Soldron® delivers soldering tools meeting global standards for ……
#9 Micro Soldering
Domain Est. 2010
Website: weller-tools.com
Key Highlights: We are the experts for micro soldering. Read more about Weller’s micro soldering equipment for the widest range of applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Micro Soldering Iron
2026 Market Trends for Micro Soldering Irons
The global market for micro soldering irons is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in electronics miniaturization, growing demand for precision tools in high-tech industries, and the expansion of repair and prototyping ecosystems. This analysis explores the key trends shaping the micro soldering iron market in the coming years.
Rising Demand from Electronics Manufacturing and Repair
As consumer electronics continue to shrink in size—particularly smartphones, wearables, and IoT devices—there is an increasing need for tools capable of handling fine-pitch components and micro-soldering tasks. Micro soldering irons, with tip sizes ranging from 0.2 mm to 1.0 mm, are becoming essential in both automated and manual assembly processes. The booming electronics repair industry, fueled by right-to-repair legislation and sustainability initiatives, is further amplifying demand. By 2026, the repair segment is expected to account for over 40% of micro soldering iron sales, particularly in North America and Europe.
Technological Advancements in Precision and Control
Innovation in temperature control, tip design, and ergonomic features is a major driver in the micro soldering iron market. Leading manufacturers are integrating digital temperature displays, USB-C power delivery, and quick-swap tip systems to enhance usability and precision. Advanced models now offer temperature accuracy within ±1°C and recovery times under two seconds, critical for working with sensitive surface-mount devices (SMDs). The adoption of ceramic heating elements over traditional copper coils improves longevity and thermal efficiency, making these tools more suitable for industrial and professional applications.
Expansion of DIY and Maker Communities
The proliferation of maker spaces, STEM education programs, and home-based electronics hobbyists is contributing to increased consumer adoption of micro soldering irons. Affordable, benchtop-friendly models from brands like Hakko, Weller, and Pinecil are gaining popularity on e-commerce platforms. By 2026, the consumer segment is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.5%, supported by accessible pricing, online tutorials, and open-source hardware projects.
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the micro soldering iron market by 2026, driven by China’s vast electronics manufacturing base and India’s growing electronics assembly sector. Meanwhile, North America and Western Europe are seeing strong growth due to stricter environmental regulations and increased investment in advanced electronics repair infrastructure. Emerging markets in Latin America and Africa are also showing potential, with rising smartphone penetration creating demand for repair tools.
Sustainability and Circular Economy Influences
Environmental concerns are reshaping product design and consumption patterns. In response, manufacturers are focusing on modular, repairable soldering irons with replaceable tips and heating elements to reduce electronic waste. Some companies are introducing take-back programs and recyclable packaging, aligning with broader circular economy trends. Regulatory pressure in the EU and Canada is expected to accelerate these sustainable practices by 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, the micro soldering iron market will be characterized by heightened demand for precision, innovation in user-centric design, and expansion across both industrial and consumer segments. As electronics continue to evolve in complexity and scale, micro soldering tools will remain indispensable, with market growth supported by technological progress, environmental awareness, and the global push for repairability.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Micro Soldering Irons (Quality & IP)
Sourcing micro soldering irons—especially for precision electronics repair, medical devices, or aerospace applications—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to poor performance, equipment failure, legal risks, or even safety hazards. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Temperature Control and Thermal Stability
Many low-cost micro soldering irons suffer from inconsistent temperature regulation. Inadequate feedback mechanisms or substandard heating elements can cause temperature swings, leading to cold joints or component damage. Always verify precise temperature accuracy (±2°C or better), fast thermal recovery, and compatibility with fine tip sizes.
Substandard Build Quality and Materials
Cheaply manufactured irons often use inferior materials in tips, heating cores, and insulation. This results in short lifespans, oxidation-prone tips, and potential safety risks like electrical leakage. Prioritize brands with proven track records, OEM certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), and transparent sourcing of components.
Lack of IP Compliance and Counterfeit Risk
A major risk when sourcing from generic suppliers—especially online marketplaces—is receiving counterfeit or IP-infringing products. Many low-cost micro soldering stations mimic branded designs (e.g., Hakko, JBC) without licensing, violating trademarks and patents. This exposes your business to legal liability, customs seizures, and poor product reliability.
Inadequate or Missing ESD Safety Features
Micro soldering often involves sensitive components vulnerable to electrostatic discharge (ESD). Some budget irons lack proper grounding, ESD-safe handles, or compliance with IEC 61340-5-1. Always confirm ESD protection features and certification to avoid damaging sensitive electronics during repair.
Non-Compliant with Safety and EMC Standards
Many imported micro soldering irons fail to meet regional safety standards like CE, UL, or RoHS. Using non-compliant tools can violate workplace safety regulations and increase fire or electrical hazard risks. Demand documentation proving compliance with relevant standards in your target market.
Unsupported Firmware and Proprietary Interfaces
Some advanced micro soldering stations rely on proprietary software or firmware. Sourcing from obscure manufacturers may mean no access to updates, calibration tools, or technical support. This creates long-term maintenance challenges and potential obsolescence.
Hidden Costs from Poor Compatibility
Low-cost irons may use non-standard tip geometries or connectors, limiting your ability to source replacement tips or accessories. This leads to higher long-term costs and downtime. Confirm tip interchangeability and availability before purchasing.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Source from authorized distributors or reputable OEMs.
– Request compliance documentation (CE, RoHS, ESD, IP rights clearance).
– Verify warranty terms and technical support availability.
– Conduct sample testing for thermal performance and build quality.
– Consult legal counsel when sourcing near-clone products to assess IP risks.
By focusing on both technical quality and intellectual property integrity, you ensure reliable performance and protect your organization from legal and operational risks.
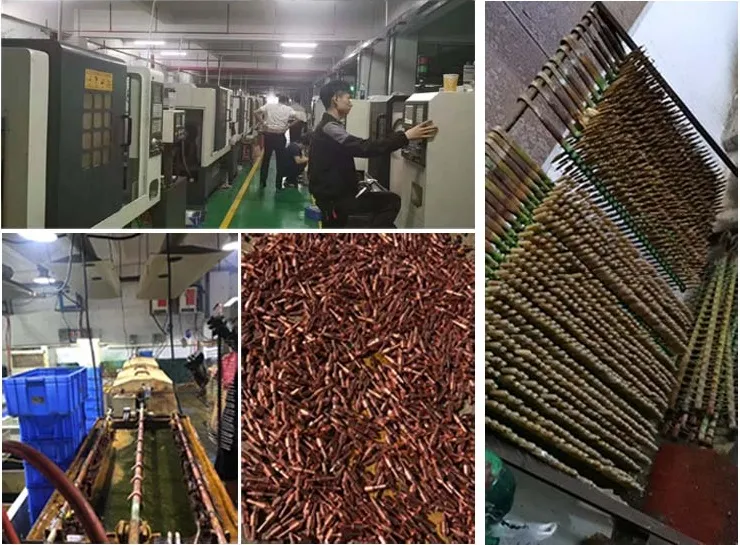

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Micro Soldering Irons
Ensure safe, legal, and efficient global movement of micro soldering irons by adhering to these critical logistics and compliance requirements.
1. H2: Regulatory Compliance & Certification
-
Electrical Safety:
- Mandatory: Obtain certification from recognized bodies:
- North America: UL/ETL Listing (UL 61010-1 for Lab Equipment, UL 60950-1/UL 62368-1 for IT Equipment, or UL 499 for Heating Appliances – specific to soldering irons).
- European Union: CE Marking based on Low Voltage Directive (LVD 2014/35/EU) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive (2014/30/EU). Requires testing to harmonized standards like EN 61010-1 and EN 55014-1/EN 55014-2.
- UK: UKCA Marking (mirroring CE requirements post-Brexit).
- Other Regions: PSE (Japan), CCC (China), KC (South Korea), RCM (Australia/NZ), BIS (India – if applicable). Verify specific national requirements.
- Documentation: Maintain valid test reports, Declarations of Conformity (DoC), and technical files. Label products with certification marks, voltage, power, and manufacturer details.
- Mandatory: Obtain certification from recognized bodies:
-
Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS):
- Compliance: Ensure the soldering iron (and all components) complies with RoHS directives (EU 2011/65/EU, China RoHS, etc.), restricting lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd), hexavalent chromium (Cr6+), PBB, PBDE, and specific phthalates.
- Verification: Obtain RoHS compliance declarations from component suppliers and conduct periodic testing. Maintain records.
-
REACH (EU):
- Compliance: Ensure no Substances of Very High Concern (SVHCs) are present above threshold limits in any component. Provide communication down the supply chain if SVHCs are present >0.1% w/w.
-
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE):
- Producer Responsibility: Register with national WEEE schemes in target markets (e.g., EAR in Germany, Recupel in Belgium). Mark products with the “crossed-out wheeled bin” symbol. Arrange/finance take-back and recycling.
-
Other Regulations:
- FCC (USA): Verify EMC compliance under Part 15 (Class B for residential environments) if applicable (especially for irons with digital controls or wireless features).
- Energy Efficiency: Comply with local regulations (e.g., EU Ecodesign Directive) if applicable (less common for basic soldering irons).
2. H2: Shipping & Transportation Logistics
-
Classification:
- UN Number: Micro soldering irons are generally NOT classified as dangerous goods solely due to the heating element. They are typically shipped as “Not Restricted” or “Consumer Commodity” (ORM-D in US, limited quantity internationally).
- Lithium Batteries (if applicable): CRITICAL: If the iron has a removable rechargeable battery (e.g., Li-ion/Li-poly), the battery must be shipped separately according to UN 3480 (Packing Instruction 965, Section IB). If the battery is non-removable, shipping under UN 3481 (PI 966/967) may apply, but regulations are stricter. Always verify the specific battery configuration.
-
Packaging:
- Protection: Use robust, cushioned packaging (corrugated cardboard, molded pulp, foam inserts) to prevent damage during transit. Protect the delicate tip and heating element.
- Insulation: Ensure the tip is securely insulated or protected to prevent contact with other items or the packaging itself (fire risk if accidentally activated).
- Moisture Protection: Use moisture-resistant materials (e.g., polybags) if shipping to humid environments.
- Marking: Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Way Up,” and required regulatory marks (e.g., CE, UL, RoHS logo, WEEE symbol). Include Safety Data Sheet (SDS) if required by carrier or destination.
-
Documentation:
- Commercial Invoice: Must detail product description (e.g., “Micro Soldering Iron, Model XYZ, 24V DC”), quantity, unit value, total value, country of origin, HS code, and Incoterms® (e.g., FOB, EXW, DDP).
- Packing List: Itemize contents per package.
- Certificate of Origin: Required by some countries for preferential tariffs.
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): While not typically required for the entire device, some carriers or customs authorities might request it, especially concerning solder tips (if containing lead solder residue) or batteries. Have one available.
- Dangerous Goods Declaration (if applicable): Only required if shipping with lithium batteries under UN 3480/3481.
-
Carrier Selection & Handling:
- Standard Freight: Use reputable couriers (DHL, FedEx, UPS) or freight forwarders experienced in electronics. Clearly declare contents.
- Battery Restrictions: Inform the carrier immediately if batteries are included. Comply with their specific requirements for battery shipment.
- Insurance: Ship with adequate insurance covering replacement value.
- Traceability: Use tracking numbers.
3. H2: Import/Export Compliance
- Harmonized System (HS) Code: Obtain the correct 6-10 digit HS code for micro soldering irons (e.g., often 8515.31 or 8515.39 – “Soldering irons and soldering guns”). This determines tariffs, duties, and import regulations. Verify country-specific classifications.
- Customs Duties & Taxes: Calculate applicable import duties, VAT/GST, and other local taxes based on the HS code, value, and origin. Factor these into pricing. Use Incoterms® clearly to define responsibility.
- Import Licenses/Permits: Check if the destination country requires specific import licenses for electrical goods (rare for standard soldering irons, but verify).
- Labeling & Language: Ensure product labels (safety, compliance, instructions) comply with destination country language requirements (e.g., French in Canada, local language in EU member states).
- End-User Documentation: Provide user manuals and safety instructions in the language(s) of the target market.
4. H2: Best Practices & Risk Mitigation
- Supplier Due Diligence: Audit component suppliers for RoHS/REACH compliance and quality.
- Product Testing: Conduct regular safety and performance testing, even after initial certification.
- Stay Updated: Regulations (especially RoHS, batteries, REACH) change. Subscribe to updates from authorities (e.g., EU Commission, CPSC, FCC).
- Consult Experts: Engage with customs brokers, freight forwarders, and regulatory consultants specializing in electronics for complex shipments or new markets.
- Record Keeping: Maintain comprehensive records (certifications, test reports, SDS, shipping docs, declarations) for at least 5-10 years.
- Clear Communication: Ensure internal teams (sales, logistics, engineering) and external partners understand compliance requirements.
Disclaimer: This guide provides general information. Regulations are complex and subject to change. Always consult with qualified legal, regulatory, and logistics professionals for specific advice tailored to your product, components, and target markets before shipping.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Micro Soldering Iron
Sourcing a micro soldering iron requires careful consideration of precision, temperature control, ergonomics, compatibility, and reliability to meet the demands of delicate electronics work such as PCB repair, component rework, and surface-mount technology (SMT) applications. After evaluating various models and suppliers, it is evident that investing in a high-quality micro soldering station—featuring adjustable temperature settings, fine interchangeable tips, quick heat-up time, and ESD safety—is essential for consistent and reliable performance.
Brands like Hakko, JBC, and Metcal offer industry-leading tools known for durability and precision, though at a higher upfront cost; however, their longevity and performance justify the investment for professionals. For hobbyists or those on a tighter budget, reputable mid-range options from brands like Quick, YIHUA, or Weller provide solid functionality and good value.
When sourcing, prioritizing suppliers with genuine products, warranty support, and access to replacement tips and accessories is crucial. Additionally, considering future needs such as modular systems or compatibility with desoldering tools can enhance long-term utility.
In conclusion, selecting the right micro soldering iron involves balancing performance, budget, and reliability. A well-chosen tool not only improves soldering accuracy and efficiency but also reduces the risk of damaging sensitive components, ultimately leading to higher success rates in micro-soldering tasks.