The global micro pump market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across medical devices, automotive systems, industrial automation, and consumer electronics. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 6.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 10.3 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of approximately 7.1% during the forecast period. Key factors fueling this expansion include the increasing adoption of wearable medical devices, advancements in miniaturized electronics, and the growing need for precision fluid control in diagnostic and drug delivery systems. As innovation accelerates and application areas diversify, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders in performance, reliability, and technological advancement. Here’s a look at the top 8 micro pump manufacturers shaping the future of this high-growth industry.
Top 8 Micro Pumps Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Manufacturer of OEM Micro Pumps for Medical, Laboratory and …
Domain Est. 1997
Website: schwarzer.com
Key Highlights: Find the perfect pump for your application here! Schwarzer Precision is a leading manufacturer of OEM micro pumps for gases and liquids….
#2 Micropump
Domain Est. 1994
Website: micropump.com
Key Highlights: Micropump’s positive-displacement magnetically-driven gear pumps are trusted by industry leaders in Printing, Industrial, Transportation and more….
#3 Kamoer: Peristaltic Pump & Diaphragm Pump Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2005
Website: kamoer.com
Key Highlights: Kamoer is a professional micro pump manufacturer in China, specializing in peristaltic pumps, diaphragm pumps, vacuum pumps and lab pumps for medical, ……
#4 TCS Micropumps
Domain Est. 2006
Website: micropumps.co.uk
Key Highlights: TCS Micropumps specialises in the design, development and manufacture of miniature pumps and systems. We manufacture a standard range of patented miniature ……
#5 TCS Micropumps
Domain Est. 2013
Website: tcsmicropumps.co.uk
Key Highlights: By controlling the pumps flow output it is able to give more power to the pump as the pressure increases, so flattening a pumps pressure/flow graph and giving ……
#6 Piezo Pumps
Domain Est. 2017
Website: darwin-microfluidics.com
Key Highlights: 4–6 day delivery 7-day returnsMicropumps from Bartels Mikrotechnik GmbH offer the best compromise between space management and cost efficiency in a microfluidic setup….
#7 Micropump for Liquids & Gases
Website: bartels-mikrotechnik.de
Key Highlights: This piezoelectric membrane micropump seamlessly integrates into fluidic systems, reliably handling liquids, mixtures, and gases….
#8 Micropumps
Website: emft.fraunhofer.de
Key Highlights: An impressive array of highly miniaturized micropumps made from silicon, stainless steel, and titanium, as well as comprehensive dosing system solutions….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Micro Pumps

H2: Emerging Market Trends Shaping the Micro Pumps Industry in 2026
By 2026, the global micro pumps market is poised for significant transformation, driven by converging technological advancements, evolving end-user demands, and shifting global priorities. Key trends emerging in the H2 of 2025 and solidifying through 2026 include:
1. Surge in Demand from Medical & Wearable Health Devices: The proliferation of point-of-care diagnostics, implantable drug delivery systems (e.g., insulin pumps, pain management), and sophisticated wearable health monitors will be the primary growth engine. Miniaturization, ultra-low power consumption, and biocompatibility are critical requirements, pushing innovation in piezoelectric and MEMS-based micro pumps. The aging global population and focus on personalized medicine amplify this trend.
2. Integration of Smart Features and IoT Connectivity: Micro pumps are evolving into “smart” components. By 2026, expect widespread integration of embedded sensors (flow, pressure, temperature), wireless communication (Bluetooth Low Energy, NFC), and onboard microcontrollers. This enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, remote control, and data collection, particularly vital in medical, industrial automation, and analytical instrumentation applications.
3. Advancements in MEMS and 3D Printing Fabrication: Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) technology will continue to dominate for high-precision, ultra-miniature pumps, enabling complex geometries and lower costs at scale. Simultaneously, additive manufacturing (3D printing) using biocompatible and chemically resistant polymers will gain traction, allowing rapid prototyping, customization, and production of novel pump designs previously impossible with traditional methods.
4. Focus on Energy Efficiency and Battery Life: As portable and wearable devices become ubiquitous, minimizing power draw is paramount. This drives demand for highly efficient actuation mechanisms (e.g., advanced piezoelectric materials, electroactive polymers) and optimized pump designs that deliver required flow/pressure with minimal energy, extending device battery life significantly.
5. Expansion in Industrial and Analytical Applications: Beyond healthcare, micro pumps are finding critical roles in lab-on-a-chip systems, portable gas/liquid analyzers, environmental monitoring sensors, and precision manufacturing (e.g., micro-dispensing, inkjet printing). The need for reliability, chemical resistance, and precise fluid handling in harsh environments will fuel demand for robust polymer and ceramic-based micro pumps.
6. Sustainability and Material Innovation: Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will push the industry towards lead-free solders, recyclable materials, and reduced use of hazardous substances. Development of bio-based polymers and improved recycling pathways for end-of-life micro pumps will become increasingly important.
7. Consolidation and Specialization: The market is likely to see consolidation as larger players acquire niche technology firms to broaden their portfolios. Simultaneously, specialized suppliers focusing on specific applications (e.g., medical implants, fuel cells) or technologies (e.g., peristaltic, diaphragm) will thrive by offering deep expertise and customized solutions.
In conclusion, the 2026 micro pump market will be characterized by intelligence, miniaturization, connectivity, and application-specific optimization, with healthcare leading innovation while industrial and analytical sectors provide substantial growth. Success will depend on the ability to deliver reliable, efficient, smart, and sustainable fluidic solutions.
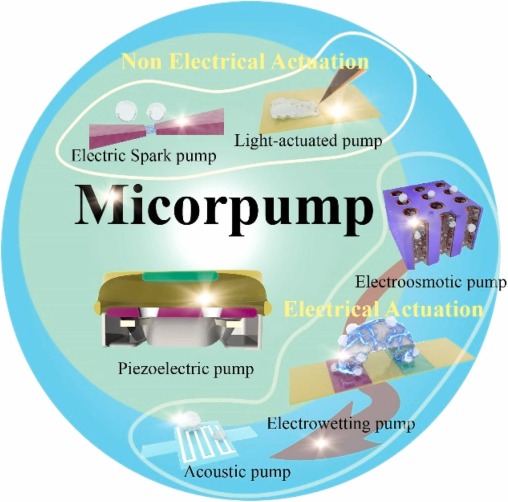
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Micro Pumps: Quality and IP Risks
Sourcing micro pumps for precision applications demands careful attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these areas can lead to product failures, supply chain disruptions, and legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Supplier Vetting
Many buyers select micro pump suppliers based solely on price or lead time, neglecting to evaluate manufacturing capabilities, quality control systems, or industry certifications (e.g., ISO 13485 for medical devices). This can result in inconsistent performance, high defect rates, or non-compliance with regulatory standards.
2. Poor Material and Component Traceability
Low-cost suppliers may use substandard materials or unverified components (e.g., seals, diaphragms, motors) to cut costs. Without full traceability, failures under stress conditions—such as chemical exposure or thermal cycling—can go undetected until late in the product lifecycle.
3. Insufficient Testing and Validation Data
Some suppliers provide only basic performance specs without detailed test reports (e.g., life cycle testing, flow rate consistency, leak rates). Relying on incomplete data increases the risk of field failures, especially in demanding environments like medical or industrial automation.
4. Lack of Process Control and Documentation
Micro pumps require tight tolerances and repeatable assembly processes. Suppliers without robust process documentation or statistical process control (SPC) may deliver inconsistent batches, affecting integration and reliability.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
1. Unprotected Design and Customization
When customizing micro pumps (e.g., form factor, voltage, flow profile), companies often fail to secure IP rights through proper contracts. Suppliers may claim co-ownership or reuse the design for competing clients, undermining competitive advantage.
2. Reverse Engineering and Clone Production
Some offshore suppliers may reverse engineer proprietary pump designs and sell clones to third parties. Without strong contractual prohibitions and monitoring, this leads to market dilution and loss of revenue.
3. Weak Contractual IP Clauses
Supply agreements that lack explicit IP ownership terms, non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), or restrictions on secondary use expose buyers to legal disputes. Ambiguity in who owns tooling, firmware, or design modifications is a common oversight.
4. Inadequate Protection in High-Risk Jurisdictions
Sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk of unauthorized replication. Even with patents, enforcement can be slow or ineffective, making prevention through secure partnerships essential.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough audits of supplier facilities and quality management systems.
- Require full material certifications and batch-level test reports.
- Use clear, legally reviewed contracts that assign IP ownership to the buyer for custom designs.
- Partner with suppliers in jurisdictions with strong IP protections or established reputations for IP integrity.
- Implement design obfuscation or modular architectures to limit exposure of critical IP.
By addressing these quality and IP pitfalls proactively, companies can ensure reliable micro pump performance and protect their innovation investments.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Micro Pumps
Product Classification & Regulatory Overview
Micro pumps fall under precision fluid handling devices used in medical, industrial, and analytical applications. Correct classification under international trade codes (e.g., HS Code 8413) is essential for customs clearance. Depending on end-use, micro pumps may be subject to additional regulations, particularly if integrated into medical devices (e.g., FDA 21 CFR in the U.S. or EU MDR). Always verify product-specific classification with local customs authorities.
Export Controls & Licensing
Micro pumps with specific technical characteristics—such as those used in biotechnology, aerospace, or defense applications—may be subject to export control regulations like the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or the EU Dual-Use Regulation. Determine if your micro pump requires an export license based on destination country, end-user, and technology specifications. Utilize screening tools to check against denied parties lists (e.g., U.S. BIS Denied Persons List).
Packaging & Shipping Requirements
Ensure micro pumps are packed to prevent damage during transit, especially given their sensitive mechanical and electronic components. Use anti-static, shock-absorbent materials and sealed containers to protect against moisture and dust. Label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”) and include necessary shipping documents such as commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
Import Compliance & Duties
Importers must comply with local regulations in the destination country, including conformity assessments, labeling requirements (e.g., CE, UKCA, or FCC marks), and payment of applicable duties and taxes. For micro pumps used in regulated sectors (e.g., healthcare), additional documentation such as Declarations of Conformity or Technical Files may be required at customs. Engage a licensed customs broker when necessary.
Environmental & Safety Regulations
Micro pumps may contain restricted substances under directives such as RoHS (EU) or China RoHS. Confirm compliance with material restrictions and ensure proper labeling and documentation. If pumps contain batteries or pressurized components, adhere to IATA/IMDG regulations for hazardous materials transport. Provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) when applicable.
Documentation & Traceability
Maintain detailed records for compliance audits, including bills of materials, test reports, conformity certificates, and shipping logs. For medical-grade micro pumps, implement a traceability system per ISO 13485 requirements. Accurate documentation supports faster customs processing and regulatory verification.
After-Sales & Returns Logistics
Establish clear procedures for handling returns, repairs, or replacements, particularly across borders. Comply with local waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) rules if pumps are discarded. For international returns, ensure reverse logistics adhere to import/export regulations and consider using regional service hubs to reduce shipping complexity.
Conclusion for Sourcing Micro Pumps
Sourcing micro pumps requires a strategic approach that balances performance, reliability, cost, and supplier capability. After evaluating technical specifications, application requirements, and market options, it is evident that selecting the right micro pump involves more than just comparing price points. Critical factors such as flow rate, pressure capacity, power consumption, size constraints, material compatibility, and duty cycle must align precisely with the intended application—whether in medical devices, industrial automation, consumer electronics, or environmental monitoring.
Additionally, supplier reliability, quality certifications (such as ISO 13485 for medical applications), production scalability, and post-sales support play a significant role in long-term success. Engaging with suppliers early in the design phase can facilitate customization, improve time-to-market, and reduce integration challenges.
In conclusion, an effective micro pump sourcing strategy integrates technical evaluation with supply chain robustness. By prioritizing both performance and partnership, organizations can ensure reliable operation, maintain product quality, and achieve cost-efficiency across their product lifecycle. Continued market monitoring and ongoing supplier relationships will further support innovation and adaptability in an evolving technological landscape.