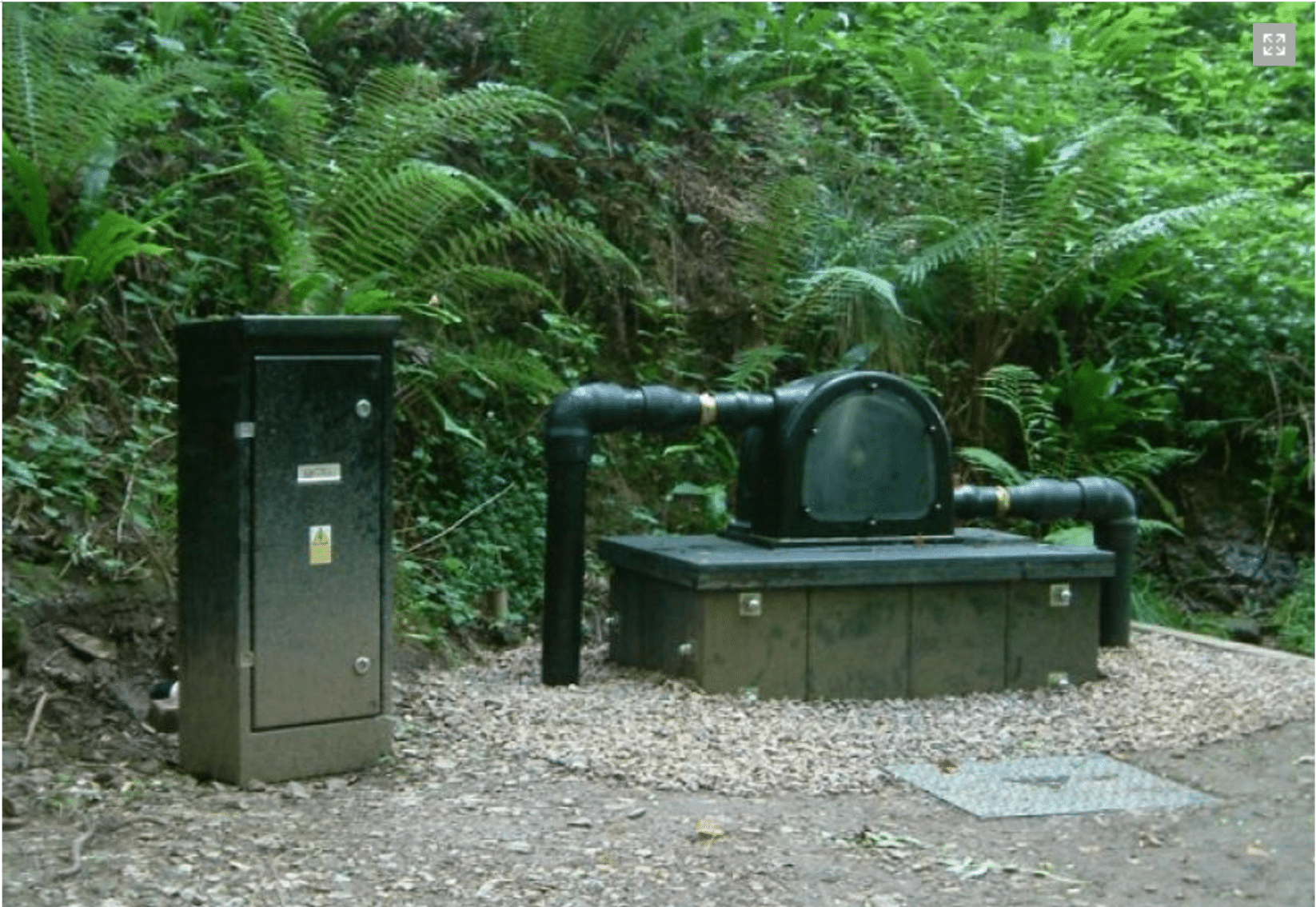
The global micro hydroelectric power generator market is gaining momentum as decentralized and renewable energy solutions become increasingly vital. According to Mordor Intelligence, the small and micro hydropower market was valued at USD 6.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is driven by rising demand for off-grid electricity in remote areas, supportive government policies, and advancements in turbine efficiency and system design. Micro hydro systems—typically defined as installations under 100 kW—are particularly well-suited for rural electrification and sustainable energy projects in mountainous or river-rich regions. As investment in clean energy infrastructure expands worldwide, manufacturers specializing in compact, reliable hydroelectric generators are playing a pivotal role in advancing energy access and resilience. Based on market presence, technological innovation, and project deployment, the following nine companies represent leading manufacturers shaping the future of micro hydroelectric power.
Top 9 Micro Hydroelectric Power Generator Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
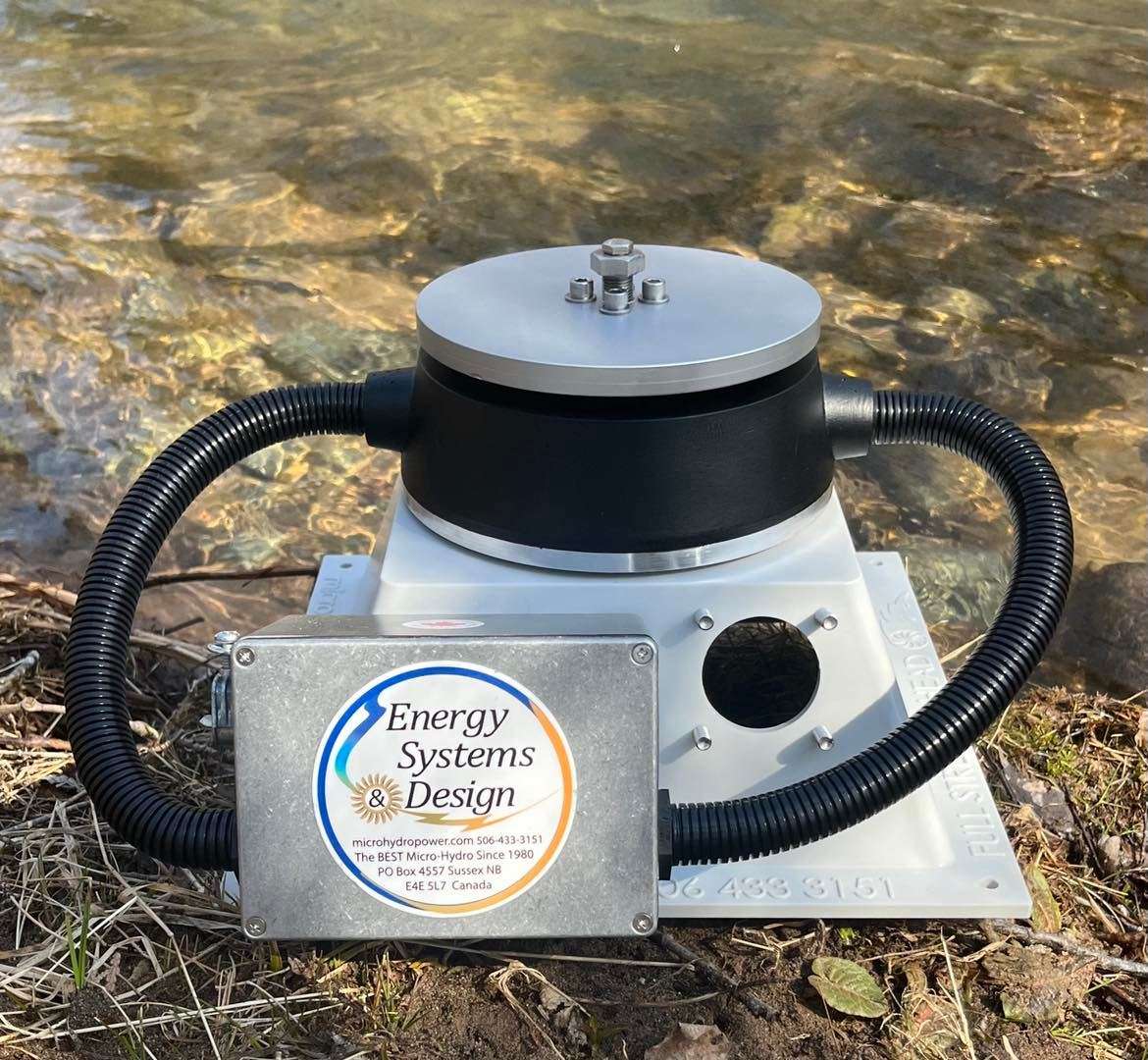
#1 Energy Systems & Design
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1980
Website: microhydropower.com
Key Highlights: Energy Systems & Design is the top international manufacturer of Micro Hydro Electric machines and components since 1980….
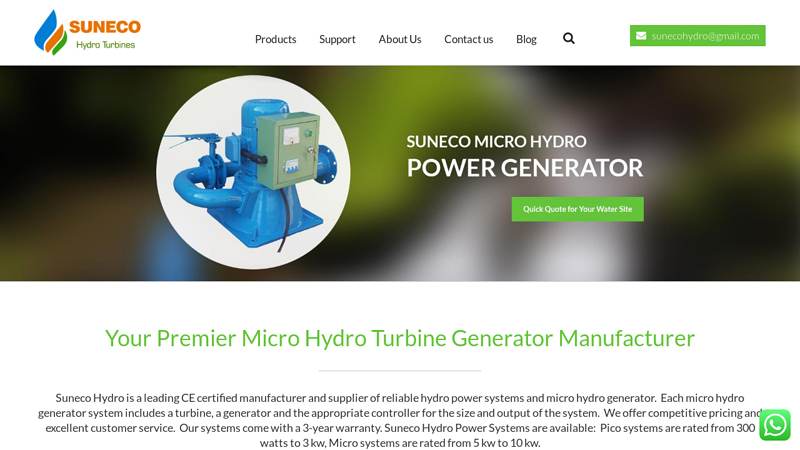
#2 Micro Hydro Turbine Generator Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2010
Website: micro-hydro-power.com
Key Highlights: Suneco Hydro is a leading CE certified manufacturer and supplier of reliable hydro power systems and micro hydro generator….
#3 Capstone Green Energy Holdings, Inc. (CGEH)
Domain Est. 2021
Website: capstonegreenenergy.com
Key Highlights: Our microturbines deliver reliable, high-quality power when and where the grid can’t—while reducing costs, lowering emissions, and operating on a wide range of ……
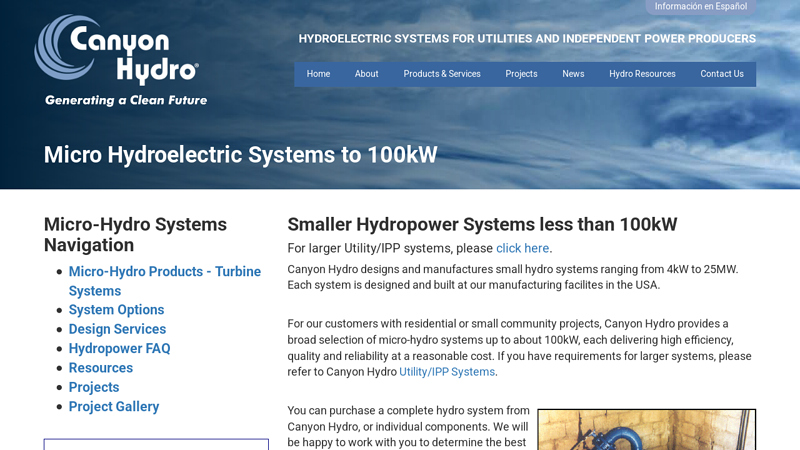
#4 Micro Hydroelectric Systems to 100kW
Domain Est. 2002
Website: canyonhydro.com
Key Highlights: Smaller Hydropower Systems less than 100kW. For larger Utility/IPP systems, please click here. Canyon Hydro designs and manufactures small hydro systems ……
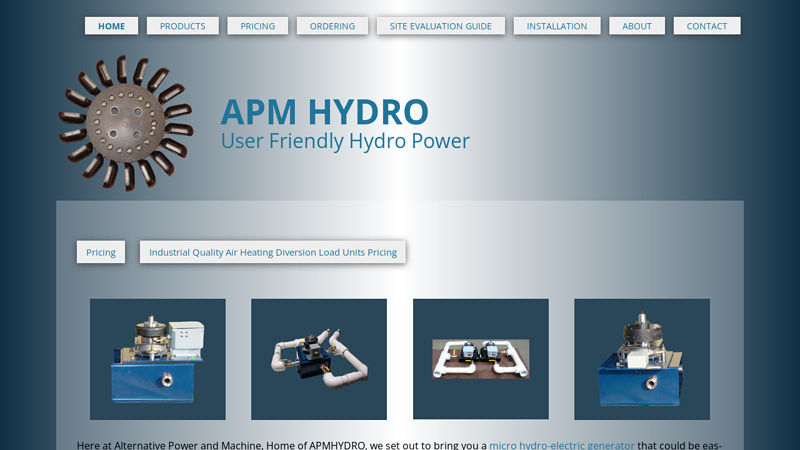
#5 Micro Hydro Generators for DIY Renewable Energy
Domain Est. 2002
Website: apmhydro.com
Key Highlights: A micro hydro-electric generator that could be easily maintained and adjusted. With our units there is no need to disassemble the manifold to change jets….
#6 HIPOWER SYSTEMS a Yanmar Company, Generator Sets
Domain Est. 2008
Website: hipowersystems.com
Key Highlights: Equipment for stationary applications. Continuous or backup power with an immediate response time to guarantee continuous supply in the event of a grid failure….
#7 PowerSpout
Domain Est. 2009
Website: powerspout.com
Key Highlights: PowerSpout turbines are reliable, clean, efficient and field proven. If you have falling water you can generate power. We have a range of turbines to suit your ……
#8 SMART HYDRO POWER
Website: smart-hydro.de
Key Highlights: We offer complete Decentralized Electrification Solutions in rural areas, renewable energy, hydrokinetic turbines, energy management systems & solar panels….
#9 Microhydropower Systems
Website: energy.gov
Key Highlights: A microhydropower system needs a turbine, pump, or waterwheel to transform the energy of flowing water into rotational energy, which is converted into ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Micro Hydroelectric Power Generator
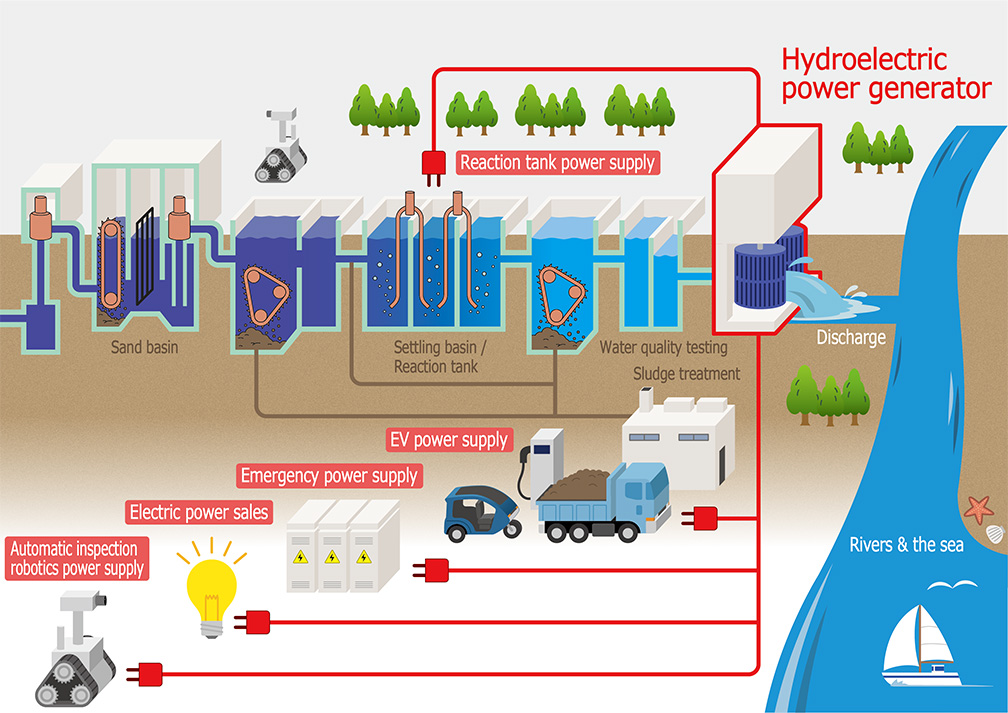
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Micro Hydroelectric Power Generators
The global market for micro hydroelectric power generators (typically defined as systems with a capacity of less than 100 kW) is poised for notable growth and transformation by 2026, driven by increasing demand for decentralized, renewable energy solutions, supportive government policies, and technological advancements. Below is an in-depth analysis of key market trends shaping the micro hydroelectric sector through 2026.
-
Rising Demand for Off-Grid and Rural Electrification
One of the most significant drivers of the micro hydro market is the growing need for reliable electricity in remote and off-grid communities, particularly in developing regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa, Southeast Asia, and the Himalayan regions. With over 700 million people still lacking access to electricity (IEA, 2023), micro hydro systems offer a sustainable, low-maintenance solution. By 2026, governments and NGOs are expected to increase investments in rural electrification programs, with micro hydro playing a central role due to its high reliability and long operational life compared to solar or diesel alternatives. -
Policy Support and Incentives
National renewable energy targets and climate commitments under the Paris Agreement are prompting governments to prioritize small-scale hydropower. Countries such as Nepal, Peru, and Indonesia have introduced subsidies, feed-in tariffs, and tax incentives for micro hydro projects. In Europe and North America, updated environmental regulations are streamlining permitting for low-impact hydro systems, making it easier for communities and small businesses to adopt micro hydro. These supportive policies are expected to accelerate market adoption through 2026. -
Technological Innovation and Efficiency Improvements
Advancements in turbine design—such as cross-flow, Pelton, and Archimedes screw turbines—are enhancing efficiency and reducing environmental impact. By 2026, manufacturers are increasingly offering modular, pre-fabricated micro hydro systems that reduce installation time and cost. Integration with smart controllers, remote monitoring, and hybrid systems (e.g., micro hydro + solar + battery storage) improves grid stability and energy optimization, making micro hydro more attractive for decentralized microgrids. -
Focus on Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Environmental concerns around traditional hydropower are prompting a shift toward low-impact designs. The 2026 market will see growing emphasis on fish-friendly turbines, minimal water diversion systems, and run-of-river installations that preserve aquatic ecosystems. Certification programs such as the Hydropower Sustainability Standard are gaining traction, influencing investment decisions and consumer preferences toward more responsible micro hydro projects. -
Growth in Decentralized Energy Systems and Energy Independence
As energy security becomes a strategic priority, especially in the wake of global supply chain disruptions and energy crises, communities and industries are investing in localized energy generation. Micro hydro systems offer a consistent baseload power source (unlike intermittent solar and wind), making them ideal for powering schools, clinics, agro-processing units, and small industries. By 2026, the trend toward energy self-sufficiency will continue to drive adoption in both rural and peri-urban areas. -
Regional Market Dynamics
- Asia-Pacific remains the largest and fastest-growing market, led by China, India, and Nepal, where abundant water resources and government electrification initiatives create strong demand.
- Latin America shows steady growth, with micro hydro supporting sustainable development in mountainous and indigenous regions.
-
Europe and North America are seeing niche growth in micro hydro, primarily driven by eco-conscious homeowners, rural communities, and sustainability-focused businesses.
-
Challenges and Barriers
Despite positive momentum, the market faces challenges including high upfront costs, site-specific feasibility requirements, and limited technical expertise in remote areas. Regulatory hurdles and lengthy permitting processes in some countries may slow deployment. However, increasing public-private partnerships and capacity-building programs are expected to mitigate these issues by 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, the micro hydroelectric power generator market will be characterized by stronger policy support, technological innovation, and integration into decentralized energy ecosystems. With its ability to provide clean, reliable, and community-based power, micro hydro is set to play a crucial role in the global energy transition—particularly in regions striving for energy access and sustainability. Continued investment in R&D, skills development, and financing mechanisms will be key to unlocking its full potential.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Micro Hydroelectric Power Generators (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing micro hydroelectric power generators presents unique challenges, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to underperforming systems, financial losses, and legal complications. Here are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Performance Verification
Many suppliers provide optimistic performance metrics based on ideal lab conditions rather than real-world hydrology. Purchasers often fail to validate claims with third-party test reports or site-specific simulations, resulting in generators that underperform due to mismatched head/flow conditions or poor efficiency.
Substandard Materials and Manufacturing
Low-cost suppliers may use inferior materials (e.g., subpar bearings, non-marine-grade coatings, or low-efficiency magnets) to cut costs. Without factory audits or material certifications, buyers risk acquiring units prone to corrosion, mechanical failure, or shortened lifespans, especially in harsh environments.
Lack of Certifications and Compliance
Reputable micro hydro systems should meet international standards such as ISO, IEC, or regional grid interconnection requirements. Sourcing from manufacturers without proper certifications increases the risk of non-compliance, safety hazards, and difficulty obtaining permits or connecting to the grid.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Warranty
Remote installations require reliable technical support and spare parts availability. Sourcing from suppliers with weak service networks or vague warranty terms can lead to prolonged downtime and high maintenance costs, undermining the project’s viability.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unlicensed or Counterfeit Technology
Some manufacturers replicate patented turbine designs, control systems, or generator configurations without authorization. Purchasing such units exposes buyers to legal risks, especially if the system is deployed in jurisdictions with strong IP enforcement, potentially leading to injunctions or fines.
Ambiguous Ownership of Custom Designs
When working with OEMs on bespoke solutions, contracts often fail to clearly assign IP rights. This can result in disputes over design ownership, preventing future modifications, replication, or resale—particularly problematic for developers planning multiple installations.
Limited Access to Technical Documentation
Suppliers may withhold critical design schematics, software algorithms, or control logic under the guise of protecting IP. This lack of transparency hinders maintenance, third-party integration, and troubleshooting, reducing operational autonomy and increasing dependency on the original vendor.
Reverse Engineering Risks
Buyers who reverse engineer purchased units to replicate or improve them without proper licensing may inadvertently infringe on patents or trade secrets, exposing their organization to litigation and reputational damage.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls—through due diligence, clear contracts, third-party verification, and engagement with reputable suppliers—project developers can ensure reliable, legally compliant, and sustainable micro hydroelectric installations.
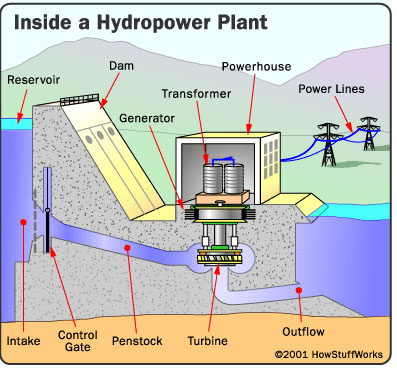
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Micro Hydroelectric Power Generator
Site Assessment and Permitting
Before initiating any logistics activities, conduct a comprehensive site assessment to evaluate water flow, head (elevation drop), land ownership, and environmental sensitivities. This foundational step informs both logistical planning and regulatory compliance. Secure necessary permits from local, state, and federal agencies, including water rights permits from the state water board, environmental clearance under the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) if applicable, and land use permits from local authorities. For projects affecting wetlands or navigable waters, a permit from the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers under Section 404 of the Clean Water Act may be required.
Equipment Procurement and Transportation
Source micro hydro components—such as turbines, generators, penstocks, control systems, and civil works materials—from certified suppliers adhering to ISO or IEC standards. Coordinate delivery schedules to match site readiness, considering seasonal access limitations (e.g., snow, flooding). Transport heavy equipment using specialized freight services; plan routes in advance to avoid low bridges or weak road infrastructure. For remote sites, consider modular systems designed for helicopter or off-road transport. Maintain documentation for all equipment, including warranties, specifications, and compliance certifications.
Installation and Construction Logistics
Develop a detailed construction plan outlining sequencing, workforce deployment, and material staging areas. Adhere to all safety standards (OSHA) and environmental protection measures during installation. Minimize ecological disruption by using low-impact construction techniques, such as pre-fabricated intake structures and erosion control measures. Schedule construction during low-flow seasons to reduce environmental impact and facilitate water diversion. Coordinate with local utilities if grid interconnection is planned.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Ensure ongoing compliance with environmental regulations throughout the project lifecycle. Implement a monitoring plan for fish passage, water quality, and downstream flow requirements as stipulated by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) for exempted small hydro projects or state equivalents. Maintain records of flow measurements and sediment management. If the project is on federal land, comply with Bureau of Land Management (BLM) or U.S. Forest Service requirements.
Grid Interconnection and Power Sales
For grid-connected systems, submit an interconnection application to the local utility or regional transmission organization (e.g., ISO or RTO). Comply with IEEE 1547 standards for distributed energy resource interconnection. If selling power, establish a Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) and ensure eligibility for incentives such as the Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) or state-level renewable energy programs. Register the system with the appropriate energy regulatory body and maintain compliance with reporting requirements.
Operations, Maintenance, and Decommissioning
Develop a long-term operations and maintenance (O&M) plan that includes routine inspections, sediment management, and vegetation control. Train local personnel on system operation and safety procedures. Maintain compliance with reporting obligations to regulatory agencies. Plan for eventual decommissioning by setting aside funds and establishing a site restoration strategy that includes removal of infrastructure and habitat rehabilitation, as required by permitting agencies.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records of all permits, environmental studies, equipment certifications, inspection reports, maintenance logs, and compliance filings. These documents are critical for audits, renewals, and ensuring long-term operational legitimacy. Use digital recordkeeping systems to enhance accessibility and regulatory transparency.
Conclusion on Sourcing a Micro Hydroelectric Power Generator
Sourcing a micro hydroelectric power generator presents a sustainable and reliable energy solution, particularly for remote or off-grid communities with access to flowing water. It offers long-term cost savings, low operational emissions, and consistent energy output compared to other renewable sources like solar or wind. However, successful implementation requires careful site assessment, understanding of local hydrology, regulatory compliance, and environmental considerations.
When sourcing the generator, key factors include matching system specifications to site conditions, selecting reputable suppliers who provide technical support and warranties, and considering total lifecycle costs—including installation, maintenance, and grid integration if applicable. Local availability of skilled technicians and spare parts also influences long-term system viability.
In conclusion, micro hydroelectric power is a viable and eco-friendly energy option when properly planned and sourced. With the right technical, financial, and environmental assessments, it can deliver clean, continuous power, enhancing energy independence and contributing to sustainable development goals.