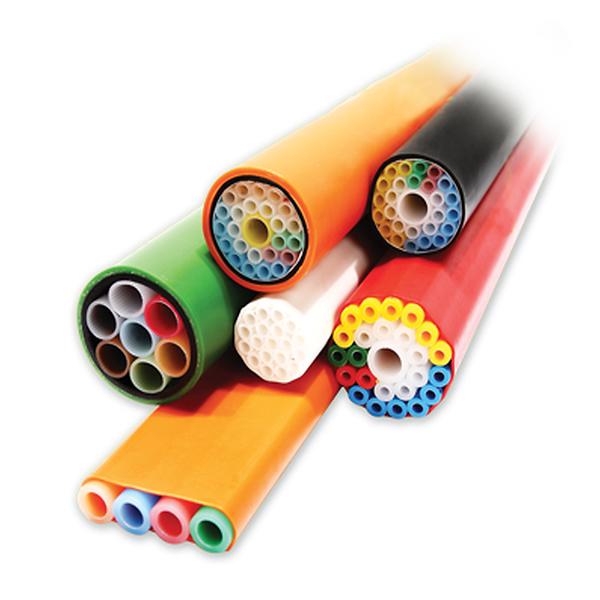
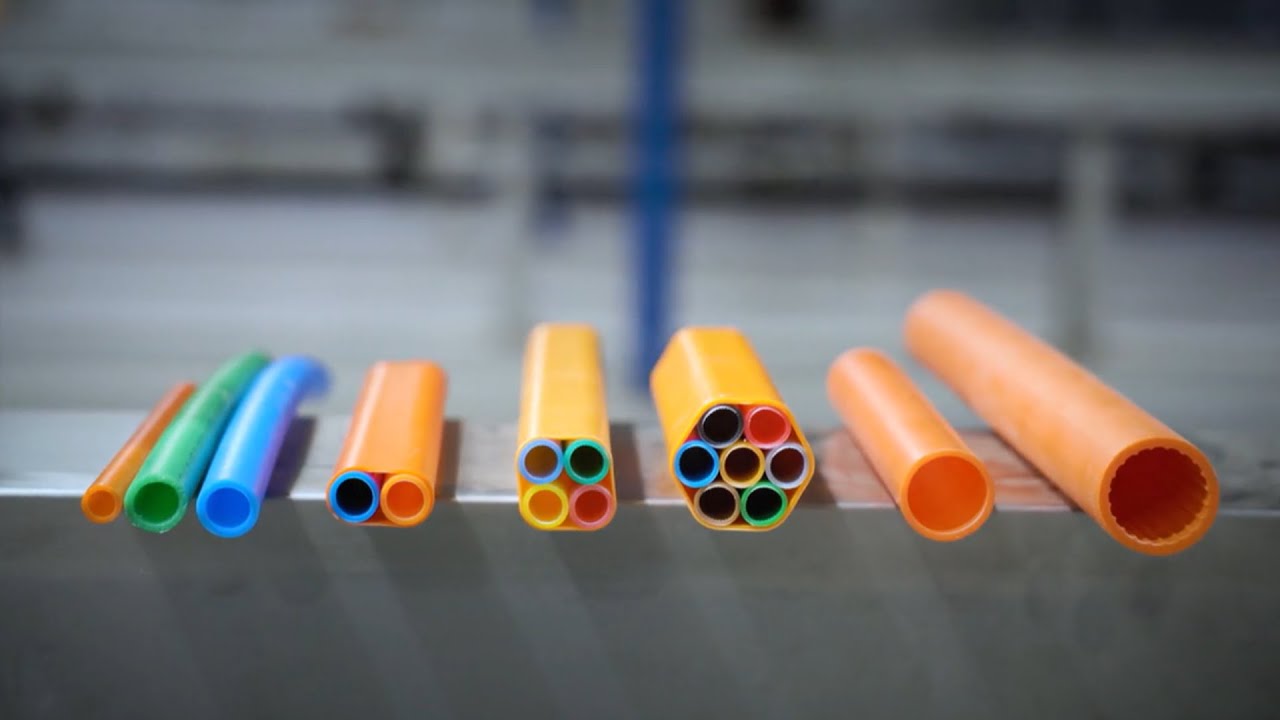
The micro duct market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by the global surge in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) deployments and the growing demand for high-speed data transmission infrastructure. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global micro duct market was valued at USD 1.27 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.8% from 2023 to 2028. This growth trajectory is fueled by increased investments in next-generation telecommunications networks, particularly in emerging economies, as well as the need for scalable, future-proof cabling solutions. Micro ducts—small, flexible pathways for fiber optic cables—are becoming foundational in dense urban networks and data center interconnects due to their space efficiency and ease of installation. As demand escalates, a select group of manufacturers have distinguished themselves through innovation, product reliability, and global reach. Based on market presence, product portfolio breadth, and technological advancements, the following eight companies represent the leading micro duct manufacturers shaping the future of network infrastructure.
Top 8 Micro Duct Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 MicroTechnology
Domain Est. 1995
Website: duraline.com
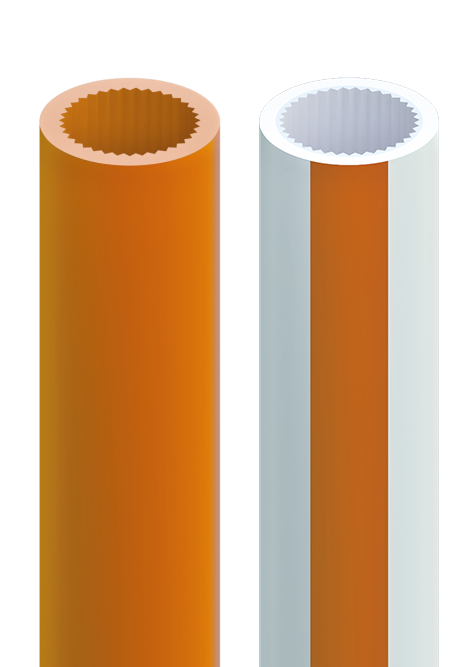
Key Highlights: MicroDucts are small diameter conduits ranging from 5-27mm OD that provide a pathway for fiber cables. They are a natural evolution of standard conduits….
#2 Sanbor Microduct. Microduct Single, Microduct Multi, Microduct Pipe …
Domain Est. 2020
Website: sanbormicroduct.com
Key Highlights: Sanbor is a leading manufacturer of microduct solutions, HDPE conduits, and accessories for a wide variety of markets including telecommunications, energy, and ……
#3 Fiber Optic Microduct Cable
Domain Est. 1991
Website: corning.com
Key Highlights: Microducts are innovative, miniaturized plastic conduits designed to maximize the use of available duct space. By subdividing traditional duct pathways into ……
#4 Microduct
Domain Est. 2004
Website: bdiky.com
Key Highlights: Blue Diamond manufactures a wide range of microduct sizes and configurations. Microducts are becoming increasingly popular with engineers and owners….
#5 Ducts
Domain Est. 2005
Website: prysmian.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture microducts with 5 mm, 7 mm, 10 mm, 12 mm, 14 mm, 16 mm and 20 mm diameters. We use 100% virgin high-density polyethylene….
#6 Microducts for different installation conditions
Domain Est. 2010
Website: nestorcables.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture microducts for both direct burial and installation in conduits. Microducts intended for direct installation in protective ducts ……
#7 Knet
Domain Est. 2011
Website: e-knet.com
Key Highlights: Knet Microduct Solutions for Feeder, Distribution and drop network Planning, Designing, Producing, Shipping, Installing, Blowing And Completing Fiber Build….
#8 Micro-Path™ Microduct Piping
Domain Est. 2011
Website: unitedpolysystems.com
Key Highlights: Atkore- United Poly Systems offers HDPE Microduct Piping with our exclusive Micro-Path™ system. Multiple sizes and configurations available….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Micro Duct

H2: Projected Market Trends for Micro Ducts in 2026
The micro duct market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by the global expansion of fiber-optic networks, rising demand for high-speed internet, and the rapid deployment of 5G infrastructure. As telecommunications providers and internet service providers (ISPs) seek cost-effective and scalable solutions for broadband connectivity, micro ducts—small-diameter conduits used to install fiber optic cables—are becoming increasingly critical components in modern network architectures.
One of the primary growth drivers by 2026 will be the continued rollout of Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) and Fiber-to-the-Premises (FTTP) projects, particularly in emerging economies across Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa. Governments and private entities are investing heavily in digital infrastructure to bridge the digital divide, and micro ducts offer a future-proof, modular approach that supports incremental network upgrades without extensive civil works.
Additionally, the adoption of micro ducts in 5G small cell deployments is expected to accelerate. As 5G networks require dense infrastructure with closely spaced antennas, micro ducts enable rapid and minimally invasive installation of fiber backhaul connections. Their flexibility and ease of blowing fiber into place make them ideal for urban environments where space and permitting are constraints.
Technological advancements will also shape the 2026 landscape. Innovations such as multi-duct micro modules, bend-insensitive materials, and pre-terminated micro duct solutions will enhance deployment speed and reduce long-term maintenance costs. Furthermore, sustainability concerns are pushing manufacturers toward recyclable and low-carbon materials, aligning with broader ESG goals in the telecom sector.
Regionally, North America and Europe will maintain strong market positions due to mature telecom markets and ongoing network modernization. However, the fastest growth is anticipated in Asia-Pacific, led by countries like India, China, and Indonesia, where national broadband initiatives are prioritizing scalable infrastructure.
In summary, by 2026, the micro duct market will be characterized by robust growth, technological innovation, and strategic importance in next-generation network deployments. Stakeholders who leverage modular, sustainable, and high-efficiency micro duct solutions will be well-positioned to meet the escalating demands of global connectivity.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Micro Ducts: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing micro ducts for fiber optic network deployments involves several hidden challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) integrity. Overlooking these aspects can lead to project delays, increased maintenance costs, and legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to watch for:
Poor Material Quality and Non-Compliance with Standards
Many suppliers offer micro ducts made from substandard polyethylene (PE) or recycled materials, resulting in reduced durability, UV resistance, and crush strength. These inferior products may not meet international standards such as ISO 12176 or EN 13476, leading to premature failure during installation or in-service. Always verify material certifications and request independent test reports for tensile strength, impact resistance, and thermal stability.
Inconsistent Dimensional Tolerances
Micro ducts require precise inner and outer diameters to ensure compatibility with blowing equipment and cables. Poor-quality products often feature inconsistent wall thickness or ovality, increasing friction and causing blockages during cable installation. This can significantly reduce blowing distance and efficiency. Insist on dimensional inspection reports and consider third-party sampling tests before large-scale procurement.
Lack of Traceability and Brand Counterfeiting
Unscrupulous suppliers may counterfeit well-known brands or provide unbranded products labeled as premium. These counterfeit items often lack proper traceability codes, batch numbers, or compliance markings. This not only jeopardizes network performance but also complicates warranty claims and liability in case of failure. Verify supplier authenticity through official distributor lists and conduct factory audits when possible.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Some manufacturers replicate patented micro duct designs—such as specific inner wall lubrication patterns, ribbing structures, or coupling mechanisms—without licensing. Using such products exposes the buyer to potential IP litigation, especially in regulated markets like Europe or North America. Ensure suppliers provide IP indemnification clauses in contracts and confirm that product designs do not infringe on existing patents.
Inadequate Documentation and Certification
Missing or falsified test reports, CE markings, or RoHS compliance documentation are red flags. Reliable suppliers provide full technical dossiers, including material safety data sheets (MSDS), flame retardancy ratings, and environmental resistance data. Lack of proper documentation often indicates non-compliance and increases project risk during regulatory inspections.
Overreliance on Price as the Primary Selection Criterion
Choosing the cheapest option often leads to hidden costs due to rework, failed installations, or early replacement. A total cost of ownership (TCO) approach—factoring in longevity, installation efficiency, and maintenance—should guide sourcing decisions. Invest in reputable brands with proven field performance to avoid long-term liabilities.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Micro Duct
Overview of Micro Duct
Micro ducts are small-diameter conduits used primarily in fiber optic network deployments to enable the installation and future expansion of optical cables via blowing or jetting techniques. Their compact size allows for dense cabling in limited spaces such as micro-trenches, existing duct networks, and urban infrastructure. Proper logistics and compliance management are essential to ensure performance, safety, and adherence to regulatory standards.
Transportation and Handling
Packaging and Storage
Micro ducts are typically supplied in coiled reels or spools. Reels must be clearly labeled with product specifications, length, batch number, and handling instructions. Store reels vertically on flat, stable surfaces to prevent deformation. Keep materials in dry, shaded areas to avoid UV degradation and moisture exposure.
Transport Conditions
During transit, protect micro duct reels from physical impact, extreme temperatures, and moisture. Secure loads to prevent rolling or shifting. Avoid dropping or dragging reels. Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., forklifts with reel attachments) when handling.
On-Site Handling
Unpack and inspect micro ducts upon delivery for damage. Use reel stands or rotating dispensers during deployment to minimize kinking. Maintain minimum bend radius specifications (typically 20x the outer diameter) to prevent internal damage.
Installation Best Practices
Route Planning and Preparation
Conduct a site survey to determine the optimal pathway, considering obstacles, existing utilities, and environmental conditions. Use micro ducts with compatible outer diameters for the host duct or installation method (e.g., micro-trenching, directional drilling).
Jointing and Coupling
Use manufacturer-approved connectors or fusion splicing methods for continuous runs. Ensure joints are sealed to prevent water ingress and maintain blowing performance. Label connection points for future maintenance.
Blowing and Jetting
Use calibrated air-assisted equipment to install fiber cables into micro ducts. Monitor air pressure and cable speed to avoid damage. Clean micro ducts before cable installation to remove debris.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Industry Standards
Micro ducts must comply with relevant international and regional standards such as:
– ITU-T G.650.1 (definitions and test methods for fiber optics)
– ETSI EN 300 019 (environmental conditions for telecommunications equipment)
– ISO 11801 (generic cabling for customer premises)
– Local building and telecommunications codes
Environmental Regulations
Adhere to environmental protection laws during installation—especially in sensitive areas. Follow protocols for micro-trenching restoration, waste management, and protection of underground utilities. Use recyclable or low-impact materials where possible.
Safety Protocols
Ensure workers are trained in:
– Safe handling of reels and installation equipment
– Confined space entry (if applicable)
– Traffic control during roadside installations
– Use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
Documentation and Traceability
Product Certification
Verify that micro ducts are certified by recognized bodies (e.g., CE marking in Europe, UL listing in North America). Retain manufacturer data sheets, test reports, and compliance certificates.
As-Built Records
Maintain detailed installation records, including:
– Route maps and GPS coordinates
– Duct type, size, and color coding
– Joint locations and test results (e.g., continuity, air pressure)
– Cable blowing logs
These records support maintenance, audits, and future upgrades.
Quality Assurance and Testing
Pre-Installation Checks
Inspect micro ducts for surface defects, ovality, and dimensional accuracy. Perform air pressure or vacuum tests on installed ducts to detect leaks.
Post-Installation Verification
Conduct cable blowing trials to validate system performance. Use OTDR (Optical Time Domain Reflectometer) testing after fiber installation to confirm integrity.
Disposal and Sustainability
Dispose of damaged or excess micro duct materials according to local waste regulations. Recycle plastic components where facilities exist. Prioritize suppliers with environmental management systems (e.g., ISO 14001 certified).
Conclusion
Effective logistics and strict compliance are critical to the successful deployment of micro duct systems. By following standardized handling, installation, and documentation practices—and adhering to safety and regulatory requirements—organizations can ensure reliable, future-proof fiber infrastructure.
Conclusion for Sourcing Micro Duct
Sourcing micro ducts requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, scalability, and reliability. As critical components in modern fiber optic network deployments—particularly in FTTH (Fiber to the Home) and dense urban infrastructure—micro ducts must meet stringent technical standards for durability, flexibility, and ease of installation. The selection of suppliers should prioritize manufacturers with proven compliance to international standards (such as ISO and ITU-T), consistent material quality (typically HDPE), and the ability to customize solutions for specific project requirements.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include evaluating supplier lead times, logistical capabilities, and after-sales support, especially for large-scale or geographically dispersed projects. Additionally, forming long-term partnerships with reliable vendors can lead to cost efficiencies, improved service levels, and better innovation adoption through access to the latest advancements in micro duct technology.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of micro ducts hinges on a comprehensive supplier assessment, clear technical specifications, and alignment with project timelines and infrastructure goals. A well-executed sourcing strategy ensures network longevity, minimizes installation challenges, and supports the scalable rollout of high-speed telecommunications networks.