The global demand for precision-engineered fasteners, particularly metric fine thread bolts, continues to rise across critical sectors such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and industrial manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global industrial fasteners market was valued at USD 87.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.6% from 2023 to 2030. This sustained expansion is driven by increasing infrastructure development, advancements in lightweight vehicle manufacturing, and the need for high-strength, vibration-resistant components—areas where metric fine thread bolts excel due to their enhanced clamping force and thread engagement.
As industries prioritize reliability and performance under extreme conditions, the importance of sourcing high-quality metric fine thread bolts from reputable manufacturers becomes paramount. With Asia Pacific dominating production and consumption—supported by strong industrial bases in China, Japan, and India—the competitive landscape features a mix of established global players and agile regional manufacturers. Drawing on market insights from Grand View Research and supply chain analytics, this list highlights the top 8 manufacturers recognized for their technical precision, product consistency, global reach, and compliance with international standards such as ISO, DIN, and ASME.
Top 8 Metric Fine Thread Bolts Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Metric Bolts
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nutty.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $100 30-day returnsBuy metric bolts online built with precision designs and reliable strength. Ideal for machinery, equipment, and structural projects that deman…
#2 The Official ARP Web Site
Domain Est. 1997
Website: arp-bolts.com
Key Highlights: 51 kits found for Metric Thread Bolt Kits All Materials – M10-1.50. — Select Diameter –, All ARP Metric Bolt Kits, M6 x 1.00 (8mm Wrenching), M8 x 1.25 (10mm ……
#3 Fine Thread Hexagon Head Screws
Domain Est. 1997
Website: metricmcc.com
Key Highlights: Fine thread hexagon head screws available fully threaded or partially threaded. Sizes available from 8mm up to 24mm. We offer fast same-day shipping….
#4 The Official ARP Web Site
Domain Est. 1997
Website: kaedings.com
Key Highlights: ARP Stainless is specially alloyed for extra durability. It’s polished using a proprietary process to produce a beautiful finish. Tensile strength is typically ……
#5 All Metric Studs
Domain Est. 1998
#6 Corrosion
Domain Est. 2009
Website: ti64.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsOur lightweight bolts, washers, and fasteners combine the benefits of strength with weight and the prevention of corrosion over time….
#7 Metric Threaded Products
Domain Est. 2010
Website: metric-threaded.com
Key Highlights: Full Thread; Fine thread Metric Hex Cap Screws are six-sided bolts. Product Specifications. Diameter, M11. Thread Pitch, 1.25. Length, 20mm. Head Wd. 16mm. Head ……
#8 Fuller Fasteners
Domain Est. 2013
Website: fullerfasteners.com
Key Highlights: Continuously increasing product range of metric and imperial fasteners. Leading Canadian supplier / importer / exporter of metric fasteners and imperial socket ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Metric Fine Thread Bolts

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Metric Fine Thread Bolts
The global market for metric fine thread bolts is poised for steady growth and notable shifts by 2026, driven by evolving industrial demands, technological advancements, and regional manufacturing dynamics. These precision-engineered fasteners, characterized by their smaller pitch and enhanced thread density compared to coarse threads, are increasingly favored in high-performance applications across aerospace, automotive, electronics, and precision machinery sectors.
-
Growing Demand in High-Precision Industries
By 2026, the aerospace and defense industries are expected to be primary drivers of demand for metric fine thread bolts. Their superior vibration resistance and tighter clamping capabilities make them ideal for critical assemblies. Similarly, the automotive sector—particularly in electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing—is adopting fine thread bolts for motor housings, battery enclosures, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), where precision and reliability are paramount. -
Expansion in Automation and Robotics
The rise of industrial automation and collaborative robotics (cobots) is increasing the need for compact, high-tolerance fastening solutions. Metric fine thread bolts offer better control during torque application and reduced risk of thread stripping, making them preferred in robotic assembly lines and modular automation systems. -
Regional Manufacturing Shifts
Asia-Pacific, especially China, India, and South Korea, is projected to dominate production and consumption by 2026 due to expanding manufacturing capabilities and government initiatives promoting advanced engineering. Meanwhile, reshoring trends in North America and the EU are boosting local demand for high-quality fasteners, including fine thread variants, to support domestic aerospace and clean energy projects. -
Material and Coating Innovations
Advancements in materials—such as high-strength alloy steels, stainless steel grades (e.g., A4-80), and titanium—are enhancing the performance of fine thread bolts in corrosive and high-temperature environments. By 2026, demand for environmentally compliant coatings (e.g., zinc-nickel, Geomet, and Dacromet) is expected to grow, aligning with stricter environmental regulations in Europe and North America. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Influence
The push toward sustainable manufacturing is prompting bolt manufacturers to adopt recyclable materials and energy-efficient production processes. Reusability and ease of disassembly—facilitated by the precision of fine threads—are becoming key design considerations in modular and serviceable products, further supporting market growth. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Digitalization
Post-pandemic supply chain disruptions have led to increased investment in digital inventory management, predictive maintenance, and smart logistics. By 2026, leading bolt suppliers are expected to integrate IoT-enabled tracking and blockchain for traceability, ensuring consistent quality and faster delivery of metric fine thread bolts to global clients.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for metric fine thread bolts will be shaped by technological sophistication, regional industrial growth, and sustainability imperatives. Companies that innovate in materials, embrace digital supply chains, and align with high-precision industry needs will be best positioned to capture emerging opportunities.
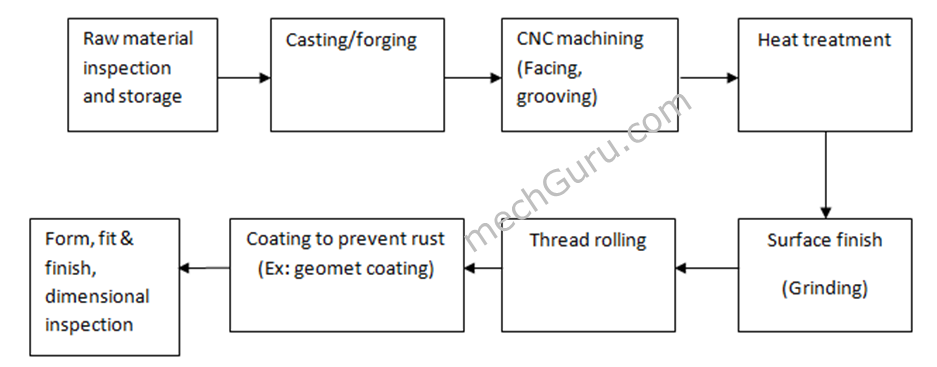
H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Metric Fine Thread Bolts (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Metric Fine Thread Bolts, especially with critical requirements around quality and intellectual property (IP), presents several common pitfalls that procurement teams and engineers must be aware of to avoid project delays, safety issues, or legal complications.
1. Compromised Material Quality
One of the most frequent issues is receiving bolts made from substandard materials. Suppliers—particularly from low-cost regions—may use inferior steel alloys or fail to meet required tensile strength specifications (e.g., Grade 8.8, 10.9, or 12.9). Without proper certification (e.g., ISO 898-1), these bolts can fail under load, leading to safety hazards or structural integrity concerns.
2. Inconsistent Thread Accuracy
Fine thread bolts (e.g., M10x1.0, M12x1.25) require precise threading due to their smaller pitch. Poor thread tolerances can lead to galling, cross-threading, or difficulty in assembly. Suppliers may not adhere strictly to ISO 965 standards, resulting in non-conforming products that increase labor costs or cause field failures.
3. Lack of Traceability and Certification
Reputable applications (e.g., aerospace, automotive, medical) require full traceability, including mill test certificates (MTCs) and compliance with ISO 17025. Many suppliers provide incomplete or falsified documentation, making it difficult to verify heat lot numbers or mechanical properties—posing serious quality and liability risks.
4. Counterfeit or Non-Compliant Fasteners
The market is rife with counterfeit bolts labeled as high-grade or certified when they are not. These may visually resemble genuine parts but fail under stress testing. Sourcing from unauthorized distributors or gray-market channels increases exposure to counterfeit goods.
5. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
When sourcing proprietary or patented bolt designs (e.g., specialized locking mechanisms or coatings), there’s a risk of IP infringement if the supplier reproduces protected features without licensing. Using such components—even unknowingly—can expose the buyer to legal action, especially in regulated industries.
6. Inadequate Surface Treatments and Corrosion Protection
Fine thread bolts used in harsh environments require durable coatings (e.g., Geomet, Dacromet, or zinc-nickel). Poorly applied or substituted coatings can compromise corrosion resistance. Some suppliers may cut costs by using inferior plating that does not meet specified salt spray test requirements (e.g., ISO 9227).
7. Mislabeling and Incorrect Specifications
Suppliers may mislabel bolts (e.g., selling coarse thread as fine thread or incorrect strength grades). This mismatch can go unnoticed until assembly, leading to rework, downtime, or field failures. Clear specifications and incoming inspection protocols are essential.
8. Supply Chain and Lead Time Instability
Overreliance on a single supplier or region can expose buyers to delays due to logistical issues, customs problems, or political instability. This is particularly critical for long-lead or custom-designed fine thread bolts where alternative sourcing is limited.
9. Poor Communication of Technical Requirements
Ambiguous purchase orders or unclear specifications (e.g., missing thread class, surface finish, or coating type) often result in incorrect deliveries. Ensuring detailed technical drawings and specifications are shared and acknowledged helps prevent misunderstandings.
10. Hidden Costs from Non-Conformance
While low initial pricing may be attractive, hidden costs from defects, rework, warranty claims, or production stoppages can far exceed savings. A total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis is crucial when evaluating suppliers.
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should conduct supplier audits, require third-party testing, enforce strict quality agreements, and maintain clear IP safeguards in procurement contracts.
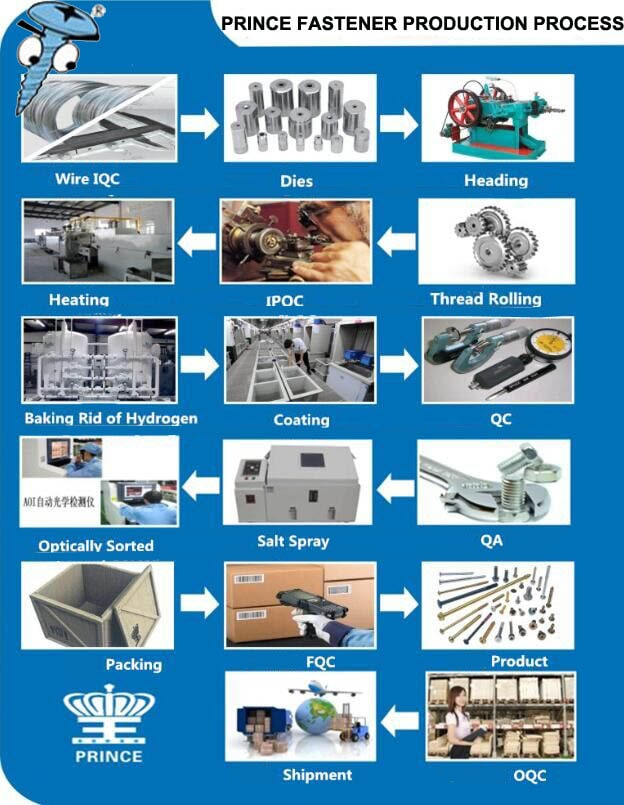
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Metric Fine Thread Bolts
Metric fine thread bolts are widely used in precision engineering, automotive, aerospace, and other industries where high strength, vibration resistance, and fine adjustments are critical. Proper logistics handling and compliance with international and regional standards are essential to ensure quality, safety, and regulatory conformity.
Overview of Metric Fine Thread Bolts
Metric fine thread bolts follow the ISO metric screw thread standard (ISO 261 and ISO 965), with a smaller pitch compared to coarse threads of the same diameter. Designated with an “M” followed by the nominal diameter and pitch (e.g., M10×1.25), these bolts offer enhanced tensile strength and resistance to loosening under vibration.
Key Standards and Compliance Requirements
Compliance with recognized standards ensures interchangeability, reliability, and safety. Key standards include:
- ISO 898-1: Specifies mechanical properties of bolts, screws, and studs made of carbon steel and alloy steel. Defines property classes (e.g., 8.8, 10.9, 12.9).
- ISO 4017 / ISO 4014: Covers hex head bolts and screws with fine pitch threads.
- DIN 933 / DIN 931: German standards equivalent to ISO 4017/4014 for fully and partially threaded bolts.
- EN 14399: For high-strength structural bolting assemblies used in preloaded joints (common in construction).
- ASTM A325 / A490 (if applicable): Though metric, some projects may reference ASTM standards; ensure conversion clarity.
Ensure all products are certified with test reports (e.g., EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2) and traceable to raw material and production batches.
Material and Finish Compliance
- Materials: Common materials include alloy steel, stainless steel (A2/A4 per ISO 3506), and weathering steel. Verify material certifications.
- Surface Treatments: Zinc plating, galvanizing, passivation, or Dacromet coatings must comply with ISO 4042 (electroplating) or ISO 10683 (zinc flake coatings). RoHS and REACH compliance is mandatory in the EU.
- Corrosion Resistance: Salt spray testing (per ISO 9227) may be required for harsh environments.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging prevents damage during transit and ensures regulatory compliance:
- Use moisture-resistant, anti-corrosion packaging (e.g., VCI paper or sealed plastic).
- Label each package with:
- Bolt designation (e.g., M12×1.5 × 50)
- Material and property class (e.g., 10.9)
- Manufacturer or supplier name/trademark
- Lot or batch number
- Quantity and net weight
- Compliance marks (e.g., CE marking if applicable under EU Construction Products Regulation)
For international shipments, include multilingual labels if required.
Transportation and Handling
- Store bolts in dry, temperature-controlled environments to prevent rust and thread damage.
- Use pallets with secure strapping; avoid overstacking.
- Prevent mixing with coarse-thread or non-metric fasteners to avoid cross-threading risks.
- Follow OSHA (in the U.S.) or local workplace safety regulations during handling.
Import/Export and Customs Compliance
- HS Code: Typically 7318.15 (steel bolts, threaded) or 7318.16 (stainless steel). Confirm based on material and finish.
- Country-Specific Regulations:
- EU: CE marking may be required; ensure compliance with Construction Products Regulation (CPR) for structural applications.
- USA: No general certification, but customer-specific requirements (e.g., DOT, FAA) may apply in automotive or aerospace.
- Canada: May require ASTM/CSA standards alignment.
- China: GB standards may be referenced; CCC certification not typically required for bolts.
- Provide commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificates of compliance/test reports.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
- Implement a documented quality management system (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Conduct batch testing for dimensions, mechanical properties (tensile, hardness), and surface integrity.
- Maintain full traceability from raw material to finished product.
- Non-conforming goods must be quarantined and documented.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
- Adhere to REACH (EU), TSCA (USA), and other chemical regulations for coatings and treatments.
- Ensure hazardous substance declarations are available.
- Provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for coated or treated fasteners if chemicals are used.
Best Practices for Supply Chain Management
- Partner with certified suppliers (ISO 9001, IATF 16949 for automotive).
- Conduct regular supplier audits.
- Use ERP or inventory systems to track lot numbers and expiry dates (if applicable).
- Perform incoming inspection upon receipt.
By adhering to this logistics and compliance guide, organizations can ensure the reliable, safe, and legal distribution and use of metric fine thread bolts across global markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing Metric Fine Thread Bolts
Sourcing metric fine thread bolts requires a strategic and thorough approach to ensure reliability, performance, and cost-efficiency. Fine thread bolts, with their smaller pitch and greater flank engagement, offer advantages such as increased tensile strength, better resistance to vibration loosening, and finer torque control—making them ideal for critical applications in automotive, aerospace, machinery, and precision engineering sectors.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include verifying material specifications (e.g., stainless steel, alloy steel), strength grades (e.g., property classes 8.8, 10.9, 12.9), thread accuracy (compliance with ISO 965 standards), and surface treatments for corrosion resistance. Supplier reliability, traceability, and adherence to international quality standards (such as ISO 9001) are equally important to ensure consistency and product integrity.
While fine thread bolts may have a higher initial cost and slightly slower assembly times compared to coarse threads, their superior performance in demanding environments justifies their use when precision and reliability are paramount. Establishing long-term partnerships with certified suppliers, conducting regular quality audits, and staying updated on material and manufacturing advancements will further enhance sourcing effectiveness.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of metric fine thread bolts hinges on balancing technical requirements with supply chain reliability, ensuring that every fastener contributes to the safety, durability, and efficiency of the final assembly.