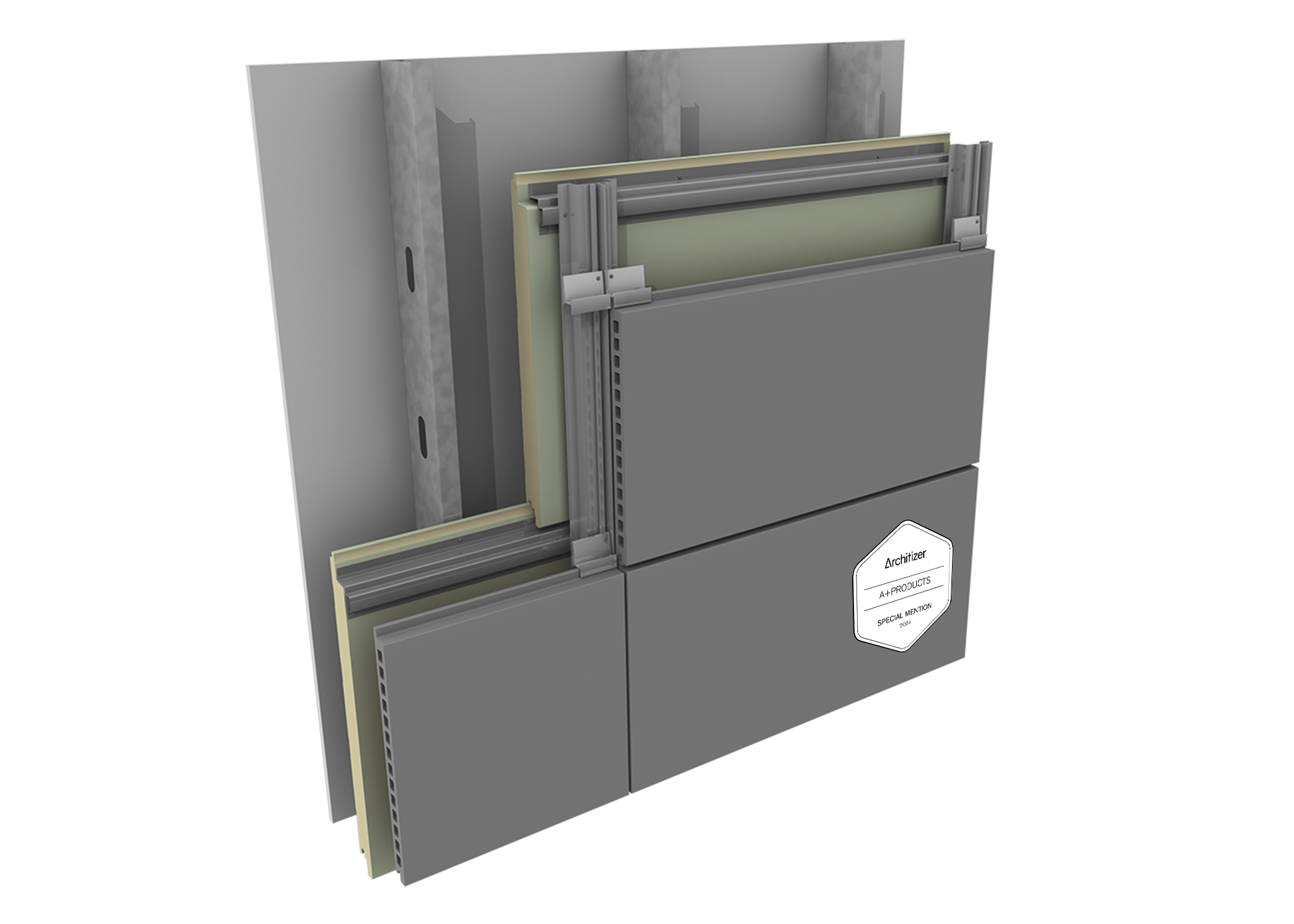
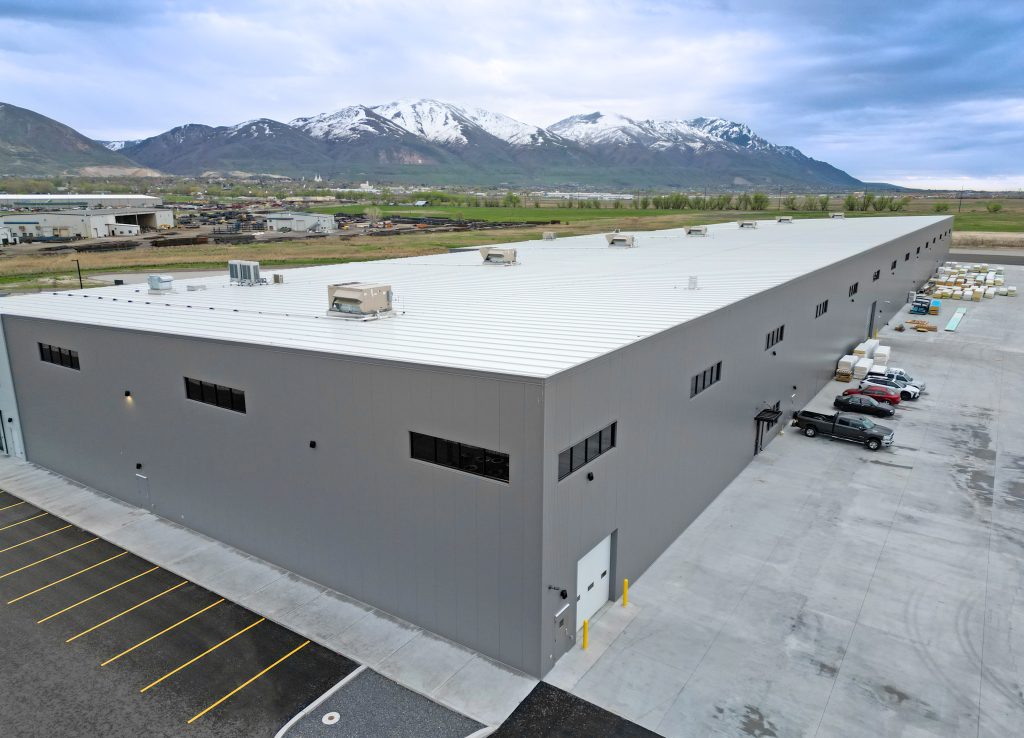
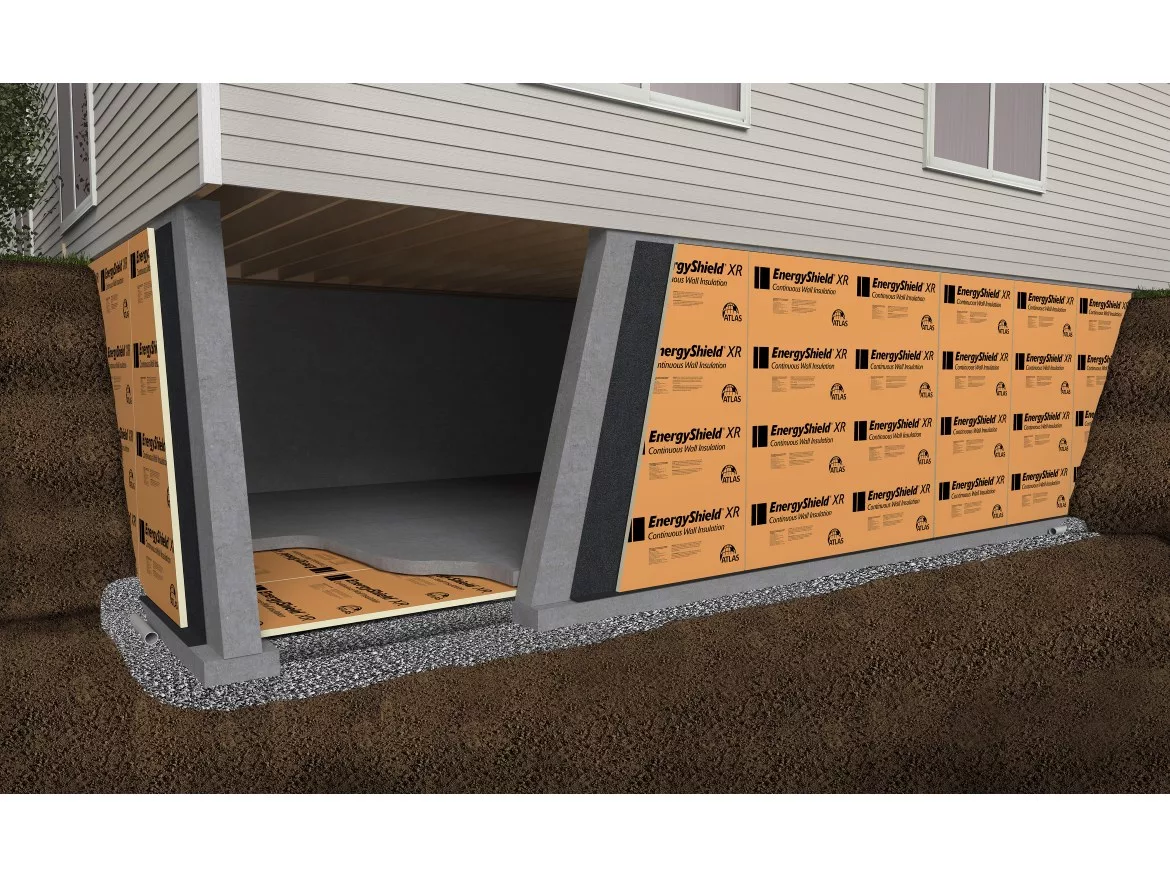
The global metal roof foam market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient building materials and the need for durable, weather-resistant roofing solutions. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global spray foam insulation market size was valued at USD 3.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030, with roofing applications accounting for a significant share. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects steady expansion in the construction chemicals and insulation sector, attributing much of this growth to increased adoption in both residential and commercial infrastructure, particularly in regions with extreme climatic conditions. As metal roofing continues to gain popularity for its longevity and sustainability, the demand for high-performance foam underlayments—critical for thermal efficiency, moisture control, and noise reduction—has surged. This increasing need has propelled innovation and competition among manufacturers, setting the stage for the top nine companies leading the charge in product development, scalability, and market reach.
Top 9 Metal Roof Foam Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 CENTRIA: Insulated Metal Panel Systems
Domain Est. 1996
Website: centria.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture high performance building envelope systems designed to provide superior protection against the elements. This system includes exterior wall, roof ……
#2 Metl
Domain Est. 1996
Website: metlspan.com
Key Highlights: Metl-Span is an industry leading manufacturer of insulated metal wall & roof panels for a variety of applications. Learn more about our panels today!…
#3 DECRA Metal Roofing: #1 Stone
Domain Est. 1999
Website: decra.com
Key Highlights: DECRA Metal Roofing is the #1 stone-coated steel manufacturer for residential and commercial roofing backed by a lifetime warranty to guarantee protection….
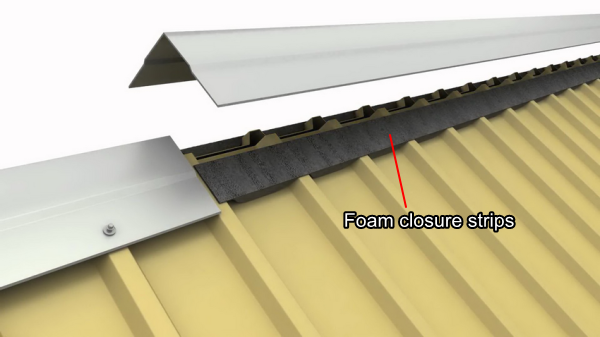
#4 Metal Roofing Closure Systems
Domain Est. 2002
Website: foamparts.com
Key Highlights: Jacobs & Thompson manufacturers our own line up of custom foam closure systems, designed to seal gaps in metal roofing constructions….
#5
Website: metalsales.us.com
Key Highlights: Metal Sales is the nation’s largest manufacturer of metal roofing, wall, and building systems. We are the most awarded and highly recognized provider of metal ……
#6 IMP Panels for Walls and Roofs
Domain Est. 1995
Website: falk.com
Key Highlights: IMP panels from the most technically advanced panel production facility in North America. Robust metal strength combined with superior insulation….
#7 Closure
Domain Est. 2004
Website: marcoindustries.com
Key Highlights: Roofing foam that designed for UV resistance and longevity, available in a variety of thicknesses and profiles for every application….
#8 Foam Closures For Metal Roofing Panels
Domain Est. 2015
Website: westernstatesmetalroofing.com
Key Highlights: Foam closures for metal roofing and metal decking. 7/8″ Corrugated, PBR Panel, Western Rib (7.2 Panel). Shop a wide variety of foam closures and foam plugs….
#9 Atlas Roof & Wall Insulation
Domain Est. 2017
Website: atlasrwi.com
Key Highlights: Atlas has more than 35 years’ experience manufacturing polyiso. The company has grown from a single manufacturing facility into an industry leader with 8 ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Metal Roof Foam

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Metal Roof Foam
The global market for metal roof foam insulation is poised for significant growth by 2026, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient building solutions, advancements in spray polyurethane foam (SPF) technology, and supportive regulatory frameworks promoting sustainable construction. Below is an in-depth analysis of key trends shaping the metal roof foam market in 2026:
-
Rising Demand for Energy Efficiency
With global emphasis on reducing carbon emissions and improving building energy performance, metal roof foam insulation—particularly closed-cell SPF—is gaining traction. Its high R-value per inch (up to R-6.8) makes it ideal for commercial, industrial, and residential metal roofing systems. In 2026, stricter energy codes in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific are expected to drive adoption, especially in retrofitting older metal roofs for better thermal performance. -
Growth in Commercial and Industrial Construction
The commercial and industrial sectors are leading end-users of metal roof foam due to large roof areas requiring durable, lightweight, and seamless insulation. By 2026, expanding logistics centers, cold storage facilities, and manufacturing plants—especially in emerging economies—will boost demand. SPF’s ability to form a monolithic barrier also reduces air infiltration and moisture issues common in metal structures. -
Technological Advancements in Foam Formulations
Innovations in low-global warming potential (GWP) blowing agents and bio-based raw materials are enhancing the sustainability profile of metal roof foam. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to offer next-generation SPF systems with improved fire resistance, UV stability, and longer service life. Integration with reflective roof coatings (cool roofs) will further increase solar reflectance and reduce urban heat island effects. -
Regional Market Expansion
North America remains the dominant market due to mature construction practices and strong SPF contractor networks. However, Asia-Pacific is projected to witness the highest CAGR by 2026, fueled by rapid urbanization in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Government incentives for green buildings and public infrastructure projects are accelerating SPF adoption in metal roofing applications. -
Sustainability and Regulatory Pressures
Environmental regulations, such as the U.S. EPA’s AIM Act and EU F-gas regulations, are pushing manufacturers toward eco-friendly foam formulations. By 2026, compliance with green building certifications (LEED, BREEAM) will be a key differentiator. Recyclability and end-of-life management of foam systems will also gain attention, prompting R&D into degradable or reusable SPF materials. -
Skilled Labor and Installation Challenges
Despite growth, the market faces constraints due to the need for trained SPF applicators. In 2026, increased investment in workforce training and certification programs—led by industry bodies like the Spray Polyurethane Foam Alliance (SPFA)—is expected to alleviate labor shortages and ensure installation quality. -
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The metal roof foam market is moderately consolidated, with key players such as BASF, Dow, Huntsman, and Carlisle Companies expanding their product portfolios and geographic reach. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions are anticipated by 2026 to strengthen supply chains and enhance R&D capabilities.
Conclusion
By 2026, the metal roof foam market will be shaped by sustainability, performance, and regulatory trends. The integration of SPF with metal roofing systems offers a compelling solution for energy savings, durability, and environmental compliance. As technology evolves and global construction standards tighten, metal roof foam is set to become a standard insulation choice across diverse building sectors.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Metal Roof Foam: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing metal roof foam insulation, overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) factors can lead to performance failures, legal disputes, and financial losses. Being aware of these common pitfalls helps ensure a reliable, compliant, and effective procurement process.
Poor Material Quality and Performance Claims
One of the most frequent issues is encountering substandard foam products that fail to meet advertised performance metrics. Suppliers may exaggerate R-values, fire resistance, or adhesion strength. Low-quality foams often degrade quickly under UV exposure, leading to cracking, shrinking, or delamination from the metal substrate. This compromises insulation effectiveness and can result in moisture infiltration and structural damage over time.
Lack of Certifications and Compliance
Many suppliers offer foam products without proper third-party testing or certifications (e.g., ASTM, UL, ICC-ES). Sourcing foam without verified compliance with building codes and fire safety standards (such as ASTM E84 or FM 4450) can result in rejected installations, failed inspections, or liability issues. Always verify that the product carries up-to-date certifications relevant to your project’s geographic and regulatory requirements.
Inconsistent Application and Curing Issues
Metal roof foams must adhere uniformly and cure properly under varying field conditions. Poorly formulated or counterfeit foams may have inconsistent mix ratios, leading to incomplete curing, shrinkage, or poor adhesion. This often stems from non-OEM (original equipment manufacturer) chemicals or untrained applicators using incompatible equipment, resulting in premature system failure.
Intellectual Property Infringement
A significant but often overlooked risk is sourcing foam systems that infringe on patented technologies. Some suppliers replicate branded formulations (e.g., closed-cell spray polyurethane foam systems) without licensing, offering “compatible” or “generic” alternatives. Using such products may expose the buyer or contractor to IP litigation, especially if the foam incorporates protected chemical compositions, application methods, or system designs. Always confirm that the supplier has proper IP rights or licensing agreements.
Hidden Costs from System Incompatibility
Foam is part of a broader roofing system, including primers, coatings, and top layers. Sourcing foam independently without ensuring compatibility with other system components can lead to adhesion failures or warranty voids. Many manufacturers tie warranties to the use of their full proprietary system—using non-approved foam invalidates coverage, resulting in unexpected repair costs.
Misleading Warranties and Support
Some suppliers offer long-term warranties that sound comprehensive but contain exclusions for workmanship, substrate preparation, or third-party materials. Without clear terms and enforceable support, these warranties offer little protection. Ensure that the warranty covers both material defects and system performance, and confirm the supplier’s track record for honoring claims.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vet suppliers thoroughly, demand test reports and IP documentation, insist on full system compatibility, and prioritize certified, reputable manufacturers over low-cost alternatives.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Metal Roof Foam
This guide outlines the essential logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the safe handling, transportation, storage, and use of Metal Roof Foam products. Adherence to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, worker safety, and product performance.
Product Classification & Regulatory Compliance
Metal Roof Foam typically consists of two-component polyurethane foam systems (Part A: isocyanate, Part B: resin blend). Key compliance areas include:
-
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration)
Comply with OSHA 29 CFR 1910 standards for hazard communication (HazCom), respiratory protection, personal protective equipment (PPE), and exposure limits for isocyanates (e.g., TDI, MDI). Ensure Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are available and employees are trained accordingly. -
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency)
Follow EPA regulations under the Clean Air Act (CAA), particularly concerning Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs). Confirm product VOC content complies with regional limits (e.g., SCAQMD, OTC regulations). Adhere to RRP (Renovation, Repair, and Painting) rules if lead-based paint is present under existing metal roofing. -
DOT (Department of Transportation)
Classify foam components for transport under 49 CFR. Part A (isocyanate) is commonly classified as a Class 8 Corrosive material (UN1830 or UN2924). Proper labeling, packaging, and shipping documentation are required for interstate transport. -
GHS (Globally Harmonized System)
Use GHS-compliant labeling on containers, including hazard pictograms, signal words, and precautionary statements as per SDS requirements.
Transportation & Handling
-
Packaging & Labeling
Ensure components are shipped in UN-rated, pressure-tested containers with proper DOT hazard labels. Drums and totes must be secured to prevent leakage or damage during transit. -
Temperature Control
Maintain storage and transport temperatures between 60°F and 80°F (15°C–27°C). Avoid freezing or excessive heat, which can degrade product quality. Use climate-controlled vehicles in extreme weather. -
Segregation & Compatibility
Do not transport Metal Roof Foam with oxidizers, acids, or alkalis. Isocyanates react violently with water and certain chemicals—ensure separation during loading. -
Driver Training
Drivers and handlers must be trained in hazardous materials transport (DOT HAZMAT certification if required) and emergency response procedures.
Storage Requirements
-
Facility Standards
Store in a dry, well-ventilated, fire-rated storage area away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Use secondary containment (e.g., spill pallets) for drums and totes. -
Shelf Life & Rotation
Adhere to manufacturer-specified shelf life (typically 6–12 months). Practice FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory management to prevent expired material use. -
Segregation
Store Part A (isocyanate) and Part B (resin) separately if required by local code. Keep away from ignition sources and incompatible materials.
On-Site Handling & Application Safety
- PPE Requirements
Workers must wear: - Nitrile or neoprene gloves
- Chemical-resistant clothing
- Full-face respirator with organic vapor and particulate cartridges
-
Safety goggles or face shield
-
Ventilation
Ensure adequate ventilation during indoor application. Use exhaust fans or supplied-air systems in confined spaces. -
Spill Response
Have spill kits (absorbents, neutralizers, disposal bags) on-site. For isocyanate spills, avoid water contact. Follow SDS instructions for cleanup and disposal. -
Waste Disposal
Dispose of unused product, contaminated materials, and empty containers according to RCRA (Resource Conservation and Recovery Act) and local hazardous waste regulations. Empty containers must be triple-rinsed or punctured and disposed of as non-hazardous if compliant.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
- Maintain updated SDS for all components.
- Keep records of employee training (HazCom, HAZWOPER, respiratory protection).
- Retain shipping manifests and waste disposal receipts for at least 3 years.
- Document equipment calibration and maintenance logs for dispensing systems.
Environmental & Sustainability Considerations
- Minimize overspray and waste through proper equipment calibration.
- Recycle metal drums and totes through certified vendors.
- Use low-VOC formulations when available to support green building standards (e.g., LEED).
By following this guide, contractors and distributors can ensure safe, compliant, and efficient logistics operations for Metal Roof Foam systems. Always consult the manufacturer’s technical data sheets and SDS for product-specific instructions.
In conclusion, sourcing metal roof foam requires careful consideration of product quality, compatibility with your specific roofing system, climate conditions, and long-term durability. Choosing the right foam insulation—whether spray polyurethane foam (SPF) or a foam board product—can significantly enhance energy efficiency, prevent moisture infiltration, and extend the lifespan of the metal roof. It is essential to work with reputable suppliers and certified installers to ensure proper application and adherence to industry standards. Additionally, evaluating cost-effectiveness, warranty options, and local building codes will contribute to a successful and sustainable roofing solution. Ultimately, investing in high-quality metal roof foam not only protects the building envelope but also delivers long-term savings and improved indoor comfort.