The global automotive oil pan market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing vehicle production, rising demand for lightweight and durable materials, and advancements in engine technology. According to Mordor Intelligence, the automotive oil pan market was valued at approximately USD 5.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.2% from 2023 to 2028. A key trend fueling this expansion is the shift from traditional steel pans to aluminum and other metal alloys, which offer improved thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and weight reduction—critical factors in enhancing fuel efficiency and meeting emissions regulations. As original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) prioritize performance and sustainability, metal oil pans have become a preferred solution across passenger and commercial vehicles. This growth trajectory underscores the importance of innovative manufacturing, with a select group of global leaders at the forefront of design, material science, and production scale. The following list highlights the top nine metal oil pan manufacturers shaping the industry through technological expertise, strategic partnerships, and strong geographic presence.
Top 9 Metal Oil Pan Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Diesel Engine Oil Pan Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1996
Website: customeng.com
Key Highlights: Custom Engineering is a Pennsylvania based manufacturer of fabricated steel, industrial diesel engine oil pans for use in specialized applications….
#2 oil pan
Domain Est. 2006
Website: ppepower.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsThis new engine oil pan is engineered as a performance replacement for the thin, stamped steel factory pan. Cast in high-strength A356-T6 aluminum alloy.Missing: met…
#3 Oil Pans
Website: wzlindustries.com
Key Highlights: By choosing to work with us, OEMs and Tier 1 manufacturers gain a trusted partner who can deliver dependable oil pans that meet exact specifications every time….
#4 BH Oil Pans
Domain Est. 2011
Website: bhoilpans.com
Key Highlights: Replace your rusted, leaking OEM oil pan with our stainless steel replacement. · Call for pricing, warranty and custom options. · Click on the tabs to see photos ……
#5 Champ Pans
Domain Est. 1999
Website: champpans.com
Key Highlights: Champ Pans manufactures over 1,000 products, from oil pans to chassis brackets. We offer products for use in Circle Track, Street, Strip, Off-Road, Road Race, ……
#6 Premium Oil Pans and Performance Engine Components
Domain Est. 2000
Website: milodon.com
Key Highlights: Browse high-performance engine parts like oil pans, pumps, timing chains, water pumps, and more with Milodon. Our components are designed to ensure peak ……
#7 Custom Oil Pans
Domain Est. 2000
Website: cantonracingproducts.com
Key Highlights: All oil pans are built using 16 or 18 gauge steel and .100 thick aluminum and are tig welded, rather then mig welded. The result is a better quality pan with ……
#8 Custom Sheetmetal Oil Pans
Domain Est. 2006
Website: mmcompetitionengines.com
Key Highlights: M&M Competition Engines provides a wide variety of custom made sheet metal oil pans & oil system components to fit just about everyone’s needs….
#9 Steel & Aluminum Racing Oil Pans
Domain Est. 2018
Expert Sourcing Insights for Metal Oil Pan

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Metal Oil Pans
The global metal oil pan market is poised for continued, albeit measured, evolution in 2026, driven by a complex interplay of automotive industry dynamics, technological advancements, and shifting regulatory landscapes. While facing long-term pressure from electrification, metal oil pans remain essential for a vast and still-growing segment of internal combustion engine (ICE) and hybrid vehicles, ensuring sustained demand. Key trends shaping the market in 2026 include:
1. Steady Demand from ICE & Hybrids, Tempered by Electrification:
* Resilient ICE Base: Despite the rise of EVs, ICE vehicles (gasoline and diesel) will dominate global fleets in 2026, particularly in emerging markets and for commercial/industrial applications. This ensures a stable core demand for metal oil pans.
* Hybrid Growth Driver: The significant growth of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs and PHEVs) is a crucial positive factor. These vehicles still require full ICE systems, including oil pans, often with specific design adaptations for packaging and thermal management. Hybrids represent a key growth segment sustaining metal oil pan demand.
* EV Pressure: The accelerating adoption of battery electric vehicles (BEVs), which eliminate the need for oil pans, creates an overarching long-term challenge. However, the transition is gradual, and the sheer volume of new ICE/hybrid production and the massive existing vehicle fleet requiring replacements will keep the market robust in the short-to-mid term.
2. Material & Manufacturing Innovation for Performance and Efficiency:
* Aluminum Dominance & Optimization: Aluminum will remain the dominant material due to its favorable strength-to-weight ratio and thermal conductivity. Expect continued focus on advanced aluminum alloys (e.g., higher silicon content for wear resistance, improved castability) and optimized casting techniques (high-pressure die casting – HPDC) to reduce weight further, enhance durability, and improve heat dissipation.
* Steel for Specific Applications: Stamped steel oil pans will maintain a presence, particularly in cost-sensitive segments, heavy-duty applications (trucks, commercial vehicles), and some performance vehicles where extreme durability or specific magnetic properties are needed. Advances in high-strength steels may offer weight reduction potential.
* Integrated Design & Functionality: Oil pans will increasingly incorporate features beyond basic oil containment:
* Baffle Systems: Enhanced baffle designs to prevent oil starvation during high-G maneuvers (critical for performance and SUVs).
* Integrated Components: Mounting points for oil level/temperature sensors, potentially integrating parts of the oil pickup tube or even aspects of the crankcase ventilation system.
* Thermal Management: Designs optimizing oil cooling, potentially incorporating cooling fins or channels integrated with engine cooling systems.
3. Stringent Emissions & Efficiency Regulations as Key Drivers:
* Weight Reduction Imperative: Global fuel efficiency and CO2 emission standards (e.g., evolving Euro 7, China 6b, US CAFE) push automakers to reduce vehicle weight. This drives demand for lighter aluminum oil pans and continuous innovation in material science and design optimization (thinner walls, strategic ribbing).
* Reducing Oil Consumption & Emissions: Regulations targeting oil consumption (a source of hydrocarbon emissions) and crankcase emissions (PCV systems) necessitate oil pans with better oil control (improved baffling, windage trays, optimized baffles) and precise integration with PCV components to minimize oil carryover into the intake.
4. Supply Chain & Sourcing Dynamics:
* Consolidation & Strategic Partnerships: The market may see further consolidation among Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers as automakers seek fewer, more capable partners capable of system integration and global supply. Partnerships focused on lightweighting R&D will be valuable.
* Regional Manufacturing & Resilience: Geopolitical factors and the push for supply chain resilience will influence manufacturing locations. Nearshoring or regionalization of production (e.g., in North America, Europe, Southeast Asia) to serve major automotive hubs may increase, impacting sourcing strategies.
* Cost Pressure: Intense competition and automaker cost targets will keep significant pressure on suppliers to optimize manufacturing processes and material costs, favoring efficient high-volume production methods like HPDC.
5. Aftermarket Strength:
* Replacement Demand: The massive global fleet of existing ICE and hybrid vehicles ensures a strong and stable aftermarket for replacement oil pans. This segment provides crucial revenue stability, less susceptible to new vehicle sales fluctuations.
* Performance & Customization: The aftermarket will continue to cater to performance enthusiasts and older vehicle owners, offering upgraded oil pans (e.g., deeper pans for higher oil capacity, enhanced baffling, improved cooling, or aesthetic finishes).
Conclusion:
In 2026, the metal oil pan market will operate in a state of transition. While the long shadow of vehicle electrification looms, the immediate future is defined by the enduring need for high-performance, lightweight, and efficient oil pans in millions of new ICE and hybrid vehicles, alongside significant replacement demand. Success will depend on suppliers’ ability to innovate in lightweight materials (especially aluminum), enhance functionality (baffling, integration, thermal management), navigate stringent regulatory requirements, manage supply chain complexities, and leverage the resilience of the global aftermarket. The market won’t see explosive growth, but it will remain a vital and technologically evolving component segment within the broader automotive industry.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Metal Oil Pans (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing metal oil pans, especially for automotive or industrial applications, involves navigating several critical challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can result in performance failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key risks to consider:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Material Substitution and Non-Compliance
Suppliers may use inferior-grade metals (e.g., substituting low-carbon steel for specified high-strength or corrosion-resistant alloys) to cut costs. This compromises durability, heat resistance, and leak prevention. Always verify material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) and conduct periodic material testing.
2. Inadequate Manufacturing Tolerances
Poor dimensional accuracy in stamping, welding, or flange alignment can lead to oil leaks, improper gasket sealing, or installation issues. Ensure suppliers adhere to OEM specifications and implement statistical process control (SPC) during production.
3. Weak Welding and Seam Integrity
Oil pans with poorly executed welds (e.g., incomplete penetration, porosity) are prone to cracking under thermal cycling and vibration. Require non-destructive testing (NDT) such as dye penetrant or ultrasonic inspection and validate with sample destructive testing.
4. Insufficient Surface Protection
Inadequate or inconsistent coatings (e.g., zinc plating, epoxy) increase susceptibility to corrosion, especially in harsh environments. Verify coating thickness and adherence to standards like ASTM B633 or ISO 12944.
5. Lack of Performance Validation
Suppliers may not conduct pressure, thermal cycle, or vibration testing. Insist on test reports simulating real-world conditions and request third-party validation when necessary.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Unauthorized Use of OEM Designs
Many oil pans are reverse-engineered from original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts. Sourcing such components without proper licensing constitutes IP infringement, including design patent and copyright violations. Always confirm the supplier has legitimate rights or produces under licensed agreements.
2. Ambiguous Design Ownership in Custom Parts
When co-developing custom oil pans, failure to define IP ownership in contracts can lead to disputes. Clearly specify in writing who retains rights to tooling, designs, and modifications.
3. Tooling and Mold IP Misuse
Suppliers may reuse or resell tooling created for your design to produce parts for competitors. Protect your investment by retaining ownership of tooling and including non-disclosure and non-compete clauses in supplier agreements.
4. Grey Market and Counterfeit Risks
Sourcing through unauthorized distributors increases the risk of counterfeit or non-compliant parts bearing OEM trademarks. Use only approved channels and conduct supplier audits to verify authenticity and traceability.
5. Inadequate Legal Protection in Contracts
Generic purchase orders often lack robust IP clauses. Ensure contracts include explicit provisions on IP ownership, confidentiality, indemnification against infringement claims, and audit rights.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough supplier qualification audits, including facility visits and quality system reviews (e.g., IATF 16949 certification).
- Require detailed documentation: material certs, test reports, design approvals, and IP clearances.
- Use legally reviewed supply agreements with strong IP and quality clauses.
- Perform incoming inspection and periodic quality audits.
- Collaborate with legal counsel to assess IP risks, especially in cross-border sourcing.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, companies can ensure reliable performance, avoid legal exposure, and maintain brand integrity in their supply chain.
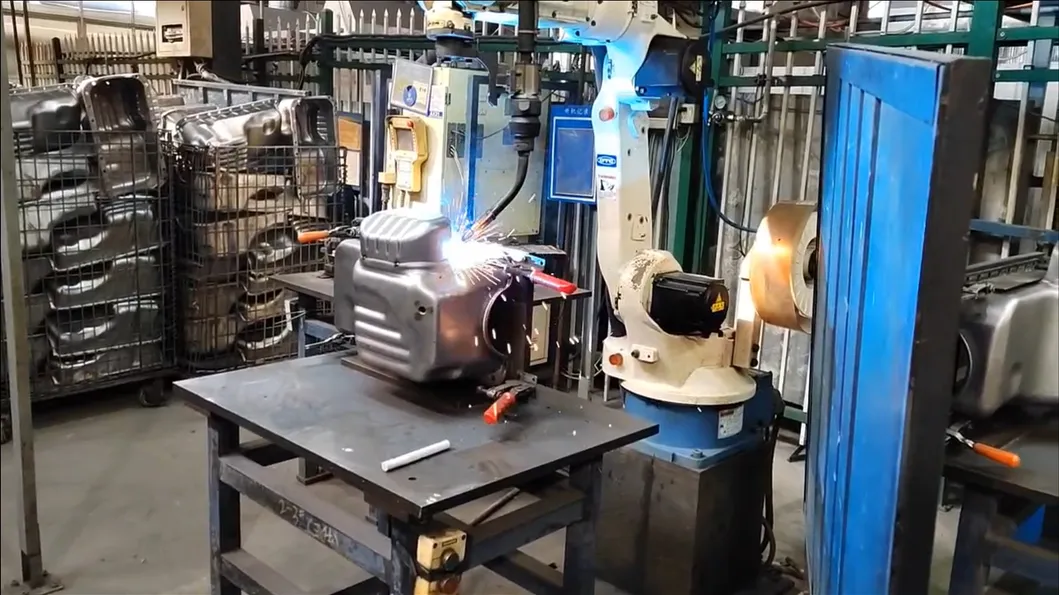
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Metal Oil Pan
Transporting and handling metal oil pans—commonly used in automotive and industrial engine systems—requires adherence to specific logistics protocols and regulatory compliance standards. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe, efficient, and compliant movement of metal oil pans across supply chains.
1. Product Classification & Identification
- HS Code: Determine the correct Harmonized System (HS) code for customs declaration. Typically, metal oil pans fall under:
- HS 8708.29.xx (Parts and accessories of internal combustion engines for vehicles)
-
Confirm with local customs authority based on material (e.g., steel, aluminum) and application.
-
UN Number & Hazard Classification: Metal oil pans are generally non-hazardous when clean and dry. However:
- If contaminated with oil or flammable residues, they may be classified as hazardous waste (e.g., UN 3082, Environmentally Hazardous Substance).
- Proper cleaning and declaration are essential to avoid regulatory penalties.
2. Packaging & Handling
- Packaging Requirements:
- Use sturdy wooden crates, pallets, or corrugated cardboard with edge protection.
- Secure pans to prevent movement during transit; use straps, corner boards, or void fill.
-
For export, ensure packaging complies with ISPM 15 (International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures No. 15) if wood is used—heat-treated and stamped.
-
Handling Precautions:
- Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., forklifts) for heavy loads.
- Protect sharp edges to prevent damage to packaging or injury.
- Label with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and weight for safe handling.
3. Transportation Modes & Requirements
- Domestic & International Shipping:
- Road: Ensure load is secured per FMCSA (U.S.) or ADR (Europe) standards.
- Sea Freight: Use containerized shipping; protect against moisture with desiccants.
-
Air Freight: Generally acceptable if non-hazardous; verify with IATA if any residue is present.
-
Stackability & Weight Limits:
- Confirm maximum stack height to avoid crushing lower units.
- Adhere to pallet weight limits (e.g., 1,500–2,000 lbs for standard GMA pallets).
4. Regulatory Compliance
- Environmental Regulations:
- If pans are used or contaminated, handle under EPA (U.S.) or equivalent regulations for waste oil and metal recycling.
-
Documentation such as Waste Manifests may be required.
-
REACH & RoHS (EU Compliance):
-
Ensure materials (e.g., coatings, alloys) comply with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives if applicable.
-
Customs Documentation:
- Provide commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill.
- Include origin declaration (e.g., Certificate of Origin) for tariff eligibility.
5. Storage Conditions
- Store in a dry, indoor environment to prevent rust or corrosion.
- Elevate pallets off the floor to avoid moisture absorption.
- Separate from chemicals or flammable materials.
6. Reverse Logistics & Recycling
- Used oil pans are often recyclable. Coordinate with certified metal recyclers.
- Follow local regulations for scrap metal transport and disposal.
- Maintain records for environmental compliance audits.
7. Key Documentation Checklist
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin (if required)
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS/SDS) – if contaminated
- ISPM 15 Compliance Mark (for wood packaging)
- Customs Declaration Forms
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for metal oil pans involve accurate classification, secure packaging, regulatory awareness, and proper documentation. By following this H2-level guidance, businesses can ensure safe transportation, avoid customs delays, and remain compliant with international and environmental standards. Always consult local regulations and update procedures as standards evolve.
Conclusion for Sourcing Metal Oil Pan
In conclusion, sourcing a metal oil pan requires a strategic evaluation of material quality, manufacturing capabilities, supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and compliance with industry standards. Selecting the right supplier involves assessing their experience in producing durable, precision-engineered oil pans that meet specific performance and environmental requirements. Factors such as material selection (e.g., stamped steel, aluminum, or reinforced composites), corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and compatibility with engine systems play a critical role in ensuring long-term reliability.
Establishing partnerships with suppliers who demonstrate consistent quality control, timely delivery, and the ability to scale production is essential for maintaining supply chain integrity. Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—beyond unit price—to include logistics, lead times, and potential warranty claims will lead to more informed sourcing decisions.
Ultimately, a well-sourced metal oil pan contributes significantly to engine performance, durability, and operational safety. By prioritizing quality, technical capability, and sustainable supplier relationships, organizations can secure a critical component that supports overall product excellence and customer satisfaction.