The global laser welding machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision, automation-compatible solutions in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 2.25 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, greater adoption of Industry 4.0 practices, and the rising need for energy-efficient manufacturing processes. Metal laser welding machines, in particular, have gained prominence due to their superior speed, accuracy, and weld strength compared to traditional methods. As manufacturers seek to enhance production efficiency and reduce operational costs, the demand for advanced metal laser welding systems continues to rise—particularly in emerging economies across Asia-Pacific and Latin America. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, setting industry benchmarks in innovation, reliability, and technological integration. The following list highlights the top 10 metal laser welding machine manufacturers shaping the future of precision manufacturing.
Top 10 Metal Laser Welding Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Focus on laser
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: Laser marking machines Laser cutting machines Laser welding machines Automation Laser generator Semiconductor packaging equipment 3D printers Motor….
#2 Laser Technology & Laser Machines from ALPHA LASER
Website: alphalaser.eu
Key Highlights: High-quality laser technology & laser sytems from ALPHA LASER: powerful laser machines for metalworking: mobile, flexible, & precise ✓ technical support ✓….
#3 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#4 Laser Machines
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: Distribution and manufacture of laser machinery. Sales of laser marking, laser cleaning, laser engraving and welding machines….
#5 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered by the most experienced engineers and design ……
#6 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#7 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: Orotig, with +30 years of experience, specializes in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding engraving and casting metals….
#8 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Discover Your Laser Welding Solution IPG is a partner for every stage of production from research and development to full-scale manufacturing….
#9 Fanuci & Falcon
Website: fanuci-falcon.com
Key Highlights: FANUCI & FALCON is an innovative high-tech enterprise specializing in the manufacturing of advanced fiber laser machines for metal processing applications ……
#10 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Get manual to fully automated laser welding machines that weld plastics and metals with speed and precision while improving throughput….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Metal Laser Welding Machine

H2: Market Trends in Metal Laser Welding Machines for 2026
As industries continue to embrace automation and high-precision manufacturing, the global market for metal laser welding machines is poised for significant evolution by 2026. Driven by technological innovation, demand from key industrial sectors, and regional economic developments, several trends are expected to shape the landscape of this market.
1. Advancements in Laser Technology
By 2026, the integration of higher-power fiber lasers and ultrafast (pulsed) lasers is expected to dominate the market. Fiber laser welding machines, known for their energy efficiency, reliability, and superior beam quality, will increasingly replace traditional CO₂ and lamp-pumped lasers. Innovations such as remote laser welding, real-time monitoring, and adaptive control systems will enhance precision and reduce cycle times, making laser welding more accessible across small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
2. Rising Demand from Automotive and EV Manufacturing
The electric vehicle (EV) revolution will be a key growth driver. As automakers scale EV production, the need for lightweight, durable, and efficiently assembled components will boost demand for laser welding in battery pack assembly, motor manufacturing, and body-in-white structures. High-speed, high-accuracy laser welding enables strong, consistent joints ideal for aluminum and mixed-material construction—critical in EV design.
3. Expansion in Aerospace and Defense Applications
The aerospace sector will continue to adopt laser welding for its ability to join high-strength alloys like titanium and Inconel with minimal heat distortion. By 2026, increased defense spending and the production of next-generation aircraft and drones will further stimulate demand for automated, high-precision laser welding systems, including hybrid laser-arc solutions.
4. Growth in Asia-Pacific Markets
China, Japan, South Korea, and India are expected to lead market expansion due to rapid industrialization, government support for advanced manufacturing (e.g., “Made in China 2025”), and rising investments in automation. Local manufacturing of laser components will reduce system costs and increase adoption, especially in electronics, consumer goods, and heavy machinery sectors.
5. Integration of Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
Laser welding machines will increasingly feature IoT connectivity, AI-driven process optimization, and digital twin technologies. By 2026, smart welding cells capable of self-diagnosis, predictive maintenance, and seamless integration with robotic assembly lines will become standard in high-end production environments, improving uptime and quality control.
6. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will push manufacturers toward energy-efficient laser systems. Fiber lasers, with wall-plug efficiency exceeding 40%, will be favored over less-efficient alternatives. Additionally, reduced material waste and lower consumable usage in laser welding will align with circular economy principles.
7. Competitive Landscape and Price Pressure
Increased competition from both established players (e.g., TRUMPF, IPG Photonics, Han’s Laser) and emerging regional manufacturers will drive price reductions and innovation. This will democratize access to laser welding, especially in developing economies, but may compress profit margins for vendors relying on standardized systems.
8. Customization and Modular Solutions
To meet diverse industrial needs, suppliers will offer more modular and customizable laser welding platforms. These systems will support quick reconfiguration for different materials, thicknesses, and geometries, appealing to job shops and contract manufacturers serving multiple sectors.
In summary, the 2026 market for metal laser welding machines will be defined by technological sophistication, sector-specific applications, and regional growth dynamics. Companies investing in automation, smart features, and cost-effective solutions will be best positioned to capitalize on these evolving trends.
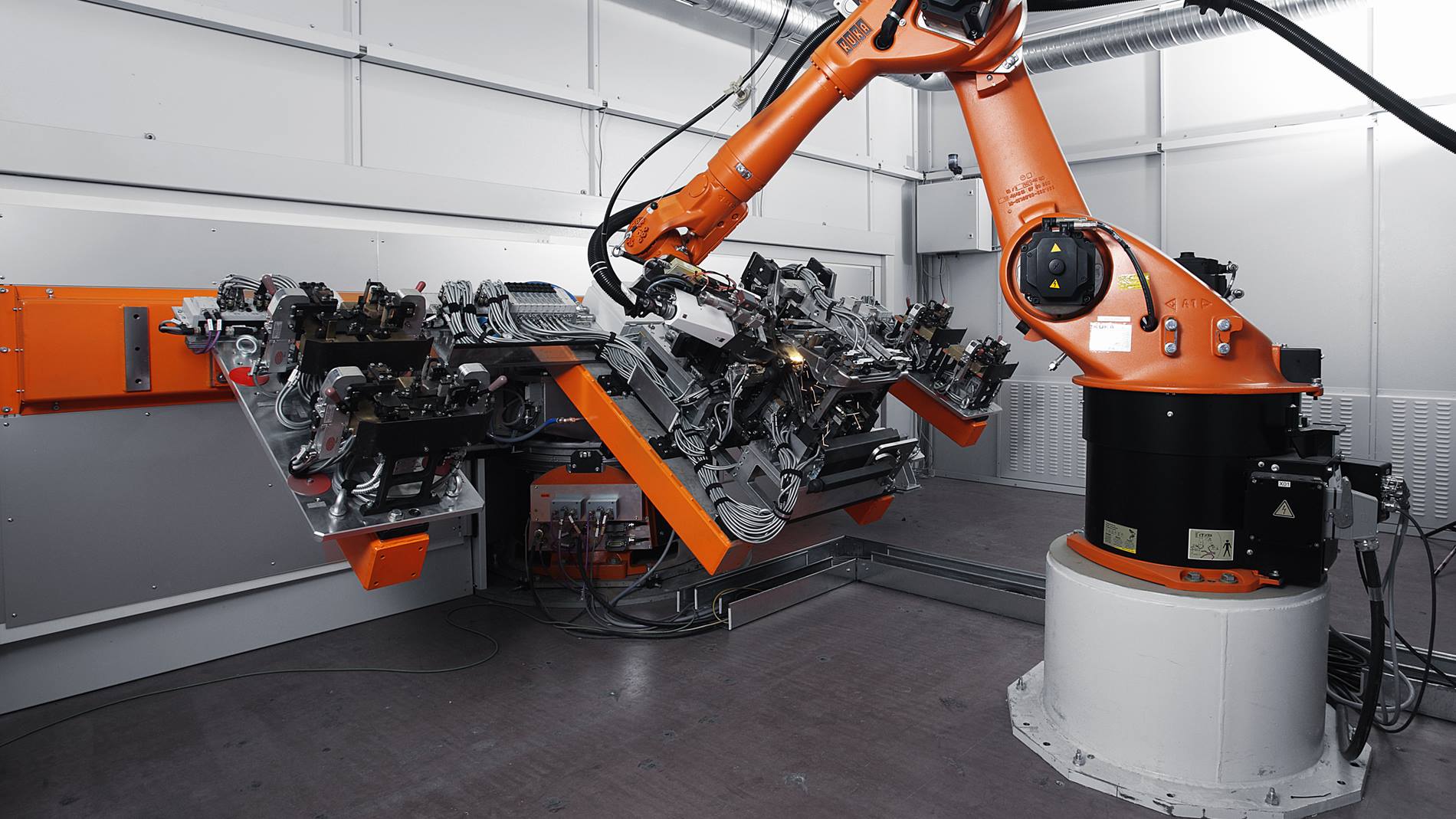
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Metal Laser Welding Machines (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a metal laser welding machine involves significant investment and technical complexity. Buyers often encounter critical pitfalls related to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) risks, which can lead to costly downtime, legal disputes, or subpar performance. Being aware of these issues upfront is essential for making informed procurement decisions.
Poor Quality Control and Inadequate Manufacturing Standards
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing laser welding machines—especially from less-established suppliers—is inconsistent quality due to weak or absent quality control processes. Some manufacturers may cut corners on materials, laser source quality, cooling systems, or motion control components to reduce costs, resulting in unreliable performance, frequent breakdowns, and shorter machine lifespan. Buyers often discover these shortcomings only after installation, by which point warranty claims may be difficult to enforce, particularly with overseas vendors.
Misrepresentation of Laser Specifications and Performance
Suppliers may exaggerate key performance metrics such as laser power output, beam quality (M² factor), welding speed, or penetration depth. For example, a machine advertised as a “2000W fiber laser” might deliver significantly less power under continuous operation due to poor thermal management or substandard laser diodes. Without independent verification or third-party testing reports, buyers risk acquiring equipment that fails to meet production requirements, leading to rework, scrap, or production delays.
Lack of Compliance with International Safety and Certification Standards
Many low-cost suppliers fail to comply with essential safety and regulatory standards such as CE, FDA (for U.S. market), or ISO certifications. Non-compliant machines may pose safety hazards (e.g., insufficient laser shielding, inadequate interlocks) and could be barred from operation in regulated environments. Additionally, operating non-certified equipment may void insurance coverage and expose the buyer to liability.
Hidden Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
A critical yet often overlooked pitfall involves intellectual property violations. Some manufacturers, particularly in regions with weak IP enforcement, may use cloned or reverse-engineered components—such as laser sources, control software, or optical systems—without proper licensing. If these components infringe on patents or copyrights held by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), buyers could face legal action, shipment seizures, or forced decommissioning of the machine. The buyer, even if unaware, may be held liable as the end-user in certain jurisdictions.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Many suppliers offer attractive upfront pricing but lack a reliable global service network. When technical issues arise, delayed response times, unavailability of spare parts, or lack of trained technicians can result in extended machine downtime. This is especially problematic with proprietary components that are not standardized or supported locally, increasing total cost of ownership significantly.
Software Limitations and Proprietary Lock-In
Some machines come with closed-source or poorly documented control software, limiting customization, integration with existing manufacturing systems (e.g., MES or ERP), or future upgrades. In extreme cases, software may be pirated or lack proper licensing, exposing the buyer to cybersecurity risks or legal challenges. Additionally, the inability to modify or maintain software in-house can create long-term dependency on the supplier.
Insufficient Testing and Validation Before Shipment
Reputable suppliers conduct comprehensive factory acceptance tests (FAT), including welding trials on actual materials, alignment verification, and performance benchmarking. However, some vendors skip or minimize these steps to expedite delivery. Without proper validation, buyers receive machines that may not perform as promised under real-world conditions, leading to unexpected requalification efforts and production delays.
By recognizing these common pitfalls—particularly those tied to quality inconsistencies and IP vulnerabilities—buyers can implement stronger due diligence, demand transparency, and select suppliers that offer not just competitive pricing, but also reliability, compliance, and legal safety.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Metal Laser Welding Machine
Product Classification and Documentation
Ensure accurate classification of the metal laser welding machine under the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) code, typically falling under 8456.11 or 8456.12 for laser-based metal cutting and welding machinery. Prepare a detailed commercial invoice stating the full technical specifications, value, country of origin, and end-use. Include a packing list, bill of lading (or air waybill), and certificate of origin. Retain technical data sheets, user manuals, and safety documentation for customs and regulatory review.
Export Controls and Licensing
Determine if the machine is subject to export control regulations such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR), depending on laser power, wavelength, and precision. Verify if an export license is required based on the destination country’s classification and end-user. Complete the necessary forms (e.g., BIS-711 for EAR-controlled items) and file through the appropriate government portal (e.g., SNAP-R). Maintain records of export authorization for at least five years.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Ensure the machine complies with international safety standards such as IEC 60825-1 (laser safety) and IEC 61496 (safety of machinery – electro-sensitive protection equipment). Confirm CE marking for EU shipments, indicating conformity with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), EMC Directive (2014/30/EU), and RoHS (2011/65/EU). For shipments to North America, verify compliance with ANSI Z136.1 and UL/CSA safety standards. Provide a Declaration of Conformity (DoC) and technical construction file upon request.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Package the machine securely using wooden crates or reinforced containers with shock-absorbing materials to protect sensitive optics and electronics. Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”) and include hazard labels if applicable (e.g., laser radiation warning). Secure all moving parts and disconnect power sources. Include desiccants to prevent moisture damage during transit, particularly for ocean freight.
Transportation and Freight Considerations
Choose a freight forwarder experienced in handling high-value industrial equipment. For air freight, ensure dimensional weight and payload limits are respected. For sea freight, consider container type (e.g., 20’ or 40’ dry container) and stowage location to minimize vibration and temperature fluctuations. Use real-time GPS tracking and temperature/humidity monitoring when possible. Insure the shipment for full replacement value against loss, damage, or delay.
Import Clearance and Duties
Provide the importer with all necessary documentation for customs clearance in the destination country, including a detailed invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, and compliance certifications. Research and account for applicable import duties, VAT, and anti-dumping taxes. Some countries may require additional inspections or product registration (e.g., China CCC, South Korea KC). Assign an in-country customs broker if needed to facilitate timely clearance.
End-of-Life and Environmental Compliance
Ensure compliance with environmental regulations such as WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) in the EU, which may require registration and reporting for proper end-of-life disposal. Inform customers of take-back obligations and recycling procedures. Design packaging to be recyclable and minimize hazardous substances in accordance with RoHS and REACH (EU) or TSCA (U.S.) requirements.
Post-Shipment Support and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records of all logistics and compliance documentation for a minimum of five years. Provide the end-user with installation support, training, and access to service manuals. Monitor regulatory updates in target markets and revise compliance protocols accordingly. Establish a process for reporting and resolving any compliance issues that arise post-delivery.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Metal Laser Welding Machine
After a thorough evaluation of technical requirements, production needs, budget considerations, and supplier capabilities, sourcing a metal laser welding machine represents a strategic investment in enhancing manufacturing precision, efficiency, and product quality. The selection process emphasized key factors such as laser type (fiber vs. CO₂), power output, automation compatibility, beam quality, and after-sales support.
By choosing a reliable machine from a reputable supplier that aligns with both current and future production demands, the organization can achieve stronger welds, reduced heat distortion, lower operational costs, and improved throughput. Additionally, features such as remote monitoring, easy integration with existing production lines, and comprehensive training and maintenance services further ensure long-term operational success.
In conclusion, the decision to source a metal laser welding machine not only meets immediate fabrication needs but also positions the company at the forefront of advanced manufacturing technologies, supporting scalability, innovation, and competitiveness in the evolving industrial landscape.