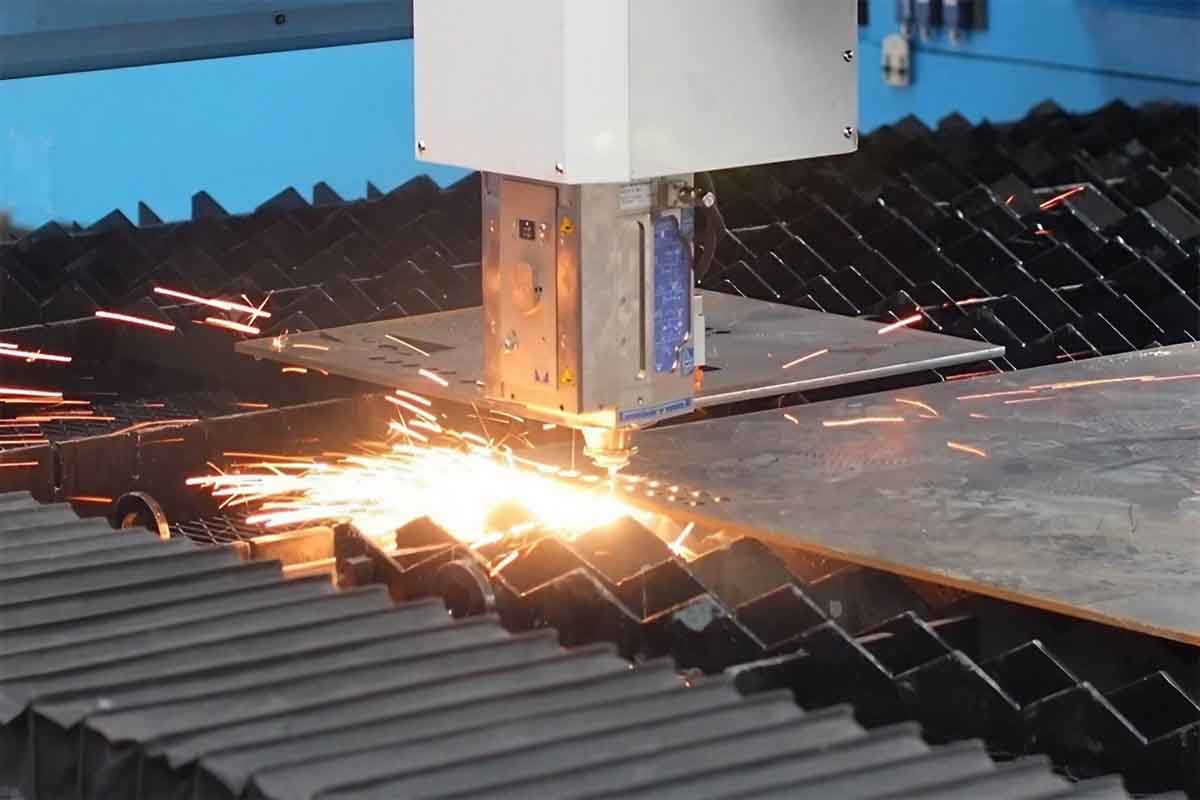
The global metal fabrication and steel manufacturing industry continues to expand, driven by rising demand from construction, automotive, and industrial sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global steel market was valued at USD 1.27 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing infrastructure development in emerging economies and advancements in sustainable steel production technologies. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence reports steady momentum in the metal fabrication market, with a projected CAGR of over 5% through 2029, supported by automation and precision engineering demands. As the industry evolves, a select group of manufacturers lead in capacity, innovation, and global reach. Here’s a data-driven look at the top 10 metal fabrication steel manufacturers shaping the future of industrial manufacturing.
Top 10 Metal Fabrication Steel Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Steel Manufacturers Association
Domain Est. 1995
Website: steelnet.org
Key Highlights: EAFs produce over 70% of all American steel, compared to just 28% globally. It’s one more reason to choose American EAF steel. Stronger, smarter, and proudly ……
#2 Nucor
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nucor.com
Key Highlights: North America’s largest steel manufacturer and recycler. We are a team forged around a vision for leading our industry by providing unparalleled customer care….
#3 Metals Supplier & Service Center
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sss-steel.com
Key Highlights: Triple-S Steel® and its subsidiaries are a leading distributor and service center of steel products and processing services. Learn more!…
#4 U.S. Steel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ussteel.com
Key Highlights: We’re bringing industry-leading steelmaking talent and technology together to help customers solve, innovate and excel. Just one example: lighter, stronger ……
#5 Steel Dynamics
Domain Est. 1999
Website: steeldynamics.com
Key Highlights: We are one of the largest domestic steel producers and metal recyclers in North America, combined with a meaningful downstream steel fabrication platform….
#6 Worthington Steel
Domain Est. 1999
Website: worthingtonsteel.com
Key Highlights: Premier value-added steel processor, producer of electrical steel laminations and automotive lightweighting solutions in North America and beyond….
#7 Fabricators and Manufacturers Association
Domain Est. 2020
Website: fmamfg.org
Key Highlights: FMA provides training programs, exclusive networking events, and market-leading publications and trade shows to help metal fabrication professionals……
#8 BTD Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1997
Website: btdmfg.com
Key Highlights: Your reliable and innovative partner for custom metal fabrication, welding, tool & die, CNC, EDM and more from locations in MN, IL and GA….
#9 Custom Sheet Metal, Stainless Steel & Aluminum Fabrication
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nobleindustries.com
Key Highlights: Noble Industries is a leader in custom sheet metal, stainless steel and aluminum fabrication services, offering precision and quality….
#10 Metal Fabrication Excellence
Domain Est. 2018
Website: sscmetalfabrication.com
Key Highlights: Metal fabrication is our true passion. Aluminum fabrication, steel fabrication, and stainless steel fabrication is the core of our capabilities….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Metal Fabrication Steel
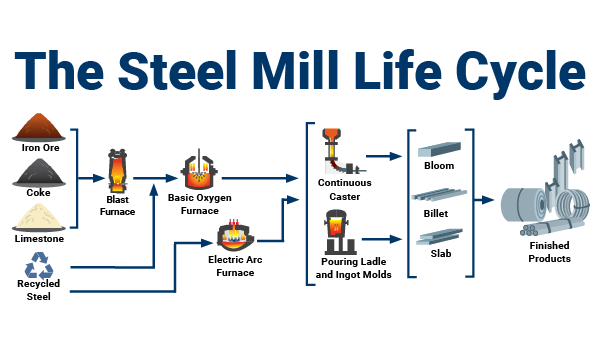
H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends in Metal Fabrication Steel
The global metal fabrication steel market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, sustainability demands, and shifting industrial priorities. Several key trends are expected to shape the landscape of steel fabrication in the coming years.
1. Growth in Infrastructure and Construction Sectors
Governments worldwide are increasing investments in infrastructure development—especially in emerging economies—as part of post-pandemic recovery and long-term urbanization strategies. Projects such as smart cities, transportation networks, and renewable energy installations will drive demand for fabricated steel. In North America and Europe, infrastructure modernization initiatives, including bridge replacements and rail expansions, will further bolster market growth.
2. Adoption of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
By 2026, digitalization and automation are expected to be deeply embedded in steel fabrication processes. Technologies such as robotic welding, AI-driven design optimization, and CNC-controlled cutting systems will enhance precision, reduce waste, and improve production efficiency. The integration of Industry 4.0 principles—such as IoT-enabled equipment monitoring and predictive maintenance—will become standard, improving operational performance across fabrication shops.
3. Rising Demand for Sustainable and Green Steel
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are accelerating the shift toward low-carbon steel production. By 2026, green steel—produced using hydrogen-based reduction or electric arc furnaces powered by renewable energy—is expected to gain market share. Fabricators will increasingly source recycled steel and partner with suppliers offering Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) to meet green building standards like LEED and BREEAM.
4. Expansion in Renewable Energy and EV Infrastructure
The rapid growth of wind, solar, and electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure will create new demand for steel fabrication. Wind turbine towers, solar panel support structures, and EV manufacturing facilities require high-strength, precision-fabricated steel components. This sector is anticipated to be one of the fastest-growing end-use markets for fabricated steel by 2026.
5. Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions have prompted a shift toward regionalized production. Nearshoring and onshoring of steel fabrication are expected to rise, particularly in North America and Europe, to reduce dependency on global supply chains. This trend will support local job creation and reduce lead times, enhancing responsiveness to customer needs.
6. Material Innovation and Lightweighting
While steel remains dominant, competition from alternative materials like aluminum and composites is pushing innovation in high-strength, low-alloy (HSLA) steels. These advanced steels offer improved strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for transportation and construction applications. Fabricators will need to adapt processes to handle new grades and ensure compatibility with emerging design requirements.
7. Labor Challenges and Workforce Development
The industry continues to face a skilled labor shortage. By 2026, investment in vocational training, apprenticeship programs, and digital upskilling will be critical. Fabricators that embrace hybrid roles—where technicians work alongside automated systems—will gain a competitive edge in productivity and talent retention.
In summary, the 2026 metal fabrication steel market will be defined by technological advancement, sustainability imperatives, and evolving demand patterns. Companies that proactively adopt innovation, prioritize environmental responsibility, and strengthen supply chain agility will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
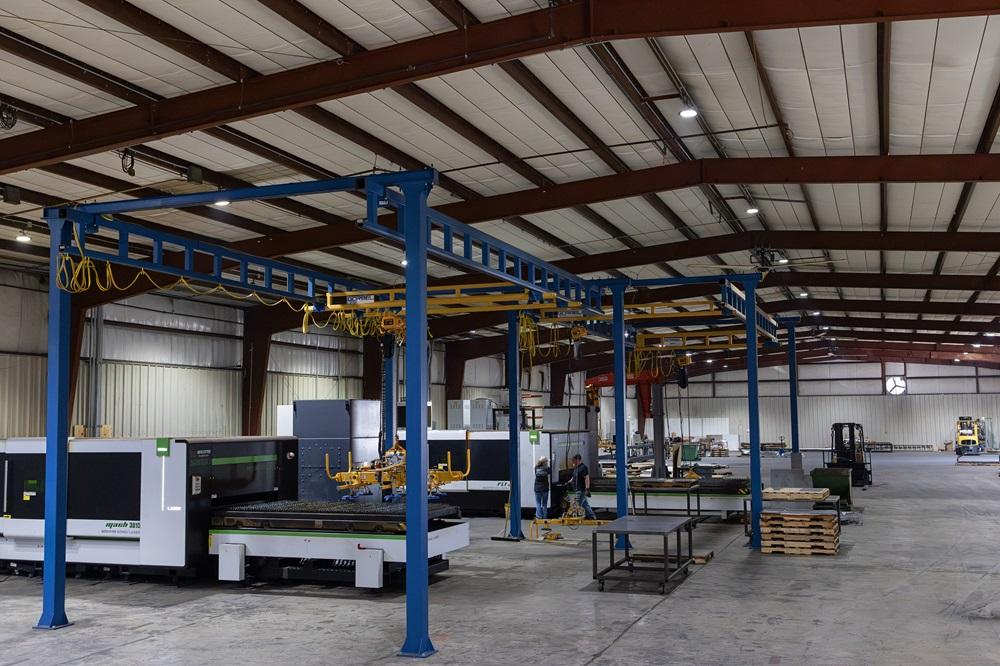

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Metal Fabrication Steel (Quality, IP)
Sourcing metal fabrication steel involves navigating a complex landscape where quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) risks can significantly impact project timelines, costs, and legal compliance. Below are critical pitfalls to avoid in both quality assurance and IP protection.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Material Certification
One of the most common issues is receiving steel without proper material test reports (MTRs) or mill certifications. Without valid documentation, there’s no verifiable proof that the steel meets required specifications (e.g., ASTM, AISI, or ISO standards), increasing the risk of structural failure or non-compliance in regulated industries.
Inconsistent Tolerances and Dimensional Accuracy
Fabrication projects require precise dimensions. Suppliers in low-cost regions may deliver steel with inconsistent thickness, flatness, or edge quality, leading to fit-up problems during assembly and costly rework.
Poor Surface Finish and Contamination
Unaddressed surface defects—such as mill scale, rust, or slag inclusions—can compromise welding integrity and final product appearance. Some suppliers may not perform adequate surface inspections or cleaning prior to shipment.
Use of Substandard or Recycled Materials
To cut costs, some suppliers may substitute specified grades with lower-grade or recycled steel that does not meet mechanical property requirements. This can lead to failures in load-bearing applications or during stress testing.
Lack of Traceability
Without full material traceability (heat number tracking), it becomes impossible to investigate the root cause of defects or comply with industry regulations in aerospace, construction, or energy sectors.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Unauthorized Use or Replication of Designs
When outsourcing fabrication, especially overseas, there’s a risk that your proprietary designs, tooling, or engineering drawings may be copied or used for third-party production without consent. Jurisdictional differences in IP enforcement can complicate legal recourse.
Weak Contractual IP Clauses
Many procurement agreements fail to explicitly assign ownership of custom tooling, jigs, fixtures, or design modifications. Without clear IP clauses, suppliers may claim partial ownership or reuse designs for competing clients.
Inadequate Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs)
Even with an NDA in place, its enforceability varies across countries. Some regions may not uphold confidentiality standards, allowing design leaks or reverse engineering by subcontractors in the supply chain.
Digital Data Exposure
Transferring CAD files or CNC programs to suppliers increases digital IP exposure. Without secure file-sharing protocols or watermarking, sensitive design data can be intercepted or misused.
Supplier Subcontracting Without Consent
Suppliers may outsource parts of the fabrication process to unauthorized subcontractors—often with less rigorous IP controls—increasing the risk of unauthorized replication and quality drift.
Mitigation Strategies
- Require full material traceability and third-party inspection reports.
- Audit suppliers regularly, including unannounced visits.
- Use detailed technical specifications and acceptance criteria in procurement contracts.
- Enforce strong IP clauses, including design ownership and usage restrictions.
- Execute jurisdiction-specific NDAs and register IP in key manufacturing countries.
- Limit digital file access and use encrypted platforms for data transfer.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures consistent quality, protects innovation, and reduces operational and legal risks in metal fabrication sourcing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Metal Fabrication Steel
Overview of Steel Logistics in Metal Fabrication
Steel logistics in metal fabrication involves the coordinated movement, storage, and handling of raw steel materials—from procurement through production to final delivery of fabricated components. Efficient logistics ensures timely material availability, reduces downtime, and maintains workflow continuity. Key elements include supply chain sourcing, transportation mode selection, inventory management, and coordination between suppliers, fabricators, and end customers.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Metal fabrication using steel is subject to multiple regulatory standards to ensure safety, environmental protection, and product quality. Key compliance areas include:
– OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration): Guidelines for workplace safety, including handling of heavy materials, machine operation, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
– EPA (Environmental Protection Agency): Regulations on emissions, wastewater discharge, and hazardous waste disposal from cutting, welding, and surface treatment processes.
– DOT (Department of Transportation): Rules governing the safe transportation of steel, including load securement, vehicle weight limits, and hazardous material classification (if applicable).
– ISO 3834 and ISO 9001: International standards for welding quality and quality management systems, often required for certification in industrial contracts.
Material Handling and Storage Best Practices
Proper handling and storage of steel materials prevent damage, corrosion, and workplace accidents:
– Store steel off the ground using pallets or racks to avoid moisture contact.
– Segregate different steel grades and coatings to prevent cross-contamination.
– Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., magnetic lifters, slings) and follow load capacity guidelines.
– Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to minimize rust and material aging.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
Transporting steel requires planning due to its weight, dimensions, and susceptibility to damage:
– Choose transportation modes (truck, rail, or sea) based on volume, distance, and delivery timelines.
– Secure loads properly using chains, straps, or dunnage to prevent shifting during transit.
– Comply with carrier requirements for weight distribution and over-dimensional loads.
– Provide accurate shipping documentation, including bills of lading, material certifications, and hazardous material disclosures (if coated or treated).
Import/Export and Trade Compliance
For international steel procurement or delivery, compliance with trade regulations is essential:
– Verify steel origin to comply with trade agreements and tariffs (e.g., Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act in the U.S.).
– Prepare necessary documentation: commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, and mill test reports (MTRs).
– Adhere to customs clearance procedures and anti-dumping regulations.
– Ensure compliance with international standards such as CE marking (Europe) or JIS (Japan), if applicable.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Traceability and quality control are critical in steel fabrication:
– Maintain detailed records of material heat numbers, certifications, and inspection reports.
– Implement in-process inspections and final quality checks per project specifications.
– Use barcoding or digital tracking systems to monitor material flow through the fabrication process.
– Retain documentation for audits and customer compliance requirements.
Environmental and Sustainability Practices
Adopt sustainable logistics and operational practices:
– Recycle steel scrap through certified processors to reduce waste and support circular economy goals.
– Optimize cutting patterns to minimize material waste (nesting software).
– Use energy-efficient equipment and reduce emissions in fabrication processes.
– Partner with suppliers who follow sustainable mining and production practices.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Identify and mitigate potential disruptions in steel supply chains:
– Diversify suppliers to avoid dependency on a single source.
– Monitor global steel market trends and lead times.
– Maintain safety stock for critical materials.
– Develop contingency plans for transportation delays, natural disasters, or regulatory changes.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management in metal fabrication steel operations ensure operational efficiency, regulatory adherence, and customer satisfaction. By integrating best practices in handling, transportation, documentation, and sustainability, fabricators can maintain competitive advantage and long-term success in a highly regulated industry.
In conclusion, sourcing steel for metal fabrication requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, lead time, and supplier reliability. It is essential to evaluate suppliers based on their certifications, production capabilities, and track record for consistency and compliance with industry standards. The choice of steel grade and form (sheet, bar, structural) should align with the specific requirements of the fabrication project, including strength, weldability, and environmental resistance. Establishing strong relationships with reputable suppliers, considering both local and global options, can enhance supply chain resilience and ensure timely delivery. Additionally, staying informed about market trends and material costs enables better negotiation and long-term planning. Ultimately, a well-executed sourcing strategy supports efficient fabrication processes, high-quality end products, and sustained operational success.