The global Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) market has experienced steady growth, driven by rising demand in the furniture, construction, and interior design sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global MDF market was valued at USD 58.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is largely fueled by the increasing adoption of engineered wood products in residential and commercial applications, particularly in emerging economies across Asia-Pacific and Latin America. As sustainability and cost-efficiency become key priorities for manufacturers and consumers alike, MDF—known for its uniform texture, ease of machining, and compatibility with finishes—has emerged as a preferred material in modern furniture production. With this rising demand, a select group of manufacturers has distinguished itself through innovation, scale, and strategic geographic positioning. Below are the top nine MDF furniture manufacturers shaping the industry’s future through quality, supply chain resilience, and data-informed production strategies.
Top 9 Medium Density Fiberboard Furniture Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard)
Domain Est. 1996
Website: uniboard.com
Key Highlights: Uniboard MDF is produced using the latest in manufacturing technology. From the 9-foot continuous press to super refining and the latest in sanding and cutting ……
#2 Particle Board and MDF
Domain Est. 1998
Website: hardwoodind.com
Key Highlights: Particle Board / MDF (medium density fiberboard) Hardwood Industries carries a diverse selection of industrial grade particle board to provide cabinet and ……
#3 Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF)
Domain Est. 1996
Website: roseburg.com
Key Highlights: Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF). Roseburg offers the most diverse and technically-advanced line of medium density fiberboard (MDF) products in North America….
#4 MDF Panels
Domain Est. 1996
Website: columbiaforestproducts.com
Key Highlights: Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) that is available at Columbia Forest Product’s, is made in a production process similar to Particleboard (PBC) except that all ……
#5 Trupan Ultralight MDF
Domain Est. 1996
Website: na.arauco.com
Key Highlights: Trupan Ultralight is ARAUCO’s lightest weight MDF board. It offers a smooth, sanded surface, homogenous surface and uniform color, making it ideal for moulding….
#6 MDF
Domain Est. 1997
Website: westfraser.com
Key Highlights: Made from western white softwoods, the purity and long fibre of West Fraser’s medium density fibreboard (MDF) make it well-suited to a variety of finishes ……
#7 Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF)
Domain Est. 1999
Website: metroply.com
Key Highlights: Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) is an engineered wood product made by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into wood fibers….
#8
Domain Est. 2009
Website: kimtinmdf.com
Key Highlights: HDF is a type of fiberboard with a higher density of wood fibers than ordinary boards. Manufactured with engineering that can be meet almost any application ……
#9 MDF Board Furniture
Domain Est. 2013
Website: vir-mdf.com
Key Highlights: This is furniture made from medium-density fiberboard (MDF), which is made from wood fibres, resins and wax that has been heated and compressed to create a ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Medium Density Fiberboard Furniture

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) Furniture
The Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) furniture market in 2026 is projected to experience nuanced growth, shaped by evolving consumer preferences, sustainability imperatives, technological advancements, and competitive pressures. While facing challenges from alternative materials and environmental scrutiny, MDF remains a cornerstone of the mid-to-lower-tier furniture segment due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Sustainability and Environmental Concerns as Primary Drivers:
By 2026, environmental sustainability will be the dominant force influencing MDF furniture production and consumer choices. Key developments include:
* Increased Adoption of Formaldehyde-Free & Low-Emission MDF: Regulatory pressure (e.g., CARB, EPA TSCA Title VI, EUTR) and consumer demand will drive widespread adoption of ultra-low formaldehyde (ULEF) and no-added-formaldehyde (NAF) resins. Furniture marketed as “green” or “healthy” will increasingly use these variants.
* Rise of Bio-Based and Recycled Content MDF: Manufacturers will innovate with MDF incorporating recycled wood fibers (post-consumer and post-industrial) and bio-based binders (e.g., soy, lignin, tannin) to reduce reliance on virgin wood and fossil-fuel-based resins, enhancing lifecycle sustainability.
* Focus on Circularity: Design for disassembly, recyclability of MDF waste streams, and take-back schemes will gain traction, moving towards a more circular economy model for MDF products.
2. Premiumization and Enhanced Performance:
To combat perceptions of MDF as a “low-quality” material and compete with solid wood and plywood, the market will see a shift towards higher-performance MDF:
* Moisture-Resistant and Water-Resistant MDF (MR-MDF/WR-MDF): Demand will surge for MDF engineered for humid environments (bathrooms, kitchens, outdoor furniture), utilizing advanced wax emulsions and resins.
* Increased Density and Strength: Development of higher-density MDF grades will improve screw-holding power, impact resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for more demanding furniture applications (e.g., structural components, heavy-duty shelving).
* Improved Surface Quality: Smoother, more consistent surfaces will facilitate high-gloss finishes, intricate laminates, and direct printing, enabling MDF furniture to mimic premium materials more effectively.
3. Design Innovation and Customization:
MDF’s inherent workability will continue to drive its appeal in design-focused and personalized furniture:
* Complex Geometries and CNC Machining: MDF’s suitability for high-precision CNC routing will fuel demand for furniture with intricate shapes, patterns (e.g., fretwork), and customized designs, particularly in the RTA (Ready-to-Assemble) and bespoke furniture sectors.
* Integrated Finishes and Laminates: Growth in pre-finished MDF (PFL) with decorative laminates, foils, or veneers applied at the board level will offer consistent, durable finishes and reduce on-site finishing costs. Digital printing on MDF surfaces will enable unique, customizable designs.
* Flat-Pack and Modular Design: MDF remains ideal for efficient flat-pack furniture due to its dimensional stability and ease of cutting. Expect continued innovation in modular, space-saving, and easily assembled MDF furniture solutions.
4. Regional Market Dynamics and Competitive Landscape:
* Asia-Pacific Dominance: APAC, led by China, India, and Southeast Asia, will remain the largest producer and consumer of MDF furniture, driven by rapid urbanization, growing middle-class demand for affordable housing and furnishings, and established manufacturing infrastructure.
* Cost-Pressure & Competition: Intense competition, particularly in price-sensitive markets, will pressure margins. MDF will face increasing competition from alternative engineered wood products (like particleboard with improved moisture resistance) and alternative materials (e.g., bamboo composites, recycled plastics) in specific applications.
* Supply Chain Resilience: Manufacturers will focus on securing sustainable wood fiber sources (certified forests, agricultural residues) and optimizing logistics to mitigate volatility in raw material prices (wood, resins, energy) and geopolitical risks.
5. Digitalization and E-commerce Integration:
* Online Sales Growth: E-commerce will be a primary sales channel for MDF furniture, especially RTA and modern designs. Product visualization tools (AR/VR) will help consumers assess quality and fit.
* Smart Manufacturing: Increased adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies (AI, IoT) in MDF panel production and furniture manufacturing will improve precision, reduce waste, enhance quality control, and enable faster customization.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the MDF furniture market will be defined by a duality: addressing environmental challenges while leveraging its core strengths in cost, design flexibility, and manufacturability. Success will hinge on manufacturers’ ability to innovate with sustainable materials and processes, enhance product performance and aesthetics, and adapt to digital sales channels and evolving consumer expectations for both affordability and responsibility. MDF will remain a vital material, but its future lies in higher-value, eco-conscious, and technically advanced applications rather than basic commodity furniture.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) Furniture
Sourcing MDF furniture can offer cost-effective and design-flexible solutions, but it comes with several potential pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Being aware of these challenges helps ensure you receive durable, compliant, and original products.
Poor Material Quality and Consistency
One of the most frequent issues is inconsistent or substandard MDF core quality. Low-grade MDF may contain excessive moisture, uneven density, or impurities, leading to warping, swelling, or delamination, especially in humid environments. Suppliers might use recycled or improperly bonded fibers, compromising structural integrity.
Inadequate Moisture Resistance
Standard MDF is highly susceptible to moisture damage. If the furniture is intended for kitchens, bathrooms, or high-humidity areas, sourcing non-moisture-resistant MDF—or poorly sealed units—can result in premature failure. Always verify whether the MDF is moisture-resistant (MR-MDF) and confirm proper sealing with edge banding and finishes.
Subpar Surface Finishing and Edge Banding
MDF relies heavily on surface treatments for aesthetics and durability. Poor lamination, paint application, or veneer bonding can result in peeling, bubbling, or chipping. Inadequate or thin edge banding—especially on visible edges—can make furniture look cheap and reduce longevity. Ensure suppliers use high-quality adhesives and precise application techniques.
Weak Joinery and Structural Design
Due to MDF’s lower screw-holding strength compared to solid wood, poor construction methods (e.g., using inadequate fasteners or insufficient reinforcement) can lead to joint failure. Avoid designs that over-rely on screw-only joints without using dowels, cam locks, or reinforcement blocks, particularly in load-bearing areas like shelves or table legs.
Lack of Compliance with Environmental and Safety Standards
MDF can emit formaldehyde, especially if low-quality resins are used. Sourcing from suppliers not adhering to emission standards (such as CARB Phase 2, E0, or E1) can lead to health risks and regulatory non-compliance. Always request certification documentation and third-party test reports for formaldehyde emissions.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Sourcing from manufacturers in regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk of replicating patented or copyrighted designs. Using furniture that mimics branded or designer pieces—even unintentionally—can result in legal disputes, product seizures, or reputational damage. Conduct due diligence to ensure designs are original or properly licensed.
Inconsistent Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances
MDF furniture often relies on precise CNC cutting and assembly. Poor manufacturing control can result in misaligned components, uneven gaps, or parts that don’t fit together. This is especially problematic for flat-pack furniture where end-users assemble the product. Request samples and inspect tolerances before placing bulk orders.
Insufficient Packaging and Shipping Protection
MDF furniture, particularly with laminated or painted surfaces, is prone to scuffing and damage during transit. Inadequate packaging—such as thin cardboard, lack of edge protectors, or insufficient internal bracing—can lead to high damage rates upon delivery. Clarify packaging standards and consider third-party inspection before shipment.
Hidden Costs and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) Traps
Suppliers may quote low per-unit prices but impose high MOQs or add unexpected costs for tooling, custom finishes, or certifications. These hidden expenses can erode margins and create inventory challenges. Always request a detailed cost breakdown and negotiate terms in writing.
Limited Customization and Design Flexibility
While MDF is highly workable, some suppliers may lack the technical capability for complex designs, custom profiles, or specialty finishes. Confirm the supplier’s machinery, design software compatibility (e.g., CAD/CAM), and sample-making process before committing to large-scale production.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—through vetting suppliers, requesting certifications, inspecting samples, and protecting IP—buyers can source high-quality MDF furniture that meets both performance and legal standards.
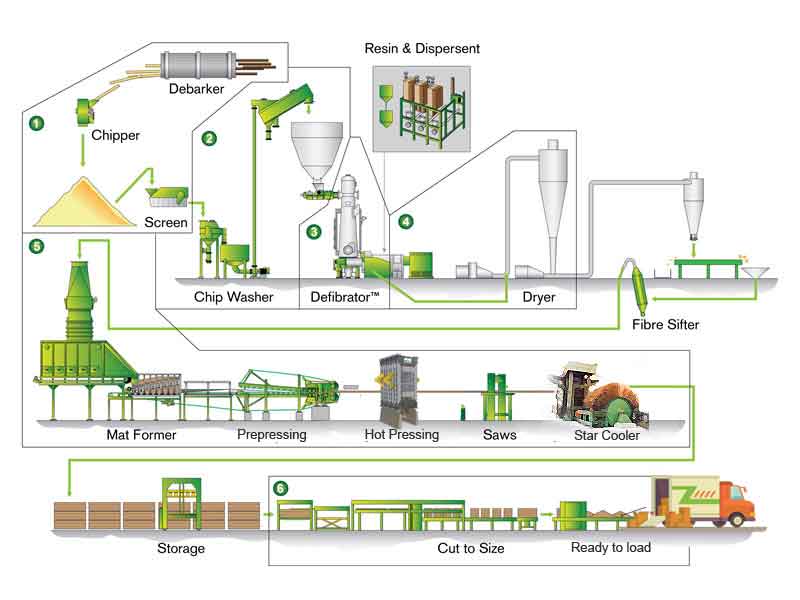
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) Furniture
Overview
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) furniture is widely used due to its affordability, smooth finish, and versatility. However, transporting and compliantly selling MDF furniture—especially across international borders—requires careful attention to logistics, environmental regulations, and safety standards. This guide outlines key considerations for the logistics and compliance of MDF-based furniture products.
Material Composition and Environmental Regulations
MDF is an engineered wood product made from wood fibers, wax, and resin binders (typically urea-formaldehyde). The use of formaldehyde-based adhesives has led to strict regulations globally due to potential off-gassing and health concerns.
- Formaldehyde Emission Standards:
- U.S. (EPA TSCA Title VI): Requires compliance with formaldehyde emission limits (≤ 0.05 ppm for MDF). Third-party certification (TPC) is mandatory.
- EU (CARB Phase 2 Equivalent): Complies with E1 standard (≤ 0.124 mg/m³ under EN 717-1 test method).
- California Air Resources Board (CARB): Mandates strict compliance for products sold in California.
- China GB 18580-2017: Enforces E1-level formaldehyde emissions.
- Japan JIS A 5908: Classifies MDF into F**** (F-4 Star), the strictest formaldehyde emission class.
Ensure suppliers provide test reports or certifications (e.g., CARB, FSC, PEFC, or EPD) to demonstrate compliance.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transit and control moisture exposure.
- Moisture Protection: MDF swells when exposed to moisture. Use moisture-resistant packaging such as plastic wraps, desiccants, or vapor barriers.
- Edge Protection: Use corner protectors or edge banding to prevent chipping during handling.
- Stacking and Palletizing: Securely stack and strap pallets. Ensure weight distribution prevents crushing of lower units.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture” indicators.
Transportation and Logistics
MDF furniture is typically shipped flat-packed (knock-down) to reduce volume and shipping costs.
- Mode of Transport:
- Ocean Freight: Most cost-effective for large volumes. Use dry, ventilated containers to minimize moisture risks.
- Air Freight: Used for urgent or high-value shipments. Higher cost but faster delivery.
-
Overland Transport: Suitable for regional distribution. Ensure vehicles are covered and dry.
-
Customs Documentation:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB)
- Certificate of Origin
- Formaldehyde Compliance Certificate (if required)
-
Import/Export Licenses (if applicable)
-
HS Code Classification:
- Typical HS codes for MDF furniture include:
- 9403.60 – Furniture of wood, other (for complete MDF furniture)
- 4411.12 – Panels of MDF (for raw MDF sheets)
- Confirm correct classification with local customs authorities to ensure accurate duties and compliance.
Import/Export Compliance
Different countries impose specific requirements on wood products to prevent pest infestation and ensure environmental safety.
- Phytosanitary Certificates: May be required for raw MDF or unfinished wood components. Issued by the national plant protection organization (e.g., APHIS in the U.S.).
- ISPM 15 (Wood Packaging): All wooden packaging (pallets, crates) must be heat-treated and marked with the ISPM 15 stamp if shipping internationally.
- REACH & RoHS (EU): Ensure no restricted substances (e.g., certain flame retardants or heavy metals) are used in finishes or coatings.
- Proposition 65 (California): Warning labels are required if products contain chemicals known to cause cancer or reproductive harm (e.g., formaldehyde).
Sustainability and Certification
Increasing consumer and regulatory demand for sustainable products requires adherence to environmental standards.
- FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) or PEFC Certification: Demonstrates responsible sourcing of wood fibers.
- EPD (Environmental Product Declaration): Provides transparent lifecycle assessment data.
- Recyclability and Waste Management: MDF is difficult to recycle; include disposal guidelines for end-users.
Safety and Labeling
- Consumer Safety: Provide assembly instructions and safety warnings (e.g., use in well-ventilated areas during assembly).
- Labeling Requirements:
- Country of Origin
- Material composition (% MDF, finishes used)
- Compliance marks (e.g., CARB, CE, FSC)
- Proposition 65 warning (if applicable)
Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Supplier Audits: Regularly audit MDF suppliers for compliance with emission standards and sustainability practices.
- Pre-Shipment Inspections: Conduct quality and compliance checks before dispatch.
- Insurance: Ensure cargo insurance covers damage, moisture, and customs seizure risks.
- Stay Updated: Monitor regulatory changes in target markets (e.g., new EU Green Deal requirements).
Conclusion
Successfully managing the logistics and compliance of MDF furniture requires a proactive approach to environmental regulations, material safety, and international trade standards. By ensuring formaldehyde compliance, proper packaging, accurate documentation, and sustainable sourcing, businesses can minimize risks and ensure smooth global distribution of MDF-based furniture products.
In conclusion, sourcing medium density fiberboard (MDF) furniture offers a cost-effective, versatile, and aesthetically consistent solution for both residential and commercial applications. Its smooth surface allows for high-quality finishes, making it ideal for painted or laminated furniture. When sourced responsibly—from suppliers that adhere to environmental standards and use low-emission adhesives—MDF can be a sustainable choice despite its synthetic composition. However, considerations around moisture resistance, weight, and structural durability must inform sourcing decisions, particularly for high-use or humid environments. By partnering with reputable manufacturers, verifying product certifications (such as CARB, EPP, or FSC), and balancing cost with quality, businesses and consumers can effectively leverage MDF furniture to meet design, budget, and sustainability objectives.