The global measuring cube market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand for precision measurement tools across manufacturing, quality control, and metrology sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global metrology equipment market was valued at USD 11.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the rising need for accuracy in production processes, especially in automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries. As a critical component in calibration and inspection workflows, measuring cubes—known for their high stability, geometric accuracy, and multi-face usability—are seeing increased adoption. Advancements in materials, such as cast iron and granite composites, along with stricter quality standards, are pushing manufacturers to innovate. In this competitive landscape, a select group of suppliers has emerged as leaders, combining engineering excellence with rigorous quality assurance. Based on market presence, product innovation, and customer reach, the following list highlights the top 8 measuring cube manufacturers shaping the industry today.
Top 8 Measuring Cube Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 attocube
Domain Est. 2000
Website: attocube.com
Key Highlights: attocube is a leading pioneer for nanotechnology solutions in industry and research. We deliver cutting edge components and systems for precision motion and ……
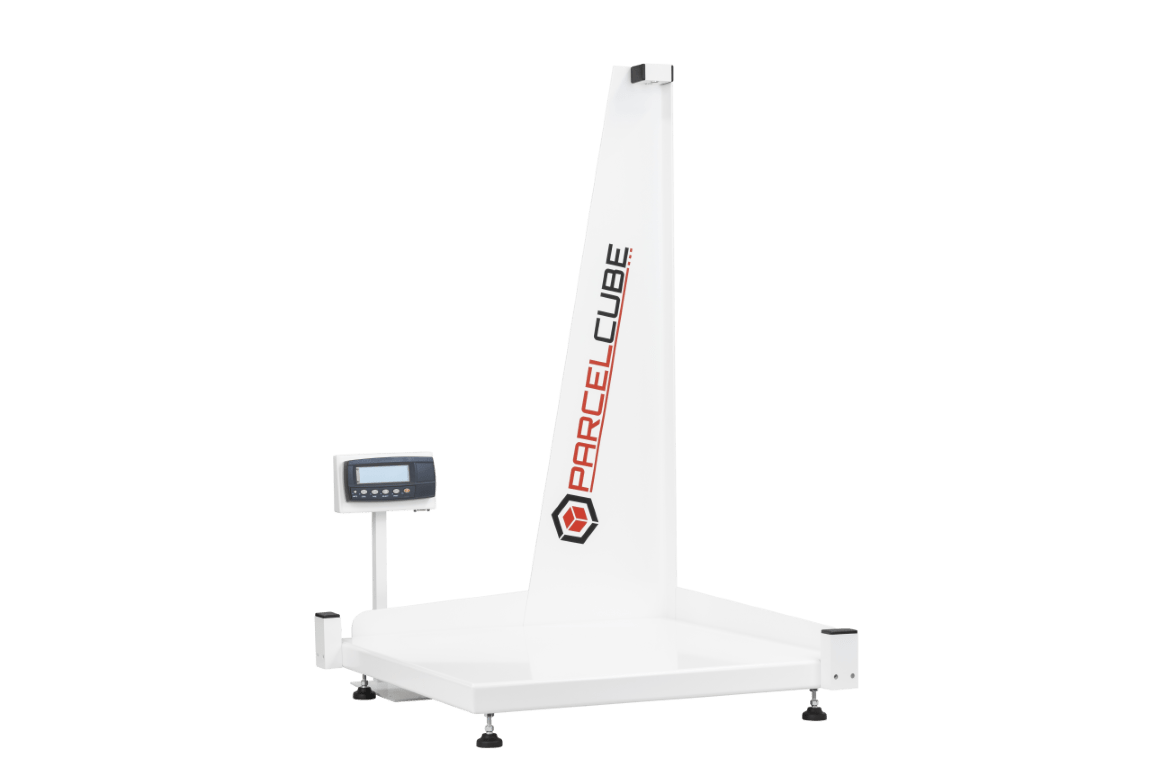
#2 Parcelcube Static Dimensioning Systems
Domain Est. 2012
Website: parcelcube.com
Key Highlights: Parcelcube 1000. Parcelcube 1000 is our largest dimensioning system, designed for measuring bigger boxes with high precision using advanced laser technology….
#3 Audiovisual Quality Management :: Cube
Domain Est. 2000
Website: cube-tec.com
Key Highlights: Cube-Tec International develops integrated solutions for large media archives. As a pioneer in quality control of media workflows, the company focuses on open ……
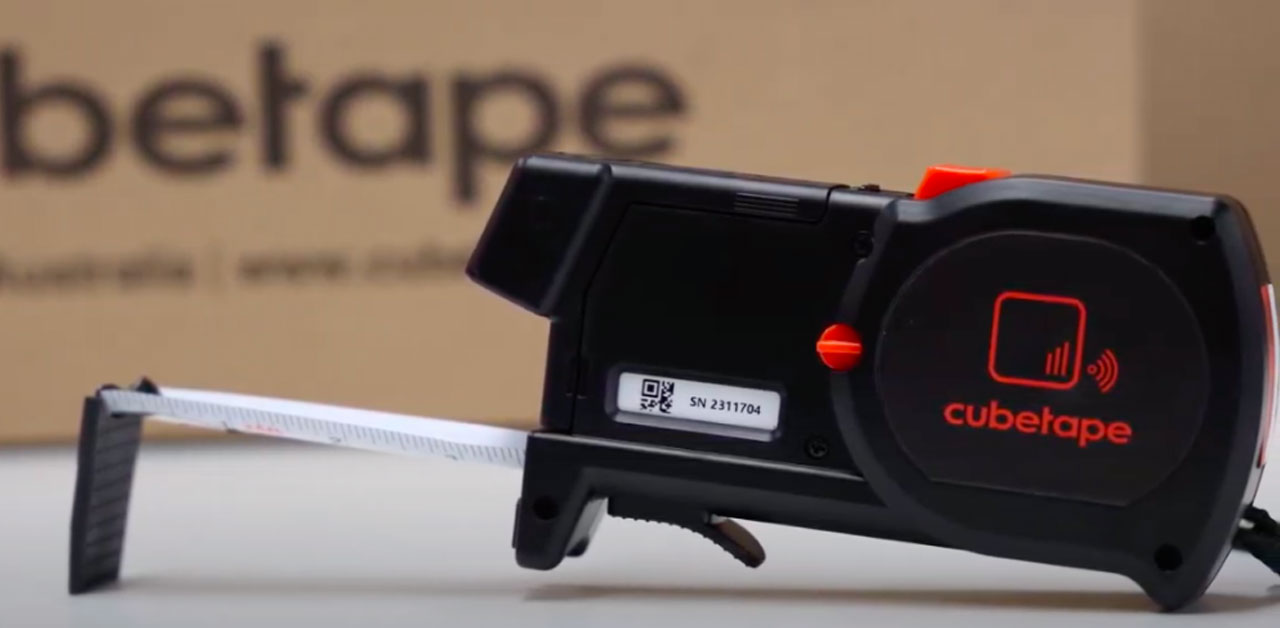
#4 Cubetapes
Domain Est. 2009
Website: cubetape.com
Key Highlights: Get accurate freight measurement with Cubetape’s dimensional scanner for shipping by cubetape.com. Perfect for handling oddly shaped freight and eliminating ……
#5 Gummicube
Domain Est. 2010
Website: gummicube.com
Key Highlights: Gummicube is the #1 App Store Optimization Company. Accurate Mobile Data Is Key for App Store Optimization….
#6 Blue Cube In
Domain Est. 2015
Website: draslovka.com
Key Highlights: We design, manufacture, distribute and support a range of analyzers for the real-time measurement of composition in dry, high temperature, solution and slurry ……
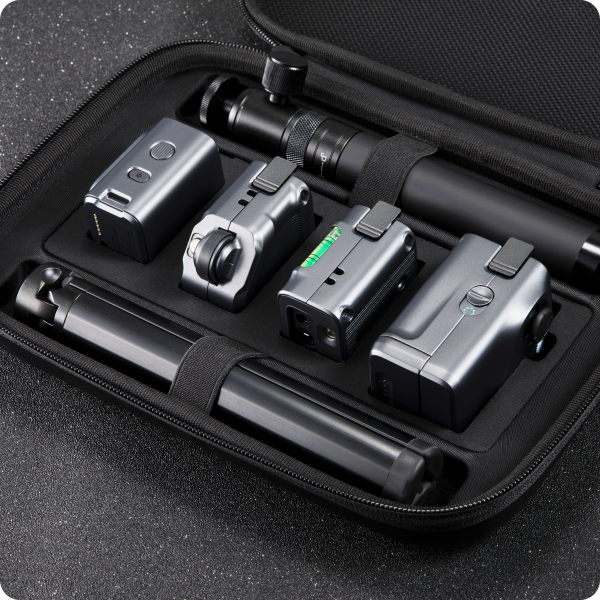
#7 M-Cube Pro Kit
Domain Est. 2017
#8 Cube
Website: primes.de
Key Highlights: The Cube, as a mobile and compact power probe, enables the determination of laser power directly beneath the processing head in the processing zone….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Measuring Cube

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Measuring Cubes
The Measuring Cube market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, evolving industry demands, and a growing emphasis on precision and efficiency. Here’s a detailed analysis of the key trends expected to shape the landscape:
1. Integration of Smart Technologies (IoT and AI)
By 2026, Measuring Cubes will increasingly incorporate Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities, enabling real-time data collection, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance. AI-powered analytics will allow these devices to identify measurement anomalies, optimize calibration schedules, and improve accuracy over time. This shift toward “smart” cubes will enhance integration with digital quality management systems and Industry 4.0 frameworks.
2. Demand for Higher Accuracy and Automation
Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing will continue to demand ultra-precise measurement solutions. In response, Measuring Cubes will feature sub-micron accuracy and automated measurement sequences, reducing human error and increasing throughput. Automated alignment and self-calibrating mechanisms will become standard in high-end models.
3. Expansion in Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific, particularly countries like India, Vietnam, and Indonesia, will see accelerated adoption of Measuring Cubes due to expanding manufacturing sectors and government initiatives promoting automation. Localized production and cost-optimized models will cater to price-sensitive markets, contributing to global market growth.
4. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will push manufacturers to develop energy-efficient Measuring Cubes with reduced material waste and longer lifespans. Recyclable materials and modular designs for easy repair or upgrade will gain traction, aligning with circular economy principles.
5. Convergence with Digital Twins and Simulation
Measuring Cubes will play a crucial role in feeding real-world data into digital twin platforms. By 2026, seamless integration with CAD/CAM systems and simulation software will allow manufacturers to validate designs against actual measurements in real time, shortening product development cycles.
6. Increased Competition and Market Consolidation
As demand grows, new entrants—especially in the mid-range segment—will challenge established players. This competitive pressure may lead to strategic mergers and acquisitions, particularly among companies offering complementary technologies (e.g., metrology software, robotics).
7. Regulatory and Standardization Pressures
Stricter global quality standards (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100) will require Measuring Cubes to comply with enhanced traceability and documentation protocols. Vendors will need to offer certified calibration services and audit-ready data logs, influencing product design and after-sales support.
Conclusion
By 2026, the Measuring Cube market will evolve from simple dimensional checkers to intelligent, networked components of advanced manufacturing ecosystems. Success will depend on agility in adopting smart technologies, meeting global quality demands, and expanding access in high-growth regions. Companies that innovate in connectivity, accuracy, and sustainability will lead the next generation of metrology solutions.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Measuring Cube (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a measuring cube—especially for precision applications in manufacturing, metrology, or research—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking key factors can lead to performance issues, compliance risks, and legal complications. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Material and Hardness Specifications
One of the most frequent mistakes is failing to specify the correct material (e.g., high-grade steel, cast iron, or granite) and hardness. Low-quality materials are prone to wear, deformation, and thermal instability, compromising measurement accuracy over time.
2. Poor Surface Finish and Flatness Tolerance
Measuring cubes must meet strict flatness and surface finish standards (e.g., ISO 8512 or ASME B89). Sourcing cubes without certified calibration reports or traceable metrology data risks introducing measurement errors into your quality control processes.
3. Lack of Calibration and Traceability
Purchasing a cube without a valid calibration certificate from an accredited lab (e.g., NIST-traceable) undermines its reliability. Untested or non-traceable cubes may appear cost-effective initially but can lead to costly rework or product recalls.
4. Insufficient Environmental Stability
Failing to consider thermal expansion coefficients and environmental operating conditions (e.g., temperature fluctuations) can result in inaccurate measurements. High-precision applications require cubes made from materials with low thermal expansion.
5. Overlooking Build Quality and Edge Integrity
Chipped edges, burrs, or inconsistent corner squareness affect usability and long-term durability. Poor craftsmanship can introduce systematic errors during setup and alignment.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Sourcing from Unverified or Non-Compliant Suppliers
Purchasing from suppliers without clear IP compliance policies risks acquiring counterfeit or infringing products. This is especially common with imported cubes that mimic patented designs or proprietary calibration methods.
2. Use of Proprietary Designs Without Licensing
Some measuring cubes incorporate patented geometries, mounting systems, or integrated technologies (e.g., embedded sensors). Using such designs without proper licensing exposes the buyer to IP litigation, even if unintentional.
3. Lack of Documentation on IP Ownership
Failing to obtain documentation confirming that the supplier owns or has rights to the design and manufacturing process can lead to legal disputes. Ensure contracts include IP indemnification clauses.
4. Reverse Engineering Without Legal Clearance
If you’re developing or modifying a measuring cube based on an existing product, ensure that reverse engineering complies with local IP laws. Unauthorized replication—even for internal use—can constitute infringement.
5. Inadequate Protection of Custom-Built Solutions
If sourcing a custom-designed measuring cube, ensure that your own IP (e.g., design specifications, software integrations) is protected through non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and clear contractual ownership terms.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, demand full certification and traceability, and engage legal counsel when IP-sensitive designs are involved. A well-sourced measuring cube ensures measurement integrity and safeguards against legal and operational risks.
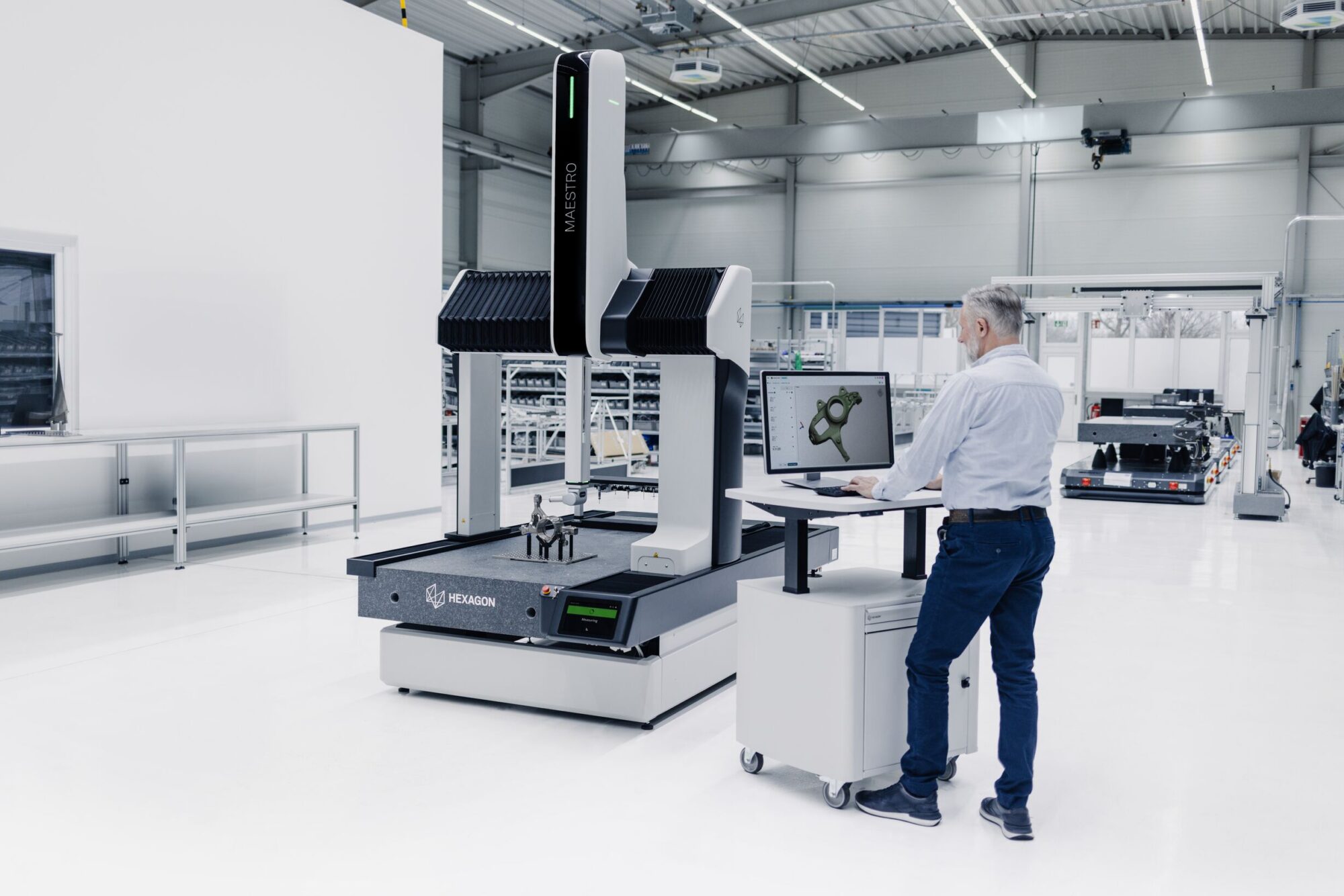

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Measuring Cube
This guide outlines the logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the handling, transportation, storage, and use of the Measuring Cube—a precision measurement device used in industrial, warehouse, and quality control environments. Adhering to these guidelines ensures product integrity, regulatory compliance, and operational safety.
Product Overview
The Measuring Cube is a calibrated 3D reference tool used to verify the accuracy of coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), robotic systems, and other metrology equipment. It is typically constructed from stabilized granite or composite materials with precision-ground surfaces and embedded reference points. Proper logistics and compliance practices are critical due to its sensitivity to environmental conditions and regulatory standards.
Packaging and Handling
The Measuring Cube must be stored and shipped in its original protective packaging, which includes shock-absorbing foam, rigid outer casing, and humidity control elements. Handlers should:
– Avoid direct contact with measuring surfaces to prevent contamination.
– Use two or more personnel for lifting units over 20 kg.
– Never stack additional cargo on top of the packaged cube.
– Follow the “This Side Up” and “Fragile” labels at all times.
Transportation Requirements
Transport must comply with international freight standards (e.g., IATA, IMDG, or ADR where applicable). Key considerations:
– Use climate-controlled vehicles to maintain temperatures between 15°C and 25°C.
– Secure the package to prevent movement during transit.
– Avoid exposure to vibrations exceeding 0.5 g; use vibration-dampening transport solutions when necessary.
– For air freight, ensure compliance with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if batteries or calibration tools are included.
Storage Conditions
When not in use, the Measuring Cube must be stored in a controlled environment:
– Temperature: 20°C ±2°C
– Relative Humidity: 40%–60%
– Clean, dust-free area free from electromagnetic interference or chemical fumes
– Stored horizontally on a calibrated surface plate or in its original storage cradle
– Avoid long-term storage in transit packaging; transfer to dedicated storage within 72 hours of receipt
Import/Export Compliance
Shipping across international borders requires adherence to:
– Harmonized System (HS) Code 9031.80 (measuring and checking instruments)
– Valid commercial invoice, packing list, and certificate of origin
– Declaration of calibration certificate (ISO 17025 accredited) for customs clearance
– Compliance with destination country’s metrology regulations (e.g., NIST traceability for U.S., UKAS for UK, DAkkS for Germany)
– Export controls: Verify that the device does not fall under dual-use or strategic technology restrictions (e.g., EU Dual-Use Regulation, U.S. EAR)
Calibration and Metrological Compliance
To maintain compliance with quality standards:
– Perform initial calibration upon receipt and at 12-month intervals thereafter
– Use only ISO/IEC 17025-accredited calibration laboratories
– Retain calibration records for at least 5 years
– Label the cube with calibration due date and unique asset ID
– Follow ISO 10360 standards for CMM verification when using the cube
Environmental and Safety Compliance
- The Measuring Cube contains no hazardous materials under RoHS or REACH regulations.
- Granite-based models may produce fine particulate during manufacturing; handling of damaged units should follow local dust control protocols.
- Comply with OSHA (or equivalent) workplace safety guidelines for manual handling and ergonomics.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain the following records:
– Certificate of Conformity (CE, UKCA, or other regional marks)
– Calibration certificates with uncertainty statements
– Shipment logs (including temperature and humidity data if monitored)
– Maintenance and inspection reports
– Import/export licenses (if applicable)
Disposal and End-of-Life
At end-of-life, dispose of the Measuring Cube in accordance with local waste regulations:
– Granite components can typically be recycled as inert construction material.
– Electronic calibration accessories must be disposed of per WEEE directives.
– No special hazardous waste classification applies to the core unit.
Adherence to this Logistics & Compliance Guide ensures the Measuring Cube remains accurate, reliable, and legally compliant throughout its lifecycle. Regular audits and staff training are recommended to maintain standards.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Measuring Cube:
In conclusion, sourcing a measuring cube requires a thorough evaluation of accuracy, material quality, calibration standards, supplier reliability, and total cost of ownership. A high-precision measuring cube is essential for ensuring dimensional accuracy and consistency in manufacturing, calibration, and quality control processes. By selecting a cube that meets international standards (such as ISO 17025 or DIN/BS standards), is made from stable materials like cast iron or granite, and comes from a reputable supplier with proper certification and after-sales support, organizations can ensure long-term reliability and measurement integrity. Careful sourcing not only enhances measurement precision but also contributes to overall process efficiency and product quality.