The global engineered wood products market, driven by rising demand for sustainable and cost-effective alternatives to solid wood, has seen consistent growth in recent years. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) market was valued at approximately USD 78 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6% through 2029. This expansion is fueled by increasing construction activities, urbanization, and heightened focus on interior design in residential and commercial spaces. MDF veneer, known for its smooth surface, dimensional stability, and compatibility with various wood finishes, has become a preferred choice across furniture, cabinetry, and architectural millwork sectors. As demand rises, manufacturers are investing in advanced pressing technologies and environmentally compliant production processes to meet global standards. Against this backdrop, identifying the top MDF veneer manufacturers becomes crucial for sourcing partners and procurement specialists aiming to align with reliable, scalable, and innovative suppliers in a competitive marketplace.
Top 10 Mdf Veneer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Columbia Forest Products
Domain Est. 1996
Website: columbiaforestproducts.com
Key Highlights: Discover Columbia Forest Products, North America’s largest manufacturer of sustainable, decorative hardwood plywood and veneers for residential and commercial…
#2 MDF Sales and Distribution
Domain Est. 1995
Website: weyerhaeuser.com
Key Highlights: A wide network of US and Canadian distributors stock our MDF products. Products can be purchased by full truckload, container or rail car throughout North ……
#3 Lumber, Plywood, MDF Boards
Domain Est. 1996
Website: timberproducts.com
Key Highlights: Timber Products has the expertise to provide top quality lumber, plywood, MDF boards and more! 100+ years of industry leadership!…
#4 MDF Board
Domain Est. 1996
Website: formwood.com
Key Highlights: FormWood offers MDF veneer panels in standard sizes from 4×8 to 5×12 (8×4 to 12×5 for cross-grain panels). Custom cut-to-size panels are also available….
#5 West Fraser Timber Co.
Domain Est. 1997
Website: westfraser.com
Key Highlights: From lumber to engineered wood products, West Fraser delivers high-quality, naturally renewable building materials to the world….
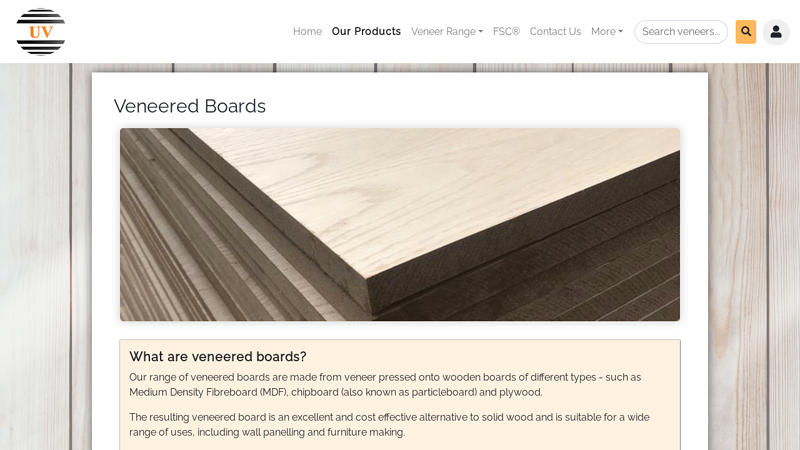
#6 Veneered Boards
Domain Est. 1999
Website: uvgroup.com
Key Highlights: Our range of veneered boards are made from veneer pressed onto wooden boards of different types – such as Medium Density Fibreboard (MDF), chipboard (also known ……
#7 Vanachai Group
Domain Est. 2000
Website: vanachai.com
Key Highlights: Our MDF board, particleboard, and OSB are the building materials for the future. Our wood-based panels are produced from agricultural and wood waste. They are ……
#8 Oak Veneered MDF Sheets
Domain Est. 2001
Website: madar.com
Key Highlights: These high-quality sheets combine the beauty of oak wood veneer with the durability of MDF. Ideal for furniture making and interior design….
#9 New Veneered MDF
Domain Est. 2005
Website: kitronik.co.uk
Key Highlights: Veneered MDF is a great value way to show off projects where appearance is important. We’ve added these new veneered MDF sheets in 600mm x 400mm ……
#10 Al
Domain Est. 2009
Website: alnoormdf.com
Key Highlights: Al-Noor Lasani is the market leader and pioneer of decorative laminate surfaces in Pakistan. From home to commercial décor, from kitchens to furniture….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Mdf Veneer

H2 2026 Market Trends for MDF Veneer
As the global market for engineered wood products evolves, Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) veneer is set to experience several defining trends during the second half of 2026. Driven by sustainability imperatives, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences, the MDF veneer sector is poised for transformation and strategic growth.
1. Accelerated Shift Toward Sustainability and Eco-Certification
Environmental concerns will dominate procurement decisions in H2 2026. Demand for MDF veneer products made from recycled fibers or sustainably managed forests (e.g., FSC or PEFC certified) will surge. Consumers and commercial clients—particularly in Europe and North America—will prioritize low-formaldehyde or formaldehyde-free MDF (such as NAF or ULEF-compliant variants) to meet stricter indoor air quality regulations. Manufacturers investing in bio-based binders and closed-loop production systems will gain a competitive edge.
2. Growth in Prefinished and Value-Added Veneer Panels
The trend toward faster, cleaner installation will drive demand for factory-finished MDF veneer panels. In H2 2026, pre-sanded, pre-stained, or UV-coated MDF veneers will gain traction in modular construction, kitchen cabinetry, and retail fit-outs. These value-added products reduce on-site labor, minimize waste, and ensure consistency—key factors in labor-constrained markets. Integration with digital printing technologies will also expand custom design options, especially in hospitality and residential interiors.
3. Rising Demand from Emerging Markets and Urbanization
Urbanization in Asia-Pacific (particularly India, Vietnam, and Indonesia), the Middle East, and parts of Africa will fuel demand for cost-effective, design-flexible interior solutions. MDF veneer’s affordability and versatility make it ideal for mass housing, commercial interiors, and affordable furniture. Local production capacity is expected to expand in these regions, reducing import dependence and shortening supply chains.
4. Technological Integration and Digital Customization
The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies—such as CNC machining, AI-driven design software, and digital inventory management—will enhance the precision and customization capabilities of MDF veneer applications. In H2 2026, we anticipate increased use of augmented reality (AR) tools by designers and retailers, allowing clients to visualize MDF veneer finishes in real-time. This trend supports the growing DIY and made-to-order furniture segments.
5. Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Following ongoing global disruptions, manufacturers will continue to regionalize supply chains in H2 2026. Nearshoring production and sourcing raw materials locally will mitigate logistics risks and reduce carbon footprints. This shift will benefit regional producers in North America, Southeast Asia, and Eastern Europe, strengthening localized manufacturing ecosystems.
6. Competitive Pressure from Alternative Materials
MDF veneer will face intensified competition from alternative substrates like plywood composites, particleboard with improved finishes, and new bio-based panels. However, MDF’s superior surface smoothness and dimensional stability will sustain its dominance in high-end applications such as painted cabinetry and intricate moldings—provided manufacturers innovate in performance and sustainability.
Conclusion:
H2 2026 will mark a pivotal phase for the MDF veneer market, defined by sustainability leadership, technological adoption, and geographic diversification. Companies that align with eco-conscious consumer values, embrace digital manufacturing, and cater to emerging market needs will be best positioned to capitalize on growth opportunities in the evolving global interior and furniture landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing MDF Veneer (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) veneer can be cost-effective and aesthetically pleasing, but it comes with several potential pitfalls related to both quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Being aware of these issues helps avoid legal, financial, and reputational risks.
Inconsistent Veneer Quality
One of the most frequent challenges is receiving inconsistent veneer quality. Variations can occur in grain pattern, color, thickness, and surface smoothness—especially when sourcing from multiple batches or suppliers. Lower-quality veneers may have voids, blisters, or delamination issues, leading to visible defects in the final product and increased rejection rates during production.
Poor Adhesion and Delamination
Substandard adhesive application or improper pressing during manufacturing can result in poor bonding between the veneer and MDF core. This increases the risk of delamination, particularly in environments with fluctuating humidity or temperature. Poor adhesion not only affects durability but can also compromise product safety and customer satisfaction.
Use of Non-Compliant or Unverified Wood Species
Some suppliers may mislabel the wood species used in the veneer, either intentionally or due to supply chain opacity. This can lead to sourcing endangered or illegally harvested wood, violating regulations such as the Lacey Act (USA) or EUTR (EU Timber Regulation). Using unverified species also poses environmental and reputational risks.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
Many premium veneer patterns—especially those replicating rare or exotic woods—are protected by design patents, trademarks, or copyright. Sourcing counterfeit or unauthorized copies of branded veneers (e.g., those mimicking high-end designer finishes) can lead to IP infringement claims, legal action, and product recalls. Always verify that the supplier has legitimate rights to reproduce or distribute the veneer design.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Without proper documentation, it’s difficult to verify the origin of the veneer or ensure compliance with sustainability standards like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) or PEFC. This lack of traceability can hinder market access, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations, and may damage brand credibility.
Hidden Costs from Rework and Waste
Due to quality inconsistencies or specification mismatches, companies may face increased waste during manufacturing or require costly rework. These hidden expenses can erode the initial cost savings expected from sourcing lower-priced MDF veneer.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, request material certifications, perform sample testing, and ensure legal agreements include IP warranties. Prioritizing transparency and quality control will help secure reliable MDF veneer supply while protecting your brand and compliance posture.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for MDF Veneer
Overview of MDF Veneer
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) veneer is an engineered wood product made from compressed wood fibers bonded with resin and topped with a thin layer of real wood or decorative veneer. It is widely used in furniture, cabinetry, and interior design due to its smooth surface, dimensional stability, and cost-effectiveness. Proper logistics and compliance are essential to ensure safe handling, legal import/export, and environmental responsibility.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
MDF veneer must be packaged to prevent damage during transit. Boards should be stacked flat with protective interleaving (e.g., kraft paper or foam) between layers to avoid surface scratches. Secure packaging with edge protectors and strapping is recommended. Palletized loads must be evenly distributed and shrink-wrapped to prevent shifting. Always handle with forklifts or lifting equipment to avoid warping or chipping.
Storage Conditions
Store MDF veneer in a dry, well-ventilated indoor environment with stable temperature and humidity (ideally 35–65% RH). Keep material off the floor on pallets and away from direct sunlight or heat sources. Allow boards to acclimatize for at least 48 hours in the installation environment prior to use to minimize expansion or contraction.
Transportation Guidelines
Use enclosed, dry vehicles (e.g., box trucks or containers) to protect MDF veneer from moisture, rain, and extreme temperatures. Secure loads with straps or braces to prevent movement. Avoid stacking heavy materials on top of MDF veneer packages. For international shipping, ensure compliance with ISPM 15 regulations for wooden packaging materials (e.g., pallets).
International Trade Compliance
Verify import/export regulations in both origin and destination countries. MDF veneer may be subject to tariffs, anti-dumping duties, or trade restrictions depending on the source of raw materials. Provide accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes—typically under 4411.13 or 4412.31 for reconstituted wood products. Maintain documentation such as commercial invoices, packing lists, and bills of lading.
Environmental and Safety Regulations
Ensure MDF products meet formaldehyde emission standards such as CARB (California Air Resources Board) Phase 2, EPA TSCA Title VI (USA), or E1/E0 standards (EU). Request test certificates from suppliers. For workplace safety, comply with OSHA (or local equivalent) guidelines regarding dust control during cutting and sanding, as MDF generates fine particulate matter.
Certification and Labeling Requirements
MDF veneer should carry relevant certifications including:
– FSC® or PEFC™ (for sustainable wood sourcing)
– CARB, TSCA, or EN 717-1 (for formaldehyde emissions)
– CE marking (for EU market compliance)
Ensure product labels include manufacturer details, batch numbers, emission class, and safety handling instructions.
Customs Documentation
Prepare complete customs documentation, including:
– Commercial invoice with product description, value, and country of origin
– Packing list specifying dimensions, weight, and packaging type
– Certificate of Origin (often required for tariff preferences)
– Phytosanitary certificate if applicable (rare for processed wood like MDF)
Restricted Substances Compliance
Confirm that resins and adhesives used in MDF veneer do not contain restricted substances under REACH (EU), RoHS, or other regional regulations. Proactively monitor updates to chemical compliance lists, particularly for substances like formaldehyde, phenols, and isocyanates.
End-of-Life and Recycling Considerations
MDF veneer is recyclable but requires specialized facilities due to resin content. Encourage responsible disposal through certified recycling programs. Inform customers about proper disposal methods to support sustainability goals and comply with WEEE or similar directives where applicable.
Summary and Best Practices
To ensure seamless logistics and compliance for MDF veneer:
– Use protective packaging and secure transport methods
– Store under controlled environmental conditions
– Maintain accurate documentation for customs clearance
– Verify environmental and safety certifications
– Train staff on handling and regulatory requirements
Adhering to this guide minimizes risks, supports sustainability, and ensures smooth global distribution.
In conclusion, sourcing MDF veneer requires a strategic approach that balances quality, sustainability, cost, and supplier reliability. By carefully evaluating suppliers based on material standards, production capabilities, and environmental certifications, businesses can ensure a consistent supply of high-quality MDF veneer suitable for a range of interior applications. Establishing strong relationships with trusted manufacturers, considering both local and international options, and staying informed about industry trends and innovations will further enhance sourcing effectiveness. Ultimately, a well-executed sourcing strategy not only supports product performance and aesthetic appeal but also contributes to long-term operational efficiency and sustainability goals.