The global stainless steel market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, automotive, and construction. According to Grand View Research, the global stainless steel market size was valued at USD 142.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2024 to 2030. A key contributor to this growth is the widespread use of Grade 304 stainless steel—the most versatile and commonly used austenitic stainless steel due to its excellent corrosion resistance, formability, and durability. Mordor Intelligence reports that increasing urbanization and industrialization, particularly in Asia-Pacific, are accelerating demand for high-performance materials like Type 304, which accounts for over 60% of global stainless steel production. As industries prioritize hygiene, sustainability, and long-term cost efficiency, sourcing from reliable, high-capacity manufacturers becomes critical. Below is a data-driven selection of the top 10 304 stainless steel manufacturers leading innovation, scale, and quality in this expanding market.
Top 10 Material 304 Stainless Steel Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
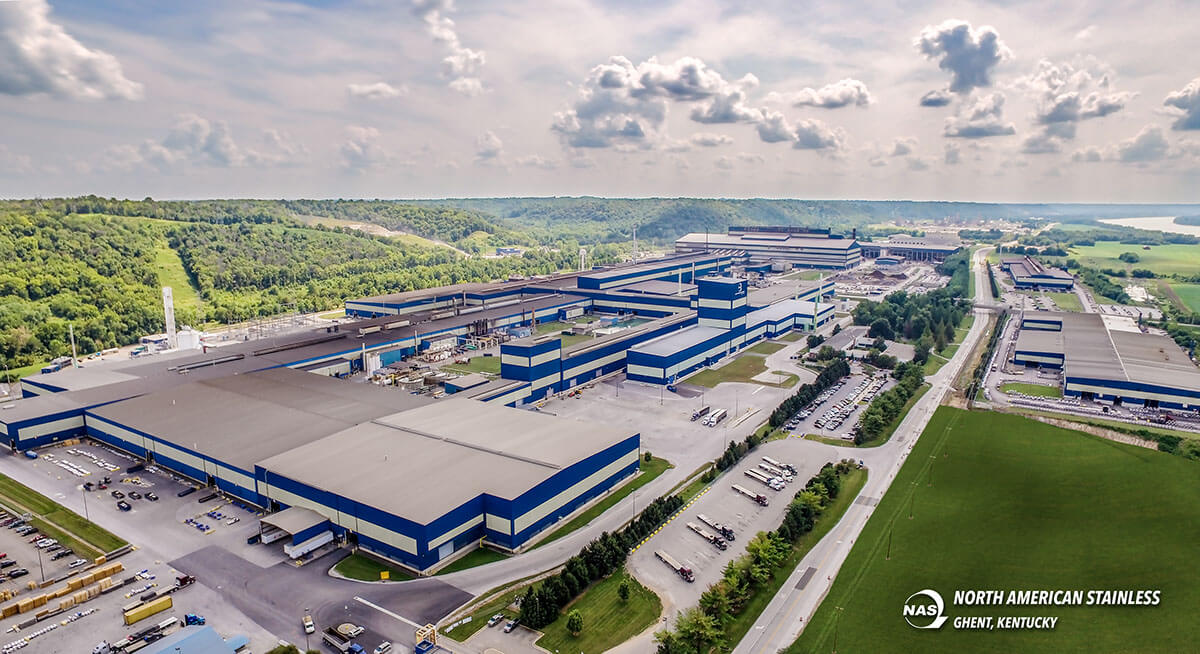
#1 North American Stainless
Domain Est. 1999 | Founded: 1990
Website: northamericanstainless.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1990, North American Stainless (NAS) has undertaken several phases of expansion to become the largest, fully integrated stainless steel producer in ……
#2 Leading Stainless Steel 304 Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2015
Website: stainlesssteelmanufacturers.org
Key Highlights: We provide the best products in the stainless steel industry. Our customers know they can trust us for quality, affordability, and convenience….
#3 STAINLESS
Domain Est. 1996
Website: castlemetals.com
Key Highlights: Castle markets a vast array of stainless steel products and grades, working closely with customers to provide highly engineered and custom solutions….
#4 Custom Size 304 Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Supplier and …
Domain Est. 1997
Website: stanch.com
Key Highlights: Stanch is an industry-leading supplier of cold rolled stainless steel sheets, we offer wide range of high quality stainless steel sheets in various finishes….
#5 304 Stainless Steel
Domain Est. 1999
Website: pennstainless.com
Key Highlights: Explore 304 stainless steel from Penn Stainless. Learn about 304 vs 316 differences, food-grade applications, rust resistance, magnetic properties, ……
#6 304 Stainless Steel Technical Data Sheet
Domain Est. 1999
Website: metalshims.com
Key Highlights: Types 302, 304, 304L, and 305 stainless steels are variations of the 18 percent chromium – 8 percent nickel austenitic alloy….
#7 Stainless Steel Supplier
Domain Est. 1999
Website: meadmetals.com
Key Highlights: Mead Metals stocks 301 and 302/304 stainless steel in gauges from 0.004 up to 0.125. We offer annealed, quarter hard, half-hard, 3/4 hard, and full hard ……
#8 AISI 304
Domain Est. 2007
Website: stahlportal.com
Key Highlights: AISI 304 and AISI 304L are the best known and most widely used chromium-nickel steels. Their excellent corrosion resistance, high strength and low carbon ……
#9 Stainless Steel Sheet Supplier
Domain Est. 2013
Website: thyssenkrupp-materials-na.com
Key Highlights: thyssenkrupp Materials NA is your supplier for stainless steel sheet in 304 and 316L. Contact us today to learn more about our stainless steel sheet stock….
#10 Stainless Steel 304
Domain Est. 2017
Website: thyssenkrupp-materials.co.uk
Key Highlights: Type 304L is the low carbon version of 304. It is used in heavy gauge components for improved weldability. Some products such as plates and pipes may be ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Material 304 Stainless Steel
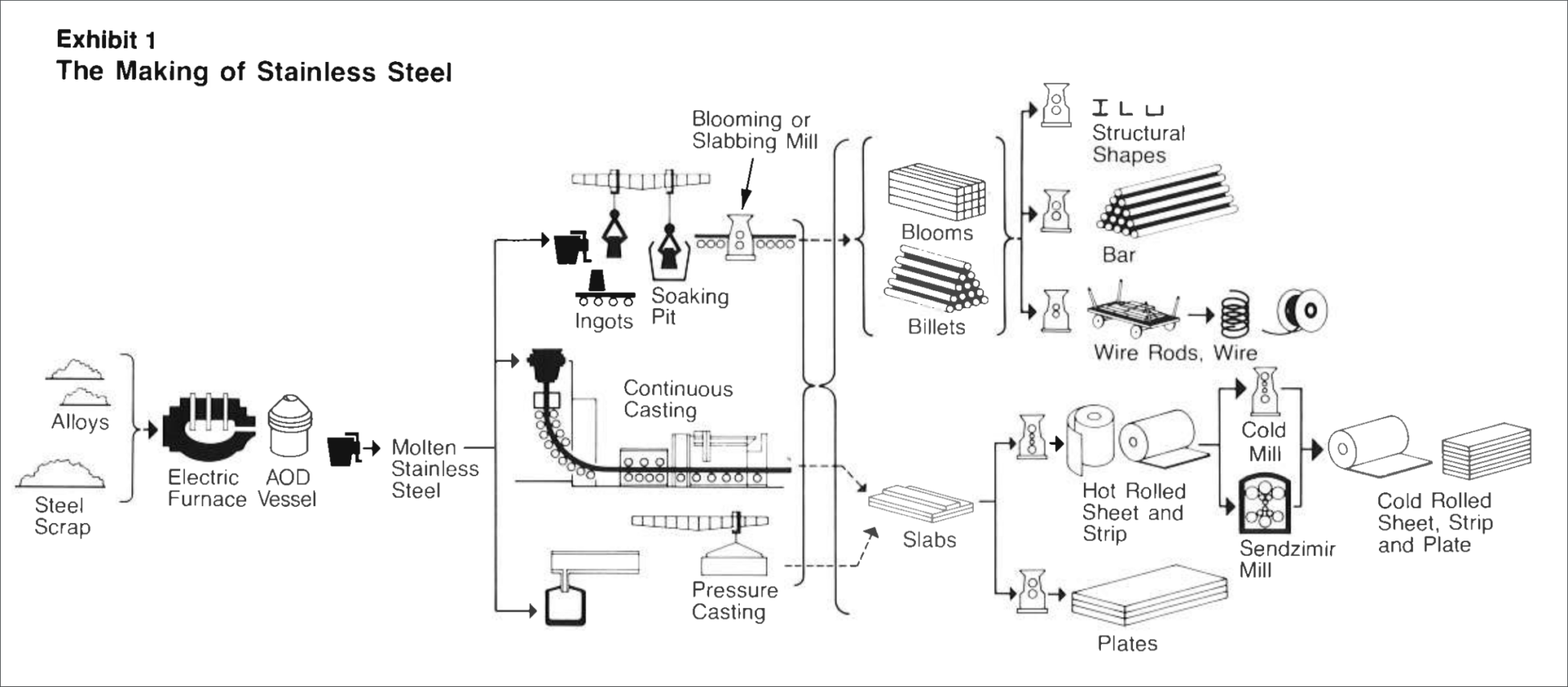
H2: 2026 Market Trends for 304 Stainless Steel
The global market for 304 stainless steel—a versatile austenitic stainless steel known for its excellent corrosion resistance, formability, and durability—is expected to experience steady growth and transformation by 2026, driven by evolving industrial demands, supply chain dynamics, and sustainability initiatives. Below are the key trends shaping the 304 stainless steel market in 2026:
-
Increased Demand from Key Sectors
The construction, automotive, and consumer goods industries remain major consumers of 304 stainless steel. In 2026, urbanization in emerging economies—particularly in Asia-Pacific (China, India, and Southeast Asia)—will continue to fuel demand for durable building materials and infrastructure components. Additionally, the rise in premium appliance manufacturing and food processing equipment will sustain industrial consumption. -
Impact of Raw Material Prices and Supply Chain Stability
Fluctuations in the prices of nickel and chromium—critical alloying elements in 304 stainless steel—will influence production costs. In 2026, geopolitical tensions and mining regulations may cause supply volatility. However, advancements in recycling technologies and increased use of scrap metal are expected to mitigate raw material dependency and stabilize input costs. -
Growth in Sustainable Manufacturing and Recycling
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt greener production methods. By 2026, the recycled content in 304 stainless steel is projected to rise, supported by closed-loop recycling systems. The inherent recyclability of stainless steel (often exceeding 90% recovery rates) positions it favorably in circular economy frameworks. -
Technological Advancements in Processing
Innovations in manufacturing, such as precision rolling, laser cutting, and additive manufacturing, are enhancing the efficiency and versatility of 304 stainless steel applications. These technologies allow for thinner gauges and complex geometries, expanding its use in high-tech industries including renewable energy systems and medical devices. -
Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific will continue to dominate global production and consumption of 304 stainless steel in 2026, led by China’s robust industrial base. However, North America and Europe are expected to see moderate growth due to infrastructure renewal projects and stricter material performance standards. Trade policies and tariffs may influence cross-border flows, encouraging regional self-sufficiency. -
Competition from Alternative Alloys
While 304 remains the most widely used stainless steel grade, cost pressures may drive some industries to consider lower-nickel alternatives like 200-series or ferritic grades. Nevertheless, 304’s superior balance of performance and reliability ensures its dominance in critical applications where quality cannot be compromised. -
Digitalization and Market Transparency
The adoption of digital platforms for supply chain management, pricing analytics, and demand forecasting will improve market transparency. By 2026, real-time data tools will enable producers and buyers to respond more agilely to market shifts, reducing inventory risks and optimizing procurement strategies.
In conclusion, the 2026 outlook for 304 stainless steel is positive, underpinned by resilient demand, technological innovation, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. While challenges related to raw material costs and global trade remain, the material’s proven performance and adaptability ensure its continued relevance across a wide range of industries.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 304 Stainless Steel (Quality & IP)
Sourcing 304 stainless steel requires diligence to avoid significant quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to component failure, safety hazards, supply chain disruptions, and legal liabilities.
Inadequate Material Certification & Traceability
One of the most frequent issues is accepting material without proper, verifiable certification. Substandard suppliers may provide falsified or incomplete Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) or Certificates of Conformance (CoCs) that claim compliance with ASTM A240, AISI 304, or equivalent standards but lack authenticity. Without full traceability—including heat/lot numbers matching the physical material—buyers cannot verify origin or confirm chemical composition and mechanical properties, risking use of non-conforming steel in critical applications.
Misrepresentation of Grade and Composition
Suppliers, particularly in less-regulated markets, may falsely label inferior grades (e.g., 201 or 202 stainless steel) as 304 to reduce costs. These substitutes have lower nickel and chromium content, compromising corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. This misrepresentation often goes undetected without third-party Positive Material Identification (PMI) testing upon receipt, potentially leading to premature failure in corrosive environments.
Poor Surface Finish and Dimensional Tolerances
304 stainless steel is available in various finishes (e.g., #2B, BA, No. 4) and forms (sheet, bar, tube). Sourcing pitfalls include receiving material that does not meet specified surface roughness, flatness, or dimensional tolerances. Inferior finishes may affect product aesthetics, cleanability (critical in food and pharmaceutical industries), or weldability, leading to rework or rejection.
Risk of Intellectual Property Infringement
When sourcing components made from 304 stainless steel—especially machined or fabricated parts—there is a risk of inadvertently purchasing counterfeit or IP-infringing products. Unauthorized manufacturers may replicate patented designs or trademarks, exposing the buyer to legal action. This is particularly prevalent in global supply chains where IP enforcement is weak. Due diligence on supplier legitimacy and design rights is essential to avoid complicity in IP theft.
Lack of Supply Chain Due Diligence
Relying on intermediaries or uncertified suppliers increases exposure to both quality and ethical risks. Without auditing suppliers for quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), environmental practices, or labor standards, companies may face reputational damage or supply interruptions. Additionally, conflict materials or unethical sourcing practices can violate compliance regulations, even if unintentional.
Insufficient Testing and Quality Control
Assuming supplier-provided data without independent verification is a critical error. Conducting incoming inspection with PMI, mechanical testing, or corrosion testing (e.g., passivation verification) is vital. Skipping these steps may allow subpar material to enter production, resulting in field failures and costly recalls.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires rigorous supplier qualification, clear technical specifications, third-party verification, and robust contractual terms protecting against misrepresentation and IP risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Material 304 Stainless Steel
Overview of 304 Stainless Steel
304 stainless steel, also known as AISI 304 or UNS S30400, is an austenitic chromium-nickel alloy widely used for its excellent corrosion resistance, formability, and durability. Commonly referred to as “18/8” stainless due to its composition (approximately 18% chromium and 8% nickel), it is one of the most versatile and widely used stainless steel grades. It is frequently employed in food processing equipment, kitchen appliances, architectural components, chemical containers, and industrial piping.
Material Specifications and Standards
To ensure consistency and quality, 304 stainless steel must conform to internationally recognized material standards. Key specifications include:
– ASTM A240/A240M: Standard specification for chromium and chromium-nickel stainless steel plate, sheet, and strip for pressure vessels and general applications.
– ASTM A276: Standard specification for stainless steel bars and shapes.
– ASTM A312/A312M: Standard for seamless, welded, and heavily cold-worked austenitic stainless steel pipes.
– EN 10088-2 (Europe): European standard for stainless steels – Technical delivery conditions for sheet/plate and strip of corrosion resisting steels.
– JIS G4304 (Japan): Japanese standard for stainless steel plates, sheets, and strips.
Procurement and quality control processes should verify compliance with these standards, including certified mill test reports (MTRs) or material test certificates (e.g., EN 10204 3.1).
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging and handling are essential to maintain the integrity of 304 stainless steel and prevent surface damage or contamination:
– Protective Coatings: Use plastic film, paper interleaving, or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) wraps to prevent scratches and moisture exposure.
– Separation from Carbon Steel: Avoid direct contact with carbon steel during storage and transport to prevent iron contamination and potential rust staining (rouging).
– Handling Equipment: Use non-ferrous or stainless steel lifting slings, clamps, and forklift attachments. Clean equipment regularly to avoid cross-contamination.
– Storage Conditions: Store indoors in a dry, well-ventilated area. Elevate material off the floor using non-metallic supports. Avoid exposure to chlorides, salt spray, and acidic environments.
Transportation and Logistics
Transportation of 304 stainless steel must safeguard against physical damage and environmental exposure:
– Domestic and International Shipping: Secure loads using non-abrasive straps and edge protectors. Use closed containers (e.g., dry vans) when possible to protect from weather.
– Marine Transport: If shipped in containers, ensure desiccants are used and container integrity is maintained to prevent condensation.
– Temperature Considerations: 304 stainless steel performs well across a wide temperature range, but prolonged exposure to extreme heat (>800°C) may affect microstructure and corrosion resistance.
– Labeling: Clearly label packages with material grade (e.g., “304 SS”), heat number, dimensions, weight, and handling instructions (e.g., “Do Not Stack,” “Protect from Moisture”).
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Adherence to environmental and safety regulations is critical when handling, transporting, and processing 304 stainless steel:
– REACH (EU): Ensure that the material and any coatings comply with Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals regulations. Nickel and chromium content must be reported if above threshold levels.
– RoHS (EU): While stainless steel itself is generally RoHS-compliant, verify that any associated finishes or treatments do not contain restricted substances.
– OSHA (USA): Follow occupational safety guidelines during cutting, grinding, or welding to minimize exposure to metal fumes (e.g., nickel and chromium hexavalent compounds). Use proper ventilation and personal protective equipment (PPE).
– EPA Regulations: Manage grinding swarf, machining chips, and coolant waste according to local environmental protection laws. 304 stainless steel scrap is recyclable and should be segregated for proper recycling.
Import/Export Documentation and Tariff Classification
When shipping across borders, proper documentation and classification are required:
– HS Code: The Harmonized System (HS) code for 304 stainless steel varies by product form:
– Flat-rolled: Typically 7219.32.xx or 7219.33.xx (varies by country)
– Bars: 7222.20.xx
– Pipes: 7304.41.xx or 7304.49.xx
– Confirm exact code with local customs authority.
– Certificates of Origin: Required for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU Free Trade Agreements).
– Material Test Reports (MTRs): Must accompany shipments to verify compliance with technical specifications.
– Customs Declarations: Accurately declare weight, value, and end use. Be aware of anti-dumping or countervailing duties that may apply depending on the country of origin.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Maintain full traceability from mill to end use:
– Heat Number Tracking: Each batch should be traceable via a unique heat number recorded on MTRs.
– Inspection Protocols: Conduct visual, dimensional, and non-destructive testing (e.g., PMI – Positive Material Identification) upon receipt.
– Certification Requirements: Depending on the application (e.g., food, pharmaceutical, aerospace), additional certifications such as 3.1 or 3.2 (EN 10204) may be required.
End-of-Life and Recycling Compliance
304 stainless steel is fully recyclable and highly sustainable:
– Recycling Rate: Over 60% of new stainless steel is made from recycled material.
– Scrap Handling: Segregate stainless steel scrap from other metals. Use licensed recyclers compliant with environmental regulations.
– Waste Management: Follow local regulations for disposal of cutting fluids, grinding dust, and contaminated packaging.
Summary and Best Practices
To ensure efficient and compliant logistics for 304 stainless steel:
– Verify material certification against recognized standards.
– Prevent contamination through proper packaging and handling.
– Comply with international shipping and customs requirements.
– Maintain documentation for traceability and regulatory audits.
– Train personnel in safe handling and environmental practices.
By adhering to this guide, organizations can ensure the integrity, legality, and sustainability of 304 stainless steel throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Material: 304 Stainless Steel
In conclusion, sourcing 304 stainless steel proves to be a reliable and cost-effective choice for a wide range of industrial, commercial, and consumer applications. Its excellent corrosion resistance, superior formability, good weldability, and high strength-to-weight ratio make it one of the most versatile and widely used stainless steel grades. The availability of 304 stainless steel from numerous global suppliers ensures consistent quality and competitive pricing, especially when sourcing from reputable mills that adhere to international standards such as ASTM, AISI, or ISO.
Additionally, its performance in both high- and low-temperature environments, coupled with low maintenance requirements and aesthetic appeal, enhances its value across various sectors including food processing, pharmaceuticals, architecture, and automotive manufacturing.
However, careful consideration must be given to factors such as material certification, supply chain reliability, lead times, and potential for counterfeit materials when finalizing suppliers. Implementing a strategic sourcing approach—including supplier audits, quality verification processes, and long-term partnerships—will ensure consistent material performance and supply security.
Overall, 304 stainless steel remains an optimal choice for applications requiring durability, hygiene, and corrosion resistance, making it a sound investment for current and future projects.