The global concrete market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising urbanization, infrastructure development, and demand for durable construction materials. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global concrete market was valued at USD 705.78 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates the market size at USD 667.2 billion in 2022, with expectations to reach over USD 1 trillion by 2030. This sustained growth underscores the critical role of leading manufacturers in advancing production technologies, sustainability practices, and supply chain resilience. As demand intensifies across residential, commercial, and public infrastructure sectors, the top players are distinguished not only by scale but also by innovation, product performance, and global reach. The following analysis highlights the top five master concrete manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 5 Master Concrete Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Masters Concrete
Domain Est. 2005
Website: mastersconcrete.com
Key Highlights: Masters is Your Source. From Step Units to Septic Tanks to Bin Block to Water Management and so much more – Masters is the only producer you need to call….
#2 Inspiring people to build better
Domain Est. 2013
Website: master-builders-solutions.com
Key Highlights: Master Builders Solutions is a leading global manufacturer of concrete admixtures, underground construction products, and other innovative solutions for the ……
#3 Careers at Master Concrete Company
Domain Est. 2014
Website: masterconcretemn.com
Key Highlights: Join our team at Master Concrete Company. We are always looking to add quality individuals to our growing team, Apply Now!…
#4 Master Concrete
Domain Est. 2024
Website: masterconcretecorp.com
Key Highlights: Master Concrete & Construction is a Fmaily owned and operated serving the Philadelphia Area for over 20 years….
#5 Masters Concrete – Concrete Contractors Company
Domain Est. 2024
Website: mastersconcretevi.com
Key Highlights: St Croix’s Premiere Concrete Services. Durable Concrete Solutions for Your Property. Masters Concrete promises our customers the highest quality Concrete in the ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Master Concrete
H2: 2026 Market Trends Analysis for Master Concrete
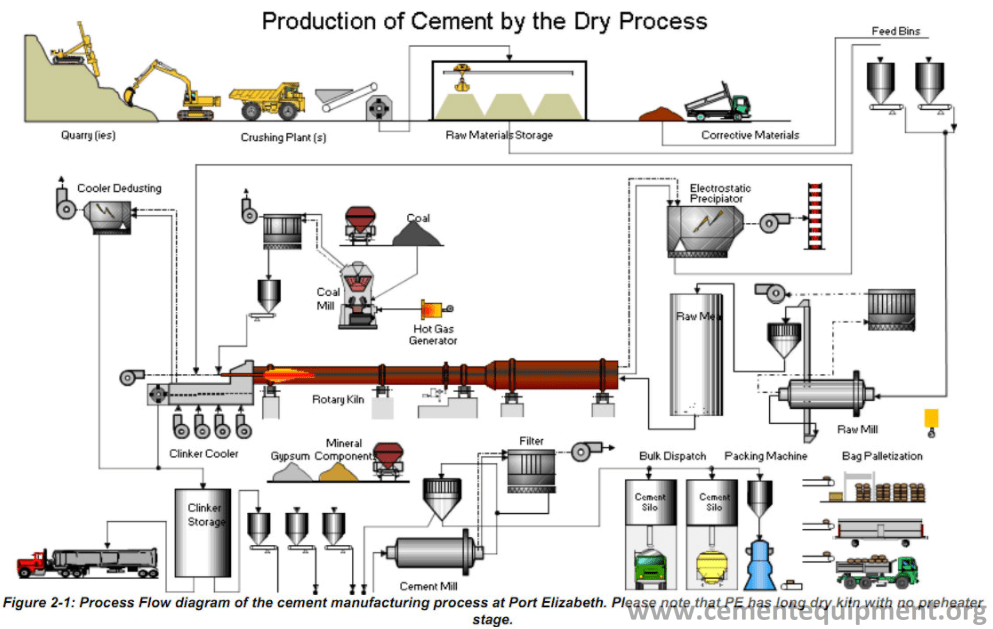
Heading into 2026, the construction and building materials industry is undergoing significant transformation, driven by sustainability mandates, technological innovation, and shifting global demand. For Master Concrete—a leading provider of concrete admixtures, solutions, and specialty construction chemicals—several key market trends are expected to shape its strategic direction and growth opportunities.
-
Sustainability and Low-Carbon Concrete Demand
Governments and private sector stakeholders are increasingly enforcing stricter carbon emissions regulations. The EU’s Green Deal, U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, and similar global initiatives emphasize low-carbon construction. Master Concrete is well-positioned to capitalize on the rising demand for carbon-reduced concrete through its eco-efficient admixtures, such as superplasticizers and supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs). By 2026, products enabling CO₂ reductions of 30–50% in concrete mixes are expected to dominate procurement decisions. -
Digitalization and Smart Construction
The integration of digital tools—such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), IoT-enabled curing sensors, and AI-driven mix optimization—is accelerating. Master Concrete is likely to expand its digital service offerings, including real-time performance monitoring of concrete elements and predictive analytics for durability. Partnerships with tech firms and construction management platforms will enhance value-added services, differentiating Master Concrete in competitive markets. -
Resilient and High-Performance Infrastructure
Climate change is driving demand for resilient infrastructure capable of withstanding extreme weather, seismic activity, and urban stressors. Master Concrete’s advanced waterproofing systems, corrosion inhibitors, and high-strength concrete formulations will be critical in transportation, coastal, and urban redevelopment projects. Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East are expected to lead infrastructure spending, creating growth avenues. -
Urbanization and Affordable Housing Initiatives
Rapid urbanization—especially in Africa, India, and Southeast Asia—will fuel demand for durable, cost-effective construction materials. Governments are launching large-scale affordable housing programs that require fast-setting, durable concrete solutions. Master Concrete can leverage its portfolio of rapid-hardening admixtures and self-consolidating concrete technologies to support these fast-track developments. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Global supply chain disruptions have prompted a shift toward regional material sourcing and manufacturing. By 2026, Master Concrete is expected to strengthen local production networks and raw material partnerships to reduce lead times and logistical costs. This localization strategy also aligns with ESG goals by lowering transportation emissions. -
Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
New international standards (e.g., ISO 22391, EN 1504) and green building certifications (LEED, BREEAM) are influencing product development. Master Concrete will need to ensure all formulations meet evolving safety, durability, and environmental benchmarks. Transparency in product lifecycle assessments (EPDs) will become a competitive differentiator.
Conclusion:
Master Concrete’s success in 2026 will depend on its agility in responding to sustainability imperatives, technological disruption, and global infrastructure needs. By focusing on innovation, digital integration, and regional market adaptation, the company is poised to strengthen its leadership in the advanced concrete solutions sector.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Master Concrete (Quality, IP)
Sourcing high-quality Master Concrete—a premium or proprietary concrete mix often involving specialized formulations, admixtures, or performance characteristics—can present several challenges related to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to substandard construction, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key issues to watch for:
Quality Inconsistencies and Specification Gaps
One of the most frequent pitfalls is receiving concrete that does not meet the specified performance criteria. Master Concrete typically requires precise mix designs (e.g., high strength, durability, workability), but inconsistencies can arise due to poor batching, substandard raw materials, or lack of process control.
- Variable Material Sources: Aggregates, cement, and chemical admixtures from different suppliers can alter the final product’s behavior, even if the mix design remains the same.
- Lack of Third-Party Certification: Without independent testing and certification (e.g., ASTM, EN standards), it’s difficult to verify claims about compressive strength, permeability, or setting time.
- Inadequate On-Site Quality Control: Poor handling, incorrect curing, or delayed delivery can compromise concrete quality regardless of the initial mix design.
To mitigate this, require suppliers to provide mix design documentation, test reports, and batch certifications. Implement strict acceptance protocols and on-site testing (slump tests, cube strength tests).
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks and Misappropriation
Master Concrete formulations often involve proprietary admixtures, dosing systems, or blending techniques that constitute valuable intellectual property. Sourcing from untrustworthy or non-contractual partners increases the risk of IP exposure.
- Unprotected Formulations: Sharing detailed mix designs without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or IP clauses can lead to reverse engineering or unauthorized replication by suppliers or competitors.
- Lack of Licensing Agreements: Using branded or patented concrete technologies (e.g., self-healing concrete, carbon-capturing mixes) without proper licensing can result in infringement claims.
- Supplier Ownership Ambiguity: If a supplier develops a custom mix, ownership of the formulation may default to them unless clearly assigned in the contract.
To protect IP, use confidentiality agreements, define IP ownership in sourcing contracts, and consider patent or trade secret protection for unique formulations. Limit disclosure of critical admixture ratios or proprietary processes.
Overreliance on Supplier Claims Without Verification
Suppliers may overstate performance attributes (e.g., “ultra-durable,” “zero carbon”) without providing verifiable data. This is especially common with marketing-driven “green” or “smart” concrete products.
- Greenwashing: Claims about sustainability or low environmental impact may lack third-party verification (e.g., EPD, LCA).
- Performance Hype: Terms like “Master Grade” or “Elite Mix” are not standardized and can be misleading without technical substantiation.
Always demand transparent, test-backed performance data and verify claims through independent laboratories or pilot trials before full-scale sourcing.
Supply Chain and Scalability Issues
Even if a Master Concrete mix performs well in testing, scaling up production can expose weaknesses in supply chain management.
- Limited Supplier Capacity: Specialized mixes may rely on niche admixtures with long lead times or limited availability.
- Geographic Constraints: Transporting high-performance concrete over long distances can affect workability and setting time, especially in extreme climates.
Ensure the supplier has the infrastructure and logistics to deliver consistent quality at the required volume and schedule. Consider local batching options with strict quality oversight.
Conclusion
Successfully sourcing Master Concrete requires balancing performance expectations with legal and operational safeguards. Prioritize suppliers with proven quality systems, enforce robust IP protections, and validate all claims through data and testing. Without due diligence, the pursuit of superior concrete can result in compromised structures or costly legal entanglements.
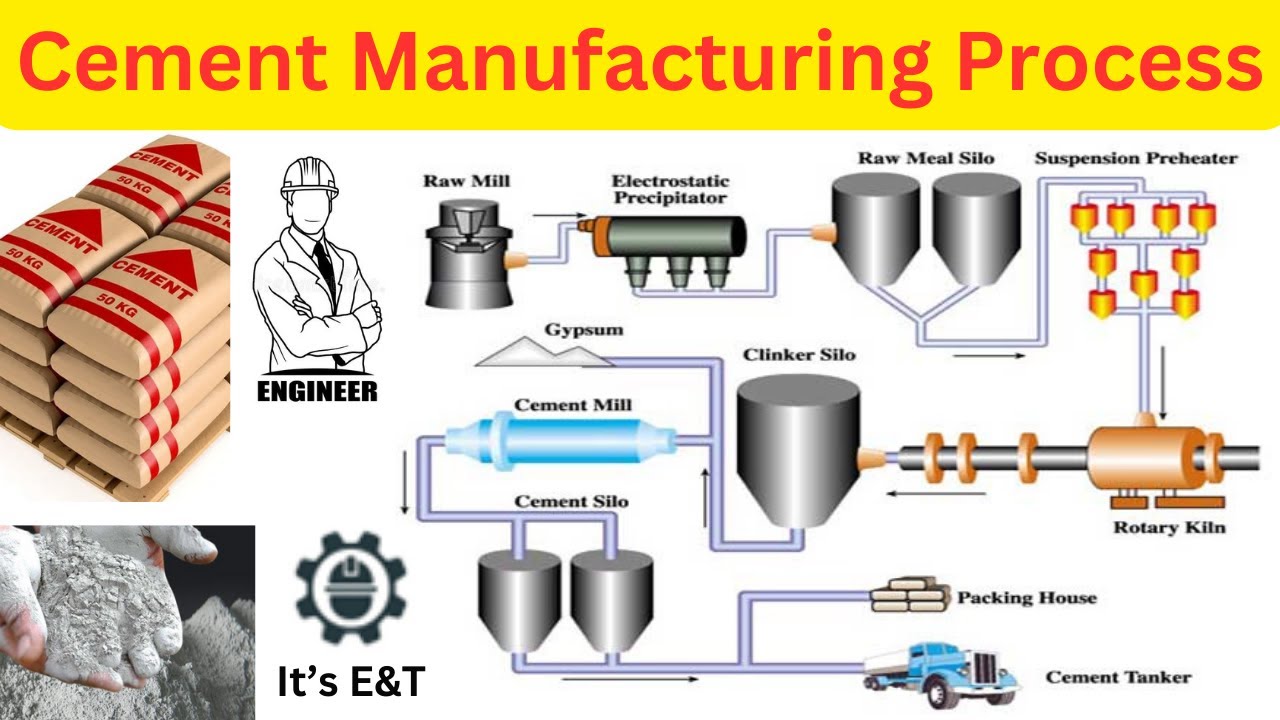
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Master Concrete
This guide outlines the essential logistics procedures and compliance requirements for Master Concrete operations. Adherence ensures efficient delivery, safety, regulatory compliance, and customer satisfaction.
Transportation & Delivery Management
Ensure all concrete deliveries are scheduled, dispatched, and executed with precision. Utilize GPS-enabled fleet tracking for real-time monitoring. Coordinate closely with dispatchers, drivers, and job site supervisors to confirm delivery times, mix specifications, and site access requirements. All vehicles must adhere to Department of Transportation (DOT) regulations and undergo routine maintenance checks.
Mix Design & Quality Control Compliance
All concrete batches must conform to approved mix designs and ASTM standards (e.g., ASTM C94). Maintain detailed batch records, including cement type, aggregate sources, admixtures, water-cement ratio, and air content. Conduct regular slump, temperature, and air content tests at the plant and upon delivery. Non-conforming batches must be rejected and documented per quality assurance protocols.
Environmental & Safety Regulations
Comply with all federal, state, and local environmental regulations, including EPA guidelines for stormwater runoff (NPDES permits) and dust control. Implement Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) plans at all facilities. Drivers and plant personnel must complete OSHA safety training, including hazard communication (HazCom), respiratory protection, and confined space entry where applicable.
Driver Certification & Hours of Service (HOS)
All drivers must possess a valid Commercial Driver’s License (CDL) with appropriate endorsements. Strictly enforce FMCSA Hours of Service regulations to prevent driver fatigue. Utilize electronic logging devices (ELDs) to monitor driving time and ensure compliance with 11-hour driving and 14-hour duty limits. Conduct pre-trip and post-trip vehicle inspections per DOT requirements.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Maintain accurate and accessible records for all deliveries, including batch tickets, delivery receipts, test reports, and driver logs. Retain documentation for a minimum of five years or as required by local jurisdiction. Digital records should be securely backed up and available for audit upon request by regulatory bodies or clients.
Customer Site Compliance & Communication
Verify site-specific requirements prior to delivery, including traffic control plans, washout containment, and safety protocols. Confirm that receiving personnel are present and qualified to accept delivery. Communicate any delays or issues promptly. Ensure washout water is collected and disposed of in accordance with environmental regulations to prevent contamination.
Regulatory Audits & Continuous Improvement
Prepare for scheduled and unscheduled audits by federal, state, or third-party agencies (e.g., DOT, OSHA, EPA). Conduct internal audits quarterly to assess compliance and operational efficiency. Use audit findings to implement corrective actions and improve logistics performance, safety, and regulatory alignment across all Master Concrete operations.
In conclusion, sourcing Master Concrete requires a strategic approach that balances quality, reliability, cost-efficiency, and long-term partnership potential. By thoroughly evaluating suppliers based on certifications, product specifications, technical support, and sustainability practices, organizations can ensure they are partnering with a provider that meets both project requirements and industry standards. Additionally, considering logistical factors such as delivery timelines, geographic proximity, and service responsiveness further enhances supply chain efficiency. Ultimately, a well-executed sourcing strategy for Master Concrete not only supports structural integrity and project success but also contributes to sustainable construction practices and overall value optimization.