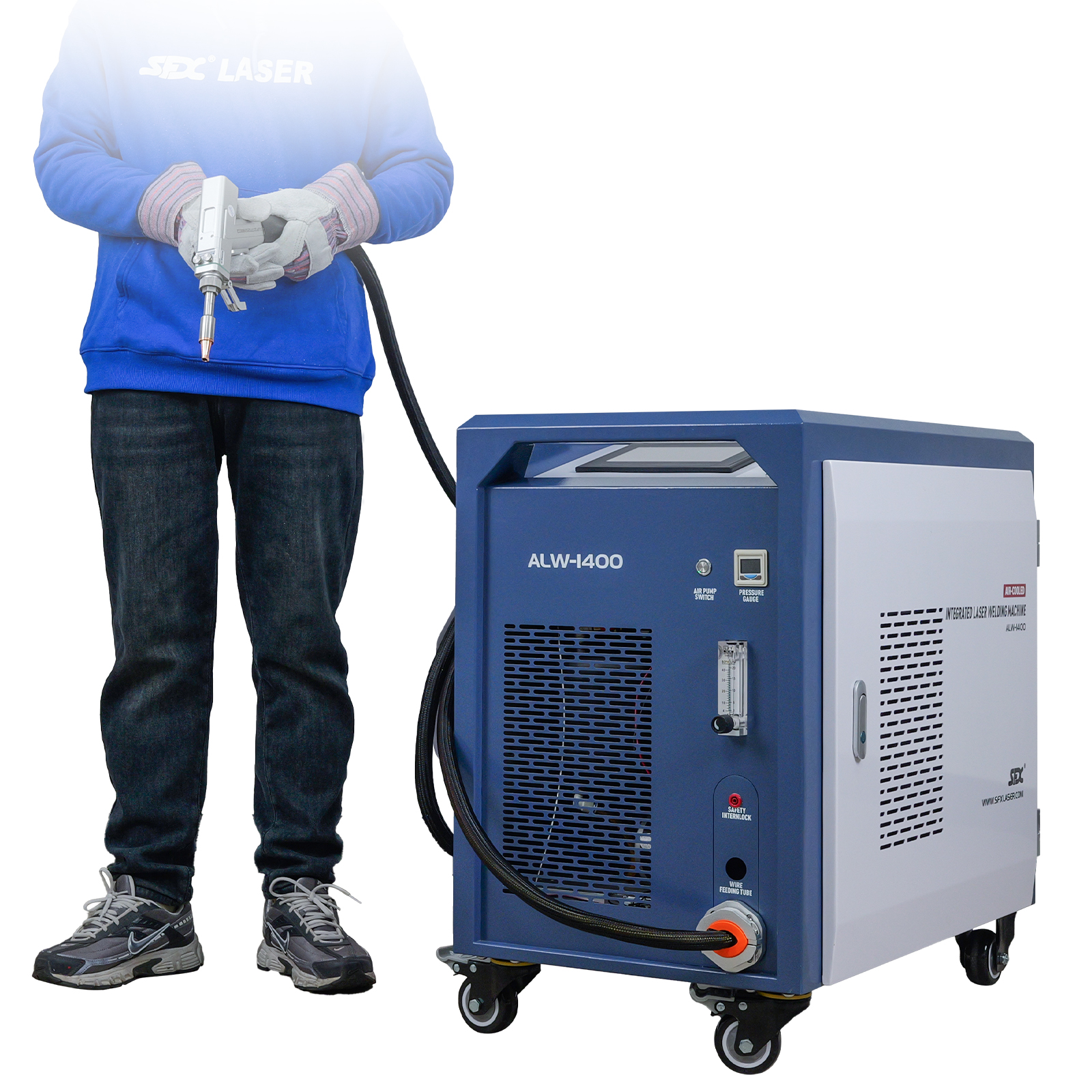
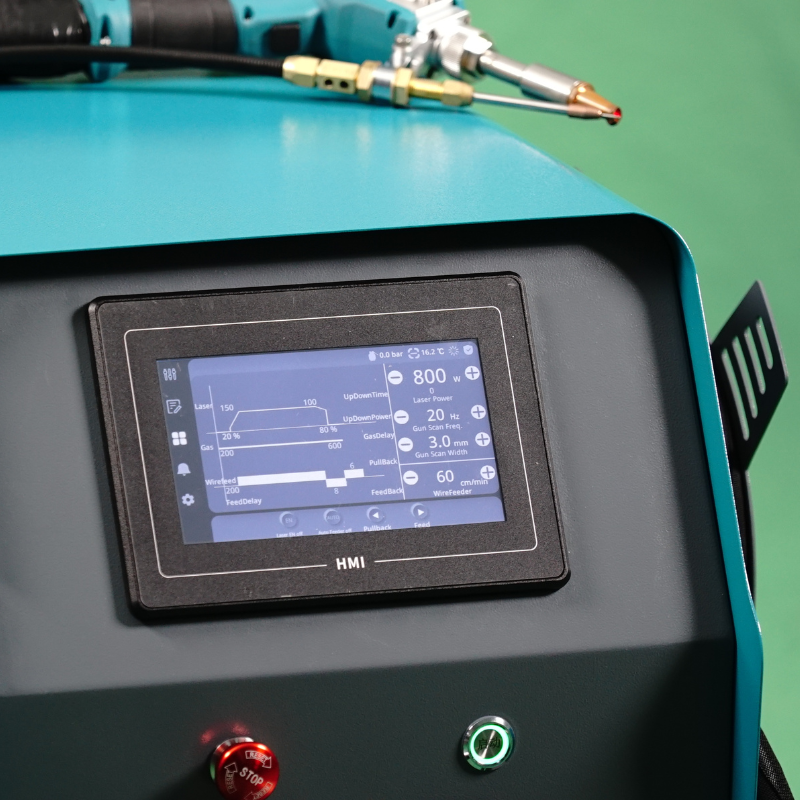
The global laser welding machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision manufacturing in the automotive, electronics, and medical device industries. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 1.37 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, increasing automation in production lines, and the push for energy-efficient joining processes. As industries prioritize high accuracy and minimal thermal distortion, machines offering optimal Maquina De Soldar Láser Precio—balancing performance and cost—are gaining significant traction. In this competitive landscape, four manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovative engineering, scalable solutions, and competitive pricing to capture a growing share of the expanding market.
Top 4 Maquina De Soldar Láser Precio Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: Ultra-portable laser welding machine (48.5 lbs) with dual welding/seam cleaning. Patented CUAL laser ensures precision on thin metals. Pre-set modes +.Missing: maquina de soldar…
#2 Soldadoras Láser Portátiles
#3 Máquina de soldadura láser SMART
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: LC-WELD SMART es la versión más pequeña de nuestros productos de soldadura láser con un software muy sencillo e intuitivo. Forma parte de la gama LC-WELD, …Missing: precio manuf…
#4 Become a Distributor
Website: viberlaser.com
Key Highlights: La máquina de soldar láser de Viber es 4 veces más rápida. Una solución todo en uno que supera nuestras expectativas. Ana García. Gerente de Fabricación ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Maquina De Soldar Láser Precio

2026 Market Trends for Maquina De Soldar Láser Precio
The global market for maquinas de soldar láser (laser welding machines) is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements, industrial automation, and growing demand across key manufacturing sectors. As we approach 2026, several key trends are shaping both the supply and pricing landscape—commonly searched as precio (price)—for these precision tools, particularly in Spanish-speaking regions such as Latin America, Spain, and parts of the U.S.
Rising Demand in Automotive and Electronics Manufacturing
One of the primary drivers influencing the precio of laser welding machines in 2026 is the increased adoption in high-precision industries. The automotive sector, especially with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), requires reliable and efficient welding for battery components, sensors, and lightweight structures. Similarly, the electronics industry demands micron-level accuracy, which only laser welding can consistently deliver. This growing demand is pushing manufacturers to scale production, which—while increasing competition—also affects machine pricing due to higher component costs and R&D investments.
Technological Advancements Impacting Price and Performance
By 2026, fiber laser technology will dominate the market, replacing older CO₂ and Nd:YAG systems due to higher efficiency, lower maintenance, and better integration with robotic systems. These advanced machines, while offering improved performance, often come with a higher initial precio. However, prices are expected to stabilize or slightly decrease due to economies of scale and growing competition among manufacturers in China, Germany, and the U.S.
Automation and AI integration are also contributing to price differentiation. Machines equipped with real-time monitoring, adaptive control, and predictive maintenance features command premium pricing. Buyers in Latin America and Southern Europe, in particular, are showing increased interest in mid-range automated systems that balance cost and functionality.
Regional Price Variations and Supply Chain Dynamics
The precio of a máquina de soldar láser in 2026 will vary significantly by region. In countries like Mexico, Brazil, and Spain, import tariffs, logistics costs, and local service support affect final pricing. Chinese manufacturers such as Han’s Laser and Maxphotonics are offering competitive pricing, making them attractive to cost-sensitive markets. Meanwhile, European and North American brands like TRUMPF and IPG Photonics maintain premium pricing due to brand reputation and after-sales service.
Supply chain resilience post-pandemic has also influenced pricing. As semiconductor and optical component shortages become less frequent, production bottlenecks are easing, leading to more stable pricing trends into 2026.
Growth of the Used and Refurbished Market
Another trend affecting precio is the expansion of the secondary market for laser welding machines. As small and medium enterprises (SMEs) seek cost-effective solutions, the demand for refurbished or second-hand systems is rising. This segment offers significant savings—up to 40–60% off new machine prices—making laser welding accessible to a broader range of manufacturers, particularly in emerging economies.
Conclusion: Price Outlook for 2026
By 2026, the average precio of a mid-range fiber laser welding machine is expected to range between $25,000 and $60,000 USD, depending on power, automation level, and region. While high-end industrial systems may exceed $100,000, increased competition and technological diffusion will likely prevent drastic price increases. Buyers should anticipate better value through modular designs, longer warranties, and bundled software features.
In summary, the maquina de soldar láser precio in 2026 will reflect a maturing market—balancing innovation, accessibility, and regional economic factors. Strategic sourcing, consideration of total cost of ownership, and evaluation of after-sales support will be critical for businesses looking to invest wisely in this evolving technology.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Máquina de Soldar Láser Precio (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a máquina de soldar láser (laser welding machine) based solely on price can lead to significant long-term issues, especially when quality and IP (Intellectual Property) protection are overlooked. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Low Price Over Machine Quality
One of the most common mistakes is selecting a laser welding machine based primarily on a low precio (price). While cost-efficiency is important, extremely low-priced machines often use substandard components, resulting in:
- Poor weld consistency and precision
- Higher maintenance and downtime
- Shorter lifespan of critical parts like laser sources and cooling systems
- Inadequate after-sales support
Always verify technical specifications, component brands (e.g., laser source from Raycus or IPG), and real-world performance data before making a purchase.
2. Overlooking Build and Safety Standards (IP Rating)
The IP (Ingress Protection) rating indicates how well the machine is protected against dust and moisture—critical in industrial environments. Many low-cost machines, especially from uncertified suppliers, either omit or falsify IP ratings.
- An inadequate IP rating (e.g., less than IP54) can lead to internal damage in humid or dusty environments.
- Lack of proper enclosure increases risk of operator exposure to laser radiation.
- Non-compliance with international safety standards (e.g., CE, IEC 60825) can lead to legal and insurance issues.
Always request certification documents and validate IP ratings through third-party testing if necessary.
3. Risk of Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
When sourcing from low-cost manufacturers, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement, there’s a risk of purchasing machines that infringe on patented technologies.
- Cloned or reverse-engineered systems may lack reliability and innovation.
- Using such equipment could expose your business to legal liability, especially in export markets with strict IP laws (e.g., EU, USA).
- Limited software updates or proprietary features may be disabled or unstable.
Choose suppliers with transparent R&D backgrounds and verifiable technology licenses.
4. Hidden Costs from Poor After-Sales Support
Low initial precio doesn’t reflect the total cost of ownership. Many budget machines come with:
- Limited or no warranty
- Delayed technical support and spare parts delivery
- Language barriers and lack of local service centers
These factors increase downtime and reduce productivity, ultimately making the cheaper option more expensive.
5. Inadequate Training and Documentation
Affordable machines often lack comprehensive user manuals, training programs, or multilingual support. This leads to:
- Improper operation and safety hazards
- Inefficient use of machine capabilities
- Increased risk of damage due to user error
Ensure the supplier provides thorough training and documentation before purchase.
Conclusion
When sourcing a máquina de soldar láser, balancing precio, quality, and IP compliance is essential. Avoid the temptation of low-cost options that compromise on safety, durability, and legal integrity. Always conduct due diligence on suppliers, request certifications, and evaluate total cost of ownership—not just the upfront price.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Maquina De Soldar Láser Precio
When importing or exporting a máquina de soldar láser (laser welding machine), understanding logistics and compliance requirements is essential to avoid delays, fines, or shipment rejection. This guide outlines key considerations related to pricing (precio), shipping, customs, and regulatory compliance.
Understanding the Precio and Total Landed Cost
The listed precio of a laser welding machine typically reflects only the base manufacturer or supplier price. To ensure accurate budgeting, calculate the total landed cost, which includes:
– Equipment price (FOB origin)
– International freight (air or sea)
– Marine insurance
– Customs duties and import taxes
– Destination handling and delivery fees
– Compliance certification costs (e.g., CE, FCC, NRCan)
– Installation and commissioning services (if applicable)
Be cautious of unusually low prices, as they may exclude critical compliance features or after-sales support.
International Shipping & Logistics
Choose the appropriate shipping method based on machine size, urgency, and cost:
– Sea Freight (FCL/LCL): Economical for heavy or large machines; suitable for full container loads (FCL) or shared containers (LCL).
– Air Freight: Faster but more expensive; ideal for urgent deliveries or lightweight units.
Key logistics considerations:
– Proper crating and shock protection for sensitive laser and optical components.
– Climate-controlled transport if required (especially for precision optics).
– Accurate labeling with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”).
– Use Incoterms clearly (e.g., EXW, FOB, CIF, DDP) to define responsibilities.
Export and Import Documentation
Ensure all required documentation is prepared accurately:
– Commercial Invoice (with detailed description, HS code, and declared value)
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB)
– Certificate of Origin
– Technical Specifications and User Manual (in the destination country’s language, if required)
– Warranty and Compliance Certificates
Missing or incorrect documents can delay customs clearance and increase costs.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Laser welding machines are regulated due to their laser radiation, electrical safety, and potential emissions. Compliance varies by destination country:
United States:
– FDA/CDRH compliance for laser products (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11)
– FCC certification for electromagnetic interference (EMI)
– OSHA safety standards for workplace use
European Union:
– CE marking under Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and EMC Directive 2014/30/EU
– Compliance with EN standards (e.g., EN 60825 for laser safety)
– Declaration of Conformity required
Canada:
– Compliance with Health Canada’s Radiation Emitting Devices Act (REDA)
– NRCan energy efficiency regulations (if applicable)
– CSA electrical safety certification
Other Regions:
– China: CCC certification
– Australia: RCM mark and compliance with AS/NZS standards
– Mexico: NOM certification
Verify local requirements before shipping.
Laser Safety and Classification
Laser welding machines typically fall under Class 4 lasers (high power). Ensure the machine includes:
– Proper labeling with laser class, wavelength, and output power
– Safety interlocks and emergency stop mechanisms
– Protective enclosures and beam shielding
– Required safety documentation (e.g., user training manual, hazard warnings)
Non-compliant safety features can result in import refusal or legal liability.
Customs Classification (HS Codes)
Correct HS (Harmonized System) code classification is crucial for duty assessment. Common codes include:
– 8515.21 – Machines for welding using laser or other light/photonic sources
– 9013.20 – Other laser machines (depending on configuration)
Consult a customs broker to confirm the appropriate code based on machine specifications.
Post-Import Considerations
After arrival:
– Arrange for customs clearance through a licensed broker
– Schedule inspection (if required by local authorities)
– Verify machine condition upon delivery and document any damage
– Ensure on-site installation meets local electrical and safety codes
– Provide operator training aligned with safety regulations
Conclusion
Successfully managing the logistics and compliance for a máquina de soldar láser requires attention to the total precio, accurate documentation, adherence to international regulations, and coordination with experienced freight and customs partners. Proactive planning ensures timely delivery, legal operation, and long-term reliability of the equipment.
Conclusión sobre la fuente de maquinas de soldar láser por precio
La búsqueda de una máquina de soldar láser por precio accesible requiere un equilibrio entre costo, calidad y rendimiento. Tras analizar diversas opciones disponibles en el mercado, se puede concluir que existen alternativas competitivas tanto en fabricantes nacionales como internacionales, especialmente en países como China, donde se ofrecen equipos a precios más bajos sin sacrificar completamente la funcionalidad.
Sin embargo, es fundamental no tomar la decisión únicamente basándose en el precio más bajo. Factores como la potencia del láser, tipo de material a soldar, precisión, automatización, soporte técnico y garantía influyen directamente en la rentabilidad a largo plazo. Máquinas más económicas pueden implicar mayores costos operativos debido al mantenimiento frecuente o menor durabilidad.
Además, las tendencias actuales apuntan a una mayor automatización y eficiencia energética, por lo que invertir en tecnologías más avanzadas, aunque con un costo inicial más alto, puede resultar más rentable en producción sostenida.
En conclusión, al seleccionar una máquina de soldar láser por precio, se recomienda realizar un análisis de costo-beneficio integral, considerar las necesidades específicas del proyecto o producción, y priorizar proveedores confiables con buen soporte técnico. El precio es importante, pero debe evaluarse en conjunto con la calidad, eficiencia y vida útil del equipo para tomar una decisión estratégica y sostenible.