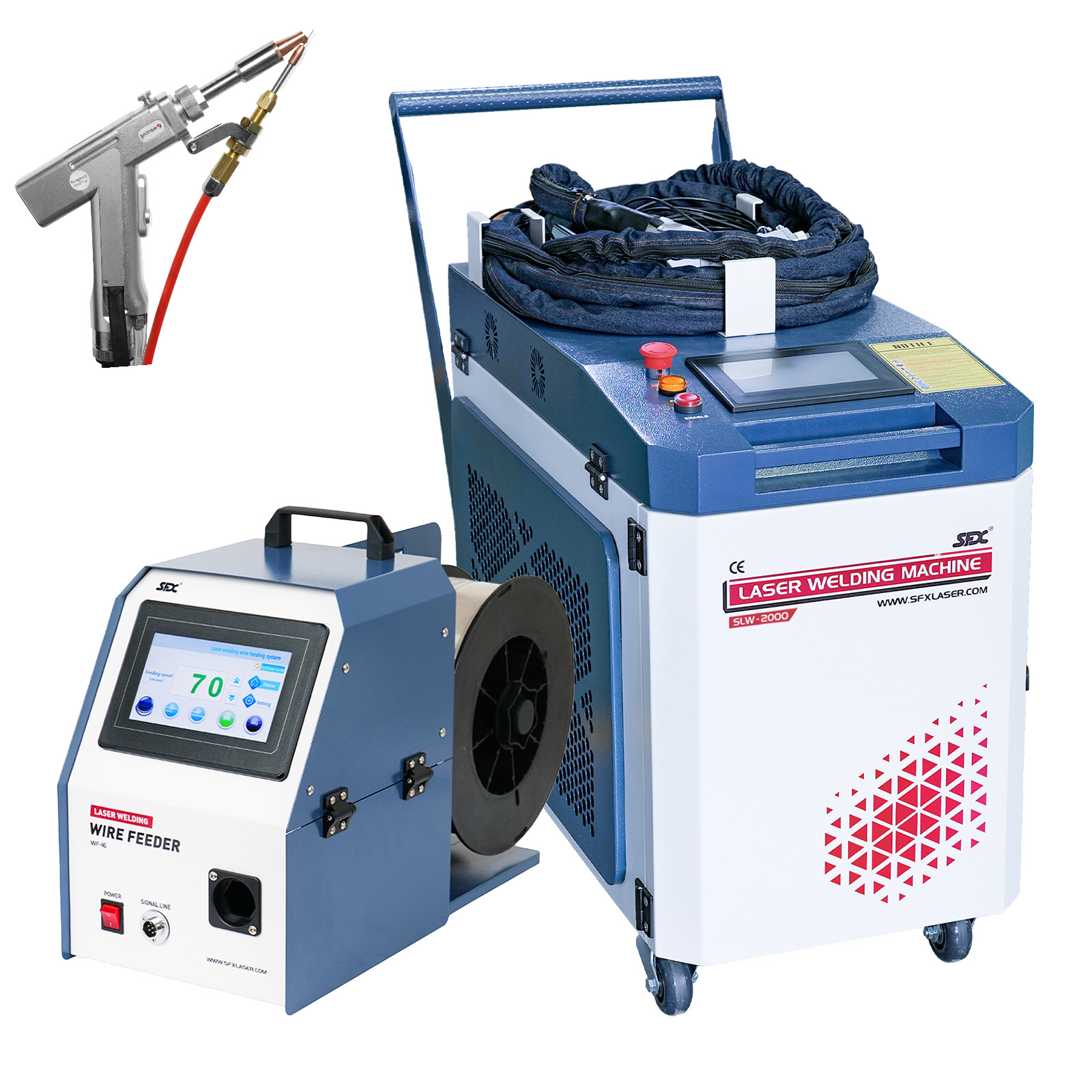
The global market for laser welding technology has experienced significant growth, driven by rising demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in high-power fiber lasers, increasing automation in production lines, and the need for stronger, cleaner welds with minimal heat distortion. As a result, demand for advanced máquinas de láser para soldar (laser welding machines) has surged, particularly in industrial centers across Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe. With the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies — such as AI-driven monitoring and robotic integration — manufacturers are now prioritizing scalable, high-efficiency systems. In this competitive landscape, eight manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovation, reliability, and global reach to meet evolving industrial standards.
Top 8 Maquina De Laser Para Soldar Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: Ultra-portable laser welding machine (48.5 lbs) with dual welding/seam cleaning. Patented CUAL laser ensures precision on thin metals. Pre-set modes +.Missing: maquina de para sol…
#2 Fiber Laser Welding Machine
Website: lmelaser.com
Key Highlights: LME Laser is a professional manufacturer with more than 12 years experience. LME laser have handheld fiber laser welder, 4 axis/5 axis/6 axis fiber laser ……
#3 Laser Welding Machine
Website: jqlaser.com
Key Highlights: The laser welding machine is the latest in welding technology. It is perfect for any business or individual who wants to get the most out of their welds….
#4 Soldadoras Láser Portátiles
#5 Become a Distributor
Website: viberlaser.com
Key Highlights: La máquina de soldar láser de Viber es 4 veces más rápida. Una solución todo en uno que supera nuestras expectativas. Ana García. Gerente de Fabricación ……
#6 LC Lasers: Máquinas Láser
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: LC-WELD GALVO Máquina de soldadura láser Galvo La soldadura láser sumada a la tecnología galvo permite realizar soldaduras automáticas y semiautomáticas. ……
#7 Máquinas de soldadura láser
Website: acctekgroup.com
Key Highlights: La máquina de soldadura láser proporciona uniones profundas y limpias en acero inoxidable, acero al carbono, aluminio y latón; las opciones manuales o ……
#8 LightWELD
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: $330 deliveryOs sistemas portáteis de soldagem a laser LightWELD™ são rápidos, fáceis de aprender e operar, e produzem resultados consistentes e de alta qualidade em uma ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Maquina De Laser Para Soldar
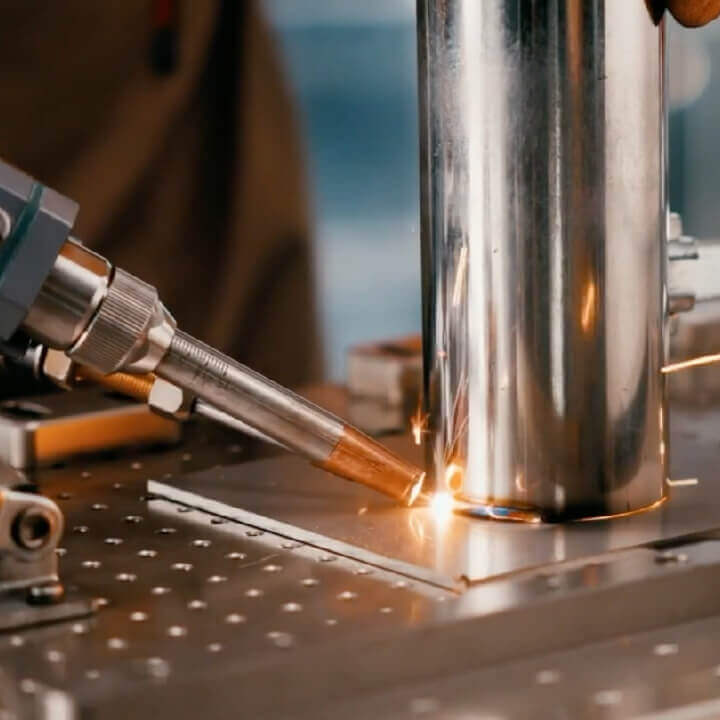

H2: Market Trends for Maquina De Laser Para Soldar (Laser Welding Machines) in 2026
By 2026, the global market for máquinas de láser para soldar (laser welding machines) is projected to experience robust growth, driven by technological advancements, rising demand across key industries, and the increasing shift toward automation and precision manufacturing. Below are the dominant market trends shaping the landscape of laser welding machines in 2026:
1. Increased Adoption in Automotive and EV Manufacturing
The automotive sector, especially electric vehicle (EV) production, will be a primary growth driver. Laser welding offers high-speed, precision joining of lightweight materials like aluminum and high-strength steel—critical for EV battery packs, power electronics, and structural components. With global EV production accelerating, manufacturers are investing heavily in laser welding systems for improved efficiency and reliability.
2. Growth in Industrial Automation and Smart Factories
Integration with Industry 4.0 technologies is transforming laser welding machines into intelligent systems. By 2026, more machines will feature IoT connectivity, real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and AI-driven process optimization. This enables higher throughput, reduced downtime, and consistent weld quality, appealing to manufacturers pursuing smart factory initiatives.
3. Advancements in Fiber and Hybrid Laser Technologies
Fiber laser welding systems continue to dominate due to their energy efficiency, lower maintenance, and superior beam quality. Innovations in hybrid laser-arc welding (HLAW) are also gaining traction, combining the deep penetration of lasers with the gap-bridging capability of arc welding—ideal for heavy industrial applications in shipbuilding and construction.
4. Expansion in Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia, will lead market expansion due to rising industrialization, government support for advanced manufacturing, and growing local production of electronics and automobiles. Latin America and parts of Eastern Europe are also witnessing increased adoption, supported by foreign investments and modernization of production facilities.
5. Demand for Compact and Portable Systems
Smaller, modular laser welding machines are gaining popularity, especially among SMEs and repair services. These systems offer ease of integration, lower upfront costs, and flexibility for on-site welding applications in aerospace, tooling, and mold repair—fueling wider accessibility beyond large-scale manufacturers.
6. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
Manufacturers are prioritizing eco-friendly production processes. Laser welding consumes less energy than traditional methods and produces minimal waste. By 2026, environmentally conscious regulations and corporate sustainability goals will further push industries to adopt laser-based solutions.
7. Rising Competition and Localization of Production
Global competition among laser welding machine suppliers is intensifying. While European and North American companies lead in high-end precision systems, Chinese manufacturers are rapidly improving quality and offering cost-effective alternatives. Local assembly and service networks are becoming critical for market penetration, especially in price-sensitive regions.
Conclusion
By 2026, the máquina de láser para soldar market will be defined by innovation, automation, and sector-specific customization. As industries demand faster, cleaner, and more precise joining technologies, laser welding machines will play a central role in next-generation manufacturing—positioning the market for sustained expansion and technological evolution.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Maquina De Laser Para Soldar (Quality and IP Issues)

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Máquina de Laser Para Soldar (Laser Welding Machine)
Import Regulations and Documentation
When importing a laser welding machine, compliance with the destination country’s import regulations is critical. Required documentation typically includes a commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading or air waybill, and a certificate of origin. Additionally, some countries may require a conformity assessment, such as CE certification (for the EU), FCC certification (for the U.S.), or other regional safety and electromagnetic compatibility standards. Ensure the machine complies with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards, particularly IEC 60825 for laser safety. Always verify if a special import license or permit is required due to the industrial nature and laser classification of the equipment.
Laser Safety Classification and Compliance
Laser welding machines are classified based on their laser output and potential hazard, as defined by standards such as IEC 60825-1. Most industrial laser welding systems fall under Class 4, which indicates a high risk of eye and skin injury, as well as potential fire hazards. Compliance with laser safety regulations involves proper labeling, inclusion of safety interlocks, emergency stop mechanisms, and protective enclosures. Importers must ensure that the machine comes with a detailed laser safety manual and that end users receive appropriate safety training. In many jurisdictions, registration of Class 4 lasers with national radiation protection agencies is mandatory.
Packaging and Transportation Requirements
Due to the sensitive optical and electronic components, laser welding machines must be packaged securely to prevent damage during transit. Use shock-absorbent materials, moisture barriers, and rigid outer crates to protect against vibration, humidity, and impact. Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” indicators. For international shipping, comply with International Safe Transit Association (ISTA) standards. Consider climate-controlled transport if moving through extreme environments. Ensure batteries (if included) are shipped according to IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations, especially for lithium-ion types.
Customs Clearance and Tariff Classification
Proper Harmonized System (HS) code classification is essential for customs clearance. Laser welding machines are typically classified under HS code 8515.21 or 8515.80, depending on specific technical characteristics and application. Accurate classification affects duty rates and eligibility for trade agreements. Provide technical specifications, including laser power (in watts), wavelength, and intended industrial use, to support classification. Be aware of anti-dumping duties or safeguard measures that may apply in certain markets. Engage a licensed customs broker to facilitate documentation review and clearance.
Electrical and Environmental Standards
Verify that the machine’s electrical specifications (voltage, frequency, plug type) match the destination country’s power grid. Transformers or power adapters may be required. The equipment should comply with regional electrical safety standards such as UL (U.S.), CSA (Canada), or CE (Europe). Additionally, ensure compliance with environmental regulations like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (EU), which restrict the use of certain chemicals in electrical equipment. Machines must also meet waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) directives for end-of-life disposal planning.
Installation, Training, and After-Sales Support
Plan for professional installation by certified technicians to ensure operational safety and regulatory compliance. Provide end users with comprehensive training on machine operation, maintenance, and laser safety protocols. Maintain records of training for compliance audits. Establish a clear support structure for spare parts, technical assistance, and software updates. Include multilingual user manuals and safety documentation. Confirm warranty terms and service availability in the destination country to meet customer and regulatory expectations.
Conclusão sobre a Fonte de Máquina de Laser para Soldagem
A escolha de uma máquina de laser para soldagem exige uma análise criteriosa de diversos fatores técnicos, econômicos e operacionais. Equipamentos a laser oferecem vantagens significativas em relação aos métodos tradicionais de soldagem, como maior precisão, menor distorção térmica, alta velocidade de processo e excelente qualidade do cordão de solda. No entanto, o alto investimento inicial, os custos de manutenção e a necessidade de operadores qualificados são desafios que devem ser considerados.
Na seleção da fonte ideal – como lasers de fibra, CO₂ ou disco – é essencial alinhar as características do equipamento com o tipo de material, espessura, produção esperada e aplicações finais. Atualmente, os lasers de fibra destacam-se pela eficiência energética, menor custo operacional e manutenção reduzida, tornando-os a opção mais viável para a maioria dos cenários industriais modernos.
Adicionalmente, o fornecedor escolhido deve oferecer suporte técnico robusto, garantia adequada e disponibilidade de peças de reposição. A possibilidade de integração com linhas automatizadas também é um diferencial importante para quem busca aumentar produtividade e repetibilidade.
Em resumo, investir em uma máquina de laser para soldagem é uma decisão estratégica que pode trazer ganhos significativos em qualidade, produtividade e competitividade – desde que bem planejada, com base nas reais necessidades da operação e com fornecedores confiáveis e experientes no setor.