The global solar panels market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising energy demand, supportive government policies, and declining technology costs. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global solar photovoltaic (PV) market size was valued at USD 184.3 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.9% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 7% during the forecast period of 2024–2029, attributing this growth to accelerating investments in renewable infrastructure and the global push toward carbon neutrality. As solar energy emerges as a cornerstone of the clean energy transition, manufacturers have scaled production, improved panel efficiency, and diversified offerings to meet evolving market needs. This growing momentum has elevated competition and innovation among leading producers, shaping a dynamic landscape dominated by companies at the forefront of technology, sustainability, and supply chain resilience. In this context, identifying the top solar panel manufacturers requires evaluating not only market share but also advancements in efficiency, global reach, and financial performance—key factors that define industry leadership in a rapidly evolving sector.
Top 10 Of Solar Panels Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Boviet Solar
Domain Est. 2017
Website: bovietsolar.com
Key Highlights: Boviet Solar is a solar energy technology company specializing in manufacturing top-performing solar PV modules for solar projects….
#2 Solar panel manufacturer, trusted since 1996
Domain Est. 2004
Website: recgroup.com
Key Highlights: REC Group is a solar panel manufacturer, trusted for almost three decades. Since its founding in 1996, REC has been a true pioneer in the solar industry….
#3 Suniva
Domain Est. 2005 | Founded: 2007
Website: suniva.com
Key Highlights: Suniva is America’s oldest and largest monocrystalline solar cell manufacturer in North America. Suniva was founded in 2007….
#4 SEG Solar
Domain Est. 2012
Website: segsolar.com
Key Highlights: We are a Leading US Solar Module Manufacturer with A Fully Integrated Supply Chain · 1GW+. Global Cumulative Module Shipments · 1GW. Global PV Module Capacity · 1 ……
#5 Illuminate USA
Domain Est. 2019
Website: illuminateusa.com
Key Highlights: Illuminate USA is the largest single-site solar panel manufacturer in North America, using advanced manufacturing to supply the American solar market….
#6 First Solar
Domain Est. 1999
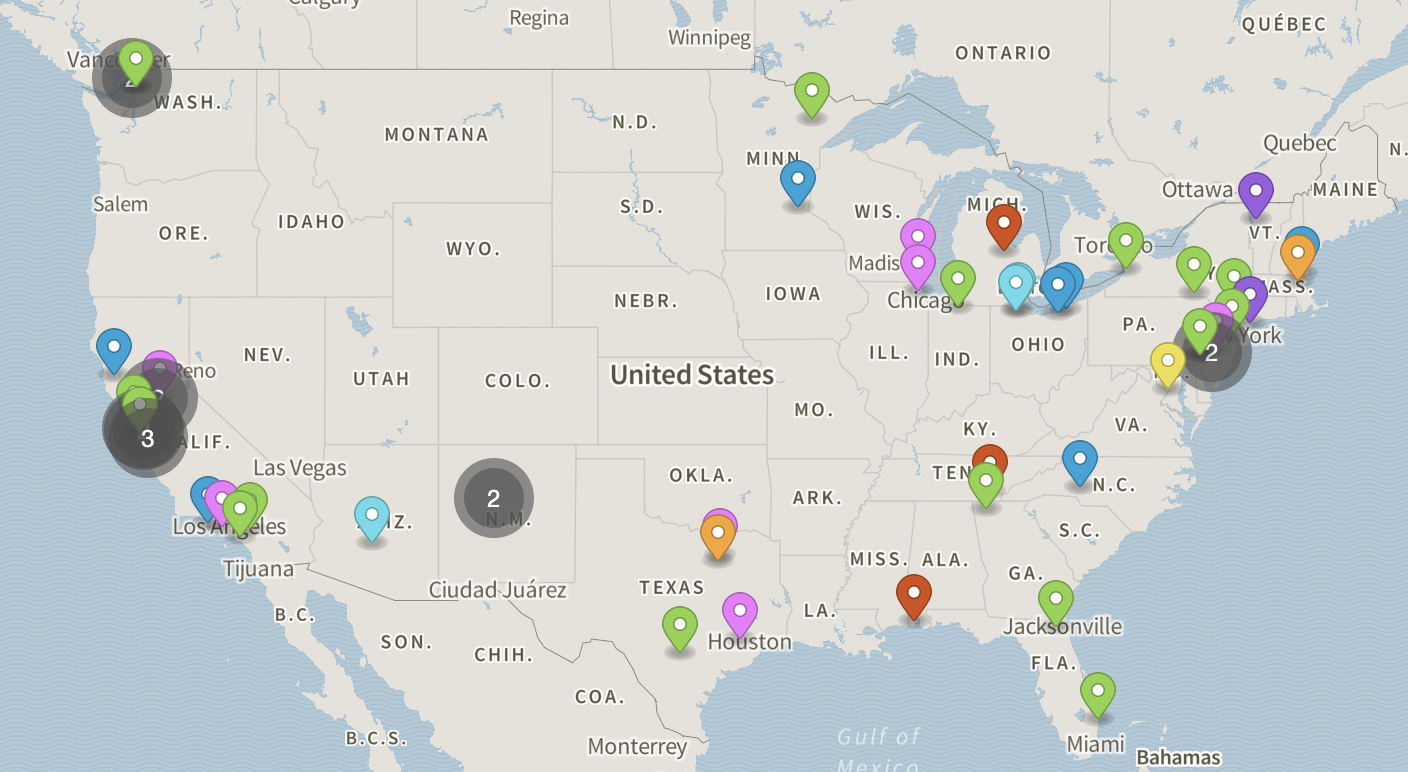
#7 Solar Manufacturing Map
Domain Est. 1999
Website: energy.gov
Key Highlights: The US Solar Photovoltaic Manufacturing Map shows only active manufacturing sites that contribute to the solar photovoltaic supply chain….
#8 Canadian Solar
Domain Est. 2001
Website: canadiansolar.com
Key Highlights: Over 20 solar & energy storage manufacturing facilities. in Asia & Americas. Canadian Solar closely examines our supply chains to ensure goods imported are ……
#9 PowerFilm Solar
Domain Est. 2005
Website: powerfilmsolar.com
Key Highlights: PowerFilm designs and manufactures custom solar cells, panels, and power solutions for energy harvesting, portable, and remote power applications….
#10 Heliene
Domain Est. 2009
Website: heliene.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture high quality solar photovoltaic modules in our American facilities. The supply chains are short, and our modules are never held up in port or ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Of Solar Panels

2026 Market Trends for Solar Panels
Rising Global Demand and Capacity Expansion
The solar panel market in 2026 is projected to experience robust growth, driven by increasing global demand for clean energy and supportive government policies. According to industry forecasts, global solar photovoltaic (PV) installations are expected to surpass 400 gigawatts (GW) annually by 2026, up from around 350 GW in 2023. This growth is fueled by national decarbonization goals, particularly in regions such as the European Union, the United States, and parts of Asia-Pacific. Countries are accelerating solar adoption through incentives like tax credits, feed-in tariffs, and renewable portfolio standards, creating a favorable environment for market expansion.
Advancements in Solar Technology
Technological innovation remains a cornerstone of the solar industry’s evolution. By 2026, high-efficiency solar cells—such as perovskite-silicon tandem cells—are expected to reach commercial scalability, offering conversion efficiencies exceeding 30%. These next-generation panels promise higher energy yields in smaller footprints, making them ideal for urban and space-constrained environments. Additionally, improvements in bifacial panels, which capture sunlight on both sides, and enhanced anti-reflective coatings are increasing energy output and lowering the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) from solar systems.
Cost Reductions and Economies of Scale
The continued decline in solar panel manufacturing costs is a key trend shaping the 2026 market. Economies of scale, driven primarily by mass production in China and increasing competition globally, have led to a sustained decrease in module prices. By 2026, the average cost of solar PV modules is projected to fall below $0.10 per watt. This cost competitiveness, combined with falling balance-of-system (BoS) expenses and streamlined installation processes, makes solar one of the most affordable sources of electricity in many parts of the world, even without subsidies.
Integration with Energy Storage and Smart Grids
A defining trend in 2026 is the deeper integration of solar panels with energy storage systems and smart grid technologies. As solar generation is intermittent, pairing solar installations with lithium-ion and emerging solid-state batteries enables reliable power supply during non-sunny periods. Residential, commercial, and utility-scale projects are increasingly deploying hybrid solar-plus-storage solutions. Smart inverters and AI-powered energy management systems further enhance grid stability and optimize energy use, facilitating higher penetration of solar power into the energy mix.
Supply Chain Diversification and Policy Shifts
Geopolitical concerns and trade policies are prompting a reevaluation of solar supply chains. In response to overreliance on Chinese manufacturing, countries like the U.S. and members of the EU are investing heavily in domestic solar production through initiatives such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and the European Green Deal. By 2026, these efforts are expected to yield a more diversified and resilient global supply chain, with increased manufacturing capacity in North America, Southeast Asia, and India. This shift aims to reduce dependency risks and support local job creation in the clean energy sector.
Sustainability and Circular Economy Focus
Environmental sustainability is gaining prominence in the solar industry. By 2026, there is a growing emphasis on reducing the carbon footprint of solar panel production and improving end-of-life management. Recycling technologies for solar panels are becoming more efficient, with companies developing processes to recover over 95% of materials like silicon, silver, and glass. Regulatory frameworks in several countries are introducing producer responsibility schemes, encouraging manufacturers to design more recyclable and longer-lasting panels, thus promoting a circular economy model.
Emerging Markets and Distributed Generation
While established markets in Europe and North America continue to grow, emerging economies in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America are becoming significant drivers of solar adoption. Off-grid and mini-grid solar solutions are expanding energy access in rural and underserved areas, supported by falling costs and innovative financing models such as pay-as-you-go (PAYG) solar. In 2026, distributed solar generation—including rooftop solar on homes and businesses—is expected to account for a growing share of total installations, empowered by digital platforms and community solar programs.
In summary, the 2026 solar panel market is characterized by rapid technological advancement, cost competitiveness, policy support, and a global shift toward energy independence and sustainability. These trends collectively position solar energy as a central pillar of the world’s transition to a low-carbon future.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Solar Panels (Quality, IP)
Sourcing solar panels, especially from international or less-regulated markets, presents several risks that can undermine project performance, longevity, and legal compliance. Two of the most critical areas of concern are product quality and intellectual property (IP) infringement.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Not all solar panel manufacturers adhere to international quality certifications such as IEC 61215 (performance), IEC 61730 (safety), or UL standards. Panels that lack proper certification may degrade faster, underperform, or pose safety hazards like hotspots or fire risks. Buyers may receive “cherry-picked” samples during audits while mass production batches fall short of specifications.
Use of Substandard Materials
To cut costs, some suppliers substitute high-quality components—such as tempered glass, ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) encapsulant, or aluminum frames—with inferior alternatives. This can lead to premature delamination, corrosion, microcracks, and reduced energy output over time.
Misrepresented Performance Ratings
Suppliers may overstate power output (e.g., labeling 380W panels as 400W) or use “nameplate” ratings under ideal lab conditions that don’t reflect real-world performance. This practice, known as “panel dumping” or “overclocking,” results in lower-than-expected energy yields and financial losses.
Lack of Long-Term Reliability Data
Many emerging manufacturers lack proven track records or independent field performance data. Without evidence of long-term durability—especially in harsh climates—buyers face uncertainty about panel lifespan and degradation rates, impacting return on investment.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Counterfeit or Cloned Panels
Some manufacturers produce panels that closely mimic the design, labeling, or technology of reputable brands without authorization. These clones may infringe on patented cell architectures (e.g., PERC, TOPCon) or module designs, exposing buyers to legal risk if deployed in markets with strict IP enforcement.
Use of Stolen or Unlicensed Technology
There are documented cases where solar companies have used proprietary cell or module technologies without licensing. Sourcing from such suppliers—even unknowingly—can result in shipment seizures, project delays, or liability if IP owners pursue legal action.
Ambiguous Supply Chain Transparency
Complex supply chains can obscure the origin of components. A panel assembled in one country might use cells or tech developed elsewhere under patent protection. Without due diligence, buyers risk supporting IP-violating supply chains, damaging their reputation and compliance standing.
Voided Warranties and Lack of Support
IP-infringing panels often come with invalid or unenforceable warranties. Reputable manufacturers may refuse service or replacement if their technology is replicated without permission, leaving end-users without recourse when failures occur.
Mitigating these risks requires rigorous supplier vetting, third-party testing, supply chain audits, and legal review of technology origins—especially when sourcing from high-volume, low-cost regions.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Solar Panels
Overview
Solar panel logistics and compliance involve managing the transportation, storage, import/export regulations, safety standards, and environmental requirements associated with photovoltaic (PV) modules. Proper planning ensures timely delivery, cost efficiency, and adherence to international and local regulations.
Transportation and Handling
Solar panels are fragile and susceptible to damage from impact, moisture, and improper handling. Key considerations include:
– Packaging: Panels must be shipped in palletized, sealed crates with edge protection and moisture barriers.
– Orientation: Always transport panels vertically or as specified by the manufacturer to prevent microcracks.
– Forklift Use: Lift only by the base of the pallet; never by the panels themselves.
– Temperature and Humidity: Avoid extreme conditions during transit; store in dry, temperature-controlled environments when possible.
Storage Requirements
- Store panels in a covered, dry area off the ground to avoid moisture damage.
- Limit stack height according to manufacturer specifications (typically no more than two pallets high).
- Minimize storage duration to reduce exposure risk; follow first-in, first-out (FIFO) practices.
Import and Export Compliance
Solar panels shipped across borders must comply with international trade regulations:
– Harmonized System (HS) Code: Typically 8541.40 for solar cells and panels. Confirm with local customs authorities.
– Certificates of Origin: Required for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU trade pacts).
– Import Duties and Tariffs: Be aware of anti-dumping duties (e.g., U.S. Section 201 tariffs on certain Asian-made panels).
– Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and compliance certificates.
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Solar panels must meet regional safety and performance certifications:
– International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): Standards such as IEC 61215 (performance) and IEC 61730 (safety) are widely recognized.
– North America: UL 1703 certification required in the U.S. and Canada.
– European Union: CE marking based on IEC standards; may require additional national approvals (e.g., VDE in Germany).
– Australia: Must comply with AS/NZS 5033 and have approval under the Clean Energy Council (CEC) scheme.
Environmental and Recycling Compliance
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Applies in the EU and other regions; restricts lead, cadmium, and other substances.
- WEEE Directive (EU): Producers must register and provide take-back and recycling options for end-of-life panels.
- State and Local Regulations: Some U.S. states (e.g., Washington) have solar panel recycling laws effective from 2024 onward.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain records for:
– Panel model numbers, serial numbers, and batch information.
– Certifications (safety, performance, origin).
– Shipping manifests and customs filings.
– Warranty and compliance documentation provided by manufacturers.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for solar panels ensures product integrity, regulatory adherence, and smooth project deployment. Partnering with experienced freight forwarders, verifying certifications early, and staying updated on evolving regulations are essential best practices.
In conclusion, sourcing a reliable manufacturer for solar panels requires a comprehensive evaluation of several key factors, including product quality, certifications, manufacturing capabilities, experience in the industry, financial stability, and compliance with international standards such as IEC, UL, and ISO. It is crucial to conduct thorough due diligence through factory audits, sample testing, and verification of references to ensure consistent performance and long-term durability of the panels. Additionally, considering the supplier’s scalability, after-sales support, and logistics capabilities will contribute to a sustainable and efficient supply chain. By selecting a reputable and technologically advanced manufacturer, businesses can ensure competitive pricing, high energy efficiency, and reliability—key drivers for success in the growing solar energy market. Ultimately, a strategic partnership with the right manufacturer not only enhances product quality but also supports long-term business growth and sustainability goals.