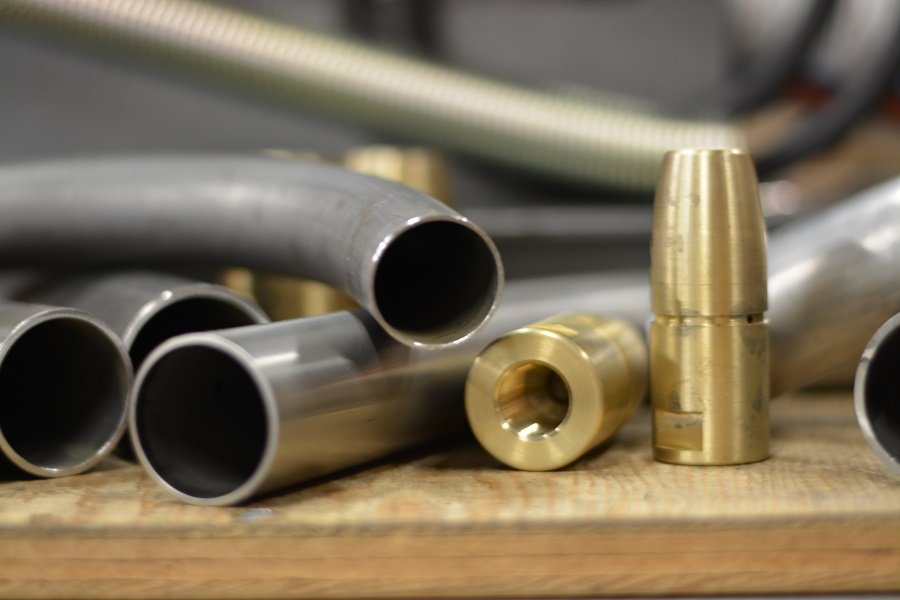
The global pipe bending equipment market is experiencing strong growth, driven by increasing demand across industries such as oil & gas, automotive, construction, and aerospace. According to Grand View Research, the global tube bending machine market size was valued at USD 5.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. Mandrel pipe bending, known for its precision in producing high-quality bends without deformation, is becoming increasingly critical in applications requiring tight tolerances and smooth internal surfaces. This sustained market expansion, supported by advancements in automation and CNC technology, has spurred innovation among manufacturers worldwide. Based on production capabilities, technological leadership, and global reach, the following nine companies stand out as leading mandrel pipe bending manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 9 Mandrel Pipe Bending Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Hines® Bending Systems
Domain Est. 2000
Website: hinesbending.com
Key Highlights: Hines Bending is the biggest provider in America for all types of bending machines. We make custom benders, provide installation and more….
#2 TUBE BENDING SPECIALISTS TUBE AND PIPE BENDING …
Domain Est. 2000
Website: tubebendingspecialists.com
Key Highlights: Tube Bending Specialists provides commercial and industrial manufacturing services focusing on pipe bending, tube bending, steel fabrication, roll forming and ……
#3 Mandrel Benders
Domain Est. 2001
#4 Mandrel Bending Stainless Steel Pipe & Tube Facts
Domain Est. 1996
Website: highpurity.com
Key Highlights: What is Mandrel Bending? Mandrel bending is a method of rotary draw bending, in which – the mandrel, a solid mandrel shaft with up to five segmented, ……
#5 Tube Bending
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1908
Website: cmrp.com
Key Highlights: Since 1908, Chicago Metal Rolled Products has provided tube bending, bending of pipes, bar bending, beam bending, structural steel bending, and plate rolling….
#6 Tulsa Tube Bending
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ttb.com
Key Highlights: Mandrel bending. Achieve smooth and uniform bends in pipes and tubes, with mandrel bending, while maintaining the internal diameter and wall ……
#7 Tube Bending Tool & Die Suppliers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: bendtooling.com
Key Highlights: Bend Tooling is the premier tube bending tool and die supplier in the US and worldwide, offering durable mandrels and wiper machine parts….
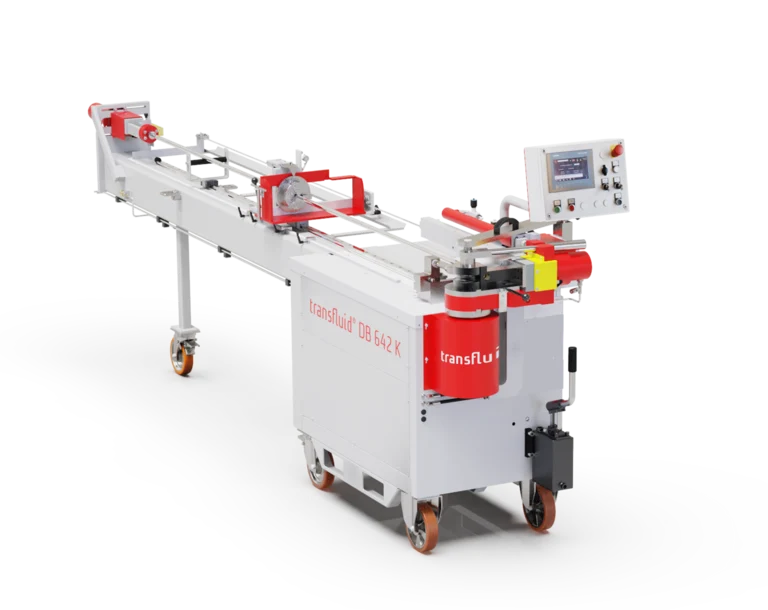
#8 transfluid
Domain Est. 2020
Website: transfluid-us.com
Key Highlights: A german mechanical engineering company serving the global market. Your solution for bending and forming tubes, pipes and more in the most efficient way….
#9 Custom Mandrel Bending
Domain Est. 2024
Website: truemandrel.com
Key Highlights: With expertise in custom mandrel bending and precision fabrication, we provide high-quality components tailored to meet diverse industry needs….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Mandrel Pipe Bending
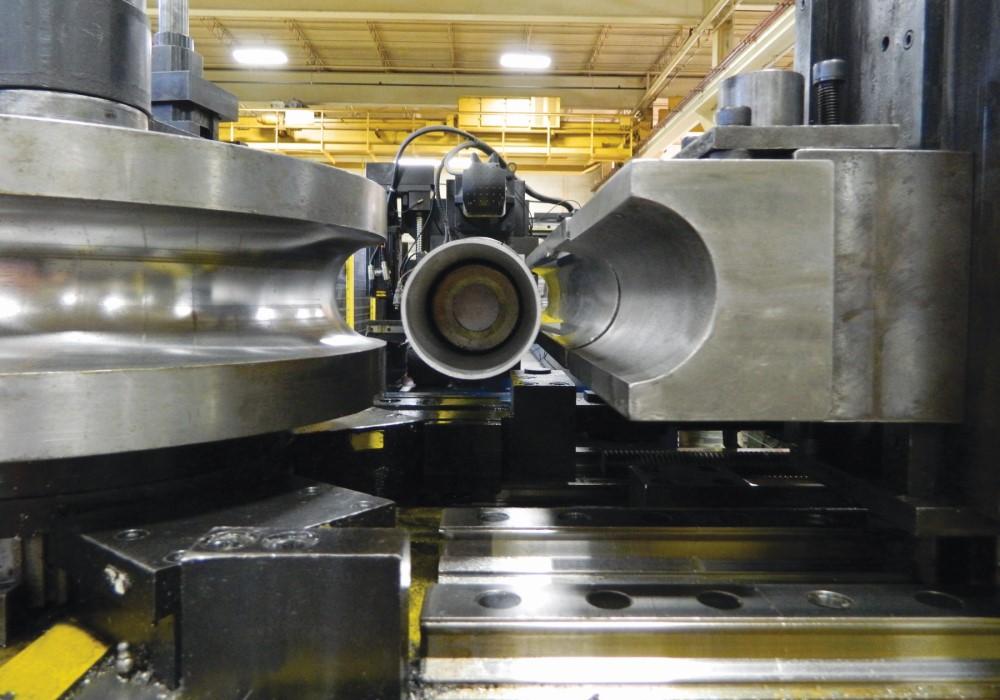

H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for Mandrel Pipe Bending
The global mandrel pipe bending market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, rising industrial demand, and evolving regulatory standards. Mandrel pipe bending—a precision technique used to bend tubes and pipes without deformation—is witnessing strong growth across key sectors such as automotive, aerospace, energy, and medical devices. This analysis explores the major trends shaping the mandrel pipe bending market in 2026.
1. Increased Adoption in Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing
With the global push toward electrification, automakers are ramping up production of electric vehicles (EVs). Mandrel bending is critical in manufacturing high-precision cooling lines, battery cooling systems, and hydraulic lines for EVs. By 2026, the EV segment is expected to be a primary growth driver for mandrel pipe bending equipment and services, especially in North America, Europe, and China.
2. Technological Advancements in CNC and Automation
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) mandrel benders are becoming more sophisticated, incorporating AI-driven predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and IoT connectivity. By 2026, smart manufacturing environments will increasingly integrate automated mandrel benders to enhance precision, reduce waste, and lower labor costs. The trend toward Industry 4.0 will accelerate the adoption of fully automated pipe bending cells.
3. Demand from Renewable Energy and Oil & Gas Sectors
Although renewable energy systems such as solar and wind use less piping than traditional infrastructure, the growth in offshore wind and hydrogen production facilities requires high-integrity tubular components. Simultaneously, the oil and gas industry, particularly in LNG (liquefied natural gas) and subsea projects, continues to rely on mandrel bent pipes for corrosion resistance and structural integrity. This dual demand will support steady market growth through 2026.
4. Expansion in the Aerospace and Defense Industries
The aerospace sector demands lightweight, high-strength bent tubing for fuel, hydraulics, and environmental control systems. Mandrel bending ensures precise geometry and smooth internal surfaces critical for safety and performance. With increased aircraft production and defense modernization programs worldwide, demand for aerospace-grade mandrel bending services is projected to rise significantly by 2026.
5. Regional Growth Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is expected to lead the mandrel pipe bending market by 2026, fueled by rapid industrialization in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will see growth driven by reshoring of manufacturing and stricter emissions standards, requiring advanced tubing systems. Regional supply chains are also adapting, with localized production hubs reducing lead times and logistics costs.
6. Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices. In response, mandrel benders are being optimized to work with advanced materials such as high-strength stainless steels, nickel alloys, and lightweight aluminum. Innovations in tooling and lubrication are reducing scrap rates and energy consumption, aligning with circular economy goals.
7. Competitive Landscape and Consolidation
The market is witnessing increased consolidation, with key players investing in R&D and strategic partnerships. Companies like Unison Limited, Beckwood Press, and AMOB Maschinenbau are expanding their product portfolios with modular and scalable mandrel bending solutions. Smaller firms are focusing on niche applications, such as medical tubing or custom automotive parts, to differentiate themselves.
Conclusion
By 2026, the mandrel pipe bending market will be characterized by high precision, automation, and sector-specific customization. Growth will be sustained by demand from advanced manufacturing, clean energy, and transportation industries. Companies that invest in digital integration, sustainable technologies, and global supply chain resilience will be best positioned to capture value in this evolving landscape.
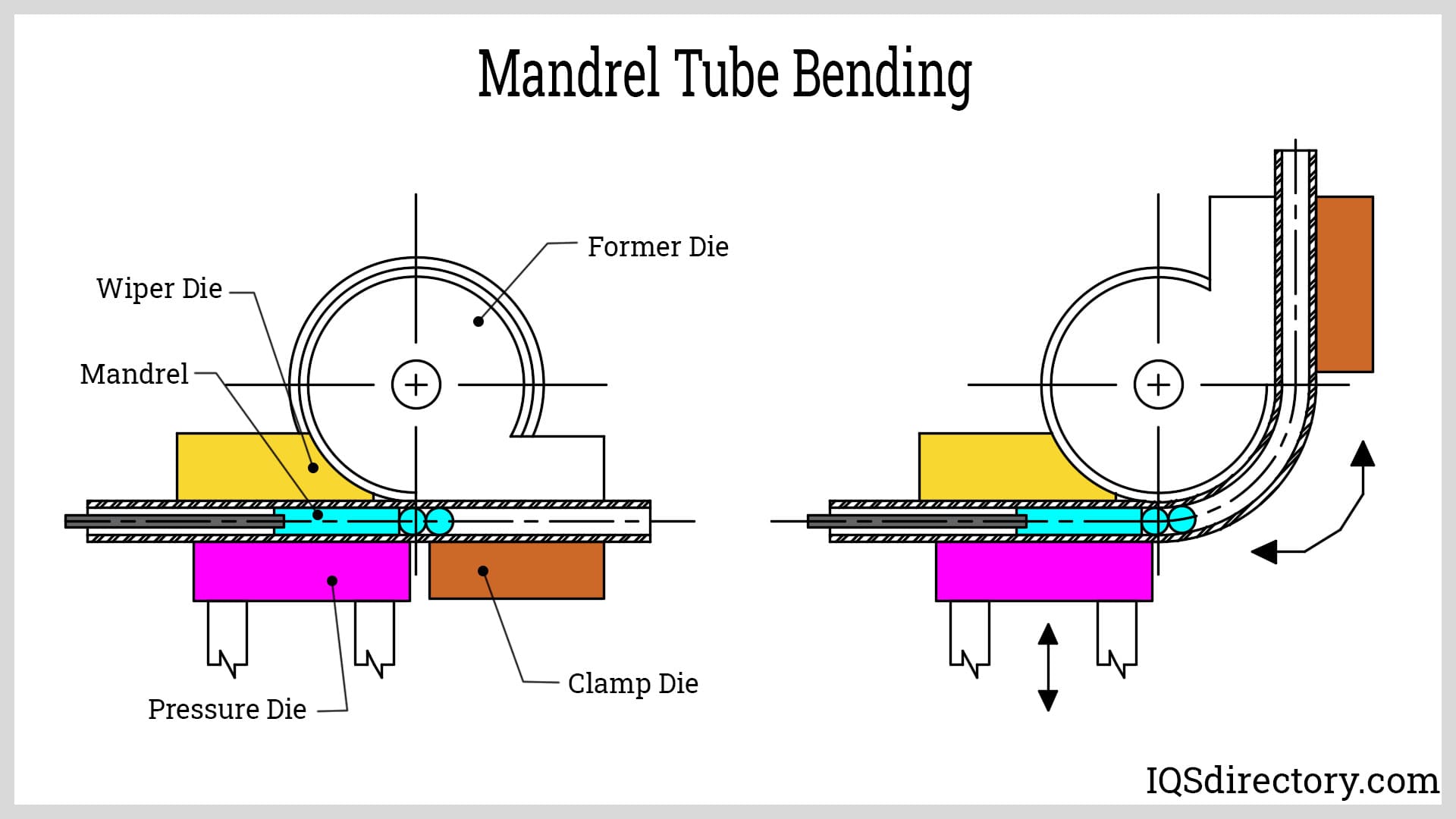
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Mandrel Pipe Bending (Quality, IP)
Sourcing mandrel pipe bending services can be complex, and overlooking key factors can lead to compromised quality, delivery delays, or intellectual property (IP) risks. Below are critical pitfalls to watch for in both quality assurance and IP protection.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Material Certification and Traceability
A frequent issue is the lack of proper material certification (e.g., mill test reports, MTRs) and traceability. Without documented proof of material grade, heat number, and compliance with specifications (e.g., ASTM, ASME), there’s a risk of using substandard or incorrect materials, leading to part failure in critical applications.
Poor Bend Consistency and Wall Thinning
Mandrel bending aims to minimize wall thinning and ovality, but low-quality suppliers may lack precise tooling or process controls. This results in inconsistent bend radii, excessive wall reduction (>15–20%), or wrinkling—especially problematic in high-pressure or structural systems.
Inaccurate Dimensional Tolerances
Tight tolerances are often required in fluid systems or assembly-critical components. Sourcing from vendors without robust in-process inspection (e.g., CMM, laser scanning) can lead to out-of-spec parts, causing fit-up issues and costly rework.
Improper Tooling and Mandrel Selection
Using incorrect or worn mandrels for specific tube alloys or diameters can degrade bend quality. Suppliers that do not customize mandrel setups per job may deliver parts with internal scarring, collapse, or poor surface finish.
Inadequate Process Validation and Testing
Some suppliers skip essential validation steps like first-article inspection (FAI), pressure testing, or destructive testing (e.g., cross-section analysis). This increases the risk of undetected defects in production runs.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Lack of Confidentiality Agreements (NDAs)
Engaging a bending supplier without a signed NDA exposes sensitive design data—such as proprietary tube layouts, bend sequences, or assembly integration—to unauthorized use or disclosure.
Unprotected Digital Models and Drawings
Sharing CAD files (e.g., STEP, IGES) or bend programs without watermarks, access controls, or encryption risks IP theft or reverse engineering, especially when sourcing overseas.
Supplier Claims on Custom Tooling or Process IP
Some vendors may assert ownership over custom-designed mandrels, bend dies, or developed bending programs. Without clear contractual terms, buyers can lose control over tooling and face future supply chain dependencies.
Inadequate IP Clauses in Contracts
General purchase orders often lack explicit IP ownership clauses. Without stating that all design data, tooling, and process improvements belong to the buyer, legal disputes may arise if the supplier reuses or sells similar solutions.
Risk of Unauthorized Subcontracting
Suppliers may subcontract work to third parties without buyer approval, increasing the risk of IP exposure. Contracts should require disclosure and consent for any subcontracting activities.
By addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls during vendor selection and contracting, companies can ensure reliable, secure, and high-performance mandrel pipe bending outcomes.
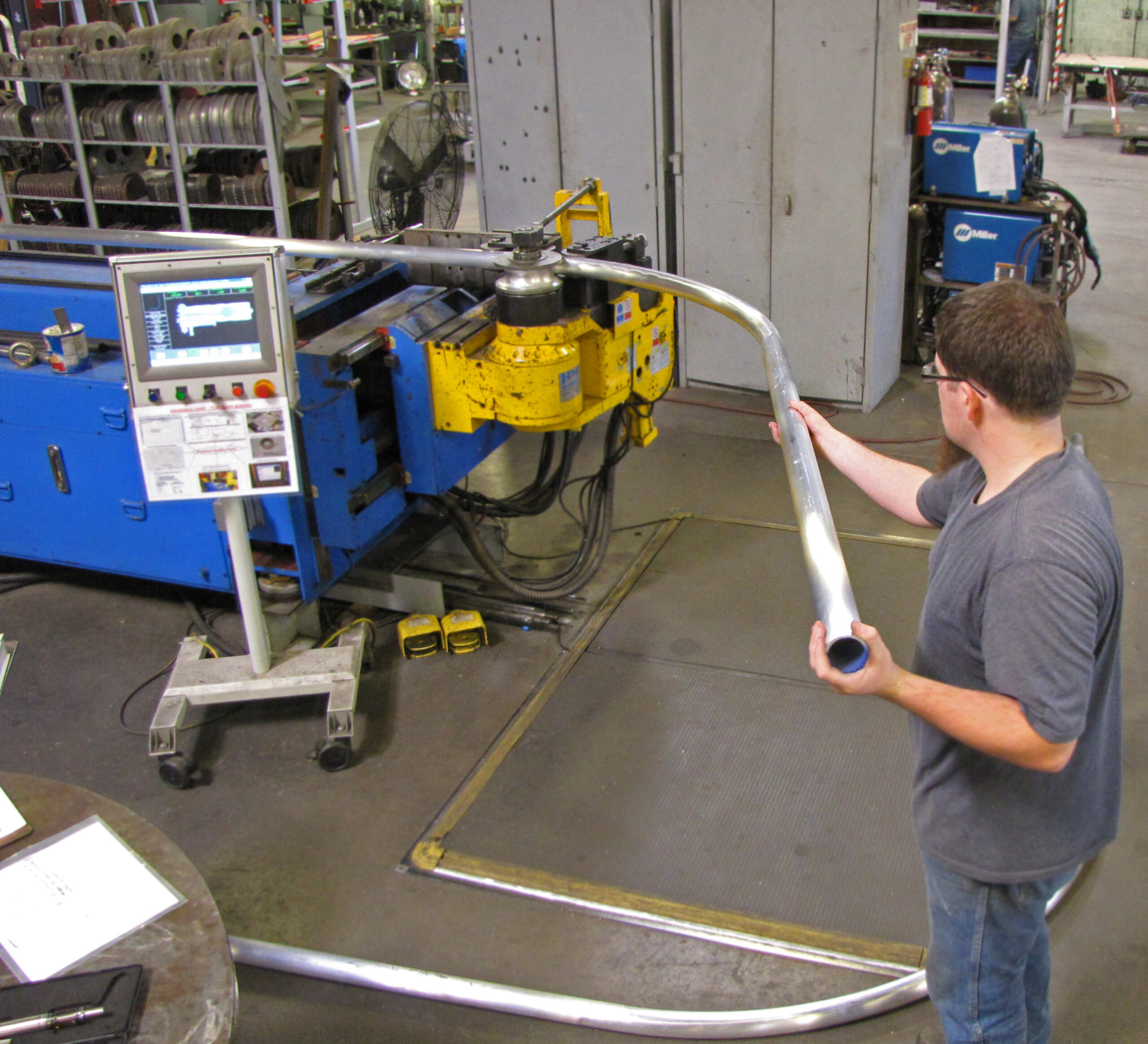

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Mandrel Pipe Bending
Mandrel pipe bending is a precision metal forming process used to bend tubes and pipes without deformation, particularly critical in industries such as aerospace, automotive, oil & gas, and medical equipment. Ensuring smooth logistics and regulatory compliance throughout the manufacturing and distribution chain is essential for quality, safety, and operational efficiency. This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements specific to mandrel pipe bending operations.
Material Sourcing and Inventory Management
Procure high-quality raw materials (e.g., stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, or specialty alloys) from certified suppliers to meet industry standards such as ASTM, ASME, or ISO. Maintain traceability through material test reports (MTRs) and ensure proper storage to prevent corrosion or damage. Implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices where feasible to reduce holding costs while maintaining buffer stock for high-demand or long-lead-time materials.
Equipment Calibration and Maintenance
Mandrel benders require regular calibration and preventive maintenance to ensure dimensional accuracy and repeatability. Follow manufacturer guidelines and maintain documented service logs. Calibration should align with ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 standards, particularly for automotive or aerospace clients. Use certified metrology tools (e.g., CMM, laser scanners) to verify bend angles, wall thickness, and ovality.
Quality Control and Inspection Protocols
Implement in-process and final inspections at defined control points. Use non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques such as visual inspection, ultrasonic testing (UT), or dye penetrant testing (DPT) when required. Document all inspection results and maintain quality records for audit readiness. For regulated industries, comply with inspection standards like ASME B31.3 (process piping) or API 5L (line pipe).
Regulatory and Industry Compliance
Adhere to relevant regulatory frameworks based on the application:
– ASME B31.3 for process piping systems
– API 5L/5CT for oil and gas tubular products
– ISO 15614 for welding procedure qualifications (if welding is involved post-bending)
– NADCAP accreditation for aerospace components
– REACH and RoHS for material chemical compliance in the EU
Ensure all personnel are trained and certified per industry-specific requirements.
Packaging, Handling, and Shipping
Protect finished bent pipes during handling and transit using custom cradles, end caps, and moisture-resistant wrapping. Clearly label packages with part numbers, heat numbers, and handling instructions. Use freight carriers experienced in transporting precision metal components. For international shipments, comply with export regulations (e.g., ITAR for defense-related parts) and provide accurate documentation (e.g., commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin).
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain full traceability from raw material to finished product. Required documentation includes:
– Material Test Reports (MTRs)
– Heat/lot traceability records
– Bend process sheets
– Inspection and test reports
– Certificates of Conformance (CoC)
Digital tracking systems (e.g., ERP or MES) enhance accuracy and audit readiness.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Compliance
Ensure operations comply with OSHA, EPA, and local EHS regulations. Use proper ventilation when handling metal dust or coolants. Train staff in safe machine operation, lockout/tagout (LOTO), and emergency procedures. Recycle metal scrap and dispose of hazardous waste (e.g., cutting fluids) according to environmental regulations.
Supplier and Subcontractor Oversight
If outsourcing any portion of the bending or finishing process, verify that subcontractors meet your quality and compliance standards. Conduct audits and require certifications (e.g., ISO 9001). Include compliance clauses in contracts and monitor performance regularly.
By aligning logistics and compliance practices with industry standards and customer requirements, mandrel pipe bending operations can ensure consistent product quality, reduce risk, and maintain regulatory adherence across global markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing Mandrel Pipe Bending
Sourcing mandrel pipe bending services or equipment requires careful evaluation of technical capabilities, material compatibility, precision requirements, and supplier reliability. Mandrel bending is essential for achieving high-quality, deformation-free bends in thin-walled or small-radius tubes, particularly in industries such as automotive, aerospace, hydraulics, and HVAC. When sourcing, it is critical to select a supplier with proven expertise in mandrel bending techniques, access to advanced CNC bending machinery, and the ability to handle specific materials and tight tolerances.
Additionally, considerations such as lead times, cost-efficiency, quality control processes, and post-bending services (e.g., cleaning, testing, packaging) play a significant role in ensuring seamless integration into the manufacturing supply chain. Partnering with a reputable supplier who offers technical support and adheres to industry standards ultimately enhances product performance, reduces waste, and improves overall production efficiency. In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach focused on quality, precision, and long-term collaboration is vital to maximizing the benefits of mandrel pipe bending in high-performance applications.