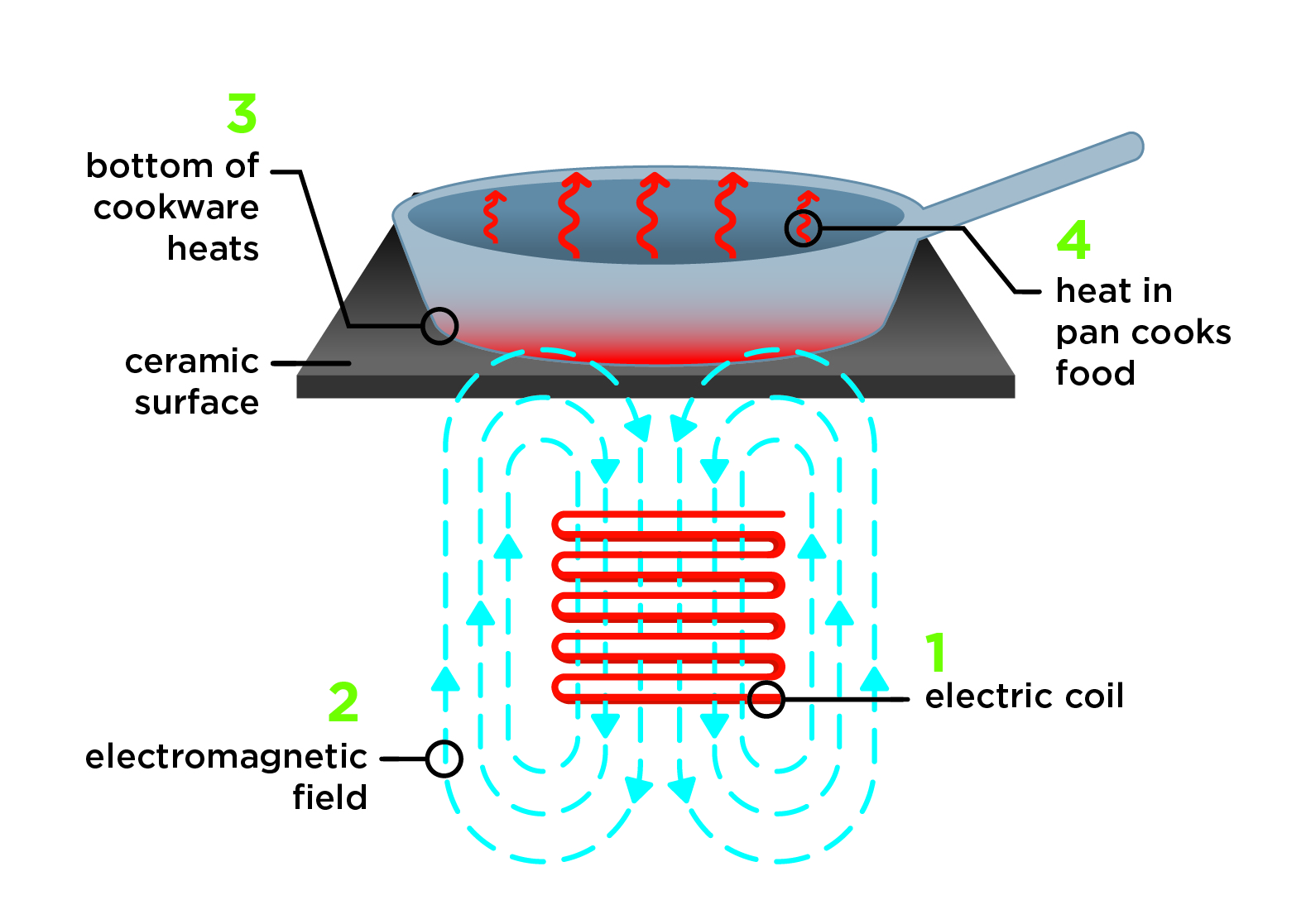
The global induction cooking market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising consumer demand for energy-efficient, safe, and high-performance kitchen appliances. According to Grand View Research, the global induction cooktop market was valued at USD 10.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing urbanization, advancements in smart home technologies, and supportive government regulations promoting energy efficiency across residential and commercial sectors. As adoption accelerates—particularly in regions like Asia-Pacific and Europe—manufacturers are investing heavily in innovation, durability, and design to capture market share. In this competitive landscape, a select group of companies have emerged as leaders in magnetic induction oven manufacturing, setting industry benchmarks for performance, safety, and technological integration.
Top 10 Magnetic Induction Oven Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Induction Technology
Domain Est. 1997
Website: egoproducts.com
Key Highlights: EGO Appliance Heating Assemblies with induction technology support this by providing a convenient and easy cooking experience, while also being fast, energy- ……
#2 About Magnetic Induction
Domain Est. 1995
Website: chantal.com
Key Highlights: Magnetic Induction uses electricity and magnetism to cause your metal cookware to heat from within instead of applying heat to the bottom of the pots….
#3 Induction cooking
Domain Est. 1999
Website: infineon.com
Key Highlights: Semiconductor solutions for energy efficient, high power, and feature-rich induction cooking applications with precise and safe heating control….
#4 Innovative Induction Heating & Melting Solutions
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ajaxtocco.com
Key Highlights: Contact Ajax TOCCO Magnethermic to receive innovative induction heating and melting services, reliable equipment, parts, engineered solutions, ……
#5 Wolf Induction Ranges
Domain Est. 2002
Website: subzero-wolf.com
Key Highlights: Wolf Induction Ranges, convection ovens and cooktops offer efficient, lightning-fast temperature cooktop response and consistent convection oven heat….
#6 Product
Domain Est. 2003
Website: impulselabs.com
Key Highlights: With up to 10,000 watts per burner, the Impulse Stove delivers 5× the power of gas and 3× more than any other induction cooktop on the market….
#7 High-Performance Induction Cooktops for Modern Kitchens
Domain Est. 2008
Website: bosch-home.com
Key Highlights: Elevate your kitchen with Bosch induction cooktops. Enjoy precision and style with our advanced electric induction stovetops today!…
#8 Dipo Induction
Domain Est. 2019
Website: dipoinduction.com
Key Highlights: Built for Professionals. Dipo’s wide range of induction appliances is designed to endure the everyday demands of high-volume professional kitchens….
#9 Induction Cooktops
Website: summitappliance.com
Key Highlights: Enjoy faster, safer, and more precise heating with Summit’s selection of induction cooktops, available for 115v or 230v connections….
#10 NuWave PIC Collection
Domain Est. 2011
Expert Sourcing Insights for Magnetic Induction Oven

H2: Key Market Trends Shaping the Magnetic Induction Oven Industry in 2026
By 2026, the magnetic induction oven market is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and broader macroeconomic and regulatory shifts. Here are the dominant trends expected to define the landscape:
1. Accelerated Adoption Driven by Energy Efficiency & Sustainability Mandates:
H2: Global push towards carbon neutrality and stricter energy regulations will be the primary catalyst. Governments (EU, US, parts of Asia) are increasingly banning or restricting gas appliances in new constructions and major retrofits. Induction’s superior energy efficiency (up to 20-30% less energy use than gas or electric coils) aligns perfectly with these goals. Consumers, facing rising energy costs, will prioritize induction for long-term savings, boosting market penetration significantly.
2. Smart Integration and IoT Dominance:
H2: Induction ovens will become central hubs in the connected kitchen. Seamless integration with smart home ecosystems (via Wi-Fi/Bluetooth) will be standard, enabling remote control, recipe-guided cooking (via apps), automatic pan detection, and energy usage monitoring. AI-powered features (e.g., automatic temperature adjustment, boil-over prevention, personalized cooking profiles) will move from premium to mid-tier models, enhancing user experience and safety.
3. Design Innovation: Seamless, Minimalist, and Flexible:
H2: Aesthetic integration will be paramount. Expect a surge in ultra-slim, frameless designs (especially for built-in models) and continuous glass surfaces that blend seamlessly with countertops. Zoneless/Free-Positioning Cooktops (allowing pots to be placed anywhere on the surface) will gain traction, offering unparalleled flexibility. Materials will shift towards more durable, scratch-resistant, and easy-to-clean ceramic glass with sophisticated finishes (e.g., matte black, color options).
4. Performance & Safety Enhancements:
H2: Focus will intensify on faster, more precise control (sub-second response times, finer temperature gradients) and extended power ranges (including ultra-low simmer for delicate tasks). Advanced safety features will become ubiquitous: automatic shut-off (pan removal, boil-dry), child locks, residual heat indicators, and improved electromagnetic field (EMF) shielding to address consumer concerns. Integration with home monitoring systems for leak/overheating detection will increase.
5. Market Expansion into Emerging Economies & Commercial Sectors:
H2: While mature markets (North America, Western Europe) see high adoption, significant growth will emerge in Asia-Pacific (India, Southeast Asia) and Latin America. Falling component costs, urbanization, and rising middle-class awareness of benefits will drive this. Simultaneously, commercial kitchens will rapidly adopt induction for its speed, precise control, reduced ambient heat (improving working conditions), and easier compliance with ventilation codes, accelerating beyond just high-end restaurants.
6. Price Compression and Accessibility:
H2: Economies of scale, increased competition (including strong Chinese OEMs), and technological maturity will drive downward pressure on prices. This will make induction technology accessible to a much broader consumer base, particularly in the mid-range segment, moving beyond the current “premium” perception in many regions.
7. Focus on Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) and Health:
H2: As adoption grows, regulatory scrutiny and consumer awareness regarding EMC and low-frequency EMFs will intensify. Manufacturers will invest heavily in transparent communication, rigorous testing standards, and advanced shielding technologies to ensure compliance and build consumer trust, making this a key differentiator.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the magnetic induction oven market will be characterized by ubiquitous smart features, seamless design, deep integration into sustainability initiatives, and expanding accessibility. Success will hinge on manufacturers’ ability to innovate in performance, safety, and user experience while navigating cost pressures and regulatory landscapes, ultimately positioning induction as the dominant standard for both residential and commercial cooking.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Magnetic Induction Ovens (Quality & IP)
Sourcing Magnetic Induction Ovens (MIOs) can offer significant energy and performance benefits, but it comes with critical risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to operational failures, safety hazards, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
Many low-cost suppliers use substandard materials and components to cut costs, resulting in unreliable ovens. Common issues include weak structural frames, low-grade electrical insulation, and inferior cooling systems. These compromises often lead to premature failures, inconsistent heating performance, and increased maintenance costs. Always verify the quality of core components like the induction coil, power electronics (IGBTs, capacitors), and thermal management systems through third-party testing or factory audits.
Inadequate Safety and Compliance Certifications
Reputable suppliers provide comprehensive safety certifications (e.g., CE, UL, CCC) and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) compliance documentation. However, some manufacturers supply falsified or incomplete certifications. Sourcing without proper validation exposes buyers to regulatory non-compliance, potential equipment seizure, and safety risks such as electric shock or fire hazards. Insist on authentic, up-to-date certification reports from accredited testing bodies.
Lack of Intellectual Property Verification
A significant risk in sourcing MIOs—especially from regions with lax IP enforcement—is inadvertently acquiring products that infringe on patented technologies. Many induction heating methods, control algorithms, and circuit designs are protected by IP rights. Using or reselling such products can result in costly litigation, import bans, and brand damage. Conduct thorough due diligence by requesting proof of IP ownership or licensing agreements from the supplier and consider independent IP clearance searches.
Misrepresentation of Technical Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate performance metrics such as power output, energy efficiency, or temperature control accuracy. For instance, an oven advertised as 90% efficient may only achieve that under ideal lab conditions. Always request real-world test data, conduct performance validation upon delivery, and include measurable specifications in contractual agreements with penalties for non-compliance.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality ovens require maintenance and spare parts over time. Some suppliers disappear after delivery or fail to maintain inventory of critical components. Ensure the supplier offers a clear warranty, technical support, and a documented supply chain for spare parts. Consider service level agreements (SLAs) to safeguard long-term operational continuity.
Hidden IP in Firmware and Software
Beyond hardware, the software controlling the induction process (e.g., PID algorithms, user interface, fault diagnostics) may incorporate proprietary or open-source code without proper licensing. Unauthorized use of such software can lead to copyright infringement claims. Require full disclosure of software origins and obtain written assurances of legal compliance from the supplier.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, businesses can mitigate risks and ensure reliable, legally sound procurement of Magnetic Induction Ovens.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Magnetic Induction Oven
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
Magnetic induction ovens fall under the category of household electrical appliances and must comply with international and regional safety, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), energy efficiency, and environmental standards. Proper classification is essential for customs clearance and market access. The product is typically classified under HS Code 8516.60 (Electro-thermal appliances of a kind used for household purposes), though local variations may apply. Manufacturers and importers must ensure adherence to regulations such as IEC 60335-1 (General safety for household appliances) and IEC 60335-2-9 (Particular requirements for grills, toasters, and similar portable cooking appliances), which cover induction cooking surfaces.
Safety and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Compliance
Induction ovens generate strong magnetic fields and must comply with strict EMC standards to avoid interference with other electronic devices. Key standards include:
– IEC/EN 61000-6-3: Emission standards for residential environments
– IEC/EN 61000-6-1: Immunity standards for residential environments
Additionally, regional safety certifications are required:
– CE Marking (Europe): Mandatory under the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and EMC Directive
– UKCA Marking (UK): Required for sale in Great Britain
– UL/cUL Certification (North America): Required under UL 1026 or UL 858 standards
– PSE Mark (Japan): Required under the Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law
Testing must be conducted by accredited laboratories, and technical documentation must be maintained for market surveillance.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Regulations
Energy efficiency regulations help reduce environmental impact and are enforced in key markets:
– EU Ecodesign Directive (Regulation 2015/1188): Sets minimum energy performance standards (MEPS) for household ovens and hobs, including induction cooktops
– ENERGY STAR (USA/Canada): Voluntary program with efficiency criteria for qualifying induction ranges
– China Energy Label (CEL): Mandatory labeling requirement for energy-consuming appliances
Additionally, compliance with RoHS (EU Directive 2011/65/EU) and REACH (EC 1907/2006) is required to restrict hazardous substances in electrical equipment. Packaging must align with local waste directives (e.g., EU Packaging Waste Directive).
Import, Export, and Customs Documentation
Ensure accurate and complete documentation for international shipments:
– Commercial Invoice (with HS code, value, and product description)
– Packing List (detailing weight, dimensions, and packaging type)
– Certificates of Conformity (CE, UL, etc.)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Import Licenses (if required by destination country)
Induction ovens are sensitive electronic equipment; proper packaging with anti-static and shock-absorbent materials is essential to prevent damage during transit. Declare all components (e.g., power cords, accessories) clearly to avoid customs delays.
Transportation and Handling Requirements
Due to sensitive electronic components and glass-ceramic cooktop surfaces, magnetic induction ovens require careful handling:
– Use original packaging or equivalent protective materials (foam, corner guards)
– Clearly label packages as “Fragile” and “This Side Up”
– Avoid stacking heavy items on top
– Maintain stable temperature and dry conditions during transit to prevent condensation
Comply with IATA/IMDG regulations if shipping via air or sea, especially concerning lithium batteries in control panels (if applicable).
Market-Specific Compliance and Labeling
Different regions impose unique labeling and compliance requirements:
– EU: CE marking, energy label (EU 2017/1369), WEEE symbol
– USA: FTC labeling for energy use, FCC ID (if equipped with wireless features), UL mark
– Australia/NZ: RCM mark, MEPS compliance per AS/NZS 60335.2.6
– India: BIS certification (IS 302-1 & IS 13952), mandatory labeling
User manuals must be provided in the local language and include safety instructions, technical specifications, and disposal information.
Post-Market Surveillance and Recalls
Manufacturers and importers must establish systems for post-market monitoring:
– Register products with national market surveillance authorities (e.g., RAPEX in the EU)
– Maintain a traceability system using serial numbers or batch codes
– Report non-compliances and initiate recalls if safety issues arise
– Provide customer support and repair services in accordance with warranty terms
Retention of technical files and test reports for at least 10 years is recommended to support regulatory audits.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Magnetic Induction Oven:
Sourcing a magnetic induction oven presents a strategic opportunity to enhance energy efficiency, improve cooking performance, and support sustainable kitchen operations. Compared to traditional gas or electric ovens, induction technology offers faster heating, precise temperature control, reduced heat loss, and improved safety due to its cool-to-touch surface. When sourcing, it is essential to consider factors such as power requirements, compatibility with existing kitchen infrastructure, brand reliability, warranty, and total cost of ownership.
Additionally, evaluating suppliers based on product certifications, energy efficiency ratings, after-sales service, and user reviews ensures long-term satisfaction and operational continuity. As the demand for eco-friendly and high-performance kitchen appliances grows, investing in a magnetic induction oven aligns with modern culinary standards and environmental goals. Ultimately, careful sourcing leads to a reliable, future-ready solution that benefits both commercial and institutional kitchens.