The global demand for innovative textile solutions has propelled the magnetic cloth material market into a phase of steady expansion, driven by increasing applications in smart wearables, industrial automation, and medical devices. According to Grand View Research, the global smart textiles market—under which magnetic cloth materials are a rapidly growing niche—was valued at USD 3.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.4% from 2024 to 2030. This surge is supported by advancements in flexible magnetic composites and rising adoption in aerospace, defense, and healthcare sectors. As industries prioritize functionality and adaptability in fabric solutions, magnetic cloth materials have emerged as a critical component. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers are leading the charge in R&D, scalability, and material innovation. Based on production capacity, technological integration, and market reach, here are the top 7 magnetic cloth material manufacturers shaping the future of functional textiles.
Top 7 Magnetic Cloth Material Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Magnetic health care fabric
Domain Est. 2017
Website: conductive-fabric.com
Key Highlights: Buy good quality Magnetic health care fabric from Magnetic health care fabric manufacturer, We provide low priced Magnetic health care fabric from China….
#2 China Magnetic Nonwoven Manufacturer and Supplier, Factory
Domain Est. 2022
Website: ydlnonwovens.com
Key Highlights: Magnetic Nonwoven is a unique material that combines the strength and durability of traditional nonwoven fabric with the added benefit of magnetic properties….
#3 Magnetic Fabric
Domain Est. 1997
Website: agico.cz
Key Highlights: Magnetic fabric is the assessment of rock fabric studied by the means of anisotropic behavior of magnetic properties and applicable to many fields of research….
#4 Joint comfort organic cotton range
Domain Est. 2004
Website: aurismagnetic.com
Key Highlights: Explore Auris’ 100% organic cotton textiles, designed to provide soft, eco-friendly support that helps promote joint comfort….
#5 Cyber
Domain Est. 2005
Website: gwjcompany.com
Key Highlights: 10-day returnsThis next generation of “magnetic” wiping fabric removes contaminants from all pre-press surfaces without the need of glass or film cleaning liquids. Key ……
#6 Shop All Baby
Domain Est. 2014
Website: magneticme.com
Key Highlights: Magnetic Me: Shop baby clothing with magnetic fasteners. Find footies, onesies, and more for easy dressing. Shop now!…
#7 Premium Clothing Magnet
Website: badgematic.de
Key Highlights: In stockThese are our premium clothing magnets with even MORE power. Compared to our clothing magnets Classic they are equipped with two strong neodym magnets….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Magnetic Cloth Material
H2: Market Trends in Magnetic Cloth Material (2026 Outlook)
The global magnetic cloth material market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in smart textiles, sustainable manufacturing, and expanding applications across industries. Magnetic cloth—fabric embedded with magnetic particles or fibers—offers unique functionalities such as electromagnetic shielding, flexible connectivity, and shape retention, making it ideal for use in electronics, healthcare, automotive, and fashion sectors.
Key trends shaping the 2026 market landscape include:
-
Growth in Smart Wearables and E-Textiles:
The rising demand for wearable health monitors, smart garments, and interactive fashion is accelerating adoption of magnetic cloth materials. By 2026, integration with sensors and IoT devices is expected to enhance user experience, enabling real-time health tracking, gesture control, and adaptive insulation. -
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Production:
Consumers and regulators are increasingly prioritizing sustainable materials. Manufacturers are responding by developing bio-based binders and recyclable magnetic composites. By 2026, eco-conscious production methods are projected to dominate, aligning with circular economy principles. -
Expansion in Automotive and Aerospace Applications:
Magnetic cloth is gaining traction in vehicle interiors for cable management, EMI shielding, and modular design. In aerospace, its lightweight and flexible properties support advanced cabin systems. The push for electric and autonomous vehicles will further boost demand through 2026. -
Innovation in Manufacturing Techniques:
Advances in nanotechnology and 3D printing are enabling precise deposition of magnetic elements onto textile substrates. These innovations reduce production costs and improve performance, making magnetic cloth more accessible across mid-tier markets by 2026. -
Regional Market Growth:
Asia-Pacific is expected to lead market expansion, fueled by strong electronics manufacturing in China, South Korea, and India. North America and Europe will follow, driven by R&D investments in smart textiles and defense applications. -
Regulatory and Standardization Developments:
As the market grows, regulatory bodies are anticipated to introduce standards for electromagnetic compatibility and material safety. Harmonized testing protocols by 2026 will enhance product reliability and global trade.
In conclusion, the magnetic cloth material market in 2026 will be characterized by technological convergence, sustainability, and diversification of applications. Companies that invest in R&D, adopt green manufacturing, and align with emerging industry standards will be best positioned to capitalize on these evolving trends.
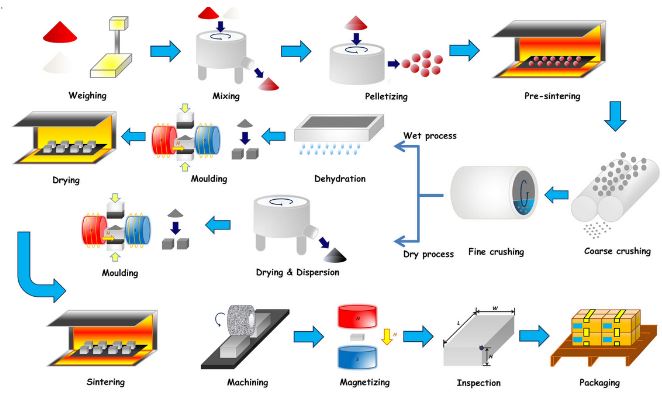
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Magnetic Cloth Material (Quality, IP)
Sourcing magnetic cloth material—often a composite of fabric and magnetized particles or layers—requires careful evaluation to avoid compromising product performance, durability, and intellectual property (IP) integrity. Below are key pitfalls to watch for in both quality and IP aspects.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Magnetic Strength
One of the most frequent quality issues is variability in magnetic field strength across batches. Poor process control during magnetization or inconsistent dispersion of magnetic particles in the base fabric can lead to weak or uneven adhesion, impacting functionality in applications like signage or closures.
Poor Durability and Delamination
Low-quality magnetic cloth may suffer from layer separation (delamination), especially when flexed or exposed to moisture. Inferior bonding between the fabric and magnetic layer reduces product lifespan and reliability, particularly in outdoor or high-use environments.
Substandard Fabric Base
The textile component may use low-grade fibers that fray, shrink, or degrade over time. This compromises both aesthetics and structural integrity, especially if the material is sewn, washed, or exposed to UV light.
Inadequate Environmental Resistance
Some suppliers fail to ensure resistance to temperature extremes, humidity, or UV exposure. Magnetic cloth used in automotive or outdoor applications may deteriorate quickly without proper protective coatings or material formulation.
Lack of Certification and Testing Data
Reputable suppliers provide test reports for magnetic flux, tensile strength, and environmental resistance. Sourcing without verified documentation increases the risk of receiving off-spec materials that fail in real-world use.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unlicensed Use of Proprietary Formulations
Many high-performance magnetic cloth materials are protected by patents covering composition, manufacturing processes, or unique layer structures. Sourcing from suppliers who replicate such materials without licensing exposes your business to IP infringement claims.
Reverse-Engineered or Knockoff Materials
Some suppliers offer “compatible” or “generic” versions of branded magnetic cloth. These may infringe on existing patents and lack performance consistency. Relying on such materials risks legal action and reputational damage.
Unclear Ownership of Custom Designs
When developing custom magnetic cloth (e.g., specific weave, magnetic pattern), failure to define IP ownership in contracts may result in the supplier claiming rights to the design. This can limit your ability to source elsewhere or protect innovations.
Insufficient Supplier Due Diligence
Failing to audit a supplier’s IP compliance—such as verifying freedom-to-operate or conducting patent landscape analysis—can lead to unintentional infringement. This is especially critical when entering regulated or competitive markets.
Export/Import Compliance Risks
Certain magnetic materials may be subject to trade restrictions or technology transfer controls. Using IP-protected materials without authorization can trigger customs issues or legal penalties, particularly across international borders.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, conduct thorough supplier vetting, request material certifications, perform independent testing, and consult legal experts to assess IP risks. Clear contracts specifying quality standards and IP rights are essential for secure, sustainable sourcing of magnetic cloth materials.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Magnetic Cloth Material
Overview
Magnetic cloth material is a composite textile embedded with magnetic particles or layers, commonly used in applications such as signage, educational tools, industrial closures, and smart textiles. Due to its unique composition—combining fabric with magnetic elements—special considerations are required during handling, transportation, and regulatory compliance.
Classification & Identification
- HS Code: Typically classified under HTS code 5911.90 (Textiles carrying a layer of other materials) or 8505.11 (Permanent magnets and articles thereof), depending on magnetic strength and primary function. Confirm with local customs authority.
- UN Number: Not usually classified as hazardous unless combined with other regulated materials. However, strong magnetic fields may require declaration under IATA/IMDG regulations.
- Product Description: Clearly label as “Flexible Magnetic Cloth” or “Magnetic Textile Composite” to avoid misclassification.
Packaging Requirements
- Use non-magnetic packaging materials (e.g., cardboard, plastic) to prevent unintended attraction during storage and shipping.
- Individually wrap or separate rolls/sheets with spacers to avoid adhesion and surface damage.
- Secure packaging to prevent shifting; use edge protectors for rolls.
- Label packages with “Handle with Care” and “Keep Away from Electronics” if magnetic strength is significant.
Transportation Regulations
- Air Transport (IATA): Magnetic materials with a field strength ≥ 0.00525 gauss at 15 feet (4.6 m) from the package must be classified as “Magnetized Material” (UN2807). Conduct a magnetic field test if in doubt.
- Sea Freight (IMDG): Similar to IATA; declare if magnetic field exceeds limits. Most flexible magnetic cloth does not require special handling unless in large quantities or high-strength versions.
- Ground Transport (ADR/RID): Generally exempt for low-strength materials, but verify based on total magnetic moment.
Storage Guidelines
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent degradation of adhesive or magnetic properties.
- Keep away from strong electromagnetic fields, sensitive electronic devices, and credit cards/pacemakers.
- Stack flat or hang vertically to prevent warping; avoid compression of multiple layers.
Regulatory Compliance
- REACH (EU): Ensure no restricted substances (e.g., certain phthalates, heavy metals) are present in the polymer or magnetic components.
- RoHS (EU): Applicable if used in electrical/electronic devices; verify lead, cadmium, and other substance limits.
- CPSIA (USA): Required if used in children’s products; ensure lead and phthalate content compliance.
- Proposition 65 (California): Check for presence of listed chemicals (e.g., nickel, cobalt) and provide warnings if applicable.
Import/Export Documentation
- Commercial Invoice with accurate description and HS code.
- Packing List detailing dimensions, weight, and quantity.
- Certificate of Origin (if required by trade agreement).
- Test Reports for magnetic field strength (if shipping air or in large volumes).
- SDS (Safety Data Sheet) – optional but recommended for industrial customers.
Handling & Safety
- No significant health hazards under normal conditions; avoid inhalation of dust if cutting or abrading.
- Use gloves and eye protection during processing.
- Keep away from medical devices (e.g., pacemakers) due to potential interference.
Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- Not classified as hazardous waste in most jurisdictions.
- Recycle fabric and magnetic components separately where facilities exist.
- Follow local e-waste or industrial textile disposal guidelines if combined with electronic elements.
Best Practices Summary
- Confirm classification based on final product use and magnetic strength.
- Test for magnetic field emissions if shipping by air.
- Maintain compliance documentation for all markets served.
- Clearly communicate handling and safety information to customers and logistics partners.
Consult with regulatory experts and freight forwarders when shipping internationally to ensure full compliance.
In conclusion, sourcing magnetic cloth material requires a strategic approach that balances performance, cost, availability, and supplier reliability. After evaluating various suppliers, material compositions, and application-specific requirements, it is evident that selecting the right magnetic cloth involves careful consideration of magnetic strength, flexibility, durability, and compatibility with end-use environments. Establishing relationships with reputable manufacturers or distributors offering customization options, quality certifications, and consistent production standards is crucial for long-term success. Additionally, conducting sample testing and validating material performance under real-world conditions ensures that the sourced magnetic cloth meets technical and operational demands. Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing strategy not only enhances product quality but also supports supply chain efficiency and cost-effectiveness.