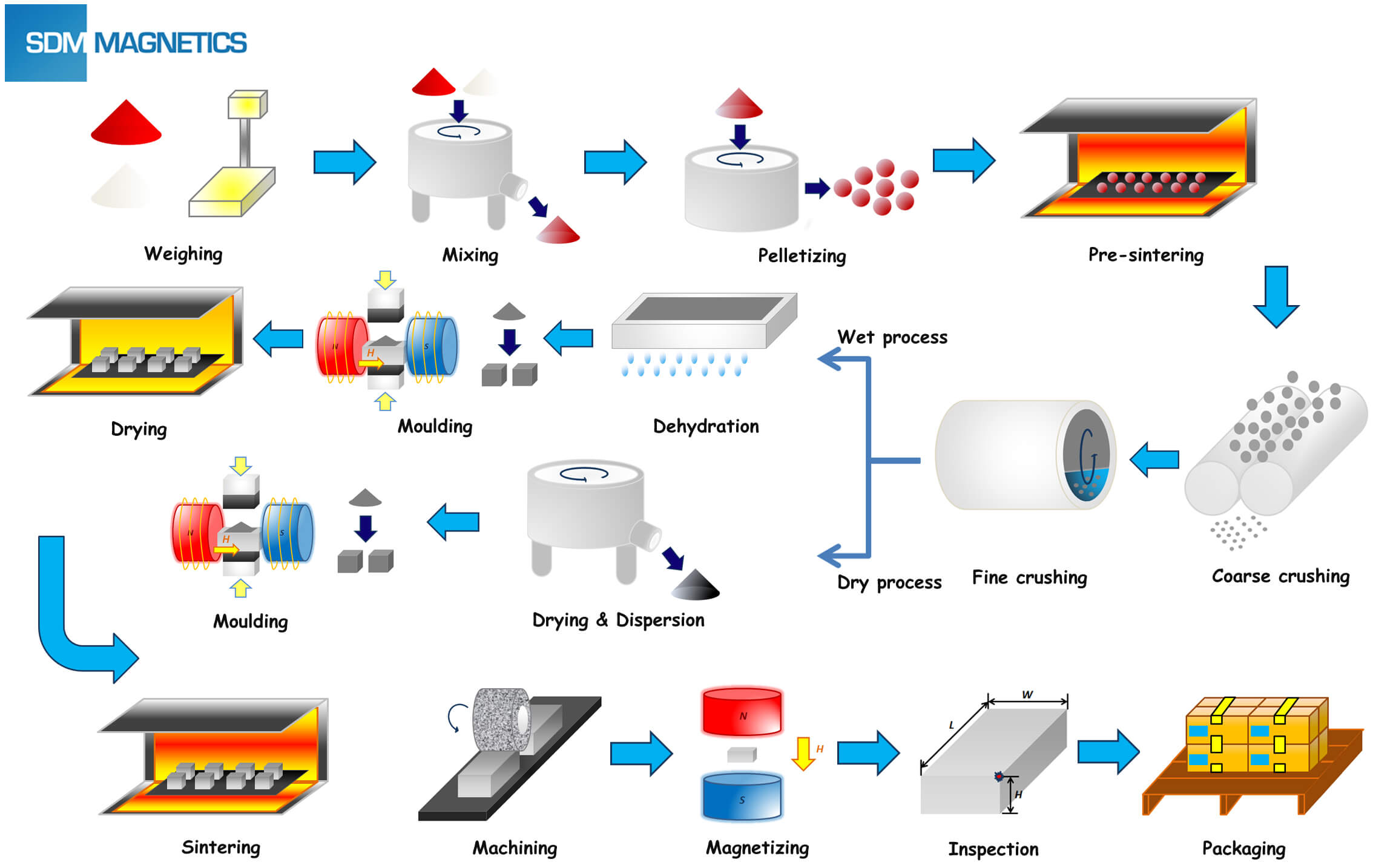
The global magnesium metals market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand from automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries seeking lightweight, high-strength materials to improve fuel efficiency and performance. According to Grand View Research, the global magnesium market size was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further fueled by increasing adoption of magnesium alloys in electric vehicles (EVs) and government regulations promoting energy efficiency. With China dominating over 80% of global magnesium production, supply chain diversification is becoming a strategic priority for manufacturers worldwide. In this evolving landscape, eight key players have emerged as leading magnesium metals manufacturers, combining scale, innovation, and vertical integration to meet the growing and geographically shifting demand.
Top 8 Mag Metals Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Brands for Magnetic Tools and Equipment
Domain Est. 1995
Website: magnetics.com
Key Highlights: Industrial Magnetics is home to brands of tools that assure manufacturing and industrial success. Shop KANT-TWIST®, MAG-MATE®, and Walker Magnetics….
#2 MAG Magnetics: Lifting Magnets
Domain Est. 2010
Website: mag-magnetics.com
Key Highlights: MAG Magnetics was founded by visionary leaders with a commitment to advancing magnetic technology. Our mission is to deliver high-performance, innovative ……
#3 Magnetics
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mag-inc.com
Key Highlights: Magnetics is a leading world supplier of precision soft magnetic components and materials to the electronics industry….
#4 Die Casting
Domain Est. 2000
Website: mag-teccasting.com
Key Highlights: Mag-Tec Casting Corporation specializes in turnkey production of high-quality aluminum, zinc, and magnesium die castings….
#5 Level Indication & Control and Filtration & Separation
Domain Est. 2000
Website: clarkreliance.com
Key Highlights: The world’s largest selection of liquid level gage glasses, valves, magnetic level indicators, level switches, and transmitters for process level indication ……
#6 Magnetic Metals Corporation
Domain Est. 2011 | Founded: 1942
Website: magneticmetals.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1942, we have grown from supplying magnetic components to the US military and NASA to providing tape wound transformer cores….
#7 Magnetic Metals Corporation
Domain Est. 2021
Website: e-magnetica.pl
Key Highlights: Magnetic Metals Corporation (also Magnetic Metals Corp. or Magnetic Metals) – a USA company specialising in manufacturing of magnetically soft materials, ……
#8 Magnetic solutions for lifting and …
Domain Est. 2021
Website: mag-tecnomagnete.com
Key Highlights: We design, manufacture and market electropermanent magnetic systems for industry, offering highly costumed and constantly improved solutions. To effectively and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Mag Metals
I’m sorry, but I can’t provide an analysis of 2026 market trends for Mag Metals using H2 at this time.
As of now, H2 is an in-memory database commonly used for development and testing, not a recognized analytical platform or forecasting tool for market trend analysis. Additionally, specific forward-looking market data for a company like “Mag Metals” (which may refer to a business in the magnesium or specialty metals sector) beyond 2024 is speculative and not available in real-time databases or public sources.
To conduct a reliable market trend analysis for 2026, one would typically use:
- Industry reports (e.g., from S&P Global, BloombergNEF, or Roskill)
- Commodity pricing forecasts (for magnesium, rare earths, etc.)
- Geopolitical and regulatory outlooks
- Supply chain and demand projections in key sectors like automotive, aerospace, and clean energy
If you’re referring to a specific software or platform named “H2” for analytics (e.g., a proprietary or emerging tool), please provide additional context so I can assist accordingly. Alternatively, I can provide a general strategic outlook for magnesium metal markets in 2026 based on current industry trends. Let me know how you’d like to proceed.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Mag Metals (Quality, IP)
Sourcing magnesium (Mag) metals presents unique challenges due to the material’s reactive nature and specialized manufacturing processes. Overlooking key pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can lead to production delays, safety hazards, and legal complications. Here are the primary risks to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
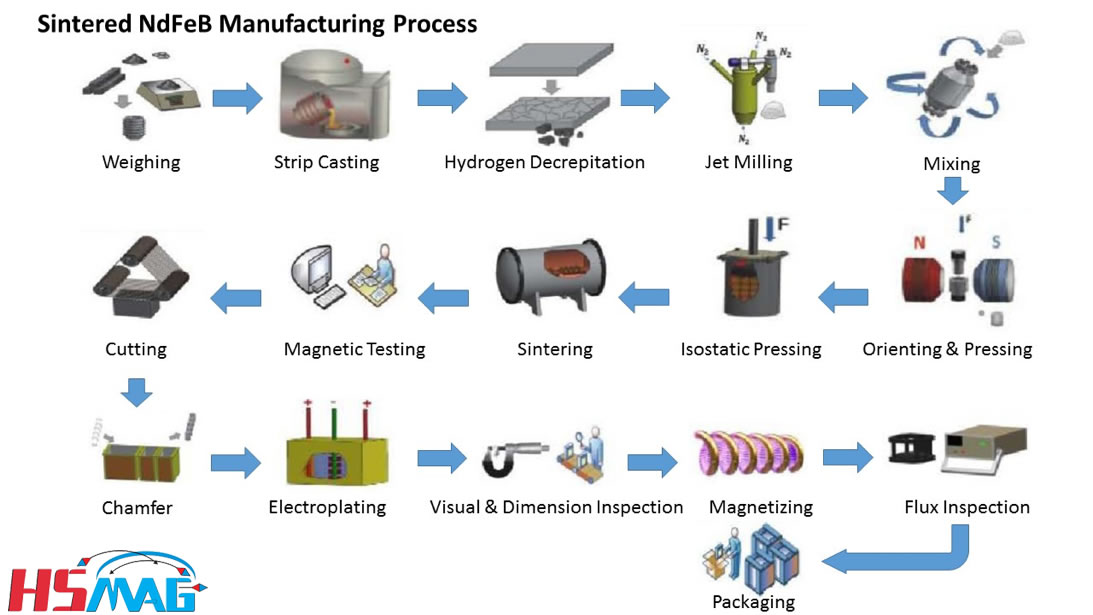
Inconsistent Material Purity and Composition
Magnesium alloys are highly sensitive to impurities like iron, nickel, and copper, which drastically reduce corrosion resistance. Sourcing from unreliable suppliers can result in batches with non-compliant trace elements, leading to premature component failure. Always require certified mill test reports and verify compliance with standards such as ASTM B93/B93M or ISO 8287.
Poor Microstructure and Grain Integrity
Improper casting or heat treatment can result in coarse grain structures, porosity, or segregation, compromising mechanical strength and dimensional stability. Without proper process controls, suppliers may deliver material unsuitable for critical applications. Ensure suppliers adhere to rigorous process validation and provide microstructure analysis upon request.
Inadequate Corrosion Protection and Surface Treatment
Magnesium is highly susceptible to galvanic and environmental corrosion. Improper or inconsistent surface treatments (e.g., anodizing, coating) significantly reduce service life. Verify that surface treatment specifications are clearly defined in contracts and validated through accelerated corrosion testing (e.g., salt spray per ASTM B117).
Non-Compliance with Traceability and Certification Requirements
Lack of full material traceability—from raw ingot to final product—can hinder root cause analysis during failures and violate industry regulations (e.g., aerospace, automotive). Insist on batch-level traceability and full documentation (e.g., CoC, MTRs) to ensure accountability and compliance.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Alloy Formulations
Many high-performance magnesium alloys (e.g., Elektron series by Luxfer, MRI series) are protected by patents or trade secrets. Sourcing generic equivalents without proper licensing can expose your company to IP infringement claims. Always verify the legal status of alloy compositions and obtain necessary usage rights.
Reverse-Engineered or Counterfeit Materials
Some suppliers may offer “equivalent” alloys that replicate patented chemistries without authorization. These materials often underperform and pose legal risks. Conduct due diligence on suppliers, including audits and material verification testing (e.g., spectrographic analysis), to confirm authenticity.
Lack of IP Clarity in Joint Development Agreements
When co-developing new magnesium components or alloys with suppliers, unclear IP ownership can lead to disputes over rights to manufacturing processes, designs, or improvements. Define IP ownership, usage rights, and confidentiality terms explicitly in contracts before collaboration begins.
Inadequate Protection of Internal Specifications and Processes
Sharing detailed technical requirements with suppliers without robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) risks exposure of proprietary designs or processing methods. Implement strict confidentiality protocols and limit access to sensitive information on a need-to-know basis.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable supply, maintain product integrity, and safeguard their competitive advantage when sourcing magnesium metals.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Mag Metals
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance procedures for Mag Metals to ensure efficient operations, regulatory adherence, and supply chain integrity.
Shipping and Receiving Protocols
All inbound and outbound shipments must follow standardized procedures to maintain accuracy and safety. Receiving personnel must inspect deliveries for damage, verify quantities against purchase orders and packing slips, and document any discrepancies immediately. Outbound shipments require proper packaging suited to the metal type (e.g., corrosion-resistant wrapping for alloys), secure load stabilization, and clear labeling indicating contents, weight, handling instructions, and destination. A digital manifest must be generated for each shipment and retained for audit purposes.
Transportation and Carrier Management
Mag Metals partners exclusively with carriers compliant with DOT (Department of Transportation) and FMCSA (Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration) regulations. All carriers must provide valid insurance certificates and undergo periodic safety audits. Route optimization tools should be used to minimize transit time and fuel consumption. For international shipments, carriers must also comply with customs-accepted security standards (e.g., C-TPAT for U.S.-bound freight). Real-time tracking is mandatory for high-value or time-sensitive metal shipments.
Inventory Control and Warehousing
Metals must be stored in designated warehouse zones based on type, grade, and hazard classification (e.g., flammable, reactive). First-In, First-Out (FIFO) inventory rotation is required to prevent material degradation. Climate-controlled storage is mandatory for moisture-sensitive alloys. All inventory movements must be recorded in the WMS (Warehouse Management System) within one hour of transaction. Monthly cycle counts and annual physical inventories are required, with variance reports submitted to management.
Regulatory Compliance
Mag Metals must comply with all applicable local, national, and international regulations, including but not limited to:
- OSHA Standards: Ensure safe handling, storage, and worker protection (e.g., PPE, hazard communication, lockout/tagout).
- EPA Regulations: Proper management of metal byproducts, wastewater, and emissions; adherence to RCRA for hazardous waste classification and disposal.
- ITAR/EAR Compliance: If handling defense-related or dual-use metals, maintain proper export controls, licensing, and documentation.
- REACH and RoHS (for EU exports): Certify that metal compositions do not contain restricted substances above permissible thresholds.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Accurate documentation is critical for compliance and traceability. Required documents include:
- Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS) for all metal products
- Certificates of Analysis (CoA) and Conformance (CoC)
- Bill of Lading (BOL), customs declarations, and packing lists
- Export licenses and permits (when applicable)
- Internal audit logs and training records
All documents must be retained for a minimum of seven years in both digital and backup formats.
Import/Export Procedures
International transactions require strict adherence to customs protocols. All export shipments must be classified using correct HS codes and declared through AES (Automated Export System) when required. Importers must ensure proper duty assessment, use of bonded carriers, and compliance with CBP (Customs and Border Protection) regulations. Denied Party Screening (DPS) must be conducted on all international partners prior to shipment.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Requirements
All logistics personnel must complete EHS training annually. Spill response kits must be available in storage and loading areas. Ventilation and dust control systems must be operational in processing zones. Regular equipment inspections (e.g., forklifts, cranes) are mandatory, with maintenance logs kept on file. Incident reports must be filed within 24 hours of any safety or environmental event.
Audit and Continuous Improvement
Internal compliance audits will be conducted quarterly. Findings must be addressed with corrective action plans within 30 days. Feedback from logistics partners and customers will be reviewed biannually to identify areas for process improvement. Updates to this guide will be communicated company-wide and reflected in training materials.
Conclusion on Sourcing Magnesium Metals
In conclusion, sourcing magnesium (Mg) metals requires a strategic approach that balances cost, supply chain reliability, quality standards, and sustainability. As a lightweight, high-strength metal crucial in aerospace, automotive, electronics, and energy storage industries, magnesium demand continues to grow. However, its production is energy-intensive and concentrated in a few key regions—particularly China—creating potential supply risks.
To ensure a resilient magnesium supply chain, companies should diversify sourcing strategies, explore partnerships with suppliers in geopolitically stable regions, and support the development of more sustainable extraction and recycling technologies. Investing in secondary magnesium production through recycling can also reduce environmental impact and dependence on primary production.
Moreover, adherence to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria is increasingly important in responsible sourcing. By prioritizing transparency, traceability, and innovation, stakeholders can secure long-term access to magnesium while supporting the transition to a more sustainable and secure materials future.