The global market for machines with magnets—encompassing applications in recycling, material handling, automotive, and industrial manufacturing—has experienced steady growth driven by rising demand for efficient separation technologies and automation. According to Grand View Research, the global magnetic separators market was valued at USD 4.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by stricter environmental regulations, increased industrialization, and the need for sustainable material recovery processes, particularly in the recycling and mining sectors. As industries prioritize precision and operational efficiency, the demand for high-performance magnetic machines continues to rise, positioning key manufacturers at the forefront of innovation and market expansion. This landscape has given rise to a competitive ecosystem of manufacturers specializing in advanced magnetic technologies—from overband and drum magnets to eddy current separators—catering to diverse industrial needs across North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific.
Top 8 Machines With Magnets Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Eclipse Magnetics
Domain Est. 2002
Website: eclipsemagnetics.com
Key Highlights: Leading manufacturer and supplier of magnets and magnetic equipment, including industrial filters, magnetic separators, metal detectors and magnetic ……
#2 Industrial Magnetics, Inc.
Domain Est. 1995
Website: magnetics.com
Key Highlights: Magnetic solutions for lifting, magnetic separation, material handling, and more. Industrial Magnetics specializes in custom magnetic equipment….
#3 Mozelt Magnet Systems
Domain Est. 2004
Website: mozelt.com
Key Highlights: Magnet systems made in Germany for the highest demands · Electromagnets for material handling · Magnet generators · Excavator magnets and industrial magnet systems….
#4 Electron Energy Corporation
Domain Est. 1998
Website: electronenergy.com
Key Highlights: Dependable magnetic solutions for critical applications from Electron Energy Corp. We work closely with our customers to create custom solutions for you….
#5 Recording at Machines with Magnets
Domain Est. 2003
Website: machineswithmagnets.com
Key Highlights: Studio A specializes in recording, mixing, mastering, post production for film and video, and voice-over and audiobook production….
#6 compact grinding machines for magnet applications
Domain Est. 2007
Website: fivesgroup.com
Key Highlights: High-precision, reliable and efficient grinding for all types of magnets. Compact machine with extensive experience in multiple industries worldwide….
#7 Magnetic solutions for lifting and …
Domain Est. 2021
Website: mag-tecnomagnete.com
Key Highlights: We design, manufacture and market electropermanent magnetic systems for industry, offering highly costumed and constantly improved solutions. To effectively and ……
#8 AML
Domain Est. 2022 | Founded: 1995
Website: mitusmagnets.com
Key Highlights: Advanced Magnet Lab (AML) was founded in 1995 to develop novel solutions to the world’s most complex challenges with superconductivity and magnetics….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Machines With Magnets

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Machines With Magnets
The global market for machines with magnets is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, rising demand for energy efficiency, and expansion in high-growth industries. Here are the key trends expected to shape the sector:
1. Accelerated Adoption in Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The EV revolution continues to be a primary growth driver for magnet-integrated machines. High-performance permanent magnet motors—especially those using rare-earth elements like neodymium—are critical for EV propulsion systems due to their superior power density and efficiency. As global EV production scales to meet emissions targets, demand for advanced magnetic machines is projected to rise sharply, particularly in Asia-Pacific and North America.
2. Growth in Renewable Energy Infrastructure
Wind turbines, especially direct-drive generators, rely heavily on permanent magnet synchronous generators (PMSGs). With increasing investments in offshore and onshore wind farms, the demand for reliable and efficient magnetic machines is expected to grow. The push for grid stability and energy transition policies will further boost installations through 2026.
3. Advancements in Miniaturization and Smart Manufacturing
Automation and Industry 4.0 are fueling demand for compact, precise magnetic actuators, sensors, and motors in robotics and smart machinery. Machines with integrated magnets are becoming smaller, more efficient, and capable of real-time feedback, enabling smarter production lines. This trend is particularly evident in semiconductor manufacturing and precision medical devices.
4. Material Innovation and Supply Chain Diversification
Concerns over the geopolitical concentration of rare-earth elements are prompting R&D into alternative magnet materials, such as ferrite hybrids, manganese-based magnets, and recycled rare-earth solutions. By 2026, increased investment in sustainable sourcing and magnet recycling is expected to ease supply chain vulnerabilities and reduce environmental impact.
5. Expansion in Consumer Electronics and Wearables
Magnetic components are essential in haptic feedback systems, speakers, vibration motors, and wireless charging. As consumer electronics evolve toward foldable devices, AR/VR headsets, and health-monitoring wearables, the need for compact, high-efficiency magnetic machines will continue to grow.
6. Regulatory and Environmental Pressures
Energy efficiency regulations, such as the IE4 and upcoming IE5 motor efficiency standards, are pushing industries to adopt magnet-based electric machines. These regulations, combined with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals, will favor high-efficiency permanent magnet motors over traditional induction types.
7. Regional Market Shifts
China remains a dominant player in both production and consumption of magnetic machines, but North America and Europe are increasing domestic manufacturing capacities to reduce dependency on imports. Government incentives for clean energy and domestic tech production will support regional growth through 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, the market for machines with magnets will be defined by innovation, sustainability, and integration across high-tech industries. Companies that invest in material science, energy efficiency, and supply chain resilience will be best positioned to capitalize on these emerging trends.
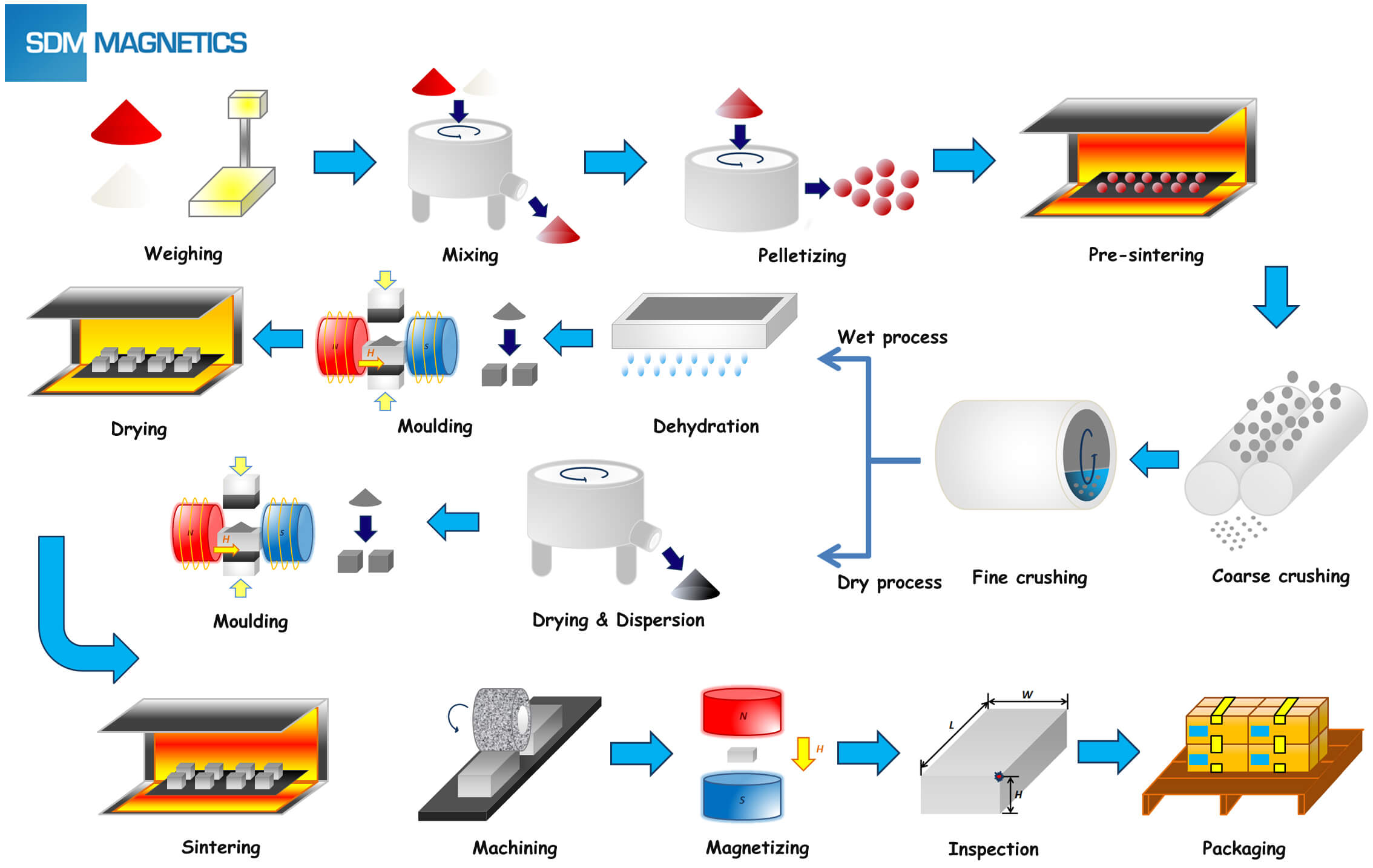
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Machines with Magnets (Quality, IP)
Sourcing machines that incorporate magnets—such as motors, generators, magnetic separators, MRI systems, or magnetic bearings—can present unique challenges. Overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations can lead to performance issues, legal risks, and supply chain disruptions. Below are common pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Magnet Quality and Material Specification
One of the most frequent issues is sourcing machines using substandard or incorrectly specified magnets. Suppliers may use lower-grade materials (e.g., N35 instead of N52 neodymium) to cut costs, resulting in reduced efficiency, lower torque, or premature demagnetization. Always verify magnet grade, temperature rating (e.g., N42SH vs. N42), and coating (e.g., Ni-Cu-Ni for corrosion resistance) to ensure they match your application’s demands.
Inadequate Thermal and Environmental Testing
Magnets degrade under high temperatures or harsh environments. Some suppliers fail to test full assemblies under real-world operating conditions. This can lead to irreversible magnetic losses or mechanical failure. Ensure suppliers provide evidence of thermal cycling, humidity, and vibration testing—especially for applications in automotive, industrial, or outdoor settings.
Counterfeit or Non-Compliant Magnets
The magnet market, particularly for rare-earth types, is prone to counterfeit materials. These may appear identical but lack the required magnetic properties or contain banned substances (e.g., excessive cobalt or non-REACH-compliant coatings). Request material certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH, ISO 9001) and conduct independent lab testing when sourcing high-volume or mission-critical components.
Lack of Traceability and Supply Chain Transparency
Magnets often originate from geopolitically sensitive regions (e.g., China for rare-earth elements). Without proper traceability, you risk supply chain disruptions or non-compliance with import regulations (e.g., UFLPA in the U.S.). Demand full supply chain transparency and documentation to ensure ethical sourcing and regulatory compliance.
Infringement of Intellectual Property (IP)
Many magnet-based machines involve patented technologies—especially in motor design (e.g., Halbach arrays, flux focusing), control algorithms, or integration methods. Sourcing from suppliers who replicate protected designs can expose your company to IP litigation. Conduct due diligence on supplier patents and require indemnification clauses in contracts.
Insufficient IP Protection in Contracts
Even when working with legitimate suppliers, failure to clearly define IP ownership in contracts can result in lost rights to custom designs or improvements. Ensure agreements specify who owns the IP for embedded technologies, software, and mechanical innovations—especially in co-developed machines.
Overlooking Magnet Safety and Handling Risks
Strong magnets pose safety hazards (pinching, interference with medical devices) and can damage nearby electronics. Machines must be designed and shipped with appropriate safety measures. Verify that suppliers comply with IEC 60335 or other relevant safety standards and provide proper handling instructions.
Inconsistent Manufacturing Tolerances
Magnetic performance is highly sensitive to dimensional accuracy and alignment. Poor manufacturing tolerances in rotor-stator gaps or magnet placement can drastically reduce efficiency. Audit supplier production processes and insist on statistical process control (SPC) data for critical dimensions.
By recognizing and addressing these pitfalls early, businesses can mitigate risks related to performance, compliance, and legal exposure when sourcing magnet-integrated machinery.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Machines With Magnets
Machines containing magnets—especially strong permanent magnets such as neodymium—require special handling, packaging, documentation, and regulatory compliance due to their potential to interfere with navigation systems, electronic devices, and medical equipment. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for shipping and handling magnet-equipped machinery globally.
Classification and Regulatory Framework
Magnet-containing machines are subject to international and national regulations based on their magnetic field strength. The primary standard is the International Air Transport Association (IATA) Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR), which classifies strong magnets as “Magnetized Material” under Class 9 (Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods), UN2803.
- IATA DGR Section 2.9: Defines magnetized materials as dangerous goods if the magnetic field strength exceeds 0.159 A/m (0.002 Gauss) measured at a distance of 2.1 meters (7 feet) from the package.
- IMDG Code: Governs maritime transport and aligns with IATA for magnet classification.
- 49 CFR (U.S. DOT): Regulates domestic transport in the United States, mirroring IATA and IMDG for air and sea shipments.
Testing and Measurement Requirements
Before shipping, machines with magnets must be tested to determine if they meet the threshold for dangerous goods classification.
- Conduct a magnetic field measurement using a properly calibrated gauss meter at 2.1 meters (7 feet) from the package’s surface.
- Testing should be performed with the machine in its final shipping configuration, including packaging.
- If the measured field exceeds the limit, the shipment must comply with Class 9 hazardous material requirements.
Packaging and Labeling
Proper packaging is critical to reduce magnetic field emissions and ensure safety.
- Use mu-metal shielding or ferromagnetic materials in packaging to contain or redirect magnetic fields.
- Secure internal components to prevent movement during transit that could alter magnetic exposure.
- Clearly label packages:
- “Magnetized Material” (Class 9 hazard label)
- UN2803 identification number
- Proper shipping name: “Magnetized Material”
- Orientation arrows if required
- For non-hazardous shipments (below threshold), include a “Contains Magnets” advisory label to alert handlers.
Documentation and Declarations
Accurate documentation is essential for customs clearance and carrier acceptance.
- For hazardous shipments:
- Complete a Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods
- Include emergency contact information
- Provide safety data sheet (SDS) if applicable
- For non-hazardous shipments:
- Include a test report or certificate confirming magnetic field levels are below the regulatory threshold
- Retain measurement records for audits or inspections
- Notify carriers in advance when shipping magnetized equipment, even if classified as non-dangerous.
Air, Sea, and Ground Transport Considerations
- Air Freight: Most restrictive; many airlines require pre-approval for Class 9 materials. Strong magnets may be prohibited on passenger aircraft.
- Sea Freight: Subject to IMDG Code; segregation from sensitive cargo (e.g., navigation equipment) is required.
- Ground Transport: Regulated by national agencies (e.g., FMCSA in the U.S.). Class 9 labeling and placarding may be required for large shipments.
Special Handling and Storage
- Store machines with magnets away from:
- Pacemakers, medical devices, and credit cards
- Sensitive electronics and navigation systems
- Ferrous materials that could become projectiles
- Train personnel in safe handling procedures, including use of non-magnetic tools and personal protective equipment (PPE).
Compliance with Regional Regulations
- EU: Follow ADR (road), RID (rail), and IMDG/IATA for international shipments. CE marking may be required for machinery under the Machinery Directive.
- USA: Comply with DOT, FAA, and Coast Guard regulations. Report quantities above threshold to PHMSA if required.
- China, Japan, Canada: Each has specific magnet transport rules—verify with local authorities or freight forwarders.
Exemptions and De Minimis Quantities
Some regulations allow exemptions for small or weak magnets integrated into equipment. However, entire machines are typically evaluated as a whole. Do not assume exemption without testing and documentation.
Best Practices Summary
- Test early: Measure magnetic field during design and packaging phases.
- Document thoroughly: Keep test records, declarations, and compliance certificates.
- Communicate clearly: Inform logistics partners, carriers, and end-users about magnetic content.
- Reassess regularly: Changes in design or packaging may affect classification.
Adhering to this guide ensures safe, compliant, and efficient global transport of machines with magnets while minimizing delays, fines, or safety risks.
In conclusion, sourcing machines that incorporate magnets requires careful consideration of several key factors, including the type and strength of magnets used, the intended application, machine compatibility, energy efficiency, durability, and compliance with safety and environmental standards. Advances in magnetic technology—such as rare-earth magnets (e.g., neodymium) and electromagnetic systems—have significantly enhanced the performance and reliability of machines across industries like manufacturing, medical, automotive, and renewable energy. When sourcing such equipment, it is essential to collaborate with reputable suppliers, verify technical specifications, and assess total cost of ownership, including maintenance and longevity. Proper due diligence ensures that the selected magnet-equipped machines deliver optimal efficiency, productivity, and return on investment.