The global demand for automated food processing equipment has surged in recent years, driven by rising urbanization, increasing labor costs, and a growing preference for convenience foods. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global food processing equipment market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% from 2024 to 2029, with significant expansion observed in the bakery and ready-to-eat segments. As staple foods like roti remain central to South Asian and diasporic diets, the need for efficient, high-volume roti-making machines has intensified. This growing demand has spurred innovation and competition among manufacturers, leading to advancements in automation, consistency, and throughput in roti production systems. With commercial kitchens, food service providers, and packaged food brands increasingly adopting mechanized solutions, the landscape of roti-making machinery is rapidly evolving. Based on market presence, technological capability, and customer reach, the following eight manufacturers stand out as leaders in the global roti machine industry.
Top 8 Machine To Make Roti Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
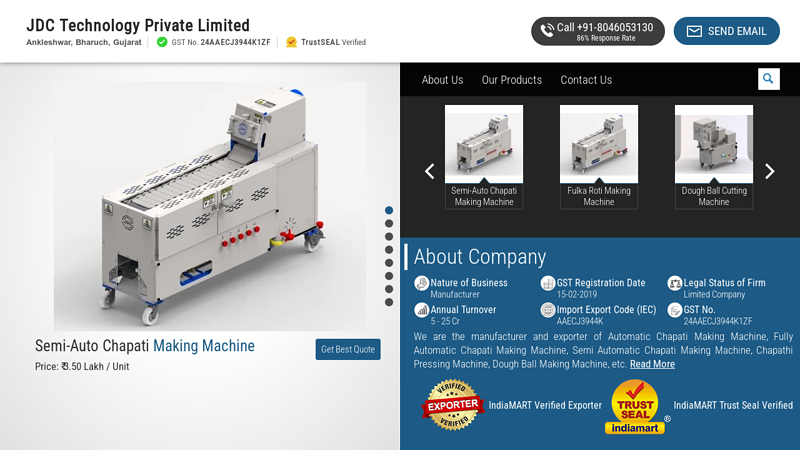
#1 JDC Technology
Domain Est. 2016
Website: jdctechnology.com
Key Highlights: Fully Automatic Roti Making Machine. Email. [email protected] · [email protected]. Phone. +91-9574066618 · +91-9574088842. Factory Address….
#2 JDC Technology Private Limited
Domain Est. 2017
Website: jdctechnology.in
Key Highlights: Compact Automatic Roti Making Machine · Rs 2,50,000 / Piece. Capacity: 500-600/hour; Usage/Application: Company Canteen, Hotel, Hostel, Temple, Hospital, ……
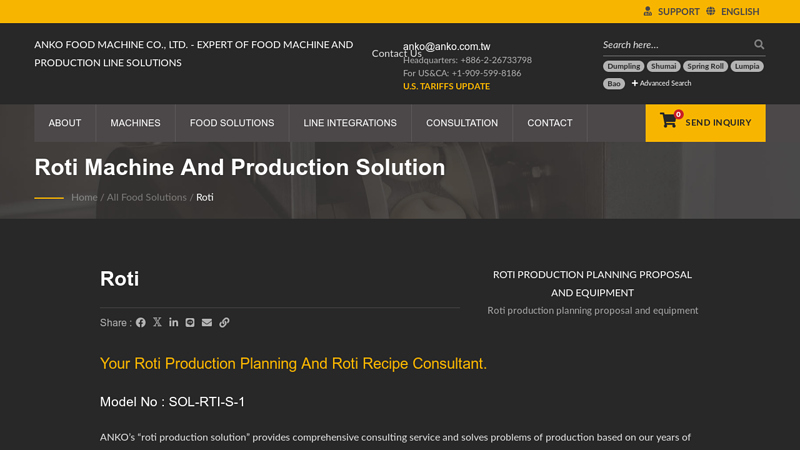
#3 Roti Machine and Production Solution
Domain Est. 1998
Website: anko.com.tw
Key Highlights: ANKO offers complete roti production solutions with automatic chapati making machines producing 3,600 pieces/hour. Get turnkey planning, recipe consulting, and ……
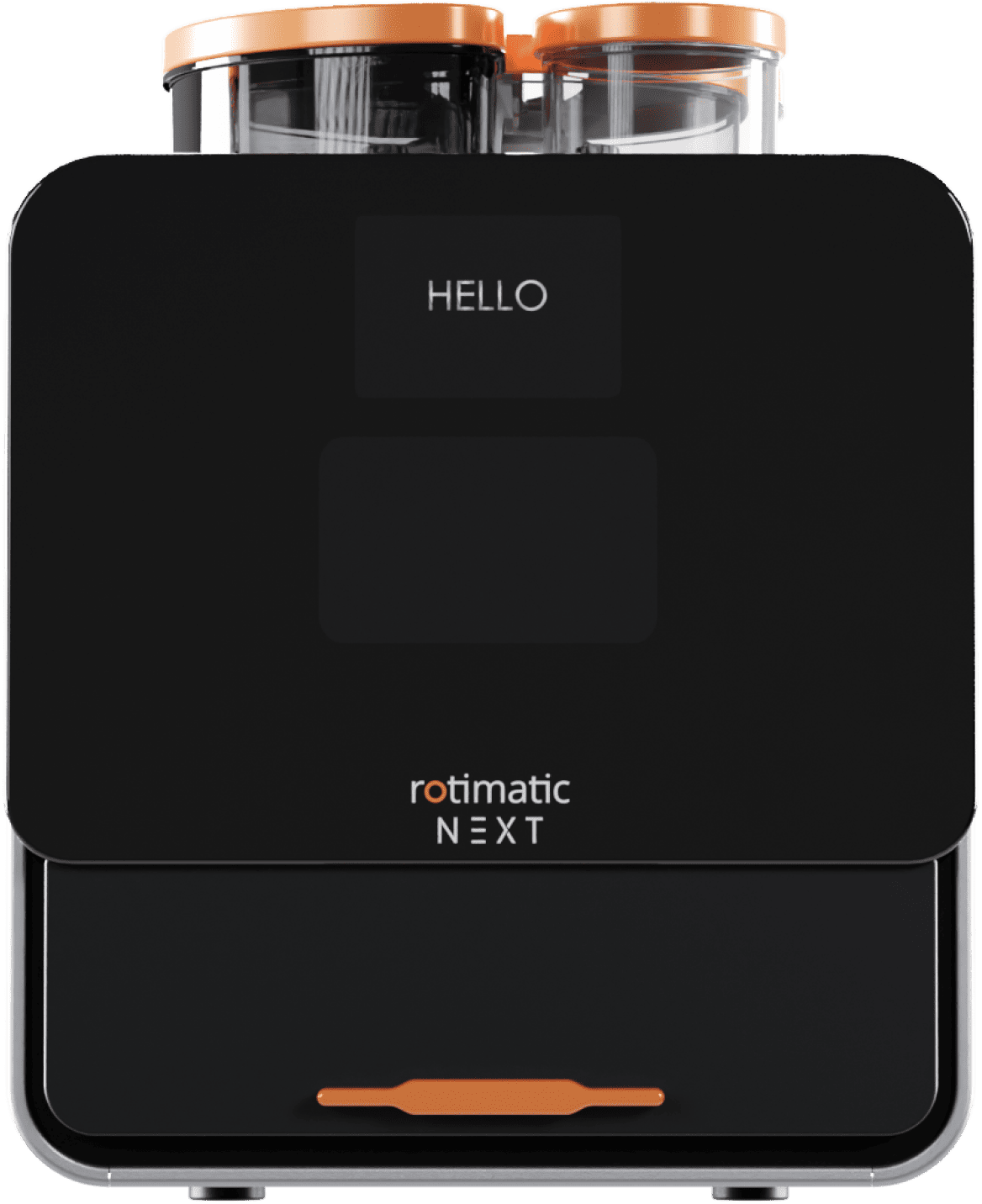
#4 Rotimatic NEXT: The Future of Roti
Domain Est. 2008
Website: rotimatic.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free deliveryMar 2, 2025 · Tired of frozen rotis? Switch to Rotimatic NEXT and enjoy fresh, thin, soft, homemade rotis in just 90 seconds. Get yours now for just ……
#5 Roti Maker Machine
Domain Est. 2022
Website: girnarmachine.com
Key Highlights: Automatic Roti Press Machine can make up to 1000 chapatis per hour. It is great for who need to meet large demands rapidly and efficiently. Also, the machine ……
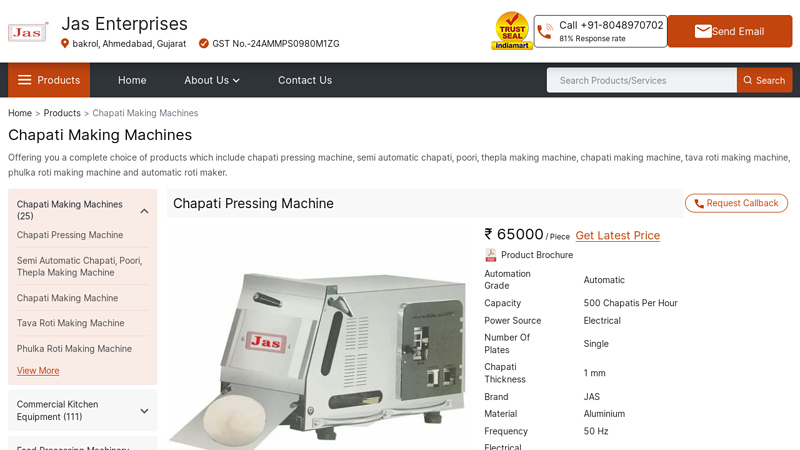
#6 Chapati Making Machines
Domain Est. 2023
Website: jasfoodmachine.com
Key Highlights: An automatic roti maker is a kitchen appliance designed to simplify the process of making rotis, a type of Indian flatbread….
#7 , Real Enjoy Guide & Demo
Domain Est. 2024
Website: rotimakingmachinemanufacturer.com
Key Highlights: Snacks Making Machine · Best Poori Making Machine Manufacturer in Delhi · Poori Making Machine · Best Roti Making Machine Manufacturer in Delhi · Fully ……
#8 A Chef’s Review of Rotimatic – The Robotic Roti Maker
Domain Est. 2011
Website: goeatgive.com
Key Highlights: Rotimatic is like a bread maker, but for rotis. It kneads the dough, rolls it out, bakes it and churns out fresh rotis – within minutes!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Machine To Make Roti

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Machines to Make Roti
The global market for machines to make roti is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by rising urbanization, evolving consumer lifestyles, and advancements in automation and food technology. As demand for convenient, hygienic, and consistent flatbread production grows across households, restaurants, and food service industries, the roti-making machine sector is witnessing accelerated innovation and market expansion.
-
Increased Demand in Urban and Emerging Markets
By 2026, rapid urbanization—especially in South Asia, the Middle East, and parts of Africa—will continue to fuel demand for automated roti-making solutions. Busy urban consumers are increasingly seeking time-saving kitchen appliances, and small-to-medium food businesses are adopting machines to meet high-volume needs efficiently. India remains the largest market, with growing penetration in tier-2 and tier-3 cities due to rising disposable incomes and digital access. -
Technological Advancements and Smart Features
Roti-making machines are becoming smarter, integrating IoT (Internet of Things), AI-based controls, and smartphone connectivity. By 2026, expect to see more models offering features such as customizable thickness, size, doneness levels, and auto-cleaning functions. Some high-end machines may include recipe storage, voice control integration, and real-time diagnostics via mobile apps, appealing to tech-savvy consumers. -
Focus on Hygiene and Food Safety
Post-pandemic awareness has heightened consumer expectations for hygiene. Manufacturers are responding by using food-grade stainless steel, non-stick coatings, and designs that minimize manual handling. Machines with enclosed systems and automatic dough feeding are gaining favor, especially in commercial kitchens and cloud kitchens aiming for standardized, safe food prep. -
Growth in Commercial and Institutional Adoption
Beyond home use, commercial roti-making machines are being widely adopted by restaurants, hotels, caterers, and institutional kitchens (schools, hospitals). With labor costs rising and consistency becoming critical, businesses are investing in high-capacity machines capable of producing thousands of rotis per hour. This shift is expected to drive B2B market growth significantly by 2026. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
As environmental concerns grow, manufacturers are focusing on energy-efficient motors, reduced power consumption, and eco-friendly materials. Machines with lower carbon footprints and recyclable components will gain competitive advantage, particularly in markets with green consumer trends like Europe and North America. -
Expansion into Global Markets
While traditionally rooted in South Asian cuisine, roti and similar flatbreads (like tortillas, naan, and chapati) are gaining popularity globally. This cultural diffusion is opening new markets in North America, Europe, and Australia. By 2026, manufacturers are likely to launch multi-functional flatbread machines capable of producing various regional variants, increasing global appeal. -
Competitive Landscape and Price Optimization
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with new entrants from China, India, and Turkey offering affordable models. Established brands are responding with value-added features and modular designs. Price points are expected to become more accessible, especially for semi-automated home units, further boosting mass-market adoption.
In conclusion, the 2026 landscape for roti-making machines will be defined by technological sophistication, broader market reach, and a strong alignment with modern consumer values—convenience, hygiene, sustainability, and versatility. As automation becomes mainstream in food preparation, the roti machine market is on track for robust growth, with innovations that bridge tradition and modernity.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Machines to Make Roti (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing machinery for roti production involves navigating several critical challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can lead to substandard output, operational inefficiencies, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Roti Output
Many low-cost or poorly engineered roti-making machines fail to produce uniform rotis in terms of size, thickness, texture, and cooking consistency. Variability in dough handling, rolling mechanisms, and heating elements can result in undercooked, overcooked, or misshapen rotis, affecting both consumer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Use of Substandard Materials
Some manufacturers cut costs by using inferior-grade stainless steel or non-food-safe components. This compromises hygiene, increases corrosion and wear, and may contaminate food. Machines built with weak mechanical parts also require frequent maintenance and have shorter lifespans.
Inadequate Temperature and Timing Controls
Precise control over cooking temperature and duration is crucial for authentic roti texture. Machines lacking advanced sensors or programmable logic controllers (PLCs) often underperform, leading to inconsistent browning or improper puffing—hallmarks of poorly made roti.
Poor Integration with Existing Production Lines
Roti machines that aren’t designed for seamless integration with dough feeders, stacking systems, or packaging units can disrupt workflow. Compatibility issues in automation protocols (e.g., lack of IoT or SCADA integration) hinder scalability and efficiency.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Many suppliers, especially overseas ones, offer limited technical support or delayed delivery of spare parts. This results in prolonged downtime, increased operational costs, and frustration for food producers dependent on continuous production.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Infringement of Patented Technology
Some roti machine designs incorporate patented mechanisms for dough feeding, rolling, or baking. Sourcing machines from manufacturers that replicate these features without licensing exposes buyers to legal liability, especially when importing into IP-enforcing jurisdictions.
Lack of IP Verification in Supplier Contracts
Buyers often overlook including IP indemnity clauses in procurement agreements. Without clear contractual assurance that the machinery does not infringe third-party IP rights, the buyer may bear legal and financial responsibility in case of infringement claims.
Counterfeit or Clone Machines
The market includes machines that are direct copies of original designs, often sold at lower prices. These clones may appear functional but lack reliability and innovation. Purchasing such machines supports IP theft and may expose the buyer to reputational and legal risks.
Ambiguous Ownership of Customized Designs
When working with suppliers to develop bespoke roti machines, unclear agreements on who owns the design modifications can lead to disputes. Without explicit IP assignment clauses, the supplier may retain rights, limiting your ability to reproduce, modify, or protect the innovation.
Failure to Protect Your Own Innovations
If your operation involves unique process improvements or machine adaptations, failing to file for patents, design protection, or trade secrets leaves your competitive edge vulnerable—especially when collaborating with external manufacturers who may replicate your ideas.
Mitigating these pitfalls requires thorough due diligence, vetting suppliers for both technical capability and IP compliance, and ensuring legal safeguards are in place before procurement.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Machine To Make Roti
Product Classification and Documentation
Ensure the roti-making machine is correctly classified under the Harmonized System (HS) Code for accurate import/export handling. Typically, such machines fall under HS Code 8438.80 (Machinery for the industrial preparation or manufacture of food or drink). Confirm this with local customs authorities. Prepare essential documentation including commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/airway bill, certificate of origin, and product specifications.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Verify that the roti-making machine meets the electrical, mechanical, and food safety standards of the destination country. In the U.S., compliance with UL or ETL standards is required. In the EU, CE marking under Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU) is mandatory. Ensure adherence to food contact material regulations such as FDA 21 CFR (U.S.) or EU Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004. Include user manuals in the local language with safety instructions.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Package the machine securely to prevent damage during transit, using shock-absorbent materials and robust outer crates. Clearly label each unit with product name, model number, voltage, power rating, manufacturer details, and handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”). Include compliance marks (e.g., CE, UL) and multilingual warning labels where applicable. Barcodes and serial numbers should be visible for traceability.
Import/Export Licensing and Duties
Obtain necessary export licenses if required by the exporting country. Check import restrictions, duties, and taxes in the destination market. Some countries may require an import license or conformity assessment for food-processing equipment. Use Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) clearly in contracts to define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance.
Transportation and Freight Management
Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial kitchen equipment. Select appropriate transport mode (sea, air, or land) based on urgency, cost, and destination. For sea freight, ensure proper container loading and moisture protection. For air freight, confirm size and weight restrictions. Provide detailed shipping instructions and track shipments in real-time.
Customs Clearance and Inspection
Submit complete documentation to customs brokers in the destination country. Be prepared for possible physical inspection of the machines. Customs may verify compliance with technical standards, labeling, and safety certifications. Respond promptly to any queries to avoid delays. Retain records for audit purposes.
After-Sales Support and Warranty Logistics
Establish a service and spare parts supply chain in the target market. Provide clear warranty terms and instructions for returns or repairs. Train local technicians if necessary. Include warranty cards and service contact information with each machine. Ensure reverse logistics processes are in place for defective units.
Environmental and Disposal Regulations
Comply with environmental directives such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) in applicable regions. Provide end-of-life disposal guidance to customers. Use recyclable packaging materials and minimize hazardous components in machine construction.
Conclusion:
After careful evaluation of various options, sourcing a roti-making machine proves to be a valuable investment for businesses aiming to enhance efficiency, ensure consistency, and meet high-volume demands. Automated roti machines offer benefits such as increased production speed, reduced labor costs, uniform quality, and improved hygiene compared to manual preparation. When selecting the right machine, key considerations include production capacity, ease of operation and maintenance, energy efficiency, durability, and after-sales support.
Ultimately, choosing a machine that aligns with your operational scale—whether for a small eatery or large-scale commercial kitchen—ensures long-term cost-effectiveness and customer satisfaction. By integrating the right roti-making machine into your food production process, you can streamline operations, maintain product authenticity, and stay competitive in the growing market for traditional flatbreads.