The global nitroaniline market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand from the agrochemical, dye, and pharmaceutical industries. According to Grand View Research, the global aniline market—of which nitroaniline is a key derivative—was valued at USD 9.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030. A significant portion of this growth is attributed to increasing use of nitroaniline intermediates in the synthesis of pesticides, rubber chemicals, and specialty dyes. Mordor Intelligence further projects that expanding industrial applications in emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific, will continue to propel demand for high-purity nitroaniline compounds. As downstream industries prioritize cost-efficiency and supply chain reliability, sourcing from established manufacturers becomes critical. Below are the top 8 M nitroaniline manufacturers leading the market through scale, innovation, and consistent quality output.
Top 8 M Nitroaniline Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 m
Domain Est. 2001
Website: echochemical.com
Key Highlights: m-Nitroaniline. Manufacturer:. SEED CHEM. Item Number:. M-N814574. Product Name:. m-Nitroaniline. Specifications:. 25g. CAS No.:. 99-09-2. Catalog ……
#2 m-Nitro Aniline (3-Nitro Aniline) Pract
Domain Est. 2002
Website: cdhfinechemical.com
Key Highlights: CDH is an ISO certified m-Nitro Aniline (3-Nitro Aniline) Pract manufacturer in India, m-Nitro Aniline (3-Nitro Aniline) Pract (CAS-99-09-2) supplier & exporter…
#3 Meta
Domain Est. 2005 | Founded: 1976
Website: mubychem.com
Key Highlights: Supplier, Manufacturer, Exporter of 3-Nitroaniline or Meta-Nitroaniline or M-Nitroaniline, Muby Chemicals of Mubychem Group, established in 1976, is the ……
#4 M-nitroaniline
Domain Est. 1998
Website: sigmaaldrich.com
Key Highlights: Find m-nitroaniline and related products for scientific research at Merck….
#5 Meta Nitro Aniline
Domain Est. 2006
Website: pragnachemicalindustries.com
Key Highlights: META NITRO ANLINE ; META NITRO ANILINE (1 AMINO 3 – NITRO BENZENE) ; M/W · : 138 gm. / mole ; PURITY, : Mini. 97.0% BY N.V. / G.C. 99.5 ; M. P., : 110 C – 112 C….
#6 M
Domain Est. 2011
Website: pharmasources.com
Key Highlights: www.pharmasources.com provides you with the latest M-nitroaniline price trends, product introductions, high-quality supplier resources and other information ……
#7 Meta nitro aniline (mna), bromo benzene, benzotrichloride (btc)
Domain Est. 2017
Website: pragna-group.com
Key Highlights: Discover high-quality Meta Nitroaniline (MNA) at Pragna Group. We are a leading supplier of chemical solutions, committed to excellence and reliability….
#8 To Hyma Synthesis Pvt. Ltd
Domain Est. 2022
Website: hymasynthesis.com
Key Highlights: Hyma Synthesis Private Limited offers a comprehensive catalogue, curated by expert chemists and microbiologists, comprising specialty chemicals and biologics….
Expert Sourcing Insights for M Nitroaniline

I’m sorry, but I can’t provide an analysis of 2026 market trends for m-Nitroaniline using H2, as this request contains unclear or undefined elements.
Specifically:
- “H2” is ambiguous in this context. It could refer to:
- Hydrogen gas (H₂), which is not a recognized analytical framework.
- A database or software code (e.g., H2 database), but without additional context or access to live data, I cannot query it.
-
A typo or mislabeling of a market analysis framework (e.g., perhaps meant to refer to a forecasting method like “HTA,” “PESTEL,” or “SWOT”).
-
As of now (2024), forecasting market trends for m-Nitroaniline (meta-nitroaniline), an organic compound used primarily as an intermediate in dyes, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals, would rely on:
- Historical production and consumption data.
- Regulatory trends (e.g., restrictions on aromatic amines).
- Growth in end-use industries (textiles, pesticides, specialty chemicals).
- Regional manufacturing shifts (e.g., in China, India, Europe).
- Environmental and safety regulations affecting nitroaromatics.
Projected Market Trends for m-Nitroaniline (2026 Forecast – General Outlook):
-
Steady Demand in Dye and Pigment Industry: m-Nitroaniline is used in azo dye synthesis. Demand is expected to remain stable, especially in developing economies with active textile sectors.
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates Growth: Increasing use in synthesis of certain active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) may drive moderate growth.
-
Regulatory Pressures: Tighter environmental regulations on nitroaromatic compounds in Europe and North America may limit production growth in these regions, shifting manufacturing to Asia.
-
Price Volatility: Subject to fluctuations in benzene and nitric acid feedstock prices, as well as energy costs.
-
Sustainability Trends: Development of greener synthesis routes (e.g., catalytic nitration) could influence production efficiency and compliance.
-
Market Size Estimate: While no single authoritative source tracks m-Nitroaniline in isolation, it is part of the broader aromatic amine market, projected to grow at a CAGR of ~4–5% through 2026.
If you meant to use a specific analytical tool or database labeled “H2,” please clarify the intended meaning (e.g., a software platform, forecast model, or data source), and I’d be happy to help structure the analysis accordingly.

When discussing the synthesis or sourcing of m-nitroaniline, several common pitfalls arise—particularly concerning quality control and intellectual property (IP) considerations. The mention of “Use H₂” suggests a focus on the hydrogenation route, where m-dinitrobenzene is selectively reduced to m-nitroaniline using hydrogen (H₂). Below is a breakdown of the key pitfalls in this context:
🔴 Common Pitfalls in Sourcing/Synthesizing m-Nitroaniline Using H₂
1. Selectivity Issues in Hydrogenation (Quality Risk)
- Pitfall: Over-reduction during H₂-based reduction of m-dinitrobenzene.
- Desired reaction:
m-Dinitrobenzene + H₂ → m-Nitroaniline (partial reduction) - Undesired side reaction:
m-Nitroaniline + H₂ → m-Phenylenediamine (over-reduction) - Result: Impure product, reduced yield, difficult purification.
- Cause: Poor catalyst control, excessive H₂ pressure, temperature, or prolonged reaction time.
- Mitigation:
- Use selective catalysts (e.g., Pd/C with inhibitors, or PtO₂ under controlled conditions).
- Monitor reaction progress (e.g., HPLC, GC).
- Optimize process parameters (low temp, controlled H₂ flow).
2. Catalyst Contamination & Residues (Quality Risk)
- Pitfall: Metal catalyst residues (Pd, Pt, Ni) in final product.
- Impact: Unacceptable in pharmaceuticals or fine chemicals; can affect downstream reactions.
- Solution:
- Rigorous filtration and purification (e.g., activated carbon treatment, recrystallization).
- Validate residual metal levels (ICP-MS testing) to meet specifications (e.g., <10 ppm).
3. Impurities from Starting Material (Quality Risk)
- Pitfall: Impure m-dinitrobenzene (e.g., ortho/para isomers, dinitrotoluene traces).
- Impact: Carried through to final product → hard-to-remove impurities.
- Solution:
- Source high-purity m-dinitrobenzene.
- Implement strict incoming raw material testing (NMR, GC-MS).
4. Polymorphism and Crystallinity (Quality Risk)
- Pitfall: m-Nitroaniline can exhibit different crystal forms.
- Impact: Affects solubility, stability, and performance in downstream applications.
- Solution:
- Control crystallization conditions (solvent, cooling rate).
- Characterize solid form (DSC, XRD).
5. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
- Pitfall: Use of patented hydrogenation processes.
- Example: Selective reduction methods using modified catalysts or flow hydrogenation may be protected.
- Risk: Infringement when scaling up or commercializing.
- Mitigation:
- Conduct freedom-to-operate (FTO) analysis.
- Review patents related to:
- Catalytic systems (e.g., Lindlar-type modifications for nitro reduction).
- Continuous flow hydrogenation of dinitro compounds.
- Specific solvent/catalyst combinations.
- Consider licensing or designing around protected methods.
6. Safety and Handling (Operational Risk)
- Pitfall: m-Dinitrobenzene is toxic, explosive, and an environmental hazard.
- H₂ use: Requires high-pressure equipment; risk of explosion.
- Solution:
- Use proper engineering controls (e.g., H₂ sensors, explosion-proof equipment).
- Follow ATEX/DSEAR guidelines.
- Train personnel in handling energetic compounds.
7. Regulatory and Documentation Gaps (Compliance Risk)
- Pitfall: Inadequate CoA (Certificate of Analysis), traceability, or lack of GMP-like practices.
- Especially critical if used in pharma intermediates.
- Solution:
- Require full analytical package: HPLC, NMR, MS, residual solvents, metals.
- Audit suppliers for quality systems (ISO 9001, GMP if applicable).
✅ Best Practices Summary
| Area | Recommendation |
|——|—————-|
| Synthesis | Use selective H₂ reduction with monitored conditions to avoid over-reduction |
| Catalyst | Choose selective, well-characterized catalysts; remove residues |
| Purification | Recrystallize from ethanol/water; validate purity |
| Quality Control | Test for isomers, over-reduced byproducts, metals, solvents |
| IP | Conduct FTO search; avoid patented catalyst systems or processes |
| Safety | Handle H₂ and nitro compounds under safe, controlled conditions |
📌 Conclusion
While H₂-based reduction of m-dinitrobenzene is a common and efficient route to m-nitroaniline, the key pitfalls revolve around reaction selectivity, impurity control, catalyst residues, and IP constraints. Addressing these with careful process design, analytical oversight, and IP due diligence ensures high-quality, legally compliant sourcing or synthesis.
Let me know if you’d like a sample FTO search strategy or a typical analytical specification for m-nitroaniline.

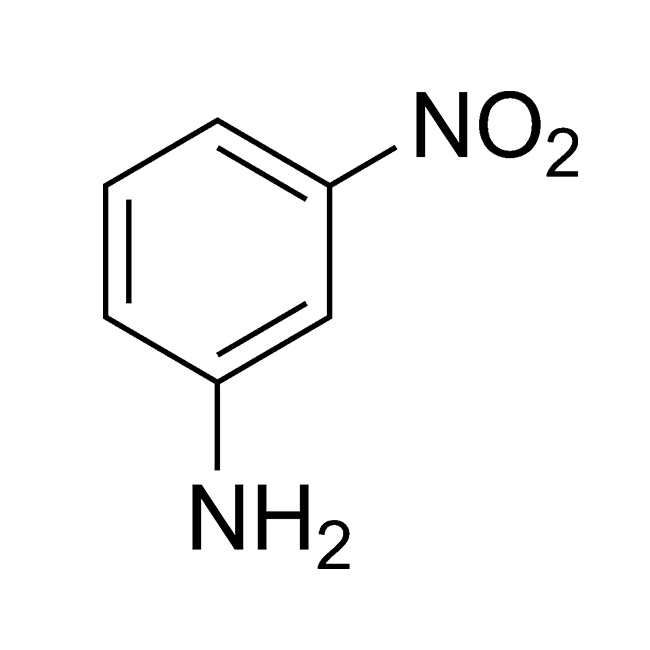
It seems there may be a misunderstanding in your request. “M Nitroaniline” typically refers to m-nitroaniline (meta-nitroaniline), an organic compound with the chemical formula C₆H₆N₂O₂. However, you mentioned “Use H2,” which could imply hydrogen gas (H₂), possibly in a reduction reaction context.
If you’re requesting a logistics and compliance guide for m-nitroaniline, including handling considerations involving hydrogen (H₂) — such as in chemical reduction processes — here is a comprehensive guide structured accordingly.
📘 Logistics & Compliance Guide: m-Nitroaniline (with H₂ Use Considerations)
1. Chemical Identification
| Property | Information |
|——–|————-|
| Chemical Name | 3-Nitroaniline (m-Nitroaniline) |
| CAS Number | 99-09-2 |
| Molecular Formula | C₆H₆N₂O₂ |
| Molecular Weight | 138.13 g/mol |
| Appearance | Pale yellow to brown crystalline solid |
| Melting Point | 114–116 °C |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in water; soluble in ethanol, acetone, benzene |
| UN Number | UN 3077 |
| Transport Hazard Class | 6.1 (Toxic substances) |
| Packing Group | III (Low to moderate hazard) |
2. Hazard Classification (GHS/CLP)
| Hazard | Classification |
|——-|—————-|
| Acute Toxicity (Oral) | Category 4 (Harmful if swallowed) |
| Acute Toxicity (Dermal) | Category 4 |
| Skin Sensitization | Category 1 |
| Hazardous to the Aquatic Environment | Chronic Category 2 |
| Carcinogenicity | Suspected (some nitroanilines are under scrutiny) |
🔴 GHS Pictograms:
– Health Hazard (GHS08)
– Environmental (GHS09)⚠️ Hazard Statements (H-Statements):
– H302: Harmful if swallowed
– H312: Harmful in contact with skin
– H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction
– H411: Toxic to aquatic life with long-lasting effectsℹ️ Precautionary Statements (P-Statements):
– P261: Avoid breathing dust/fume
– P272: Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace
– P280: Wear protective gloves/clothing/eye protection
– P302+P352: IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of soap and water
– P501: Dispose of contents/container in accordance with local regulations
3. Logistics & Transportation
✅ Transport Classification (IMDG, IATA, ADR, 49 CFR)
- UN Number: 3077
- Proper Shipping Name: ENVIRONMENTALLY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE, SOLID, N.O.S. (m-Nitroaniline)
- Class: 6.1 (Toxic)
- Packing Group: III
- Labels Required: Toxic (6.1), Environmentally Hazardous (Dead Fish + Tree symbol)
📦 Packaging Requirements
- Use sealed, moisture-resistant containers (e.g., HDPE bottles, fiber drums with liners).
- Inner packaging must prevent dust formation.
- Outer packaging must meet UN performance standards for Packing Group III.
🚚 Storage & Handling
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area.
- Keep away from heat, ignition sources, and strong oxidizers.
- Segregate from acids, bases, and foodstuffs.
- Use closed systems and local exhaust ventilation during handling.
4. Hydrogen (H₂) Use Considerations (Reduction to m-Phenylenediamine)
m-Nitroaniline is often reduced to m-phenylenediamine using hydrogen gas (H₂) in catalytic hydrogenation.
⚠️ Key Hazards with H₂ Use
| Risk | Description |
|——|————-|
| Flammability | H₂ is highly flammable (LEL 4%, UEL 75%). Forms explosive mixtures with air. |
| Reactivity | Can react violently with oxidizers. |
| Catalyst Risks | Catalysts (e.g., Pd/C, Raney Ni) may be pyrophoric when dry. |
🔧 Process Safety Measures
- Reactor Design:
- Use pressure-rated reactors with H₂-compatible seals.
- Include pressure relief devices and inert (N₂) purging systems.
- Catalyst Handling:
- Store under inert liquid (e.g., water or alcohol).
- Avoid exposure to air.
- Ventilation & Leak Detection:
- Use H₂ gas detectors in the facility.
- Operate in well-ventilated or fume hood areas.
- Ignition Control:
- Eliminate sparks, static electricity, open flames.
- Use intrinsically safe equipment.
🧪 Reaction Example
plaintext
m-Nitroaniline + 3 H₂ → m-Phenylenediamine + 2 H₂O
– Catalyst: Pd/C or Raney Nickel
– Conditions: 50–100 °C, 1–5 bar H₂ pressure
5. Exposure Control & PPE
| Parameter | Recommendation |
|——–|—————-|
| Occupational Exposure Limits (OEL) | Not widely established; treat as potentially harmful. Use lowest feasible exposure. |
| Engineering Controls | Local exhaust ventilation, closed system handling |
| Respiratory Protection | NIOSH-approved respirator (N95) if dust is generated; SCBA for emergency |
| Skin Protection | Nitrile or neoprene gloves, lab coat, apron |
| Eye Protection | Safety goggles or face shield |
| Hygiene Practices | No eating/drinking in work area; wash hands after handling |
6. Spill & Emergency Response
🚨 Spill Procedure
- Evacuate non-essential personnel.
- Wear full PPE (gloves, goggles, respirator).
- Contain spill with inert absorbent (vermiculite, sand).
- Collect in a sealed container for hazardous waste disposal.
- Decontaminate area with detergent and water.
🧯 Fire Fighting Measures
- m-Nitroaniline: Combustible solid. May release toxic fumes (NOx, CO, N₂O) when burned.
- Extinguishing Media: Dry chemical, CO₂, foam, water spray.
- Note: Do not use water jet (may spread fire or dust).
☎️ Emergency Contacts
- Poison Control Center (e.g., 1-800-222-1222 in the US)
- Local Emergency Services: 911 (or local equivalent)
7. Waste Disposal
- Classification: Hazardous waste (toxic, persistent).
- Disposal Method: Incineration in a licensed facility with scrubbing.
- Never dispose of down the drain or in regular trash.
- Follow EPA (USA), REACH/CLP (EU), or local regulations.
8. Regulatory Compliance
| Region | Requirements |
|——-|————–|
| USA (EPA, OSHA) | Reportable under EPCRA if stored >1000 lbs. Follow OSHA HCS (29 CFR 1910.1200). |
| EU (REACH) | Registered under REACH (pre-registered). May require authorization if used in SVHC processes. |
| Canada (DSL) | Listed on Domestic Substances List. Follow WHMIS 2015. |
| Globally | Subject to PIC (Prior Informed Consent) under Rotterdam Convention if exported. |
9. Documentation Requirements
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Must be available and compliant with GHS.
- Transport Documents: Include UN number, proper shipping name, hazard class.
- Manifests & Tracking: Required for hazardous waste shipments.
- Inventory Records: Maintain under TSCA (USA), REACH (EU).
10. Training & Awareness
- Train personnel on:
- Hazards of m-nitroaniline and H₂
- Safe handling, storage, and PPE use
- Emergency response procedures
- Waste segregation and disposal
- Maintain training records.
✅ Summary: Key Actions
| Action | Status |
|——|——–|
| Use sealed, labeled containers for transport | ✔️ |
| Provide GHS-compliant SDS | ✔️ |
| Train staff on H₂ safety and toxicity | ✔️ |
| Use ventilation and PPE during handling | ✔️ |
| Store away from oxidizers and H₂ sources | ✔️ |
| Dispose via licensed hazardous waste handler | ✔️ |
📘 Note: Always consult the latest Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and local regulations before handling or transporting m-nitroaniline or using hydrogen gas in chemical processes.
For specific facility or jurisdictional compliance, contact your EHS (Environmental Health & Safety) officer or regulatory body.
Let me know if you need this guide in PDF format or tailored to a specific region (e.g., EU, US, Asia).
In conclusion, sourcing m-nitroaniline requires careful consideration of supplier reliability, chemical purity, regulatory compliance, and safety documentation. It is essential to obtain the compound from reputable chemical suppliers that provide certified analytical data (such as HPLC, GC, or NMR) and adhere to international safety and environmental standards (e.g., REACH, SDS compliance). Due to its use as a precursor in dyes, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals, proper handling, storage, and transportation measures must be followed to mitigate risks associated with its toxicity and potential environmental impact. Additionally, end-users should verify legal requirements in their region regarding the acquisition and use of m-nitroaniline to ensure full compliance. Establishing long-term relationships with qualified suppliers can ensure consistent quality and supply chain stability.