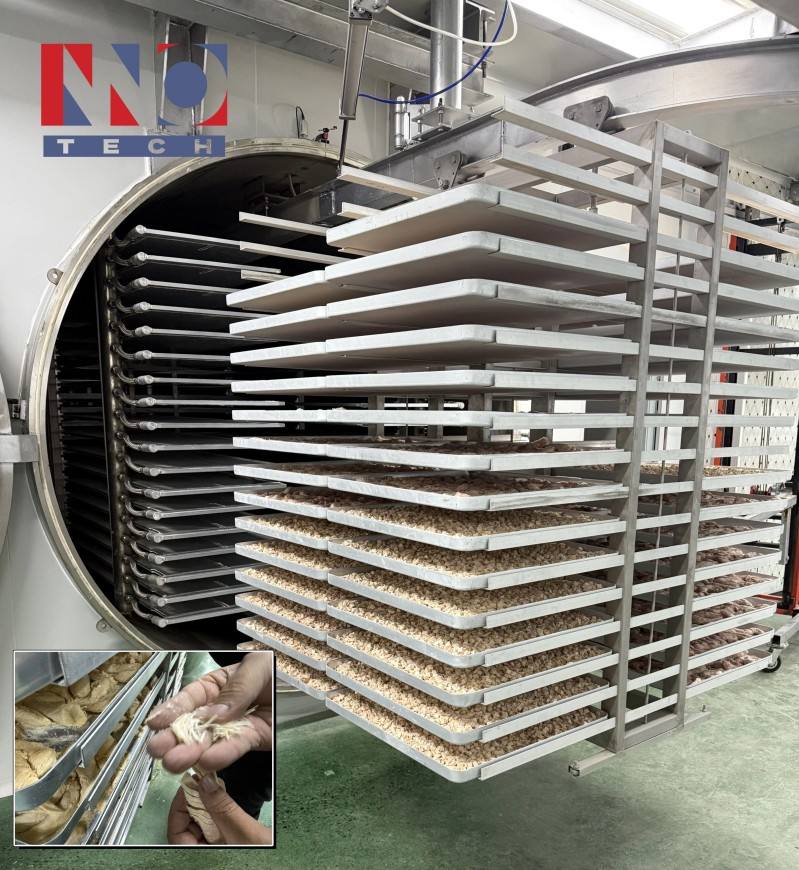
The global freeze-dried products market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand across pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food, and nutraceutical sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global lyophilization market was valued at USD 56.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% through 2029. This growth is propelled by the rising need for extended shelf-life, enhanced product stability, and cold-chain-independent solutions—especially critical in vaccine and biologic drug development. Furthermore, advancements in lyophilization technology and the proliferation of contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) are expanding production capacity and innovation. As industries increasingly rely on freeze-dried formulations, identifying reliable and high-capacity manufacturers has become essential. Below is a data-informed overview of the top nine lyophilized and freeze-dried product manufacturers shaping the global landscape.
Top 9 Lyophilized Freeze Dried Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LYOFOOD
Domain Est. 2009
Website: lyofood.com
Key Highlights: We combine over 30 years of experience in freeze-drying technology, gourmet small-batch cooking and natural, high-quality ingredients….
#2 KEMOLO
Domain Est. 2013
Website: kemolo.com
Key Highlights: Kemolo is a large manufacturer of all kinds of freeze drying equipment for food, pet treats, nutraceutical, extract, biological, pharmaceutical products….
#3 Glacial Freeze Dry
Website: glacialfreezedry.com
Key Highlights: Innovative private label freeze drying bringing products to market quickly and safely with state-of-the-art technology. Hands-on, transparent, flexible….
#4 Oregon Freeze Dry
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ofd.com
Key Highlights: Oregon Freeze Dry has over 50 years of lyophilization and freeze drying experience. Contact us today for your preservation needs….
#5 B2B Freeze
Domain Est. 1999
Website: freeze-dry-foods.com
Key Highlights: Our vision is gently freeze-dried and air-dried premium ingredients. 100% natural, fully aromatic, versatile and with a long best-before date….
#6 Arctic Farms
Domain Est. 2010
#7 Canature
Domain Est. 2012
Website: canature.ca
Key Highlights: Located in Langley, British Columbia, Canada, Canature Processing Ltd. is a global leader in the production of premium, freeze-dried pet food and treats….
#8 Thrive Freeze Dry
Domain Est. 2015
Website: thrivefreezedry.com
Key Highlights: We can produce stand-up pouches, pillow packs, bag in box or totes. Our packing rooms control temperature and humidity in our processing rooms….
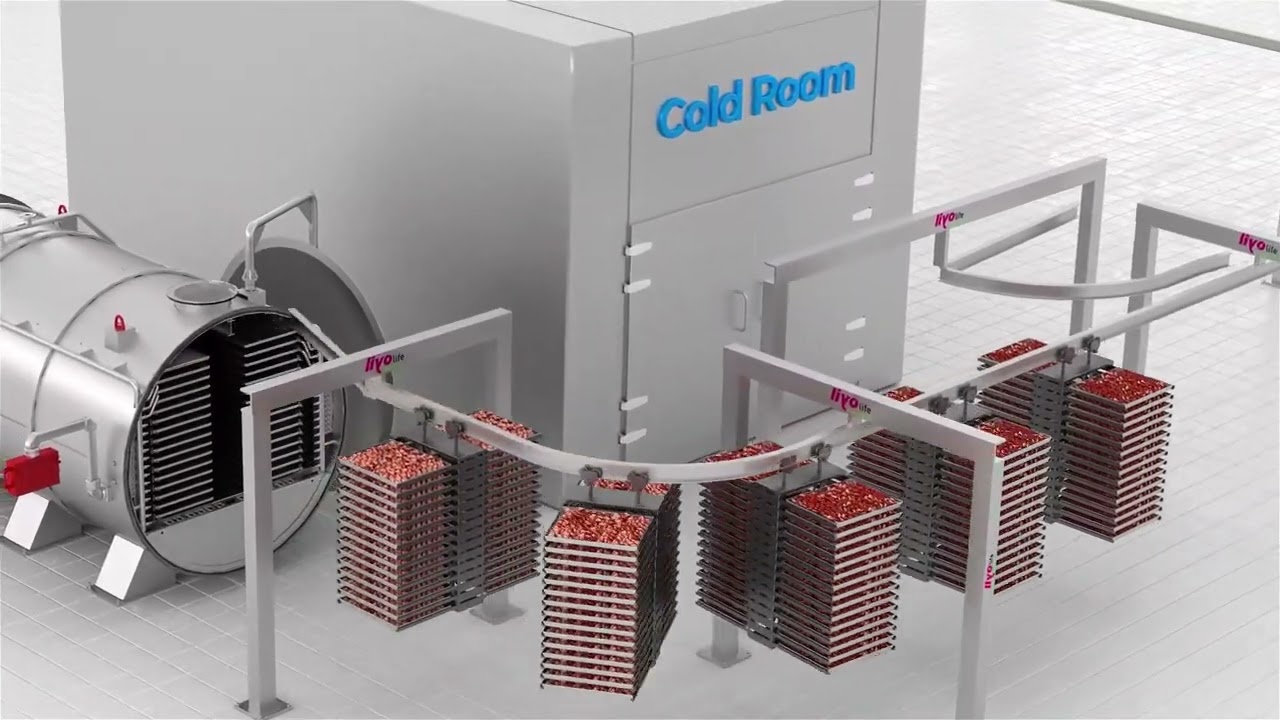
#9 Liyolife
Domain Est. 2021
Website: liyolife.com
Key Highlights: Liyolife freeze dryers produce food that looks and tastes better than store-bought freeze-dried food. Experience the Liyolife difference!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Lyophilized Freeze Dried

H2: Market Trends for Lyophilized Freeze-Dried Products in 2026
The global lyophilized (freeze-dried) products market is poised for significant growth and transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and expanding applications across industries. Below are the key market trends expected to shape the lyophilized freeze-dried sector in 2026:
1. Rising Demand in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Lyophilization continues to be a critical process in pharmaceutical manufacturing, particularly for biologics, vaccines, and temperature-sensitive drugs. With the increasing development of complex biopharmaceuticals and personalized medicines, the demand for stable, long-shelf-life formulations will drive adoption of freeze-drying technologies. The success of mRNA-based vaccines during recent global health crises has further underscored the importance of lyophilization in ensuring thermostability and global distribution—a trend expected to persist through 2026.
2. Expansion in the Food and Beverage Sector
The freeze-dried food market is experiencing robust growth, fueled by consumer demand for convenient, healthy, and long-lasting food products. By 2026, the market will see increased innovation in freeze-dried snacks, ready-to-eat meals, and functional foods enriched with probiotics and vitamins. E-commerce and direct-to-consumer models will amplify accessibility, especially in urban and health-conscious demographics. Freeze-dried fruits, vegetables, and coffee are expected to dominate, with Asia-Pacific emerging as a high-growth region.
3. Technological Advancements and Process Optimization
Ongoing R&D efforts are focused on improving lyophilization efficiency, reducing cycle times, and lowering energy consumption. By 2026, smart freeze-drying systems integrated with IoT, AI-driven process control, and real-time monitoring will become more widespread. These innovations will enhance product consistency, reduce manufacturing costs, and support scalable production—particularly beneficial for small and medium-sized enterprises entering the market.
4. Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Sustainability is becoming a key driver in the lyophilized products sector. Manufacturers are investing in energy-efficient freeze-drying technologies and exploring alternative drying methods to reduce carbon footprints. Additionally, consumer preference for eco-friendly packaging and minimal food waste positions freeze-dried products as sustainable solutions—especially in reducing spoilage and extending product life without preservatives.
5. Growth in Emerging Markets
While North America and Europe remain dominant markets, the Asia-Pacific region—including China, India, and Southeast Asia—is expected to witness the fastest growth by 2026. Rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and increasing awareness of health and wellness are driving demand for high-value freeze-dried pharmaceuticals and foods. Local production capabilities and government support for biotech and food processing industries will further accelerate market expansion.
6. Regulatory and Quality Standardization
As the market grows, regulatory scrutiny on lyophilized products—especially in pharma and nutraceuticals—will intensify. Harmonization of international quality standards and increased emphasis on Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) will shape production protocols. Companies investing in compliance and quality assurance will gain competitive advantage in global supply chains.
Conclusion
By 2026, the lyophilized freeze-dried market will be characterized by innovation, diversification, and global reach. Cross-sector applications—from pharmaceuticals to functional foods—will fuel demand, while technological and sustainability advancements will redefine production standards. Stakeholders who adapt to these evolving trends will be well-positioned to capitalize on the expanding opportunities in this high-value market.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Lyophilized (Freeze-Dried) Products: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing lyophilized (freeze-dried) products—commonly used in pharmaceuticals, biologics, nutraceuticals, and food ingredients—presents unique challenges, particularly regarding product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these issues can lead to supply chain disruptions, regulatory non-compliance, or legal disputes. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Inadequate Quality Control and Process Validation
Lyophilization is a complex process sensitive to temperature, pressure, and time. Poorly controlled freeze-drying can result in compromised product stability, reduced potency, or inconsistent reconstitution.
– Pitfall: Sourcing from suppliers without validated lyophilization cycles or documented Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliance.
– Risk: Batch-to-batch variability, shortened shelf life, or product failure in end-use applications.
– Mitigation: Require detailed process validation data, stability studies, and third-party audits of manufacturing facilities.
2. Lack of Defined Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs)
Lyophilized products must meet specific physical and chemical criteria (e.g., moisture content, cake structure, residual solvents).
– Pitfall: Absence of clear specifications or testing protocols in procurement agreements.
– Risk: Receiving substandard material that fails to meet performance requirements.
– Mitigation: Define CQAs upfront in supplier contracts and require Certificates of Analysis (CoA) for each batch.
3. Misrepresentation of Lyophilization Claims
Some suppliers may label products as “freeze-dried” when they use alternative drying methods (e.g., spray drying) that do not yield the same product characteristics.
– Pitfall: Assuming lyophilization was performed without verification.
– Risk: Inferior product performance (e.g., poor reconstitution, reduced bioactivity).
– Mitigation: Conduct independent verification through analytical testing (e.g., scanning electron microscopy, moisture analysis) and request lyophilization cycle documentation.
4. Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Lyophilized formulations may be protected by patents covering composition, process, or method of use.
– Pitfall: Sourcing materials that incorporate patented technologies without proper licensing.
– Risk: Legal liability, import bans, or forced product reformulation.
– Mitigation: Perform freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses and require suppliers to warrant IP compliance.
5. Inadequate Chain of Custody and Traceability
Lyophilized products are often derived from biological or high-value raw materials.
– Pitfall: Poor documentation of sourcing, processing, and handling.
– Risk: Contamination, adulteration, or inability to trace issues during recalls.
– Mitigation: Enforce strict traceability requirements and audit supplier documentation practices.
6. Unverified Supplier Claims on Stability and Shelf Life
Suppliers may overstate shelf life or storage conditions without proper accelerated stability testing.
– Pitfall: Relying solely on supplier-provided data without independent verification.
– Risk: Product degradation during storage or transport, leading to financial loss or safety issues.
– Mitigation: Conduct or commission stability studies under real-world conditions.
7. Regulatory Non-Compliance
Depending on application (e.g., pharmaceutical vs. dietary supplement), lyophilized products are subject to different regulatory frameworks (e.g., FDA, EMA).
– Pitfall: Sourcing from facilities not compliant with relevant regulations.
– Risk: Delayed market entry, product rejection, or regulatory penalties.
– Mitigation: Verify regulatory status (e.g., FDA registration, EU GMP certification) and ensure appropriate documentation (e.g., Drug Master Files).
In conclusion, sourcing lyophilized freeze-dried products requires rigorous due diligence on both quality assurance and IP integrity. Establishing strong supplier agreements, conducting technical audits, and validating product specifications are essential to mitigate risks and ensure supply chain reliability.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Lyophilized (Freeze-Dried) Products
Lyophilized (freeze-dried) pharmaceuticals, biologics, diagnostics, and high-value food ingredients present unique logistical and compliance challenges due to their sensitivity to moisture, temperature, and physical stress. Ensuring product integrity from manufacturing through distribution to the end-user is critical for safety, efficacy, and regulatory approval. This guide outlines key considerations across the supply chain.
H2: Regulatory Framework & Quality Standards
- Primary Regulations:
- Pharmaceuticals/Biologics: FDA 21 CFR Parts 210, 211 (cGMP), ICH Q7 (GMP for APIs), ICH Q1A(R2) (Stability Testing), EU GMP Annex 1 (Manufacture of Sterile Medicinal Products), EU GDP (Good Distribution Practice).
- Diagnostics: FDA 21 CFR Part 820 (QSR), IVDR (In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation) in EU.
- Food/Supplements: FDA 21 CFR Part 117 (Current Good Manufacturing Practice, Hazard Analysis, and Risk-Based Preventive Controls for Human Food), EU Food Safety Regulations.
- Key Quality Standards:
- Stability Testing: Mandatory ICH Q1A(R2)-compliant studies defining storage conditions (typically 2-8°C or -20°C, sometimes 25°C/60% RH for certain products) and shelf life. Real-time and accelerated data required.
- Container Closure Integrity Testing (CCIT): Critical to ensure the vial, stopper, and seal maintain sterility and prevent moisture ingress (e.g., helium leak testing, mass extraction).
- Moisture Content: Strict specifications (e.g., <1-2% w/w) must be met post-lyophilization and maintained. Karl Fischer titration is standard.
- Residual Solvent Testing: If organic solvents used, residual levels must comply with ICH Q3C guidelines.
- Documentation: Comprehensive batch records, COAs (Certificates of Analysis), stability data, and shipping validation reports are essential.
H2: Cold Chain & Temperature Control
- Storage Requirements:
- Primary: Typically 2-8°C (refrigerated) or -20°C / -80°C (frozen). Never assume room temperature stability without robust data.
- Validation: Storage areas (warehouses, fridges, freezers) must be formally qualified (IQ/OQ/PQ) with continuous monitoring.
- Transportation (Critical Phase):
- Packaging: Use validated, insulated shippers (e.g., EPS, vacuum insulated panels) with sufficient phase change materials (PCMs) like gel packs (for 2-8°C) or dry ice (for -20°C/-80°C). Ensure PCMs are conditioned to the correct temperature.
- Validation: Perform transport validation studies (worst-case scenarios) simulating summer/winter conditions, transit times, and potential delays. Include door-open events for air freight.
- Monitoring: Employ qualified, calibrated data loggers (temperature, and potentially humidity) inside the primary packaging or adjacent to product. Loggers must have NIST traceability. Real-time GPS/temp tracking is highly recommended for high-value shipments.
- Transit Times: Minimize duration. Plan routes carefully, considering air vs. ground, customs delays, and hub handling times.
- Handling: Train personnel on cold chain protocols. Minimize exposure time during loading/unloading. Use “cold rooms” for staging.
H2: Moisture & Environmental Protection
- Primary Packaging: Glass vials with high-quality, properly seated lyo stoppers (often fluoropolymer-coated) and aluminum crimps/seals are standard. Vials must meet USP/Ph. Eur. standards.
- Secondary Packaging: Use desiccants within secondary packaging (e.g., cartons) if specified by stability data. Ensure desiccants are pharmaceutically acceptable and correctly specified. Barrier materials (e.g., foil pouches) may be used for extra protection.
- Humidity Control:
- Storage/Handling: Maintain low relative humidity (RH) in manufacturing, packaging, and storage areas (e.g., <45% RH). Use dehumidifiers.
- Transport: Validated shippers provide a temporary micro-environment. Avoid shipping during high-humidity seasons/regions if possible. Monitor humidity if feasible.
- Sealing Integrity: Ensure capping processes (e.g., capping machines) are validated and routinely monitored to guarantee consistent seal quality.
H2: Physical Protection & Handling
- Shock & Vibration: Lyophilized cakes can be fragile. Use adequate cushioning (foam inserts, bubble wrap) within shippers to protect vials from breakage and cake disturbance.
- Orientation: Ship vials upright whenever possible to prevent stopper movement or cake dislodgement. Clearly label packaging (“This Way Up”).
- Light Protection: Protect light-sensitive products from direct sunlight and strong artificial light using amber vials or opaque secondary packaging.
- Personnel Training: Train all handlers (warehouse, couriers, receiving) on the product’s sensitivity to temperature, moisture, shock, and orientation.
H2: Documentation & Traceability
- Critical Documents:
- Certificate of Analysis (COA): Includes sterility, moisture content, potency, endotoxins, particulates, CCIT results, and residual solvents.
- Stability Data Summary: Supporting shelf life and storage conditions.
- Shipping Validation Report: Proof the chosen shipper maintains conditions.
- Temperature Monitoring Data: Downloaded logger data from each shipment.
- Batch-Specific Instructions: Reconstitution instructions, storage after reconstitution.
- Traceability: Implement robust systems (e.g., barcode/RFID scanning) for full traceability from batch to final destination. Track shipment progress in real-time.
- GDP Compliance: Adhere strictly to Good Distribution Practice requirements for documentation, storage, transport, and handling. Maintain records for the required period (e.g., 1 year after expiry + 1 year).
H2: Contingency Planning & Risk Management
- Temperature Excursions: Have a defined procedure for investigating and assessing the impact of any temperature deviation (e.g., >2°C above/below range for >15-30 mins). Utilize stability data and potentially retest product if appropriate.
- Delays: Plan for potential delays (customs, weather, flight cancellations). Use sufficient PCM capacity or arrange for cold storage at intermediate points.
- Dry Ice Shipments: Comply strictly with IATA DGR (Dangerous Goods Regulations) for air transport (UN 1845, Class 9, Limited Quantity or Excepted Quantity rules). Ensure adequate ventilation, labeling (“Dry Ice,” “Keep Ventilated”), and declaration. Monitor sublimation.
- Recalls: Have a clear, tested product recall procedure in place.
Summary: Managing lyophilized products requires a holistic approach prioritizing temperature control, moisture protection, physical integrity, and rigorous documentation throughout the entire supply chain. Proactive validation, continuous monitoring, comprehensive training, and strict adherence to relevant cGMP, GDP, and transportation regulations are non-negotiable for ensuring patient safety and product efficacy. Always refer to the specific product’s approved labeling and regulatory filings for definitive requirements.
Conclusion on Sourcing Lyophilized (Freeze-Dried) Products:
Sourcing lyophilized (freeze-dried) products offers significant advantages in terms of product stability, extended shelf life, and preservation of biological activity, making it an ideal choice for pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, biologics, and food ingredients. However, successful sourcing requires careful consideration of several key factors. These include selecting reliable suppliers with proven expertise in lyophilization technology, ensuring compliance with relevant quality standards (such as cGMP, ISO, or FDA regulations), and evaluating the consistency and scalability of the manufacturing process.
Additionally, cost implications, lead times, and logistics—especially temperature-sensitive storage and transportation—must be factored into the sourcing strategy. Partnering with vendors who offer robust analytical support, documentation, and batch traceability further mitigates risks and ensures product integrity. Ultimately, a well-structured sourcing approach that balances quality, reliability, and cost-efficiency is essential to harnessing the full benefits of lyophilized products in any supply chain or product development initiative.