The global low-torque (LT) motor market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across industrial automation, HVAC systems, and consumer appliances. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global electric motor market — which includes LT motors — is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% from 2023 to 2028, with rising energy efficiency regulations and the adoption of smart manufacturing technologies serving as key growth accelerators. Similarly, Grand View Research reports that the global electric motor market size was valued at USD 132.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030, underpinned by advancements in motor design and growing electrification in emerging economies. Within this landscape, low-torque motors play a critical role in applications requiring precision and compact power solutions, from robotics to medical devices. As competition intensifies and innovation accelerates, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in performance, efficiency, and market reach. Here are the top 8 LT motor manufacturers shaping the future of motion control.
Top 8 Lt Motor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 GM Electric Vehicles, Charging & Technology
Domain Est. 1992
Website: gm.com
Key Highlights: Powerful partnerships, manufacturing innovations, and a charging network poised for exponential growth. We’re making sure the future for EVs is bright….
#2 ACDelco: OEM & Aftermarket Auto Parts
Domain Est. 1996
Website: gmparts.com
Key Highlights: ACDelco offers the only aftermarket parts backed by GM. ACDelco’s Gold and Silver lines of premium aftermarket parts offer a precise fit for GM vehicles….
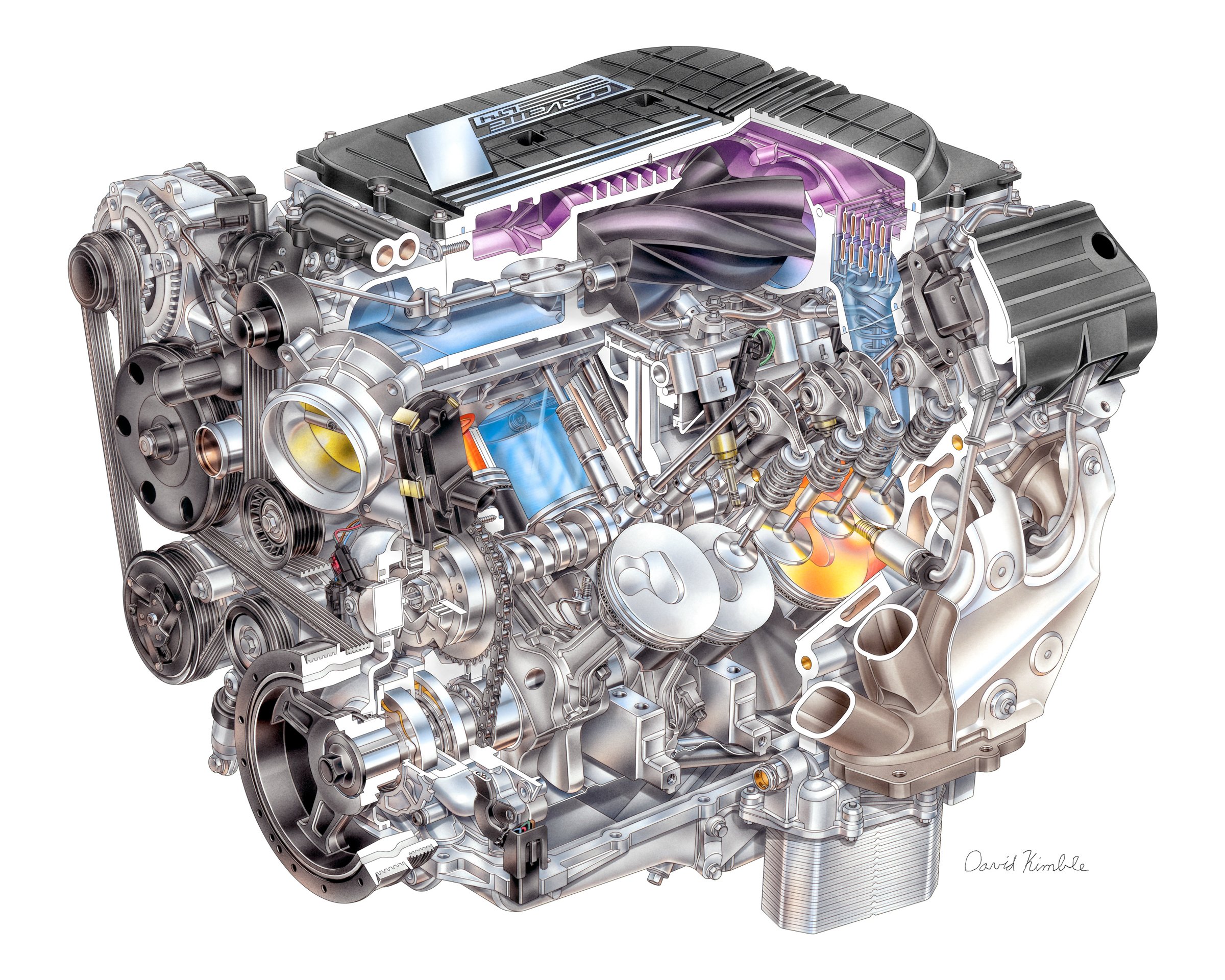
#3 6.6L V-8 L8T Gasoline Engine
Domain Est. 1992
Website: poweredsolutions.gm.com
Key Highlights: The 6.6L V-8 L8T engine boasts an impressive torque of 464 lb-ft perfect for a variety of large-scale engine applications….
#4 LT4 Crate Engines
Domain Est. 1994
Website: chevrolet.com
Key Highlights: Chevy’s LT4 crate engines offer unmatched performance and durability for your project car. Explore engine specs, installation details, and more….
#5 Everything You Want To Know About The GM Gen V / LT Engine
Domain Est. 1995
Website: holley.com
Key Highlights: General Motors’s Gen V LT-series direct-injected engines, the LT1, LT4, LT5 and more are worthy successors to the loved LS engines and the ……
#6 Commercial Trucks, Buses, Engines & Parts
Domain Est. 1998
Website: international.com
Key Highlights: Proud makers of trucks, buses, engines, parts, and history….
#7 Crate Engines
Domain Est. 2007
Website: gmperformancemotor.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 14-day returnsWe have some of the lowest prices on Chevrolet Performance Parts, Chevrolet Performance Engines, and Chevrolet Performance Transmissions. Our large inve…
#8 Innomotics
Domain Est. 2023
Website: innomotics.com
Key Highlights: Innomotics’ motors, generators, converters, motor spindles, geared motors, and drive systems are powerful, resource-efficient, modular, and versatile. See ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Lt Motor

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Lithium Motors (Lt Motor)
As we approach 2026, the market for Lithium Motors (Lt Motor)—a term interpreted here as electric motors powered by lithium-ion battery technology, particularly within the electric vehicle (EV) and sustainable transportation sectors—exhibits several transformative trends shaped by technological innovation, regulatory pressure, and evolving consumer preferences. The following analysis outlines key developments expected to influence Lt Motor’s market position and performance in H2 2026.
-
Accelerated EV Adoption and Infrastructure Expansion
By H2 2026, global electric vehicle penetration is projected to surpass 40% of new car sales in major markets such as China, Europe, and North America. This surge is driven by improved lithium battery energy density, faster charging capabilities, and expanded charging infrastructure. Governments are meeting 2030 climate targets with aggressive EV incentives, directly benefiting manufacturers integrating Lt Motor technology. Demand for high-efficiency, lightweight motors optimized for lithium powertrains will remain strong. -
Advancements in Lithium Motor Efficiency and Integration
Lt Motor systems are expected to feature next-generation silicon-anode lithium batteries and integrated motor-inverter designs, reducing weight and boosting range. By H2 2026, motor efficiency is anticipated to exceed 95%, enabled by advanced rare-earth-free permanent magnet alternatives and AI-driven thermal management. These innovations will lower production costs and improve scalability across vehicle segments—from urban EVs to heavy-duty trucks. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Localized Production
Geopolitical tensions and raw material volatility (e.g., lithium, cobalt, nickel) have prompted manufacturers to regionalize battery and motor production. In H2 2026, companies are increasingly adopting closed-loop recycling and forming strategic partnerships with mining firms to secure lithium supply. North American and European Lt Motor producers are benefiting from local content incentives under policies like the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act, strengthening domestic manufacturing ecosystems. -
Regulatory Tailwinds and Emissions Standards
Stricter global emissions regulations—such as Euro 7 and China’s Phase VI standards—will phase out internal combustion engines in urban fleets by 2030. This regulatory push is accelerating commercial and municipal adoption of Lt Motor-powered vehicles. Additionally, carbon pricing mechanisms and zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) mandates are making lithium-based electric motors the default choice for new vehicle platforms. -
Growth in Adjacent Markets
Beyond automotive, Lt Motor technology is expanding into e-bikes, electric aviation, and industrial automation. In H2 2026, lightweight, high-torque lithium motors are enabling urban air mobility (eVTOL) prototypes and last-mile delivery drones. The convergence of AI, IoT, and predictive maintenance in industrial motors further enhances demand for intelligent Lt Motor systems. -
Consumer Expectations and Brand Differentiation
Consumers in 2026 prioritize sustainability, performance, and total cost of ownership. Brands leveraging Lt Motor technology for superior acceleration, quiet operation, and over-the-air updates are gaining market share. Transparency in battery sourcing and recyclability is becoming a key differentiator, pushing companies toward ethical supply chains and circular economy models.
Conclusion:
By H2 2026, Lithium Motors are poised to dominate the electrified mobility landscape, supported by technological maturity, policy support, and infrastructure readiness. Companies investing in integrated lithium motor systems, sustainable sourcing, and modular designs will lead the market. Challenges remain—particularly in raw material availability and recycling scalability—but the overall trend points to robust growth and mainstream adoption of Lt Motor solutions across global transportation and industrial sectors.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing LT Motors (Quality, IP)
When sourcing Low Tension (LT) motors, overlooking key quality and Ingress Protection (IP) factors can lead to costly failures, downtime, and safety hazards. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Assessment
Many buyers focus solely on price and overlook long-term performance indicators. Choosing suppliers without verifying material quality, manufacturing standards, or certifications (e.g., ISO, IEC, or ISI) can result in motors with poor insulation, substandard windings, or inefficient cooling—leading to premature failure and higher total cost of ownership.
Misunderstanding IP Ratings
A frequent mistake is assuming a higher IP rating is always better. While IP65 offers dust-tight and water-jet protection, it may not be necessary for indoor, climate-controlled environments. Over-specifying increases cost unnecessarily. Conversely, under-specifying—such as using an IP23 motor in a wet or dusty area—exposes the motor to contamination, corrosion, and short circuits.
Ignoring Environmental Conditions
Failing to match motor IP and build quality to the operating environment is a critical error. For example, using standard motors in humid, coastal, or chemical-exposed areas without corrosion-resistant coatings or sealed enclosures accelerates degradation and compromises reliability.
Lack of Supplier Verification
Procuring from unverified or non-accredited suppliers increases the risk of counterfeit or reconditioned motors being passed off as new. Always audit suppliers for traceability, test reports, and compliance with international standards to ensure genuine quality.
Overlooking Thermal and Load Performance
LT motors must handle variable loads and thermal cycles. Selecting motors without reviewing duty cycle specifications, insulation class (e.g., Class F), or temperature rise ratings can result in overheating and insulation breakdown—especially in continuous or high-cycle applications.
Neglecting Maintenance and Serviceability
High IP-rated motors (e.g., IP55) often have sealed designs that complicate maintenance. Procurement decisions should balance environmental protection with ease of servicing, bearing access, and availability of spare parts to minimize downtime.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable, efficient, and safe operation of LT motors across diverse industrial applications.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Lt Motor
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance procedures for Lt Motor, ensuring efficient operations and adherence to regulatory standards. Proper management of logistics and compliance helps mitigate risks, reduce delays, and maintain legal and operational integrity across all transportation and supply chain activities.
Overview of Logistics Operations
Lt Motor’s logistics framework involves the planning, implementation, and control of the movement and storage of goods, services, and related information from origin to destination. Key components include:
- Transportation Management: Coordination of inbound and outbound freight via road, rail, air, or sea.
- Warehousing & Distribution: Secure storage and timely dispatch of goods through strategically located facilities.
- Fleet Management: Maintenance, tracking, and optimization of motor vehicles used in transportation.
- Inventory Control: Real-time monitoring of stock levels to prevent shortages or overstocking.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
To operate legally and safely, Lt Motor must comply with national and international regulations. Key compliance areas include:
Vehicle & Driver Regulations
- Licensing and Permits: Ensure all drivers hold valid commercial driving licenses (CDLs) and necessary permits for operating vehicles.
- Vehicle Inspections: Conduct regular safety and emissions inspections as mandated by local transportation authorities.
- Hours of Service (HOS): Adhere to driver working hour limits to prevent fatigue-related accidents.
Cargo & Transportation Compliance
- Weight and Dimension Limits: Observe legal load restrictions to avoid fines and road hazards.
- Hazardous Materials Handling: If transporting dangerous goods, comply with ADR (European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road) or equivalent local standards.
- Cargo Securing: Follow ISO and national standards for load restraint to ensure safety during transit.
Environmental & Safety Standards
- Emissions Control: Maintain vehicles to meet Euro emission standards and support sustainability initiatives.
- Waste Management: Proper disposal of used parts, oils, and packaging materials in accordance with environmental laws.
- Accident Reporting: Implement protocols for reporting and investigating incidents as required by law.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Accurate documentation is critical for legal compliance and operational transparency. Required records include:
- Driver logs and duty status reports
- Vehicle maintenance and inspection records
- Transport manifests and delivery receipts
- Insurance policies and certificates of coverage
- Import/export documentation (if applicable)
All documents must be securely stored and retained for the legally mandated duration (typically 3–5 years).
International Trade Considerations
For cross-border operations, Lt Motor must comply with additional requirements:
- Customs Clearance: Submit accurate declarations, tariffs, and required paperwork (e.g., commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin).
- Import/Export Licenses: Obtain necessary permits for restricted or regulated goods.
- Trade Agreements: Leverage preferential tariffs under applicable free trade agreements (e.g., EU, USMCA).
Training & Internal Audits
- Staff Training: Regularly train employees on compliance, safety procedures, and updated regulations.
- Internal Audits: Conduct periodic reviews of logistics operations to identify gaps and ensure adherence to policies and legal standards.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and strict compliance are foundational to the success and reputation of Lt Motor. By following this guide, the organization can ensure smooth operations, avoid penalties, and maintain high standards of safety and service. Regular updates to policies and ongoing staff education are recommended to adapt to evolving regulations and industry best practices.
Conclusion for Sourcing LT Motor:
In conclusion, sourcing a low-tension (LT) motor requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, reliability, energy efficiency, supplier credibility, and total cost of ownership. Selecting the right LT motor involves aligning motor specifications—such as power rating, speed, insulation class, protection level (IP rating), and duty cycle—with the specific needs of the application. Prioritizing energy-efficient models (e.g., IE3 or IE4 standards) not only reduces operational costs but also supports sustainability goals. Additionally, choosing a reputable supplier with proven after-sales support, warranty terms, and timely delivery ensures long-term performance and minimal downtime. A well-structured sourcing strategy ultimately leads to improved system reliability, reduced maintenance costs, and optimized operational efficiency across industrial and commercial applications.