The global whiteboard and interactive display market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for collaborative tools in education, corporate, and remote work environments. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global interactive whiteboard market was valued at USD 6.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research reported that the broader digital signage market—which includes smart boards and collaborative display solutions—is expected to expand at a CAGR of 7.3% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by digital transformation initiatives and hybrid work adoption. As demand for dynamic, user-friendly presentation tools rises, loom boards—hybrid solutions combining tactile weaving elements with visual planning capabilities—have emerged as innovative tools in creative and strategic workflows. This growing market landscape has led to an influx of manufacturers specializing in high-quality, durable loom boards tailored for educators, designers, and project managers. Below, we highlight the top 8 loom board manufacturers leading the charge in innovation, design, and functionality.
Top 8 Loom Board Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Weaving Looms
Domain Est. 2002
Website: kromski.com
Key Highlights: WELCOME TO THE OFFICIAL WEBSITE OF KROMSKI & SONS … Built-In Warping Board; Metal Ratchet and Pawl tension mechanisms; 5 year Manufacturer Warranty ……
#2 HELLO! LOOM
Domain Est. 2018
Website: helloloom.com
Key Highlights: Hello! Looms are portable laser cut looms in a variety of sizes for quick, easy, and fun weaving. Weave with new textures and patterns on tablet sized loom, …Missing: board manu…
#3 Manuals & Software Downloads
Domain Est. 2019
Website: avllooms.com
Key Highlights: AVLDrive is loom driver software linked to specific Compu-Dobby versions, and it comes in three variants: Version 5 for Compu-Dobby 5 and Little Weaver v2….
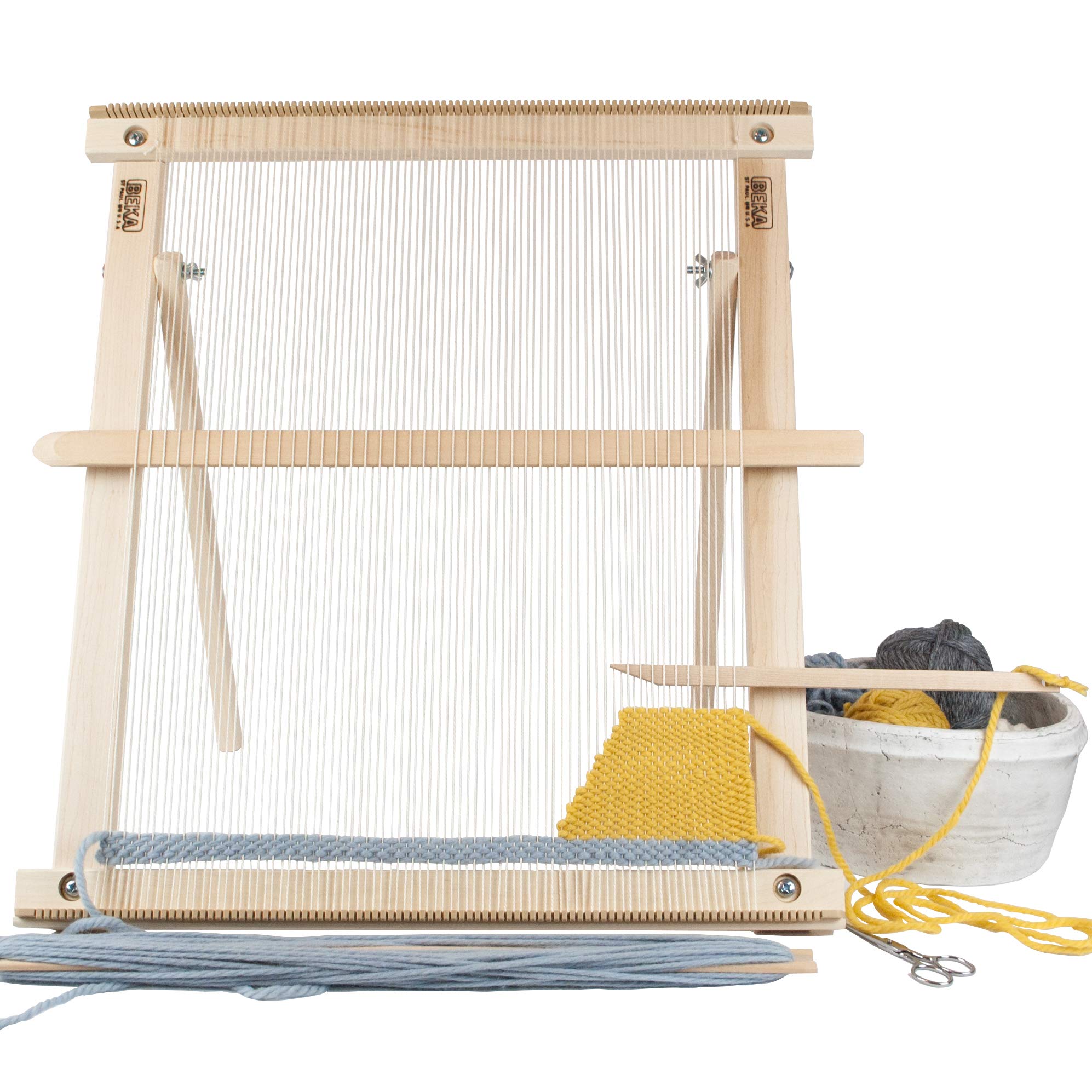
#4 Beka Looms & Crafts
Domain Est. 1998
Website: bekainc.com
Key Highlights: Tools used in fiber crafts — weaving, knitting, etc. This is the category that got us started back in 1973. We offer looms for both beginning and advanced ……
#5 Knitting Looms & Boards
Domain Est. 2001
Website: knittingboard.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $80 · 30-day returnsExplore our wide selection of knitting looms and unlock endless possibilities with our free knitting patterns—from simple stitches to intric…
#6 Instructions & Tutorials
Domain Est. 2012
Website: rainbowloom.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $35 · 30-day returns…
#7 Jewel Loom® Official Store
Domain Est. 2013
Website: jewelloom.com
Key Highlights: 6-day delivery 14-day returnsOur looms are designed for ease of use, precision, and durability, enabling you to craft beautiful, intricate beadwork with confidence….
#8 Ashford Wheels and Looms
Website: ashford.co.nz
Key Highlights: Ashford blending board with some rolags being made on it and some off to the side ashford inkle loom and inklette loom with weaving on. Made in New Zealand ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Loom Board

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Loom Board
As we approach 2026, the market for enterprise collaboration and project management platforms like Loom Board (assuming it refers to a visual collaboration tool, possibly integrated with or inspired by Loom’s video messaging, or a whiteboarding solution) is poised for significant transformation. Driven by evolving work models, AI integration, and heightened user expectations, several key trends will shape its competitive landscape and strategic direction.
1. Deep Integration of AI and Automation
By 2026, AI will no longer be a value-add feature but a core expectation. Loom Board will likely leverage AI to:
– Automate workflow creation based on team behavior and project goals.
– Deliver intelligent summarization of visual boards, turning whiteboard sessions into structured action items and documentation.
– Enable predictive insights, such as identifying project bottlenecks or suggesting optimal task routing.
– Support generative design, allowing users to create wireframes, diagrams, or content templates via natural language prompts.
2. Hybrid and Async-First Collaboration Dominance
With hybrid and remote work becoming standard, tools must support asynchronous collaboration seamlessly. Loom Board will need to:
– Enhance contextual continuity, allowing team members to catch up quickly via embedded video summaries, threaded comments, and playback timelines.
– Integrate non-linear participation, enabling users to contribute at their own pace with clear indicators of progress and feedback.
– Offer time-zone-aware notifications and updates to reduce friction across global teams.
3. Convergence with Communication Platforms
The boundary between collaboration boards and communication tools (like Slack, Teams, or Loom video messages) will blur. Loom Board’s success will depend on:
– Tighter integrations with video messaging, enabling instant video annotations on boards or embedding clips directly into workflows.
– Unified activity streams that surface board updates within chat platforms, reducing context switching.
– Embeddable, real-time collaborative canvases within emails, documents, or project trackers.
4. Focus on User Experience and Accessibility
As competition intensifies (with players like Miro, FigJam, and Microsoft Loop), UX will be a key differentiator. Expect:
– Simplified onboarding with AI-guided tours and adaptive interfaces.
– Enhanced accessibility, including screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation, and inclusive design for neurodiverse users.
– Mobile-first capabilities with gesture-based editing and offline functionality.
5. Data Security, Compliance, and Governance
Enterprise adoption will demand robust security. Loom Board must:
– Offer granular permissions, audit trails, and compliance with standards like SOC 2, GDPR, and HIPAA.
– Provide admin dashboards for usage analytics, license management, and data retention policies.
– Support on-premise or private cloud deployment options for highly regulated industries.
6. Industry-Specific Solutions and Vertical Expansion
Generic tools will face pressure to specialize. Loom Board may see growth by:
– Launching pre-built templates and workflows for sectors like product management, education, agile development, or customer journey mapping.
– Partnering with domain-specific software (e.g., Jira, Salesforce, Notion) to embed board functionality directly into vertical workflows.
Strategic Implications for Loom Board:
To thrive in 2026, Loom Board must evolve from a visual canvas into an intelligent, context-aware collaboration hub. Prioritizing AI-driven automation, seamless async workflows, and deep ecosystem integration will be critical. Moreover, balancing innovation with enterprise-grade security and usability will determine its ability to capture market share in an increasingly crowded and sophisticated landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Loom Boards: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing Loom Boards—modular textile looms often used in prototyping, education, or craft—can introduce several risks, particularly related to product quality and intellectual property (IP). Avoiding these pitfalls is essential for businesses, educators, and developers relying on consistent performance and legal compliance.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Standards
Loom Boards made from low-grade wood, plastic, or metal may warp, crack, or degrade quickly with regular use. Sourcing from suppliers without strict material specifications can result in boards that lack durability, especially in educational or industrial environments.
Poor Precision in Manufacturing
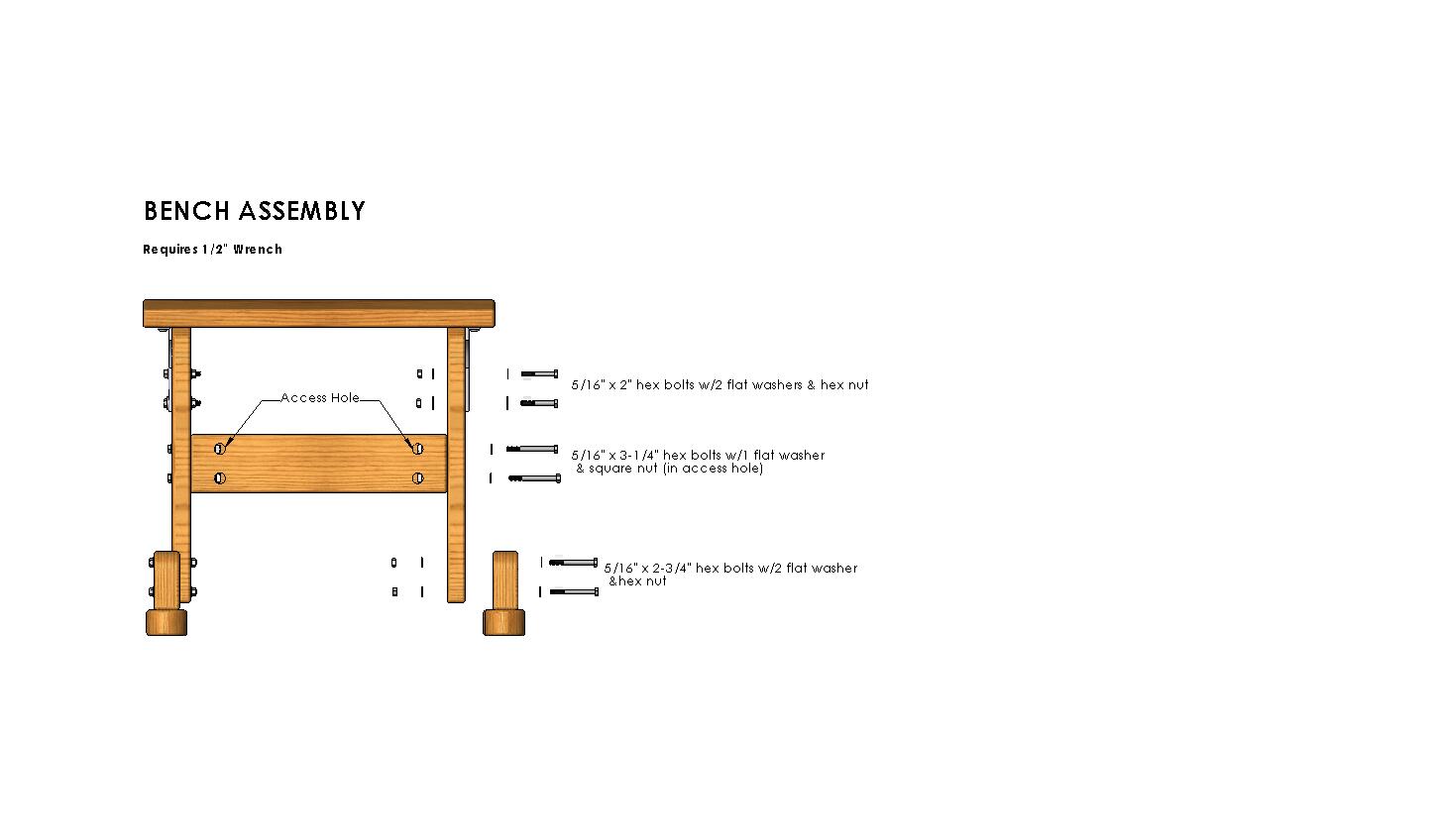
The functionality of a Loom Board depends on accurately spaced pegs, slots, or connectors. Inconsistent manufacturing tolerances can lead to misaligned weaving patterns, difficulty in tension control, or incompatibility with accessories—significantly impacting user experience.
Lack of Standardization Across Batches
When sourcing from multiple manufacturers or over extended periods, differences in design or dimensions between production runs can disrupt workflows. This is particularly problematic for institutions or developers creating curriculum or software integrations based on specific board dimensions.
Insufficient Testing and Quality Control
Suppliers may skip rigorous durability, stress, or user testing. Without documented quality assurance processes, buyers risk receiving products that fail under normal operating conditions or pose safety hazards (e.g., splintering wood or sharp edges).
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Inadvertent Use of Patented Designs
Some Loom Board configurations, especially those with unique modular or interlocking features, may be protected by utility or design patents. Sourcing from manufacturers who replicate patented elements without licensing can expose the buyer to infringement claims, even if unintentional.
Trademark and Branding Conflicts
Using names, logos, or branding similar to established Loom Board products (e.g., “Loominary” or “Weavix”) may lead to trademark disputes. Buyers should verify that sourced products do not infringe on existing brand identities.
Unclear Ownership of Custom Designs
When commissioning custom Loom Boards, failure to define IP ownership in contracts can result in disputes. Suppliers might claim rights to design modifications or tooling, limiting the buyer’s ability to reproduce or modify the product elsewhere.
Use of Open-Source Designs Without Compliance
Some Loom Board designs are shared under open-source hardware licenses (e.g., CERN OHL or TAPR OHL). Sourcing based on these designs without adhering to license terms—such as attribution or sharing modifications—can lead to legal and reputational risks.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including site audits and sample testing.
- Require material certifications and quality control documentation.
- Perform IP searches and consult legal counsel before mass production.
- Use clear contracts that define design ownership, specifications, and compliance responsibilities.
- Verify open-source license terms and ensure adherence when applicable.
Avoiding these common pitfalls ensures reliable product performance and protects against legal exposure when sourcing Loom Boards.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Loom Board
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the manufacturing, distribution, and sale of Loom Board—a hypothetical smart loom device for textile production. Adherence to these guidelines ensures smooth operations, regulatory compliance, and customer satisfaction.
Product Classification & Regulatory Requirements
Determine the correct product classification based on international and regional standards. Loom Board, as an electronic textile manufacturing device, may fall under industrial machinery (HS Code 8444–8448) and electronic equipment (HS Code 85). Key regulatory standards include:
– CE Marking (EU): Comply with Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive (2014/30/EU), and Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU).
– FCC Certification (USA): Ensure electromagnetic interference (EMI) compliance under Part 15 for digital devices.
– RoHS & REACH Compliance: Restrict hazardous substances (RoHS) and disclose chemical content (REACH) in the EU.
– UL/CSA Certification (North America): Safety certification for electrical components.
Export & Import Documentation
Ensure accurate and complete documentation for international shipments:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB)
– Certificate of Origin
– Export Declaration (e.g., AES in the U.S.)
– Import License (if required by destination country)
Verify tariff codes and duty rates using the destination country’s customs database to avoid delays and overpayment.
Packaging & Labeling Standards
Design packaging to protect the Loom Board during transit while meeting international requirements:
– Use anti-static and shock-absorbent materials for electronic components.
– Clearly label packages with:
– Product name and model number
– Weight and dimensions
– Handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”)
– Regulatory marks (CE, FCC, etc.)
– Barcodes for inventory and tracking
– Include multilingual user manuals and safety warnings where applicable.
Shipping & Distribution Logistics
Select reliable logistics partners with experience in handling electronic machinery:
– Use tracked and insured shipping methods (air freight for urgent deliveries, sea freight for bulk).
– Partner with 3PL (third-party logistics) providers in key markets for faster local fulfillment.
– Implement inventory management systems to monitor stock levels across warehouses.
– Comply with Incoterms® 2020 (e.g., FOB, DDP) to define responsibilities between buyer and seller.
Customs Clearance & Duties
Ensure timely customs clearance by:
– Pre-submitting electronic documentation via customs portals.
– Working with licensed customs brokers in destination countries.
– Paying applicable import duties, VAT, or GST. Use duty drawback programs where eligible.
– Preparing for customs inspections; maintain detailed product specifications and compliance certificates.
Environmental & Sustainability Compliance
Adhere to environmental regulations throughout the product lifecycle:
– Implement WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) compliance for take-back and recycling in the EU.
– Follow local e-waste regulations in other markets (e.g., EPA guidelines in the U.S.).
– Minimize packaging waste and use recyclable materials.
– Document carbon footprint for sustainability reporting.
Data Privacy & Cybersecurity (if applicable)
If Loom Board includes connected features (IoT, cloud integration):
– Comply with GDPR (EU), CCPA (California), or other data protection laws.
– Secure user data transmission and storage (encryption, access controls).
– Provide clear privacy policies and obtain user consent.
– Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
Recordkeeping & Audit Readiness
Maintain comprehensive records for at least 5–7 years:
– Compliance certificates (CE, FCC, RoHS, etc.)
– Test reports and risk assessments
– Shipping and customs documentation
– Supplier agreements and component traceability
– Customer communications and warranty claims
Prepare for internal or external audits by regulatory bodies or certification agencies.
Ongoing Compliance Monitoring
Regulations evolve; implement a compliance monitoring system:
– Subscribe to regulatory updates from trade associations and government agencies.
– Conduct annual compliance reviews.
– Train staff on logistics and compliance procedures.
– Update technical documentation and labels as needed.
By following this guide, Loom Board manufacturers and distributors can ensure legal compliance, reduce operational risks, and deliver products efficiently to global markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing Loom Board:
Sourcing loom board requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, and reliability. After evaluating various suppliers, materials, and manufacturing methods, it is clear that selecting the right loom board involves careful consideration of factors such as dimensional accuracy, durability, material composition (typically high-grade plywood or MDF), and compatibility with specific weaving requirements. Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers—whether local or international—can ensure consistent quality and timely delivery. Additionally, sustainability and ethical sourcing practices are becoming increasingly important in material selection. In conclusion, a successful sourcing strategy for loom boards combines thorough supplier vetting, cost-efficiency, and a focus on long-term performance to support high-quality textile production.