The global logarithmic amplifier market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for precision signal processing across industries such as telecommunications, healthcare, aerospace, and defense. According to Mordor Intelligence, the analog amplifier market—which includes logarithmic amplifiers—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6% during the forecast period 2023–2028, fueled by advancements in RF and data acquisition systems. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights the rising integration of high-performance amplifiers in test and measurement equipment, contributing to a robust expansion of the niche logarithmic amplifier segment. As system complexity grows and applications require wide dynamic range signal compression, the need for reliable logarithmic amplification solutions has intensified. This demand has positioned several key manufacturers at the forefront of innovation, setting the stage for the following list of the top eight logarithmic amplifier manufacturers shaping the industry landscape.
Top 8 Logarithmic Amplifier Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Macom
Domain Est. 1991
Website: macom.com
Key Highlights: MACOM designs and manufactures high-performance semiconductor products for the Telecommunications, Industrial and Defense, and Data Center industries….
#2 Logarithmic amplifiers product selection
Domain Est. 1986
Website: ti.com
Key Highlights: Select from TI’s Logarithmic amplifiers family of devices. Logarithmic amplifiers parameters, data sheets, and design resources….
#3 Integrated DC Logarithmic Amplifiers
Domain Est. 1990
Website: analog.com
Key Highlights: The DC log amp continues to be a very powerful, cost-effective solution for compressing wide-dynamic-range sensor signals….
#4 Logarithmic Amplifiers Scale Input Signals
Domain Est. 1995
Website: digikey.com
Key Highlights: Log amps are non-linear, analog amplifiers that produce an output that is the logarithm of the input signal or the signal’s envelope….
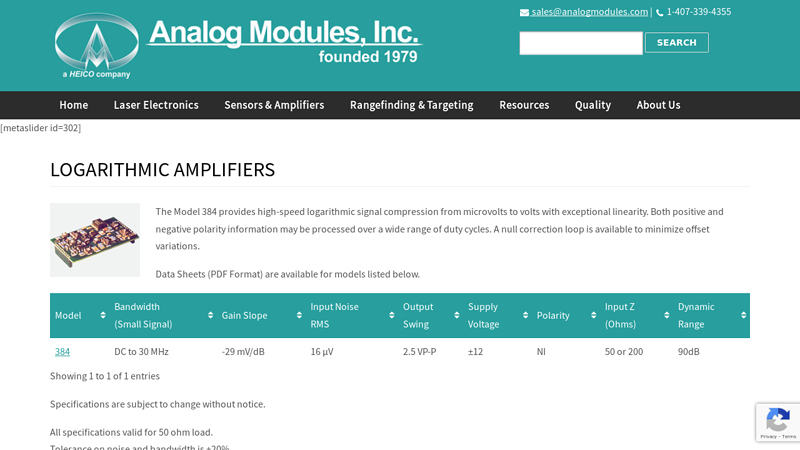
#5 Logarithmic Amplifier
Domain Est. 1997
Website: analogmodules.com
Key Highlights: The Model 384 provides high-speed logarithmic signal compression from microvolts to volts with exceptional linearity….
#6 Logarithmic Amplifiers
Domain Est. 2013
Website: 3peak.com
Key Highlights: 3PEAK’s logarithmic amplifiers convert current signals across 140dB into precise voltage signals, delivering accurate logarithmic signal processing within ……
#7 AR RF/Microwave Instrumentation
Domain Est. 2014
Website: ar.ametek-cts.com
Key Highlights: At AR RF/Microwave Instrumentation, we offer comprehensive RF test solutions designed to meet the most rigorous demands of EMC testing and high-power amplifier ……
#8 Logarithmic Amplifiers (Log Amps)
Domain Est. 2021
Website: rf.uec-corp.com
Key Highlights: Find the right logarithmic amplifier for your system among our collection of DLVAs and SDLVAs. Click here to learn more….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Logarithmic Amplifier

2026 Market Trends for Logarithmic Amplifiers
The logarithmic amplifier (log amp) market is poised for notable evolution by 2026, driven by advancements in high-frequency communication, industrial automation, and test and measurement technologies. While niche compared to general-purpose amplifiers, log amps are gaining renewed importance due to their unique ability to handle wide dynamic range signals, particularly in emerging high-speed and precision applications.
Increasing Demand in 5G and Beyond-5G Infrastructure
One of the primary drivers shaping the 2026 landscape is the continued rollout and densification of 5G networks, with early developments toward 6G research. Logarithmic amplifiers play a critical role in RF power detection and automatic gain control (AGC) circuits for base stations and small cells. Their ability to compress large input signal ranges into manageable output voltages makes them indispensable for ensuring signal integrity in millimeter-wave (mmWave) and massive MIMO systems. By 2026, demand is expected to rise significantly, particularly for high-bandwidth log amps capable of operating beyond 10 GHz, as telecom equipment manufacturers seek to improve power efficiency and dynamic range performance.
Growth in Industrial and Automotive Sensing Applications
The industrial automation and automotive sectors are adopting log amps for precision sensing in harsh environments. In LiDAR systems—especially for autonomous vehicles and robotics—logarithmic amplifiers are used to process return signals that vary dramatically in strength based on target distance and reflectivity. As safety and autonomy requirements increase, the need for reliable, high-dynamic-range signal conditioning grows. Additionally, industrial process control systems are integrating log amps in optical and temperature sensing, where input signals can span several orders of magnitude. By 2026, this trend is expected to expand, supported by the miniaturization of log amp ICs and improved temperature stability.
Advancements in Integrated Circuit Design and Performance
Technological improvements in semiconductor processes, particularly SiGe (Silicon-Germanium) and advanced CMOS nodes, are enabling higher performance log amplifiers with lower noise, wider bandwidth, and improved linearity. Vendors are focusing on integrating log amps with analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) and digital interfaces to offer system-on-chip (SoC) solutions that reduce board space and design complexity. The push toward energy-efficient designs is also influencing product development, with low-power log amps becoming essential for battery-operated and portable test equipment. By 2026, integration and power optimization will be key differentiators in the competitive landscape.
Expansion in Test and Measurement Equipment
High-precision test instruments such as spectrum analyzers, network analyzers, and oscilloscopes rely on logarithmic amplifiers for accurate signal level measurement across wide dynamic ranges. As electronic systems become faster and more complex, the demand for test equipment capable of handling multi-gigahertz signals with high resolution increases. Log amps remain a core component in these systems. The trend toward modular and software-defined instruments is also driving demand for compact, high-performance log amp modules. Market growth in this segment is expected to remain steady through 2026, supported by R&D investments in electronics and telecommunications.
Regional Market Dynamics and Competitive Landscape
Geographically, North America and Asia-Pacific are expected to lead log amplifier adoption. The U.S. and China are investing heavily in 5G infrastructure, defense electronics, and autonomous technologies—all key application areas. Japan and South Korea are also strong markets due to their advanced semiconductor and consumer electronics industries. Key players such as Analog Devices, Texas Instruments, and Maxim Integrated (now part of ADI) continue to innovate and consolidate their market positions. By 2026, competition will likely intensify around performance specifications, integration levels, and support for emerging standards.
In conclusion, the 2026 logarithmic amplifier market will be shaped by the convergence of communication technology, sensing innovation, and semiconductor advancement. While the overall market size remains specialized, its strategic importance in high-performance systems ensures sustained growth and technological evolution.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Logarithmic Amplifiers (Quality and IP)
Sourcing logarithmic amplifiers requires careful evaluation to ensure performance, reliability, and legal compliance. Overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to design failures, supply chain disruptions, or legal exposure. Below are critical pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Verification of Performance Specifications
Logarithmic amplifiers are highly sensitive to input signal ranges, temperature variations, and process tolerances. A common mistake is accepting manufacturer datasheet claims without independent verification or understanding test conditions. Parameters such as log conformance error, dynamic range, temperature drift, and response time must be validated under real-world operating conditions. Relying solely on typical values—rather than min/max specifications—can result in inconsistent system performance.
Ignoring Long-Term Supply and Obsolescence Risks
Logarithmic amplifiers are often used in niche applications (e.g., medical instrumentation, test equipment, or industrial sensing), leading to limited production volumes. Sourcing from vendors without a strong track record in long-term availability can result in unexpected obsolescence. Always evaluate the manufacturer’s product lifecycle policy, availability of last-time buys, and potential for second sourcing. Lack of a clear obsolescence plan can jeopardize product sustainability and after-sales support.
Overlooking IP Rights and Licensing Restrictions
Some logarithmic amplifier designs incorporate proprietary architectures or calibration algorithms protected by patents or trade secrets. Sourcing from lesser-known or unverified suppliers—especially through third-party distributors—risks acquiring counterfeit or IP-infringing components. Always confirm the supplier’s legitimacy, verify authorized distribution channels, and review any end-use restrictions. Using IP-protected technology without proper licensing may expose your organization to legal liability or product recalls.
Failure to Assess Process and Calibration Consistency
High-precision logarithmic amplifiers often require factory trimming or calibration to achieve specified accuracy. A key pitfall is not confirming whether the component is individually tested and calibrated, and if the process is documented and repeatable. Inconsistent calibration across batches can introduce significant measurement errors in critical applications. Request process control documentation and statistical test data to ensure consistency.
Underestimating the Impact of Packaging and Thermal Effects
Logarithmic amplifiers are sensitive to thermal gradients and package parasitics, which can affect logarithmic accuracy and stability. Choosing a package type without considering thermal resistance, PCB layout compatibility, or long-term mechanical reliability (e.g., moisture resistance, CTE mismatch) may degrade performance. Always review the thermal performance characteristics and ensure the package is suitable for the target environment (industrial, automotive, etc.).
Assuming Drop-in Replacements Are Interchangeable
Due to subtle differences in transfer functions, bandwidth, or power requirements, logarithmic amplifiers are rarely true drop-in replacements. Assuming compatibility based on pinout alone can lead to system-level issues such as incorrect gain, saturation, or instability. Always perform thorough bench validation when substituting parts, even from the same manufacturer.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, engineering and procurement teams can reduce risk, ensure compliance, and maintain the performance integrity of systems relying on logarithmic amplification.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Logarithmic Amplifier
This guide outlines the key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the handling, transportation, storage, and use of logarithmic amplifiers, ensuring adherence to international standards and regulatory frameworks.
Product Classification and Documentation
Logarithmic amplifiers are typically classified under Harmonized System (HS) Code 8542.39 (Other electronic integrated circuits) or 8543.70 (Electrical apparatus for line transmission). Accurate classification is essential for customs clearance and duty assessment. Required documentation includes commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and technical datasheets specifying electrical parameters, RoHS compliance, and country of manufacture.
Export Controls and Regulatory Compliance
Logarithmic amplifiers may be subject to export control regulations due to potential dual-use applications in defense or telecommunications. Confirm compliance with relevant regulations such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or the EU Dual-Use Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2021/821). Determine the appropriate Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) — often EAR99 if no specific controls apply. For products incorporating encryption or high-frequency components, additional scrutiny may be required.
Environmental and Safety Standards
Ensure logarithmic amplifiers comply with environmental directives including:
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Limits the use of lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous materials.
– REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals): Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
– WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment): Mandates proper end-of-life disposal and recycling.
Products must also meet safety standards such as IEC/UL 62368-1 for audio/video and information technology equipment, depending on the application context.
Packaging and Storage Conditions
Package logarithmic amplifiers using anti-static materials to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage. Use moisture barrier bags (MBB) if devices are moisture-sensitive (MSL rating per J-STD-020). Store in a controlled environment with temperatures between 15°C and 30°C and relative humidity of 30%–60%. Avoid exposure to corrosive atmospheres or direct sunlight.
Transportation Requirements
Ship logarithmic amplifiers via air, sea, or ground using ESD-safe containers and humidity indicators where applicable. For air freight, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if batteries or other regulated components are included in associated systems. Clearly label packages with ESD warnings, handling instructions, and proper shipping names.
Import Regulations and Duties
Verify import requirements in the destination country, including conformity assessment procedures (e.g., CE in the EU, FCC in the U.S., KC in South Korea). Some countries may require additional product certification or local representative registration. Duties and Value Added Tax (VAT) vary by jurisdiction; leverage free trade agreements where applicable to reduce tariffs.
End-of-Life and Recycling Compliance
Ensure take-back and recycling processes comply with local WEEE regulations. Provide customers with information on proper disposal and offer return programs where legally required. Maintain records of recycling partners and disposal certifications for audit purposes.
Recordkeeping and Audit Readiness
Maintain detailed records of compliance documentation, shipping manifests, export licenses (if applicable), and test certifications for a minimum of five years. Regular internal audits should verify ongoing compliance with environmental, safety, and trade regulations to prepare for potential regulatory inspections.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Logarithmic Amplifier:
Sourcing a logarithmic amplifier requires careful consideration of application requirements, performance specifications, and environmental factors. Key parameters such as dynamic range, accuracy, response speed, temperature stability, and power supply constraints must align with the intended use—whether in RF power measurement, audio processing, medical instrumentation, or industrial control systems. Both discrete designs using operational amplifiers and dedicated integrated logarithmic amplifiers offer trade-offs in cost, complexity, and performance.
Integrated logarithmic amplifier ICs (such as the AD8307, LOG114, or LTC1966) are often preferred for their reliability, compact footprint, and consistent logarithmic response, especially in high-frequency or precision applications. When sourcing, it is essential to evaluate availability, manufacturer support, longevity, and compliance with industry standards.
Ultimately, the selection process should balance technical performance with supply chain reliability. Engaging with reputable suppliers, reviewing datasheets thoroughly, and considering future scalability will ensure a robust and sustainable solution. Proper sourcing not only enhances system performance but also reduces long-term maintenance and replacement costs.