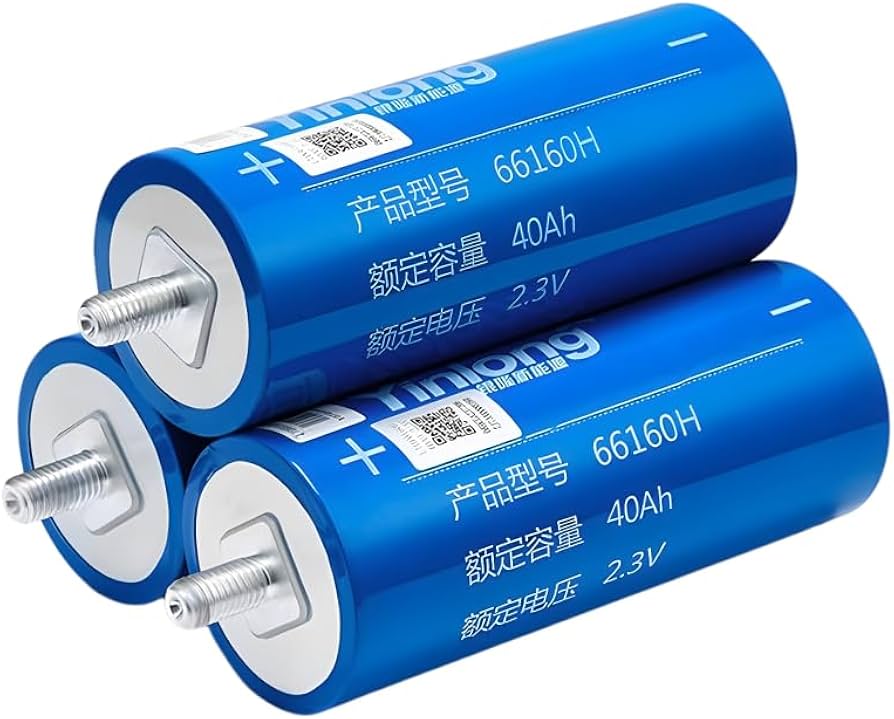
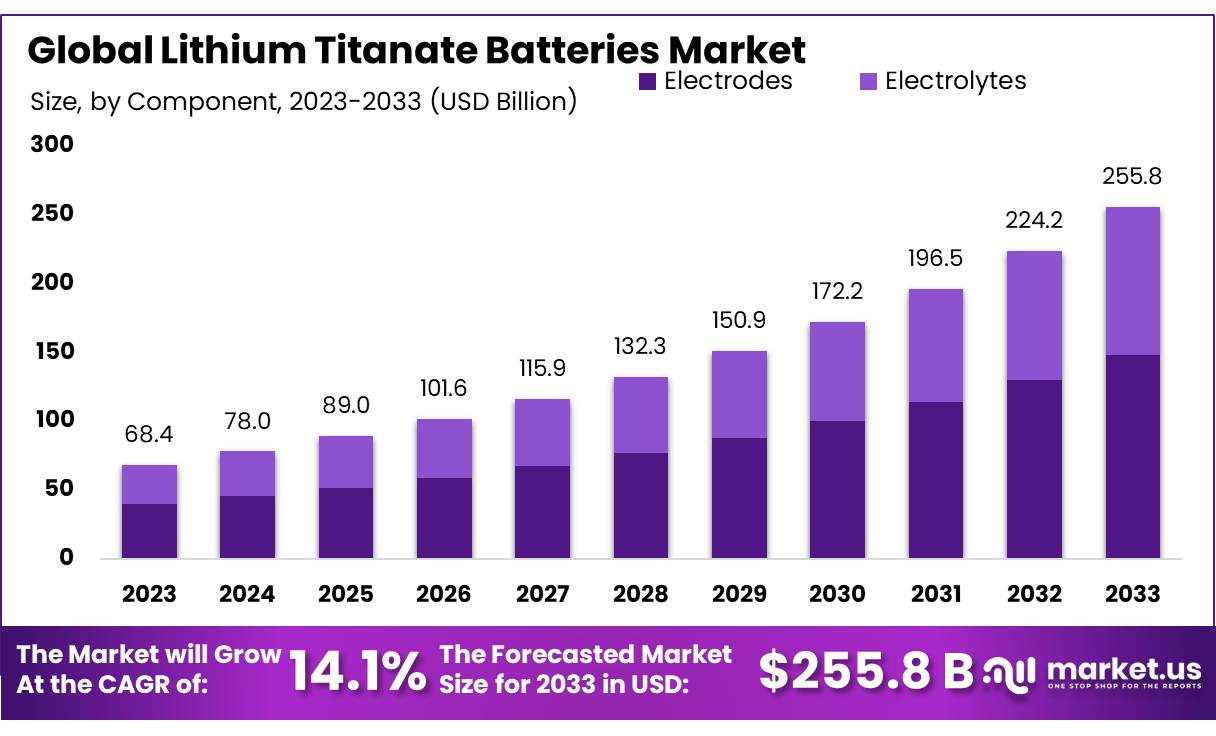
The global lithium titanate oxide (LTO) battery market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for fast-charging, long-cycle-life energy storage solutions in electric vehicles, grid storage, and industrial applications. According to Grand View Research, the global LTO battery market was valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the technology’s superior safety, exceptional thermal stability, and ability to operate efficiently in extreme temperatures compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. As industries prioritize reliability and durability, manufacturers specializing in LTO chemistry are gaining strategic importance. Based on market presence, production capacity, technological innovation, and global reach, the following five companies have emerged as leaders in the lithium titanate battery space.
Top 5 Lithium Titanate Battery Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Lithium Titanate Battery Management SystemAltairnano
Domain Est. 2002
Website: altairnano.com
Key Highlights: Altairnano offers a battery management system for electric grids, heavy-duty vehicles, and transportation, incorporating nano lithium titanate (nLTO) cells….
#2 Lithium Titanate Battery
Domain Est. 2021
Website: ecolithiumbattery.com
Key Highlights: The lithium titanate battery have big advantage in low temperature performance(-50℃), only need 6-15 minutes full-charge time), but 39000 times lifespan….
#3 Yinlong LTO Batteries
Website: yinlong.energy
Key Highlights: Advantages of Lithium-Titanate-Oxide Batteries Yinlong lithium-titanate-oxide batteries boast an expansive operating temperature range from -40°C to +60°C….
#4 Top 100 Lithium Titanate (LTO) Battery Companies in 2025
Domain Est. 2022
Website: ensun.io
Key Highlights: Discover all relevant Lithium Titanate (LTO) Battery Companies worldwide, including Altairnano Inc. and Livent….
#5 Best Lithium Titanate Battery
Domain Est. 2018
Website: lithium-titanate-battery.com
Key Highlights: The Lithium Titanate Battery (LTO) is characterized by fast charge, extended battery life, extraordinary safety and wider operating temperature….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Lithium Titanate Battery

H2. 2026 Market Trends for Lithium Titanate (LTO) Batteries
As the global energy storage landscape evolves in anticipation of 2026, Lithium Titanate Oxide (LTO) batteries are emerging as a niche but strategically significant player in specific high-performance applications. While traditional lithium-ion chemistries like NMC and LFP dominate the broader battery market, LTO batteries are carving out a distinct position due to their unique combination of safety, longevity, and rapid charge capabilities. The 2026 market trends for LTO batteries reflect a mix of technological maturation, targeted deployment, and growing demand in specialized sectors.
1. Surge in High-Reliability and Safety-Critical Applications
LTO batteries are gaining traction in industries where safety, reliability, and long cycle life are paramount. By 2026, markets such as public transportation (especially electric buses), grid-level energy storage, and industrial backup systems are increasingly adopting LTO batteries due to their exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal runaway. This is especially relevant in regions with stringent safety regulations, such as the European Union and parts of East Asia.
2. Expansion in Fast-Charging Infrastructure
One of the most compelling attributes of LTO batteries—ultra-fast charging (some systems charge in under 10 minutes)—positions them as ideal candidates for next-generation charging infrastructure. Forecast models for 2026 indicate rising integration of LTO-based energy storage in fast-charging stations for electric vehicles (EVs), where they serve as buffer storage to reduce grid strain during peak demand. This trend is supported by public and private investments in urban mobility and smart grid development.
3. Growth in Niche Electric Mobility Segments
While LTO’s lower energy density makes it less suitable for long-range passenger EVs, it is finding strong adoption in niche electric mobility applications. By 2026, manufacturers of electric buses, shuttle vehicles, last-mile delivery fleets, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) in logistics and warehousing are increasingly incorporating LTO batteries to capitalize on their durability and rapid recharge cycles. These applications benefit from frequent, short-duration operations where downtime for charging is minimized.
4. Advancements in Hybrid Battery Systems
A key innovation shaping the 2026 LTO market is the development of hybrid battery systems that pair LTO with high-energy-density chemistries (e.g., NMC or LFP). In such configurations, LTO handles peak power demands and regenerative braking, thereby extending the life of the primary battery and improving overall system efficiency. This hybrid approach is particularly attractive in heavy-duty transport and renewable energy integration, where performance and lifecycle costs are critical.
5. Cost Reduction and Supply Chain Improvements
Historically, the high cost of LTO batteries—driven by raw material (titanium) pricing and lower production scale—has limited widespread adoption. However, by 2026, improved manufacturing processes, economies of scale, and advancements in titanium sourcing (including recycling and alternative precursor materials) are beginning to lower costs. While LTO remains more expensive per kWh than LFP or NMC, its total cost of ownership (TCO) is becoming more competitive due to its 15,000–20,000+ cycle life.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, led by China and Japan, remains the dominant region for LTO battery production and deployment. Chinese manufacturers such as CATL and Gotion High-Tech have expanded LTO production lines, while Japanese firms like Toshiba (with its SCiB™ technology) continue to innovate. In North America and Europe, adoption is growing more slowly but is accelerating in public transit and critical infrastructure projects supported by green energy policies and funding.
7. Sustainability and Circular Economy Considerations
With increasing focus on battery sustainability, LTO’s long lifespan and inherent safety reduce the frequency of replacement and lower environmental impact over time. By 2026, LTO is being highlighted in lifecycle assessments (LCAs) as a sustainable option for applications where longevity outweighs energy density requirements. Additionally, recyclability of titanium-based anodes is drawing interest from circular economy initiatives.
Conclusion
In 2026, the Lithium Titanate battery market is not expected to displace mainstream lithium-ion technologies but will solidify its role as a premium solution for safety-critical, high-cycle, and fast-charging applications. Strategic investments, technological hybrids, and growing emphasis on system-level durability are driving steady growth. As energy ecosystems demand more resilient and responsive storage solutions, LTO batteries are poised to play a vital supporting role in the global transition to electrification and renewable integration.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Lithium Titanate Oxide (LTO) Batteries
Sourcing Lithium Titanate Oxide (LTO) batteries presents unique challenges beyond standard lithium-ion procurement. Understanding these pitfalls is crucial for ensuring performance, longevity, and protecting intellectual property.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
- Misrepresentation of Core Chemistry: The most critical pitfall is suppliers claiming “LTO” while actually supplying cells with a blended or entirely different anode (e.g., graphite or hard carbon). True LTO offers exceptional safety, cycle life, and low-temperature performance, but is more expensive. Verify the anode material through independent testing (e.g., XRD, SEM-EDS) and demand detailed technical specifications.
- Inconsistent Cell-to-Cell Performance: Poor manufacturing processes lead to significant variations in capacity, internal resistance, and impedance among cells from the same batch. This imbalance drastically reduces pack performance and lifespan. Demand strict Bin A/B/C grading specifications and require statistical data (e.g., standard deviation of capacity/IR) from the supplier.
- Overstated Specifications: Suppliers may publish inflated cycle life, power density, or temperature range claims under unrealistic test conditions (e.g., shallow depth of discharge, ideal temperature, low C-rate). Scrutinize test protocols (DoD, C-rate, temperature, voltage limits) and demand real-world validation data relevant to your application.
- Poor Quality Control & Traceability: Inadequate QC processes result in defects (micro-shorts, impurities, sealing issues) and lack of cell traceability (batch/lot numbers). This makes failure analysis impossible and risks entire batches. Require robust QC documentation, full traceability systems, and access to manufacturing audits.
- Substandard Cell Construction & Materials: Using inferior separators, electrolytes, or casing materials compromises safety (increased risk of thermal runaway despite LTO’s inherent safety), cycle life, and performance under stress. Insist on detailed BOM information and material certifications (e.g., separator ceramic coating, electrolyte additives).
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
- Reverse Engineering & Design Theft: Sharing detailed application requirements, test data, or even physical samples for qualification exposes your unique design and performance targets. Unethical suppliers can reverse engineer your pack design or identify a valuable niche market. Implement strict NDAs before sharing sensitive information and limit data disclosure to the absolute minimum required for quotation.
- Lack of Clear IP Ownership in Agreements: Contracts often fail to explicitly state who owns IP developed during customization (e.g., specific cell form factors, BMS algorithms tuned for your LTO pack, proprietary testing methods). Assume ownership defaults to the supplier. Negotiate explicit clauses defining ownership of pre-existing IP, joint developments, and background IP.
- Supplier Becomes a Direct Competitor: A supplier gaining deep insight into your successful LTO application (e.g., a unique energy storage system or specialized EV) might use that knowledge to develop and sell competing products to your customers or market. Include non-compete or non-solicitation clauses in contracts and diversify your supply chain where possible.
- Inadequate Protection of Test Data & Performance Results: Data generated during qualification testing (cycling, abuse tests, thermal performance) is valuable IP. Ensure agreements cover confidentiality of all shared data and results, specifying how it can be used (e.g., only for fulfilling the order, not for marketing or product development).
- Weak Contractual Enforcement & Jurisdiction: Agreements lacking strong enforcement mechanisms or governed by jurisdictions unfavorable to IP protection make it difficult and costly to pursue infringement. Ensure contracts have clear dispute resolution clauses (preferably arbitration in a neutral, IP-respectful jurisdiction) and include provisions for injunctive relief and damages for IP breaches.

H2. Lithium Titanate (LTO) Battery Logistics & Compliance Guide
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the safe and legal transportation, storage, and handling of Lithium Titanate (LTO) batteries in accordance with international and national regulatory frameworks.
H2.1 Classification & Regulatory Framework
Lithium Titanate (LTO) batteries are a type of rechargeable lithium-ion battery. While generally considered safer than other lithium-ion chemistries due to their thermal and structural stability, they are still regulated as dangerous goods during transport due to their lithium content.
Primary Regulations:
– United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods, Model Regulations (UN Model Rules)
– International Air Transport Association (IATA) Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR)
– International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code
– 49 CFR (U.S. Department of Transportation – Hazardous Materials Regulations)
– ADR (European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road)
Classification:
– UN Number: UN 3480 (for lithium-ion batteries, not installed in equipment)
– UN Number: UN 3481 (for lithium-ion batteries contained in or packed with equipment)
– Proper Shipping Name: “Lithium ion batteries”
– Class: 9 – Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods
– Packing Group: III (typically, unless tested otherwise)
– Hazard Label: Class 9 Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods label required
Note: LTO batteries are not assigned a unique UN number; they fall under the broader UN 3480/3481 classification.
H2.2 Packaging & Marking Requirements
Packaging:
– Must meet the UN performance standards outlined in the applicable regulations (e.g., drop, vibration, pressure differential tests).
– Inner packaging must prevent short circuits and protect terminals (e.g., terminal protection using caps, insulating tape, or individual packaging).
– Use rigid outer packaging with sufficient cushioning to prevent movement or damage.
– For air transport, packages must pass the 1.2-meter drop test and stacking test.
Marking & Labeling:
– Proper Shipping Name: “Lithium ion batteries”
– UN Number: “UN 3480” or “UN 3481”
– Class 9 hazard label
– Cargo Aircraft Only label (if applicable – based on state and airline approval)
– Shipper and consignee information
– Lithium Battery Mark (Mandatory for air transport per IATA DGR):
– Contains the UN number (e.g., “UN3480”)
– Proper shipping name
– Telephone number
– 12 x 11 cm minimum size
– Red diagonal stripe not required for LTO if proven to be non-hazardous under test criteria (subject to testing and approval)
H2.3 State of Charge (SoC) Limitations
- Batteries must be shipped at a state of charge not exceeding 30% of their rated capacity, as per IATA and IMDG requirements for lithium-ion cells and batteries (unless approved by the competent authority).
- This reduces the risk of thermal runaway during transport.
- Documentation must confirm SoC compliance.
H2.4 Documentation Requirements
- Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods (required for air and sea transport when shipping in regulated quantities).
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS) in accordance with GHS (Globally Harmonized System) – typically Section 14 covers transport information.
- Air Waybill or Bill of Lading must include:
- Proper shipping name
- UN number
- Hazard class
- Packing group
- Net quantity of batteries
H2.5 Mode-Specific Regulations
Air Transport (IATA DGR):
– LTO batteries may be eligible for exceptions if proven non-hazardous (e.g., passing UN Manual of Tests and Criteria, Part III, subsection 38.3).
– Packages must not exceed 30 kg gross weight unless approved.
– Passenger aircraft: limited quantities may be allowed; larger shipments typically restricted to cargo-only aircraft.
– E-commerce shipments must comply with Section II of Packing Instruction 965/966/967 (if applicable).
Sea Transport (IMDG Code):
– Must be stowed in accordance with segregation rules.
– Ventilation and temperature control may be required depending on quantity and configuration.
– Documentation must include Dangerous Goods Manifest and Container/Packaging Certificate.
Road Transport (ADR):
– Requires proper labeling, vehicle placarding (for large quantities), and trained drivers (ADR certification).
– Load securing and terminal protection are mandatory.
– Transport document must include dangerous goods description.
H2.6 Storage & Handling
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
- Avoid contact with conductive materials to prevent short circuits.
- Do not stack packages beyond recommended limits.
- Use non-conductive pallets and ensure terminals are insulated.
- Fire protection: Class D fire extinguishers or specialized lithium battery fire suppression systems are recommended.
- Emergency response plan must be in place, including spill/leak and thermal runaway procedures.
H2.7 Testing & Certification
- All LTO batteries must pass the UN Manual of Tests and Criteria, Part III, subsection 38.3:
- Altitude simulation
- Thermal cycling
- Vibration
- Shock
- External short circuit
- Impact/Crush
- Overcharge
- Forced discharge
- Test summaries may be required for regulatory compliance or airline acceptance.
H2.8 Special Considerations for LTO
- LTO batteries are more thermally stable and less prone to thermal runaway than other lithium-ion chemistries.
- Some regulatory authorities or carriers may allow exceptions (e.g., higher SoC or reduced labeling) if supported by testing and certification proving reduced hazard.
- Always verify with the carrier and destination country regulations before shipping.
H2.9 Training & Responsibilities
- Personnel involved in packing, labeling, documenting, or transporting LTO batteries must receive dangerous goods training in accordance with IATA, IMDG, or ADR requirements.
- Training must be refreshed every 2 years.
- The shipper is responsible for proper classification, packaging, marking, labeling, and documentation.
H2.10 Environmental & End-of-Life Compliance
- LTO batteries are recyclable and must be disposed of in accordance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive (EU) or equivalent local regulations.
- Producers may be subject to extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes.
- Do not dispose of in regular trash.
Conclusion:
While Lithium Titanate batteries offer enhanced safety, they remain regulated under global dangerous goods frameworks. Adherence to classification, packaging, documentation, and training requirements is essential for compliant and safe logistics operations. Always consult the latest edition of relevant regulations and coordinate with carriers and regulatory bodies for specific shipment approvals.
Conclusion: Sourcing Lithium Titanate (LTO) Batteries
In conclusion, sourcing lithium titanate (LTO) batteries presents a strategic opportunity for applications that demand high power density, exceptional cycle life, rapid charging capabilities, and superior safety. Despite their higher upfront cost compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries, LTO batteries offer long-term value through durability, reduced maintenance, and reliable performance in extreme temperatures and demanding environments.
When sourcing LTO batteries, it is crucial to evaluate suppliers based on quality certifications, manufacturing standards, scalability, and technical support. Geopolitical factors, supply chain resilience, and raw material availability—particularly for lithium and titanium—should also inform procurement decisions. Leading manufacturers in China, Japan, and South Korea currently dominate the LTO market, offering a range of products suitable for applications in electric vehicles, energy storage systems, industrial equipment, and backup power solutions.
Ultimately, while LTO batteries may not be the optimal choice for all energy storage needs due to cost and energy density limitations, they remain a compelling solution where performance, safety, and longevity are paramount. A well-considered sourcing strategy that balances cost, performance, and supply chain reliability will ensure successful integration of LTO battery technology into future-ready energy systems.