The global lithium heparin tube market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for efficient blood collection and diagnostic testing. According to Grand View Research, the global blood collection market was valued at USD 5.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1% from 2024 to 2030, fueled by expansion in healthcare infrastructure, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and growing emphasis on preventive diagnostics. Lithium heparin tubes, in particular, are gaining prominence due to their effectiveness in plasma separation for critical chemistry tests, including electrolyte, glucose, and therapeutic drug monitoring. With the Asia Pacific region showing accelerated growth and hospitals remaining the largest end-users, the demand for high-quality, reliable blood collection devices is rising significantly. As a result, several manufacturers have emerged as key players, combining innovation, regulatory compliance, and scalable production to meet evolving clinical needs. The following list highlights the top six lithium heparin tube manufacturers shaping this expanding landscape.
Top 6 Lithium Heparin Tube Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
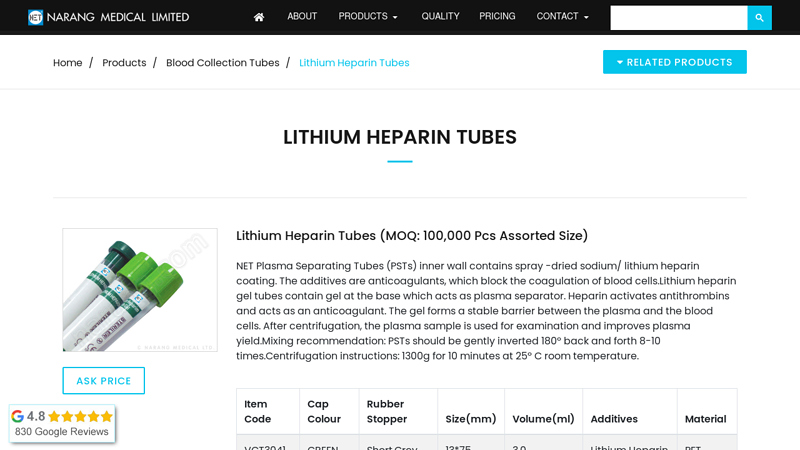
#1 Lithium Heparin Tubes
Domain Est. 1996
Website: narang.com
Key Highlights: Lithium Heparin Tubes – We are manufacturer and suppliers of Lithium Heparin Blood Tube. The inner wall of the NET Heparin tubes is coated with spray-dried ……
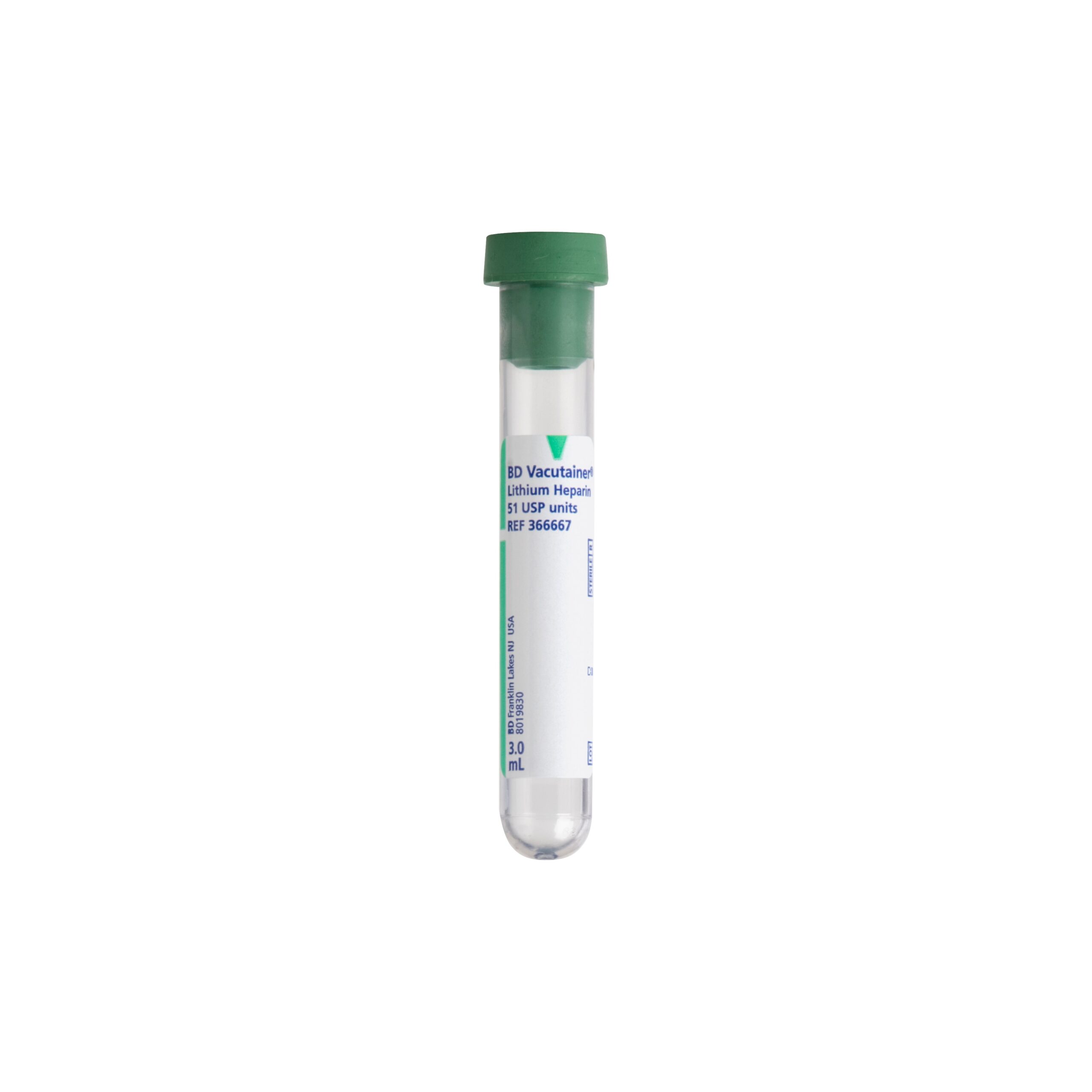
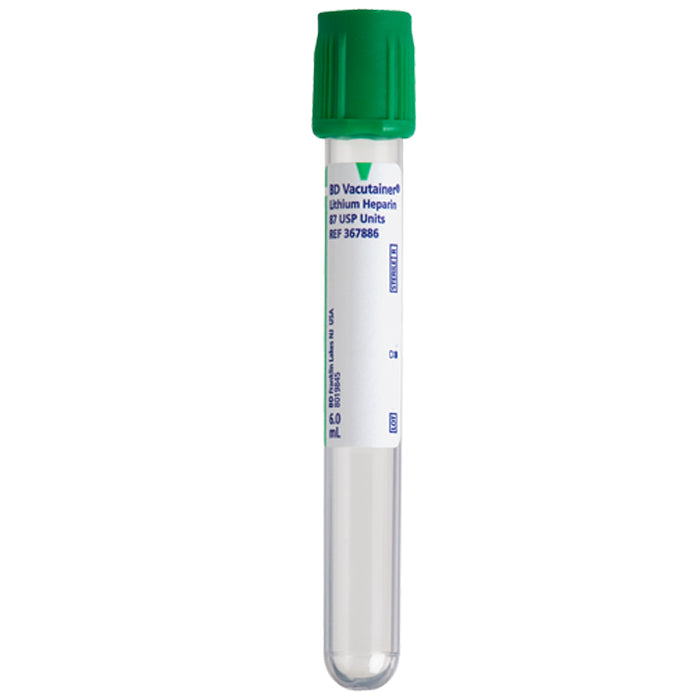
#2 BD Vacutainer ® Blood Collection Tubes
Domain Est. 1990
Website: bd.com
Key Highlights: BD Vacutainer Blood Collection Tubes support reliability, accuracy and integrity in the specimen pathway so clinicians get a quality specimen the first time….
#3 Blood Collection Tubes, Lithium Heparin Tubes
Domain Est. 1995
Website: thomassci.com
Key Highlights: 1–2 day delivery 30-day returnsThe Thomas Scientific collection includes separator tube and lithium heparin tube options. Microcapillary tubes are ideal for the centrifugation of b…
#4 Prepared blood tubes
Domain Est. 1996
Website: sarstedt.com
Key Highlights: Our product range contains prepared tubes of various different dimensions and volumes for the individual requirements of blood collection….
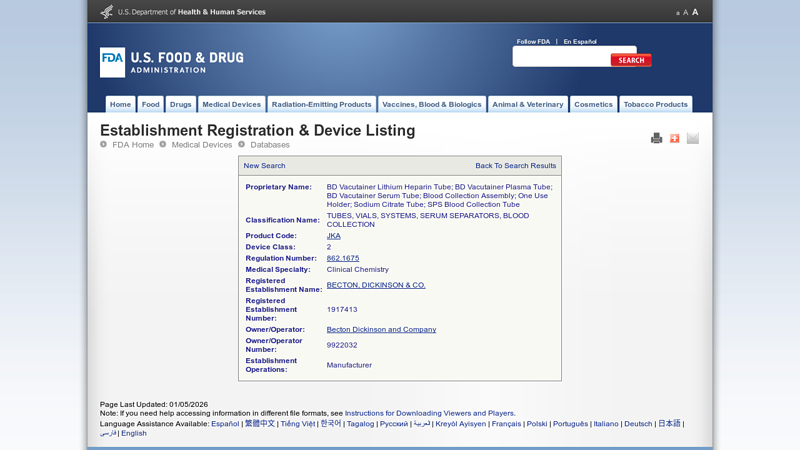
#5 Establishment Registration & Device Listing
Domain Est. 2000
Website: accessdata.fda.gov
Key Highlights: Proprietary Name: BD Vacutainer Lithium Heparin Tube; BD Vacutainer Plasma Tube; BD Vacutainer Serum Tube; Blood Collection Assembly; One Use Holder; Sodium ……
#6 Dk green Lithium heparin (Li hep) vial/tube (no gel)
Domain Est. 2012
Website: labs.allinahealth.org
Key Highlights: Item Description: 13×75 mm 4.0 mL BD Vacutainer® Plus plastic plasma tube. Green BD Hemogard™ closure. Paper label. Lithium Heparin 75 USP units….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Lithium Heparin Tube

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Lithium Heparin Tubes
The global market for lithium heparin tubes is projected to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by rising demand for accurate and rapid blood diagnostics, expansion of healthcare infrastructure, and increasing prevalence of chronic diseases requiring routine blood monitoring. Lithium heparin tubes, which prevent blood coagulation by inhibiting thrombin and other clotting factors, are widely used in clinical laboratories for plasma separation in chemistry, electrolyte, and metabolic testing.
A key trend shaping the 2026 market landscape is the integration of automation in clinical diagnostics. As laboratories adopt high-throughput automated systems, there is growing demand for standardized, barcode-enabled lithium heparin tubes compatible with robotic sample handling. This shift enhances sample traceability, reduces human error, and improves turnaround times—critical factors in acute care and emergency settings.
Additionally, the expansion of point-of-care testing (POCT) in decentralized healthcare settings is influencing product innovation. Manufacturers are focusing on developing lithium heparin tubes with faster clotting inhibition, improved plasma yield, and enhanced stability for transport and storage. These features are particularly beneficial in rural and remote areas where immediate analysis is not feasible.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate by 2026 due to increasing healthcare investments, rising geriatric population, and growing awareness of preventive healthcare in countries like China and India. North America and Europe will maintain significant market shares, supported by stringent regulatory standards, advanced diagnostic facilities, and strong R&D activities.
Sustainability is also emerging as a key consideration. Leading suppliers are exploring eco-friendly materials and packaging solutions to reduce the environmental footprint of blood collection tubes, aligning with global sustainability goals.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for lithium heparin tubes will be characterized by technological innovation, automation compatibility, geographic expansion, and a focus on sustainability—positioning the segment for continued relevance in modern diagnostic workflows.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Lithium Heparin Tubes (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing Lithium Heparin tubes, critical for plasma separation in clinical diagnostics, involves navigating significant quality and intellectual property (IP) challenges. Overlooking these can lead to unreliable test results, regulatory non-compliance, and legal risks. Key pitfalls include:
Inadequate Quality Control and Manufacturing Standards
- Non-Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: Sourcing from manufacturers not adhering to ISO 13485 (Medical Devices Quality Management) or lacking certifications like FDA 510(k) clearance or CE Marking for IVDs can result in non-compliant products unsuitable for clinical use.
- Inconsistent Heparin Coating and Dosing: Poor process control leads to tube-to-tube variability in lithium heparin concentration. This inconsistency can cause under- or over-anticoagulation, directly impacting plasma quality and assay accuracy (e.g., falsely elevated potassium levels due to cell lysis from inadequate anticoagulation).
- Contamination Risks: Substandard materials or manufacturing environments can introduce contaminants (e.g., endotoxins, heavy metals, plasticizers) that interfere with sensitive assays or compromise sample integrity.
- Poor Sample Stability: Inferior tube design or formulation may fail to maintain analyte stability (e.g., glucose, lactate, hormones) during transport and storage, leading to erroneous results.
- Defective Components: Issues like faulty closures (causing leaks or evaporation), poor vacuum consistency (leading to incorrect fill volumes), or weak tube walls (risk of breakage) compromise sample handling and integrity.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement and Design Copying
- Direct Patent Infringement: Sourcing tubes that replicate patented designs (e.g., specific closure mechanisms, proprietary coating processes, unique tube geometries, or specialized additives) without licensing exposes the buyer and supplier to significant legal liability, injunctions, and financial penalties.
- Trade Dress Infringement: Copying the distinctive visual appearance (e.g., specific color-coding, labeling, or packaging) of established brands can mislead users and violate trade dress rights, leading to legal action.
- “Me-Too” Products with Subtle Design Flaws: Some suppliers offer look-alike tubes that avoid direct IP infringement but sacrifice performance (e.g., using cheaper, less effective heparin salts, inferior plastic, or less precise manufacturing). These “knock-offs” may appear functional but deliver inconsistent or unreliable results.
- Lack of IP Due Diligence: Failing to verify a supplier’s freedom to operate (FTO) – confirming they have the right to manufacture and sell the product without infringing others’ IP – is a major risk. Buyers may be drawn into litigation even if they weren’t the direct infringer.
- Counterfeit or Gray Market Goods: Sourcing through unauthorized channels increases the risk of receiving counterfeit tubes (fake packaging, incorrect contents) or gray market goods (diverted legitimate products), which may lack proper quality control, have compromised storage conditions, or involve IP violations.
Mitigating these pitfalls requires rigorous supplier qualification, demanding proof of certifications, requesting detailed quality documentation (e.g., CoA, CoC), conducting performance testing, and performing thorough IP due diligence before finalizing sourcing agreements.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Lithium Heparin Tubes
1. Overview
Lithium Heparin Tubes are blood collection devices containing lithium heparin as an anticoagulant. These tubes are used for plasma separation in clinical diagnostics, including chemistry, therapeutic drug monitoring, and some hematology tests. Proper handling, storage, transportation, and regulatory compliance are critical to ensure sample integrity and adherence to health and safety standards.
2. Storage Conditions
- Temperature: Store at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F).
- Environment: Keep in a dry place, protected from direct sunlight and moisture.
- Shelf Life: Typically 15 months from the date of manufacture—verify expiration date before use.
- Packaging: Maintain original sealed packaging until ready for use to prevent contamination or moisture exposure.
3. Transportation Requirements
- Temperature Control: During transit, ensure ambient temperature remains within the specified storage range (2°C–25°C). Use insulated packaging if extreme conditions are expected.
- Packaging: Use sturdy, leak-proof secondary containers to prevent breakage. Tubes should be secured to avoid movement.
- Labeling: Outer packaging must be labeled with:
- Product name and catalog number
- Quantity and lot number
- Manufacturer/distributor information
- “Fragile” and “This Way Up” indicators
- Hazard Classification: Lithium Heparin Tubes are generally classified as non-hazardous for transport under IATA, IMDG, and ADR regulations when empty and unused. However, verify with current regulatory editions.
4. Regulatory Compliance
- FDA (U.S.): Must comply with 21 CFR Part 809 (In Vitro Diagnostic Devices) and 21 CFR Part 820 (Quality System Regulation). Ensure tubes are labeled with proper UDI (Unique Device Identifier) if applicable.
- CE Marking (EU): Must conform to IVDR (In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation) 2017/746. Technical documentation and EU Declaration of Conformity must be available.
- ISO Standards: Compliant with ISO 10993 (biocompatibility), ISO 80369 (small-bore connectors), and ISO 6710 (specifications for blood collection tubes).
- CLSI Guidelines: Follow CLSI H3-A7 and H1-A8 for blood collection tube labeling and performance.
5. Handling and Use
- Pre-use Check: Inspect tubes for cracks, leaks, or expired dates. Discard damaged or expired tubes.
- Blood Collection: Follow standard phlebotomy procedures. Invert tube 8–10 times immediately after draw to ensure proper mixing with anticoagulant.
- Centrifugation: Centrifuge within 2 hours of collection at recommended speed and duration (e.g., 2,200–2,500 x g for 10–15 minutes) to separate plasma.
- Sample Stability: Plasma in lithium heparin tubes is typically stable for up to 24 hours at room temperature or 72 hours refrigerated (2–8°C), depending on the analyte. Refer to test-specific guidelines.
6. Waste Disposal
- Contaminated Tubes (post-blood draw): Treat as biohazardous waste. Dispose in accordance with local, state, and federal regulations (e.g., OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030).
- Unused/Expired Tubes: Dispose as non-hazardous medical waste unless local regulations specify otherwise. Confirm with institutional waste management policies.
- Packaging Waste: Cardboard and plastic packaging may be recyclable where facilities exist.
7. Documentation & Traceability
- Maintain records of:
- Lot numbers and expiration dates
- Storage and transport temperature logs (if required)
- Supplier certificates of analysis (CoA) and conformity
- Inventory management and usage logs
- Ensure full traceability from receipt through disposal, particularly in regulated laboratory environments (e.g., CAP, CLIA, ISO 15189).
8. Emergency Procedures
- Spill of Unused Tubes: No special hazards. Collect broken glass safely and dispose as sharps if applicable.
- Spill of Blood-Contaminated Tubes: Follow biohazard spill protocol: wear PPE, decontaminate area with 10% bleach or EPA-registered disinfectant, and dispose of materials in biohazard containers.
9. Supplier & Manufacturer Requirements
- Source tubes only from certified suppliers compliant with ISO 13485.
- Verify that manufacturer provides:
- Product inserts (Instructions for Use)
- Stability data
- Regulatory certifications (FDA, CE, etc.)
- Change notifications (e.g., formulation or labeling updates)
10. Training & Personnel
- Staff involved in handling, storing, or using Lithium Heparin Tubes must be trained in:
- Proper blood collection techniques
- Biohazard safety and PPE use
- Regulatory compliance requirements
- Emergency response procedures
- Training records should be maintained and updated annually.
Note: Always consult the manufacturer’s Instructions for Use (IFU) and local regulatory authorities for the most current guidelines specific to your region and institution.
Conclusion on Sourcing Lithium Heparin Tubes
In conclusion, sourcing lithium heherin tubes requires a strategic approach that balances quality, regulatory compliance, cost-efficiency, and supply chain reliability. These tubes are essential for clinical laboratories requiring plasma separation for critical diagnostic testing, particularly in chemistry and electrolyte panels, where accurate lithium heparin concentration and sample integrity are vital.
When selecting suppliers, it is imperative to prioritize manufacturers that adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 13485 and CE marking, and that demonstrate compliance with FDA or other relevant regulatory bodies. Consistent product performance—ensuring proper anticoagulant concentration, clotting efficacy, and absence of sample contamination—must be rigorously evaluated through qualification and validation processes.
Additionally, considerations such as packaging configuration (e.g., gel barrier, tube size, and labeling), availability of barcoding, and compatibility with automated laboratory systems can significantly enhance operational efficiency. Establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers, potentially including dual sourcing to mitigate supply disruptions, supports continuity of operations.
In summary, a well-structured sourcing strategy for lithium heparin tubes—rooted in quality assurance, regulatory compliance, and supplier reliability—ensures optimal diagnostic outcomes and supports the overall integrity of laboratory testing processes.