The global liquid filter market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for clean water, stricter environmental regulations, and rising industrialization. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 19.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts steady expansion, citing heightened applications in pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and wastewater treatment as key growth drivers. With industries prioritizing process efficiency and contamination control, the need for reliable filtration solutions has never been greater. In this evolving landscape, selecting the right manufacturer is critical. Below, we spotlight the top 10 liquid filter manufacturers recognized for innovation, global reach, product diversity, and performance—companies shaping the future of fluid purification across sectors.
Top 10 Liquid Filter Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Engine and Industrial Air, Oil and Liquid Filtration
Domain Est. 1995
Website: donaldson.com
Key Highlights: Donaldson Company, Inc. is a global leader in providing engine and industrial air, oil and liquid filtration solutions….
#2 Buy AQUAPHOR water filters. Manufacturer’s
Domain Est. 1998
Website: aquaphor.com
Key Highlights: Company. At AQUAPHOR, we design and manufacture reliable and convenient water filters so that you enjoy using them in the kitchen, bathroom or country house — ……
#3 Liquid filter bags
Domain Est. 1999
Website: liquidfiltration.com
Key Highlights: Industrial Filter Manufacturing Ltd. produces a complete line of specialty and custom filter bags to suit your unique application….
#4 Liquid Filter Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2002
Website: liquid-filters.net
Key Highlights: Clean Liquid Systems is a leading manufacturer of air and liquid filters. Our number one priority is to create the best filters that match the needs of our ……
#5 Freudenberg Filtration Technologies
Domain Est. 2007
Website: freudenberg-filter.com
Key Highlights: Discover your world of filtration solutions. Freudenberg Filtration Technologies provides a wide range of air, gas and liquid solutions….
#6 Orthos Liquid Systems
Domain Est. 2019
Website: orthosfilters.com
Key Highlights: Orthos Liquid Systems is the leading manufacturer of nozzle-based filter systems and nozzle products in water and wastewater treatment….
#7 3M Filtration & Separation
Domain Est. 1988
Website: 3m.com
Key Highlights: 3M Filtration & Separation · Filter Cartridges & Media · Liquid Filtration Components · Process Filtration & Purification · Water Filtration….
#8 Pall Corporation
Domain Est. 1995
Website: pall.com
Key Highlights: Pall offers innovative purification and filtration technologies for new and expanding markets, leading the way with consistent, reliable performance for state- ……
#9 Filtration Group
Domain Est. 1998
Website: filtrationgroup.com
Key Highlights: We are a global market-leading provider of mission-critical filtration solutions designed to enable advanced healthcare capabilities, provide clean air and ……
#10 Global Filter
Domain Est. 1999
Website: globalfilter.com
Key Highlights: Global Filter’s filtration solutions are designed to meet the needs of a wide variety of applications and industries where liquid filtration is required….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Liquid Filter

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Liquid Filtration
The global liquid filtration market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by converging forces of industrial modernization, environmental regulation, technological innovation, and shifting end-user demands. Here’s a breakdown of the key trends expected to shape the market:
1. Accelerated Adoption of Advanced Membrane Technologies:
* Dominance of Nanofiltration (NF) & Reverse Osmosis (RO): Driven by stringent water quality standards (especially in pharma, food & beverage, and electronics) and the need for water reuse/recovery, NF and RO will see accelerated adoption. Demand will be fueled by zero liquid discharge (ZLD) mandates and process intensification.
* Growth of Ultrafiltration (UF) & Microfiltration (MF): These will remain crucial for pre-treatment in RO systems and for specific applications like bioprocessing clarification and cold sterilization in beverages, benefiting from improved membrane durability and lower fouling.
* Emergence of Advanced Materials: Research and commercialization of novel membrane materials (e.g., graphene oxide, carbon nanotubes, biomimetic membranes) will gain traction, promising higher flux, better selectivity, enhanced chemical resistance, and reduced energy consumption, though widespread commercial impact might be more evident post-2026.
2. Intensifying Focus on Sustainability & Circular Economy:
* Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) & Minimal Liquid Discharge (MLD): Regulatory pressure and water scarcity will make ZLD/MLD systems a major growth driver, particularly in mining, power generation, and chemical processing. This demands highly efficient filtration and concentration technologies.
* Water Reuse & Recycling: Industries will increasingly treat and reuse process water, reducing freshwater intake and wastewater discharge. Filtration is the cornerstone of advanced water recycling systems.
* Reduced Chemical Usage: Development and adoption of filtration systems requiring fewer or milder cleaning chemicals (CIP) will grow, driven by environmental, safety, and cost concerns.
* Focus on Filter Media Lifecycle: Increased scrutiny on the environmental impact of filter media (e.g., single-use cartridges, spent media disposal) will push demand for reusable, cleanable, and more recyclable filter solutions.
3. Digitalization & Smart Filtration Systems:
* Integration of IoT & Sensors: Real-time monitoring of pressure drop, flow rates, turbidity, and even membrane integrity will become standard. This enables predictive maintenance, optimizing filter change schedules, reducing downtime, and improving process control.
* Data Analytics & AI: Platforms analyzing filtration performance data will provide insights for optimizing system design, operation, and maintenance, leading to higher efficiency and lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
* Remote Monitoring & Diagnostics: OEMs and service providers will offer remote support, diagnostics, and performance optimization based on real-time data streams.
4. Stringent Regulatory Compliance Driving Demand:
* Pharmaceutical & Biotech: Evolving USP, EP, and FDA guidelines on water for injection (WFI), bioburden control, and extractables/leachables will necessitate highly reliable, validated filtration solutions (especially sterile filtration and viral clearance).
* Food & Beverage: Increasing consumer focus on safety and quality, along with regulations (FDA, EU) on pathogens, allergens, and contaminants, will drive demand for advanced filtration (e.g., pathogen removal in juice, oil clarification, beer/wine stabilization).
* Electronics: The push for smaller semiconductor nodes demands ultra-pure water (UPW) and chemicals. Filtration specifications (especially particle and TOC removal) will become even more stringent, requiring advanced membrane and depth filtration.
* Environmental Regulations: Stricter global discharge limits for pollutants (heavy metals, organics, nutrients) in industrial effluents will mandate more sophisticated multi-stage filtration and treatment systems.
5. Growth in Key End-Use Industries:
* Water & Wastewater Treatment: Remains the largest segment. Growth will be driven by urbanization, aging infrastructure upgrades, industrial wastewater treatment, and water scarcity solutions (desalination, reuse).
* Pharmaceuticals & Biotechnology: Continuous growth fueled by biologics production, personalized medicine, and vaccine development, all requiring sophisticated liquid filtration.
* Food & Beverage: Rising demand for packaged foods, beverages, and functional foods necessitates safe, shelf-stable products, boosting filtration for clarification, stabilization, and sterilization.
* Chemicals & Petrochemicals: Demand for high-purity process streams and catalyst protection, coupled with stricter environmental controls on effluents.
* Power Generation: Focus on cooling water treatment, boiler feed water purification (especially for ultra-supercritical plants), and wastewater treatment from flue gas desulfurization (FGD).
* Electronics: Exponential growth driven by semiconductor manufacturing expansion and the need for extreme purity.
6. Consolidation and Innovation in the Supplier Landscape:
* M&A Activity: Continued consolidation among filter media manufacturers, module suppliers, and system integrators to achieve scale, broaden portfolios, and offer integrated solutions.
* Focus on Value-Added Services: Suppliers will increasingly compete on service offerings (design, validation, monitoring, maintenance contracts) rather than just hardware.
* Regional Manufacturing Shifts: Production may increasingly localize or nearshore to serve key regional markets (e.g., Asia-Pacific, North America) and mitigate supply chain risks.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the liquid filtration market will be characterized by higher performance requirements, deep integration with digital technologies, and an unwavering focus on sustainability. Success will depend on suppliers’ ability to innovate with advanced materials and smart systems, while helping customers meet stringent regulatory demands and environmental goals through efficient, reliable, and digitally connected filtration solutions. The convergence of these trends points towards a market that is not just larger, but fundamentally more sophisticated and integral to industrial and environmental processes.
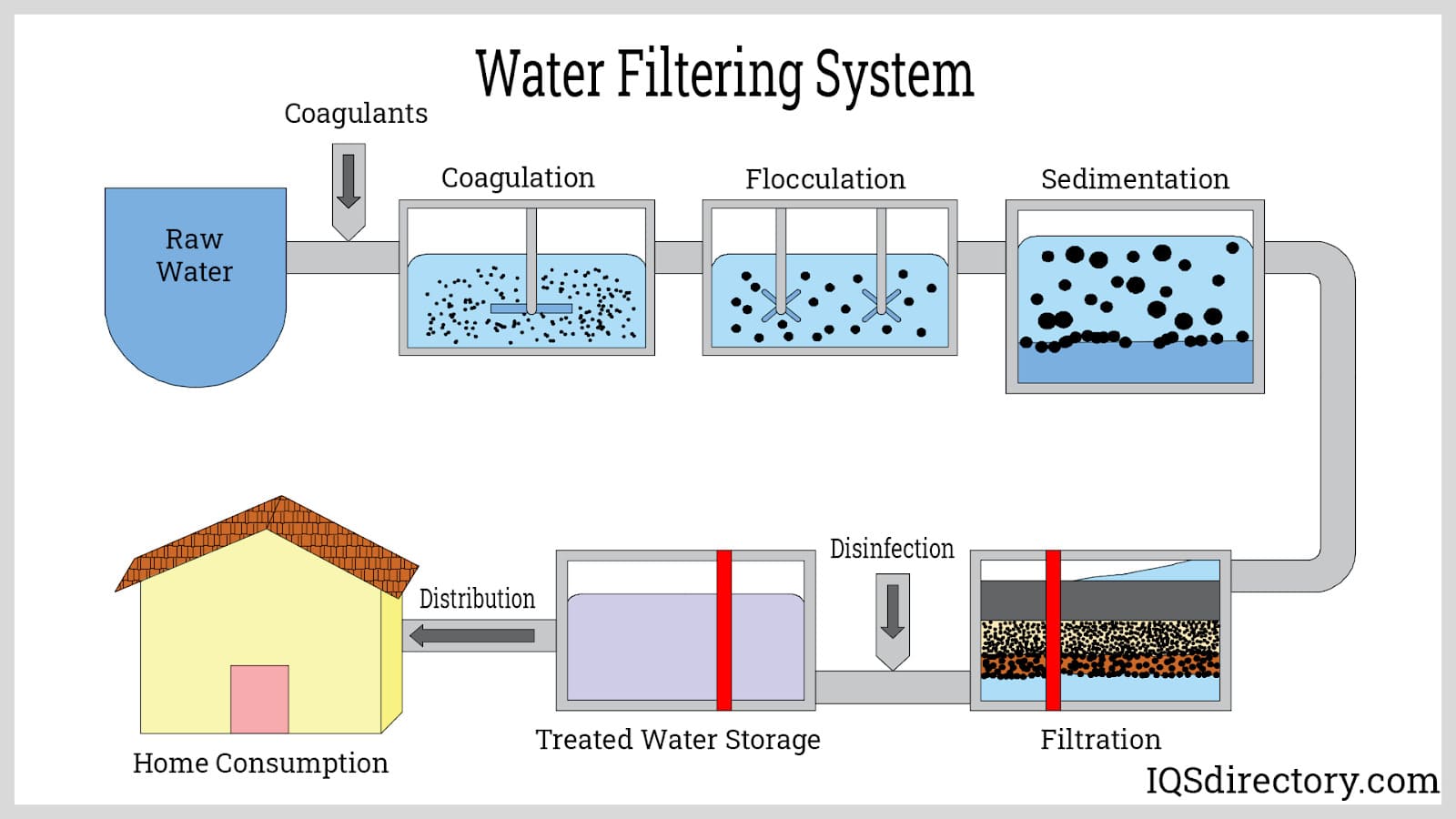
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Liquid Filters (Quality, IP)
Sourcing liquid filters involves critical considerations around both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance failures, supply chain disruptions, and legal risks. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Filtration Specifications
Failing to define precise filtration requirements—such as micron rating, flow rate, chemical compatibility, and temperature tolerance—can result in filters that underperform or fail prematurely. Using filters not suited to the operating environment leads to contamination, system damage, or increased maintenance costs.
2. Poor Material Compatibility
Selecting filters made from materials incompatible with the liquid being filtered (e.g., aggressive solvents or high-pH fluids) can cause degradation, leaching, or filter breakdown. Always verify chemical resistance data and ensure materials meet industry standards (e.g., FDA, USP Class VI for food/pharma).
3. Lack of Certifications and Testing Documentation
Procuring filters without proper certifications (e.g., ISO, NSF, ASTM) or test reports (e.g., bubble point, particle retention) increases the risk of substandard quality. Reputable suppliers should provide full traceability and validation data.
4. Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Sourcing from suppliers with inconsistent quality control processes may lead to batch-to-batch variability. This is especially critical in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals or semiconductors, where filter consistency directly impacts product safety and yield.
5. Counterfeit or Substandard Products
Purchasing from unauthorized or unverified distributors increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or off-spec filters. These may appear identical but fail to meet performance or safety standards, potentially causing system contamination.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Infringement of Patented Designs
Using or sourcing filters that replicate patented technologies (e.g., proprietary pleating methods, housing designs, or media compositions) without licensing can expose your company to legal action, fines, or forced redesigns.
2. Lack of IP Clarity in Custom Filters
When developing custom filter solutions, failing to define IP ownership in contracts can lead to disputes. Ensure agreements specify whether designs, tooling, or formulations are owned by the buyer, supplier, or jointly.
3. Reverse Engineering Risks
Some suppliers may offer “compatible” or “equivalent” filters that closely mimic branded products. While some are legal equivalents, others may cross into IP infringement, especially if they copy protected features. Due diligence on technical specifications and legal status is essential.
4. Unprotected Innovation in Supplier Collaboration
When working with suppliers on new filter development, sharing sensitive application details without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or IP protections can lead to misuse or unauthorized replication of your proprietary processes.
5. Grey Market and Unauthorized Replicas
Purchasing from third-party suppliers in grey markets may involve IP-violating replicas. These not only risk legal exposure but also lack quality assurance, undermining process reliability.
Mitigation Strategies
- Qualify Suppliers Rigorously: Audit suppliers for quality systems (e.g., ISO 9001) and IP compliance practices.
- Require Full Documentation: Demand material certifications, test reports, and IP disclaimers.
- Use Legal Agreements: Include IP ownership clauses and confidentiality terms in contracts.
- Source from Authorized Channels: Prefer OEMs or authorized distributors to avoid counterfeit or infringing products.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Monitor ongoing compliance with quality and IP standards throughout the supply chain.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable filtration performance while minimizing legal and operational risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Liquid Filters
Overview
Liquid filters are essential components in various industries, including automotive, industrial manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and food & beverage. Due to their application in fluid systems and potential handling of regulated substances, proper logistics and compliance practices are critical to ensure safety, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency.
Classification and Regulatory Standards
Liquid filters may be subject to classification under international and regional regulations based on their materials, intended use, and transported contents. Key standards include:
– HS Code Classification: Typically falls under 8421.21 or 8421.23 (filters for liquids), depending on design and application.
– REACH & RoHS (EU): Compliance required if filters contain substances of very high concern (SVHC) or restricted hazardous materials.
– FDA 21 CFR (USA): Mandatory for filters used in food, beverage, or pharmaceutical applications to ensure material safety.
– ATEX/IECEx: Applicable if filters are used in potentially explosive environments.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging ensures product integrity during transit and meets regulatory labeling standards:
– Use moisture-resistant, shock-absorbent packaging to protect filter media and housings.
– Label with:
– Product name and model number
– Manufacturer details
– Compliance marks (e.g., CE, FDA, ISO)
– Handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile”, “This Way Up”)
– Batch/lot number and expiration date (if applicable)
– Include multilingual labels for international shipments where required.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
Transport logistics must account for product sensitivity and international trade regulations:
– Mode of Transport: Air, sea, or ground—select based on urgency, cost, and destination. Air freight is preferred for time-sensitive or high-value shipments.
– Hazardous Material Status: Most liquid filters are non-hazardous when dry. However, if pre-wetted or containing residual fluids, they may be classified as hazardous (e.g., under IATA/IMDG). Conduct a hazard assessment before shipping.
– Temperature Control: Maintain recommended storage temperatures (typically 5–40°C) to prevent degradation of filter media.
– Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of conformity, and material safety data sheet (MSDS/SDS) as needed.
Import/Export Compliance
Cross-border shipments require adherence to customs and trade regulations:
– Verify import restrictions or tariffs in destination countries.
– Complete export declarations per local laws (e.g., AES filing for U.S. exports).
– Ensure filters comply with destination country standards (e.g., UKCA for the UK, INMETRO for Brazil).
– Use Incoterms® 2020 clearly (e.g., FOB, DDP) to define responsibilities.
Storage and Handling
Proper warehouse practices preserve filter performance:
– Store in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment.
– Avoid direct sunlight and contact with chemicals or solvents.
– Follow FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory rotation.
– Handle with clean gloves to prevent contamination, especially for sterile or high-purity filters.
Quality and Traceability
Maintain compliance through robust quality systems:
– Implement ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 standards where applicable.
– Keep detailed records of manufacturing, testing, and shipping for full traceability.
– Conduct regular audits of suppliers and logistics partners.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
End-of-life management must follow environmental regulations:
– Provide disposal guidelines based on filter materials (e.g., plastic, metal, cellulose).
– Comply with WEEE (EU) or local e-waste regulations if applicable.
– Offer recycling programs or take-back schemes where feasible.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for liquid filters require a proactive approach to classification, packaging, transportation, and regulatory adherence. By following this guide, businesses can ensure safe, legal, and efficient distribution while maintaining product quality and customer trust. Regular review of regulatory updates and supply chain performance is recommended to stay compliant in evolving markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing Liquid Filters
In conclusion, sourcing the appropriate liquid filter is a critical decision that directly impacts the efficiency, safety, and longevity of industrial processes and equipment. A thorough evaluation of filtering requirements—including the nature of the liquid, contaminant type and size, flow rate, temperature, pressure, and compatibility with materials—is essential to ensure optimal performance.
By carefully assessing suppliers based on quality certifications, technical expertise, reliability, and cost-effectiveness, organizations can secure filtration solutions that meet both regulatory standards and operational demands. Additionally, considering factors such as maintenance requirements, filter lifespan, and total cost of ownership helps in achieving long-term savings and operational continuity.
Ultimately, strategic sourcing of liquid filters not only enhances process purity and product quality but also contributes to reduced downtime and improved sustainability. Investing time and resources into selecting the right filtration system and supplier is a vital step toward operational excellence and competitive advantage.