The global power supply market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient and compact power conversion solutions across industrial, telecommunications, consumer electronics, and automotive sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global power supply market was valued at USD 33.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. A key factor in this expansion is the increasing adoption of switch mode power supplies (SMPS), which offer higher efficiency, smaller size, and better thermal performance compared to traditional linear power supplies—despite linear supplies still being preferred in applications requiring ultra-low noise and simplicity. Grand View Research further highlights that the shift toward miniaturization and energy conservation in electronic devices has significantly favored SMPS technologies, with the switch mode segment expected to dominate future market trends. As demand evolves, leading manufacturers are differentiating themselves through innovation in efficiency, reliability, and electromagnetic compatibility. This sets the stage for a data-informed comparison of the top six linear and switch mode power supply manufacturers shaping the industry landscape.
Top 6 Linear Vs Switch Mode Power Supply Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 FAQ
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meanwell.com
Key Highlights: MEAN WELL is one of the world’s few standard power supply mainly professional manufacturers, covering 0.5 to 25600W products are widely used in industrial ……
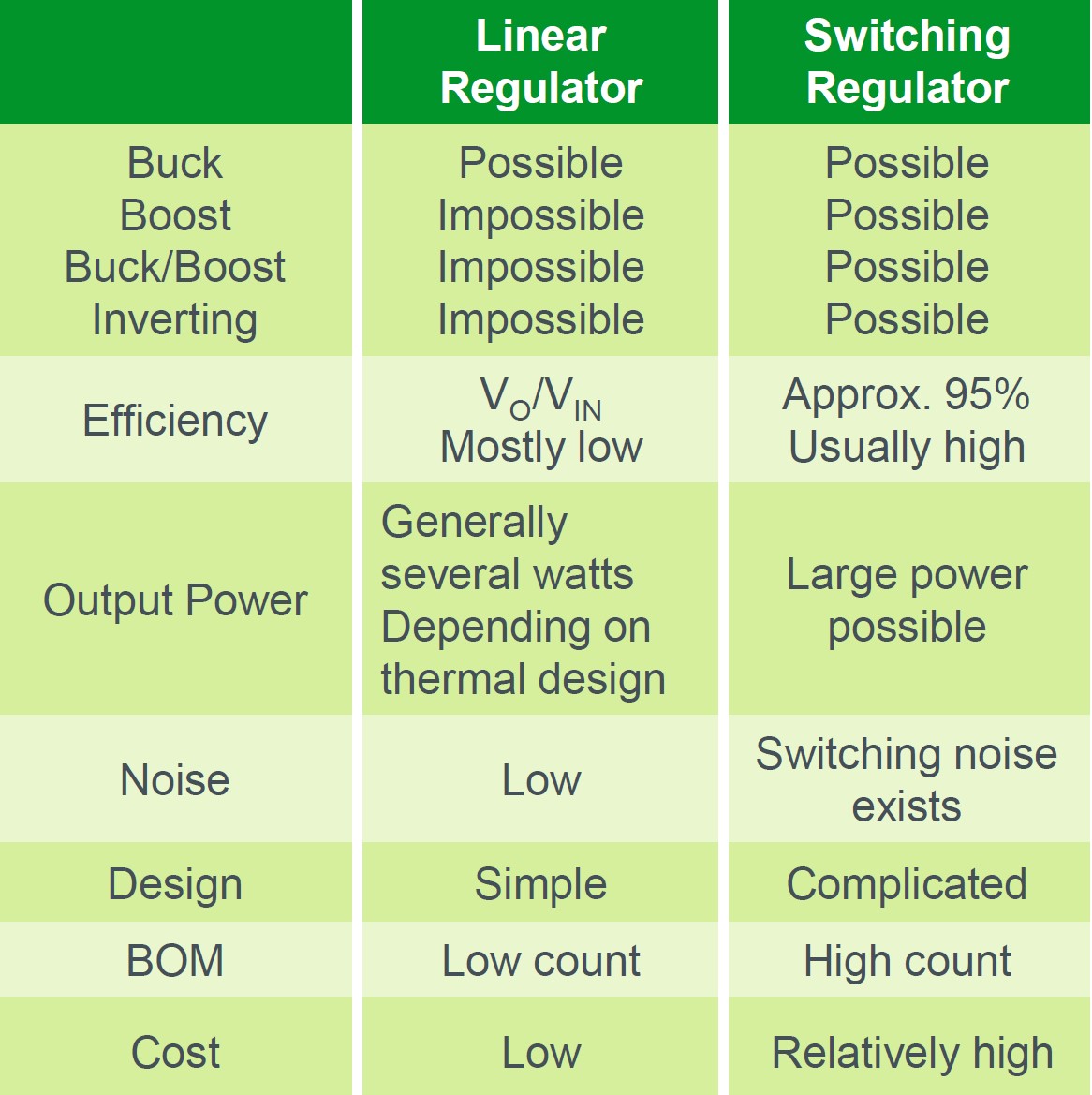
#2 Linear Power Supply vs. Switching Power Supply
Domain Est. 1989
Website: resources.pcb.cadence.com
Key Highlights: Explore distinctions between linear power supply vs. switching power supply, focusing on efficiency, design, complexity, and suitability….
#3 Linear versus Switch Mode Power Supplies
Domain Est. 1995
Website: spellmanhv.com
Key Highlights: Linear power supplies do have a notable benefit, they tend to be very quiet in terms of output noise and ripple since no switching element is used for their ……
#4 Linear vs. Switching Power Supplies
Domain Est. 1997
Website: actpower.com
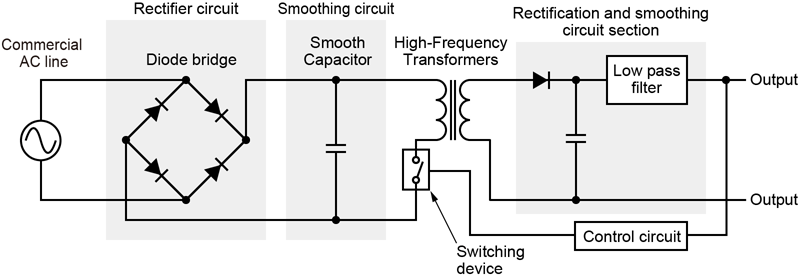
Key Highlights: A switch power supply has greater efficiency than linear regulators because the switching transistor dissipates little power when acting as a switch. However, ……
#5 Linear vs Switching Power Supply Differences and Rockwell …
Domain Est. 1997
Website: support.rockwellautomation.com
Key Highlights: What are the differences between linear and switched mode power supplies? Answer. Rockwell Automation does not offer a Linear Power Supply ……
#6 Hybrid power supplies (part linear part switching)
Domain Est. 2021
Website: modwiggler.com
Key Highlights: Switching power supplies can be (and are) made to be very excellent sources of power. Better suited than linear in certain applications, really….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Linear Vs Switch Mode Power Supply
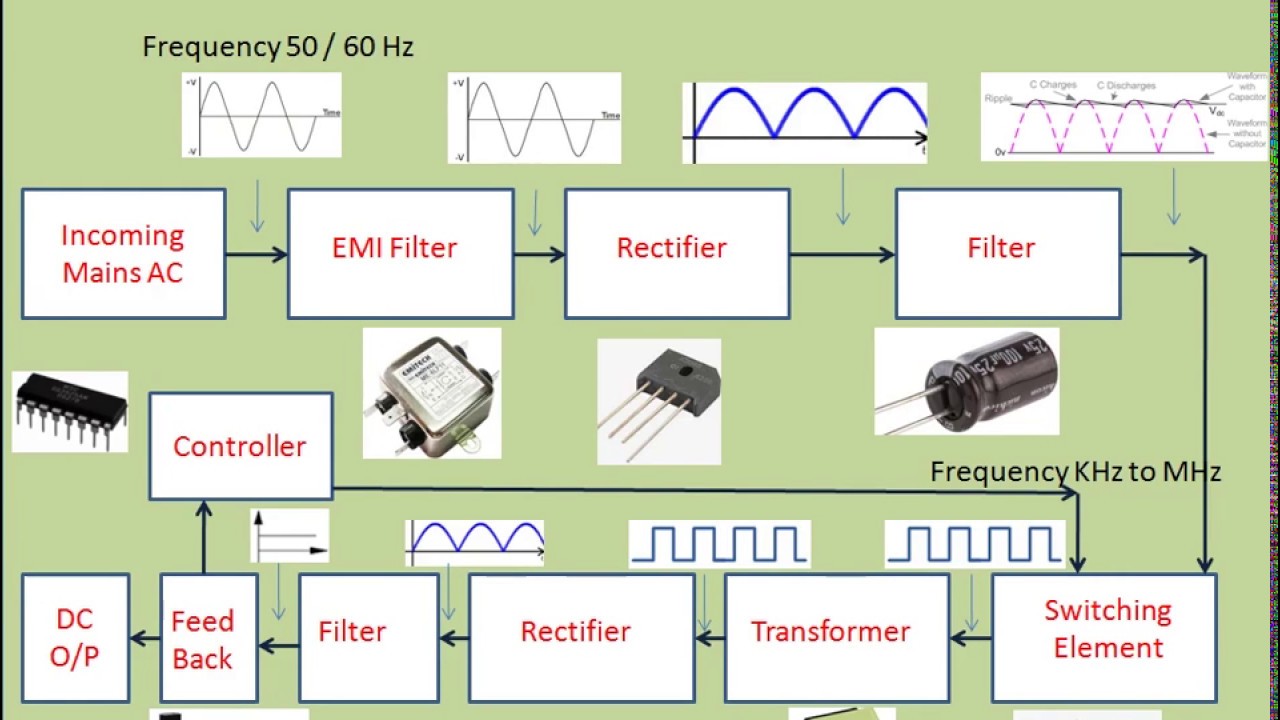
H2: Market Trends in Linear vs. Switch Mode Power Supplies (2026 Outlook)
As the global electronics and industrial sectors continue to evolve, the demand for efficient, compact, and reliable power supply solutions is shaping the competitive landscape between Linear Power Supplies (LPS) and Switch Mode Power Supplies (SMPS). By 2026, several key trends are expected to influence the adoption and market share of both technologies across various industries.
1. Dominance of Switch Mode Power Supplies in Growth Sectors
Switch Mode Power Supplies are projected to maintain a dominant market share by 2026, driven by their high efficiency (typically 70–95%), compact size, and lower heat dissipation. Key growth areas fueling SMPS demand include:
– Consumer electronics (smartphones, laptops, wearables)
– Renewable energy systems (solar inverters, battery storage)
– Electric vehicles (EV charging infrastructure, onboard chargers)
– Data centers and telecommunications (5G infrastructure, cloud computing)
The push for energy efficiency standards—such as the U.S. Department of Energy Level VI and EU CoC Tier 2—favors SMPS adoption, further accelerating their penetration.
2. Niche Resilience of Linear Power Supplies
Despite the broader shift toward SMPS, Linear Power Supplies retain a strong foothold in applications requiring ultra-low noise and high signal integrity. By 2026, LPS will continue to serve niche markets such as:
– High-precision medical equipment (e.g., MRI machines, patient monitors)
– Audio and RF amplification systems
– Laboratory and test instrumentation
Improvements in thermal management and hybrid designs may extend the relevance of LPS in low-power, noise-sensitive applications.
3. Technological Convergence and Hybrid Solutions
A growing trend by 2026 is the integration of linear and switch mode topologies into hybrid power supplies. These systems leverage the efficiency of SMPS with the filtering and regulation capabilities of linear regulators, offering optimized performance in mixed-signal environments. Such solutions are gaining traction in industrial automation and advanced sensor networks.
4. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is expected to lead SMPS adoption due to rapid industrialization, booming consumer electronics manufacturing (especially in China, India, and Vietnam), and government investments in smart infrastructure. In contrast, mature markets in North America and Europe show steady demand for high-reliability LPS in medical and aerospace applications.
5. Sustainability and Miniaturization Driving Innovation
Environmental regulations and the demand for smaller, lighter electronics are pushing SMPS innovation in gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors. These wide-bandgap technologies enable higher switching frequencies, greater efficiency, and reduced component size—factors that will further widen the performance gap between SMPS and traditional LPS.
Conclusion
By 2026, Switch Mode Power Supplies are expected to account for over 70% of the global power supply market, outpacing Linear Power Supplies in volume and revenue growth. However, linear supplies will remain indispensable in high-fidelity, low-noise applications. The future lies in intelligent power management systems that selectively combine the strengths of both technologies to meet the diverse needs of an increasingly electrified world.
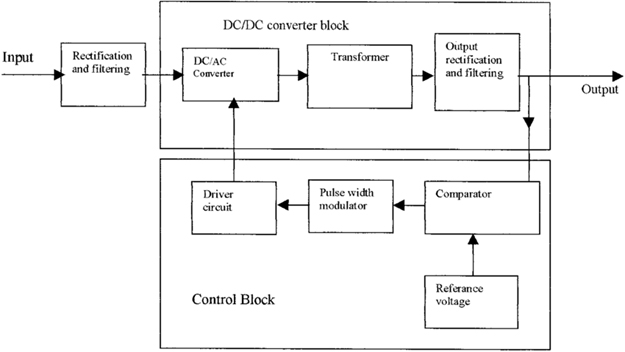
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Linear vs. Switch Mode Power Supplies (Quality, IP)
Choosing between linear and switch mode power supplies (SMPS) involves more than just electrical specifications—quality and intellectual property (IP) risks are often overlooked. Here are common pitfalls in sourcing both types:
1. Underestimating Quality Variability in SMPS
Switch mode power supplies are more complex than linear supplies, involving high-frequency switching components, control ICs, and magnetics. Sourcing low-cost SMPS units—especially from unverified suppliers—can lead to significant quality issues:
- Poor Component Selection: Use of substandard capacitors, MOSFETs, or transformers that degrade quickly under load or temperature stress.
- Inadequate Thermal Management: Lack of proper heatsinking or airflow design leads to premature failure.
- EMI/RFI Compliance Gaps: Many low-cost SMPS units fail to meet electromagnetic interference (EMI) standards, causing interference with sensitive electronics.
- Inconsistent Output Regulation: Voltage ripple and load regulation may exceed specifications, affecting downstream electronics.
Pitfall: Assuming all SMPS units with similar specs perform equally. Always verify through independent testing or trusted certifications (e.g., UL, CE, FCC).
2. Overlooking Heat and Efficiency in Linear Supplies
Linear power supplies are simpler but inherently inefficient, especially when stepping down high input voltages.
- Excessive Heat Dissipation: High power loss as heat requires large heat sinks and ventilation, increasing system size and cooling needs.
- Thermal Runaway Risk: Poor thermal design or inadequate heatsinking can lead to component failure.
- Hidden Quality Issues: Even in linear supplies, cheap designs may use under-rated pass transistors or inadequate filtering capacitors.
Pitfall: Choosing linear supplies for high-current or high-voltage-differential applications without considering thermal and efficiency impacts—leading to larger, hotter, and less reliable systems.
3. IP Risks in Reverse-Engineered or Clone SMPS Designs
Many SMPS units, especially from certain regions, are based on reverse-engineered reference designs or cloned ICs.
- Patented Topologies: Using control circuits or architecture that infringe on existing IP (e.g., resonant LLC, active clamp flyback).
- Counterfeit ICs: Use of cloned or re-marked control ICs that may fail prematurely or behave unpredictably.
- Lack of Design Ownership: ODM/OEM suppliers may not own the design, exposing buyers to legal or supply chain risks.
Pitfall: Sourcing SMPS modules without verifying original design rights or component authenticity—risking product recalls or legal action.
4. Ignoring Certification and Compliance Claims
Both supply types may claim regulatory compliance, but verification is critical.
- Falsified Certifications: Some suppliers display fake UL or CE marks.
- Partial Compliance: A unit may pass safety tests but fail EMI or efficiency standards (e.g., 80 PLUS for SMPS).
- Lack of IP Rating Verification: Claimed ingress protection (e.g., IP67) may not be validated through proper testing.
Pitfall: Assuming documentation equals compliance. Always request test reports or use third-party verification.
5. Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
- Linear Supplies: Often contain fewer components, but sourcing of transformers and regulators can still involve counterfeit or gray-market parts.
- SMPS: Higher component count increases risk of mixed batches, especially passive components and ICs.
Pitfall: Not auditing supplier manufacturing processes or requiring full BoM traceability—leading to inconsistent quality or compliance issues.
Conclusion
When sourcing either linear or switch mode power supplies, focus on more than price and specs. Evaluate quality through testing and certifications, ensure IP compliance, and verify supply chain transparency. Linear supplies offer simplicity and low noise but suffer in efficiency; SMPS provide high efficiency and compact size but introduce complexity and potential IP risks. A thorough sourcing strategy mitigates these pitfalls and ensures long-term product reliability.
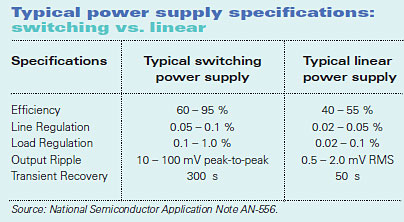
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Linear vs Switch Mode Power Supplies
Understanding the differences between linear and switch mode power supplies (SMPS) is essential not only for performance and efficiency but also for logistics, regulatory compliance, and global market access. This guide outlines key considerations for each type across critical logistics and compliance domains.
Regulatory Compliance
Linear Power Supplies
Linear power supplies generally have simpler electromagnetic characteristics, producing minimal electromagnetic interference (EMI). This makes them easier to certify under international standards such as:
– EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility): Typically meet EN 55032/EN 55014 and FCC Part 15 Class B with minimal filtering.
– Safety Standards: Comply with IEC 61010-1 (laboratory equipment), IEC 60950-1 (IT equipment), or IEC 60601-1 (medical devices) due to lower switching noise and reduced risk of high-frequency hazards.
– RoHS & REACH: Compliance is straightforward due to fewer components and simpler circuit design.
Switch Mode Power Supplies
SMPS require more rigorous compliance due to high-frequency switching:
– EMC Standards: Must pass stringent conducted and radiated emissions tests (e.g., EN 55032, CISPR 32, FCC Part 15). Often require additional EMI filters, shielding, and layout optimization.
– Harmonics & Power Quality: Subject to IEC 61000-3-2 for harmonic current emissions, especially for higher power units. May require active power factor correction (PFC).
– Safety Certification: Require thorough evaluation under IEC 62368-1 (replacing IEC 60950-1 and IEC 60065) due to higher voltage stresses and isolation requirements.
– RoHS, REACH, and WEEE: Compliance is mandatory; design complexity may involve conflict minerals reporting (e.g., under EU Conflict Minerals Regulation).
Global Market Access
Linear Power Supplies
– Certification Simplicity: Easier to obtain CE, UKCA, FCC, and CCC marks due to lower EMI and simpler design.
– Market Use Cases: Preferred in sensitive environments such as medical, audio, and laboratory applications where low noise is critical.
– Labeling & Documentation: Requires standard safety labels, input/output ratings, and compliance marks. Instruction manuals must meet local language requirements.
Switch Mode Power Supplies
– Broader Certification Needs: Often require multiple certifications per region (e.g., CCC in China, KC in Korea, PSE in Japan).
– Energy Efficiency Regulations: Must comply with global efficiency standards such as:
– DoE Level VI (USA)
– EU CoC Tier 2 (European Union)
– MEPS (Australia/New Zealand)
– Labeling Requirements: Efficiency logos (e.g., ENERGY STAR), input/output specifications, and multiple safety certifications must be clearly marked.
Logistics & Handling
Linear Power Supplies
– Weight & Size: Heavier and bulkier due to large transformers and heat sinks. Increases shipping costs and storage footprint.
– Fragility: Less sensitive to vibration due to fewer high-frequency components.
– Thermal Management: Generates more heat; requires adequate ventilation in transit and storage to prevent degradation.
Switch Mode Power Supplies
– Compact & Lightweight: Smaller transformers and higher efficiency reduce size and weight, lowering shipping and warehousing costs.
– Sensitivity to ESD and Handling: More susceptible to electrostatic discharge (ESD); requires anti-static packaging and handling procedures.
– Moisture Sensitivity: Some SMPS components (e.g., ICs) may be moisture-sensitive (MSL rated), requiring dry packaging and humidity control during storage and transport.
Environmental & Sustainability Compliance
Linear Power Supplies
– Lower Efficiency: Typically 40–60%, leading to higher energy consumption and carbon footprint over lifecycle.
– Recyclability: Simpler construction facilitates easier disassembly and recycling.
– Compliance with ErP Directive: May not meet EU Ecodesign requirements for energy-related products due to inefficiency.
Switch Mode Power Supplies
– High Efficiency: Often 80–95%, complying with modern energy efficiency directives.
– Use of Rare Materials: May include rare earth elements in inductors or advanced semiconductors, requiring responsible sourcing.
– End-of-Life Management: Must comply with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives, including take-back programs and proper disposal.
Supply Chain & Sourcing
Linear Power Supplies
– Component Availability: Relies on standard components (transformers, capacitors, regulators) with long-term availability and low risk of obsolescence.
– Manufacturing Locations: Often produced in regions with less automation due to simpler assembly processes.
Switch Mode Power Supplies
– Component Complexity: Requires precision components (e.g., MOSFETs, PWM controllers, high-frequency magnetics), which may face supply chain volatility.
– Counterfeit Risk: High demand for SMPS ICs increases risk of counterfeit parts; requires trusted suppliers and traceability.
– Geopolitical Factors: Subject to export controls (e.g., ECCN classification) if containing dual-use technologies.
Summary
Choosing between linear and switch mode power supplies involves balancing technical performance with logistics and compliance demands. Linear supplies offer simplicity and low noise but face challenges in efficiency and size. Switch mode supplies provide high efficiency and compact design but require more rigorous compliance, handling care, and supply chain oversight. A thorough understanding of these factors ensures smooth global deployment and regulatory adherence.
Conclusion: Sourcing Linear vs. Switch Mode Power Supply
When sourcing a power supply, the choice between linear and switch mode power supplies (SMPS) depends on the specific requirements of the application. Linear power supplies offer simplicity, low electromagnetic interference (EMI), and excellent voltage regulation, making them ideal for sensitive analog circuits and audio equipment where noise must be minimized. However, they are typically less efficient, larger, heavier, and generate more heat, especially under high voltage conversion ratios.
In contrast, switch mode power supplies provide high efficiency, compact size, lighter weight, and greater flexibility in handling wide input voltage ranges. These advantages make SMPS suitable for modern digital systems, consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and applications where energy efficiency and space are critical. However, they can introduce electrical noise and require more complex circuitry for EMI suppression.
Ultimately, the decision should be guided by priorities such as efficiency, size, thermal performance, noise sensitivity, and cost. For low-noise, low-power applications, linear supplies remain a strong choice. For most modern high-efficiency and high-density designs, switch mode power supplies are generally preferred. A thorough evaluation of technical needs, operating environment, and long-term operational costs will ensure the optimal power supply selection.